Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function by speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with coronary heart disease after percutaneous coronary intervention
-
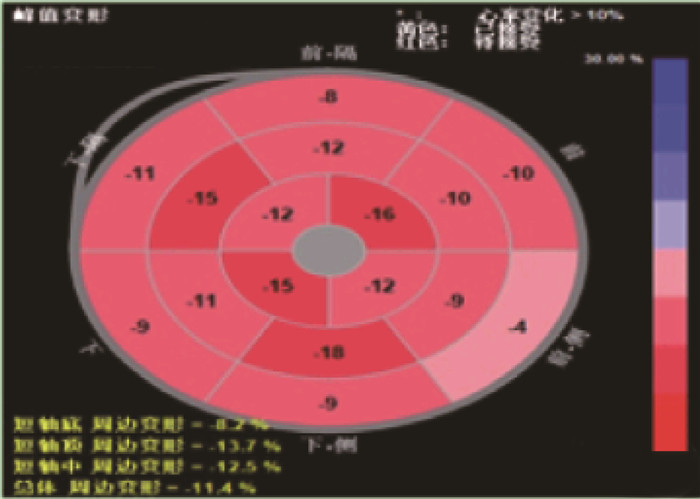
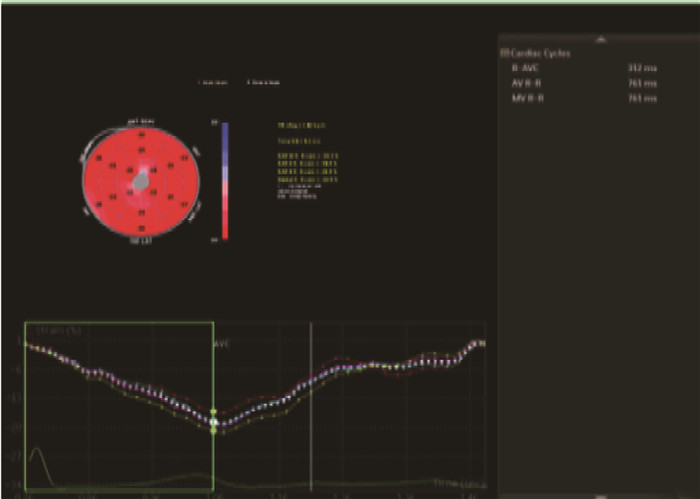
摘要:目的 探讨超声斑点追踪技术对冠心病(CAD)患者经皮冠状动脉介入术(PCI)术后评价左室收缩功能的作用。方法 选择51例行PCI手术的CAD患者为研究组,选择51例志愿者为对照组。2组应用彩色多普勒超声诊断仪斑点追踪技术检测左室收缩功能,其中研究组分别在PCI术前与术后3个月进行检测,对照组在体检时检测。比较2组左室心室舒张末内径(LVDd)、左心室收缩末内径(LVDs)、二尖瓣口舒张早期峰值血流速度(E)、舒张晚期峰值血流速度(A)、E和A的比值(E/A)、左心室射血分数(LVEF)。分析研究组整体径向应变峰值(GPRS)、整体纵向应变峰值(GPLS)、整体环向应变峰值(GPCS)与LVEF检测变化的相关性。观察2组超声二维斑点追踪显像(STI)曲线与纵向应变牛眼图。结果 研究组PCI术前、术后的A高于对照组,E/A与LVEF低于对照组;研究组PCI术后LVEF高于术前;研究组PCI术前、术后GPRS低于对照组,GPLS、GPCS高于对照组;研究组PCI术后GPRS高于术前,GPLS、GPCS低于术前;上述差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。研究组GPRS、GPLS、GPCS与LVEF存在相关性(r=-0.722,-0.545,-0.667,P < 0.05)。PCI术前,STI曲线各节段运动曲线形态幅度不一致,轮廓不规则,明显分离,PCI术后,STI曲线发现各节段运动曲线形态幅度基本一致,曲线已趋于正常;对照组17节段纵向应变牛眼图与运动曲线显示应变曲线轮廓规则,达峰时间统一,波峰波谷一致。结论 超声斑点追踪技术可有效评价CAD患者PCI术后左室收缩功能,并具有可重复追踪、方便、无痛苦等优势。Abstract:Objective To investigate the roles of speckle tracking echocardiography in the evaluation of left ventricular systolic function for patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).Methods Fifty-one CAD patients undergoing PCI were selected as study group, and 51 volunteers were selected as control group. The left ventricular systolic function was detected by speckle tracking technology of color Doppler ultrasound diagnostic instrument in the two groups. The study group was detected before PCI and 3 months after PCI, and the control group was detected at physical examination. The left ventricular end diastolic diameter (LVDd), left ventricular end systolic diameter (LVDs), peak early flow velocity (E)in mitral, peak late flow velocity (A), the ratio of E to A (E/A), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) were compared between the two groups before and after PCI. The correlations between global peak radial strain (GPRS), global peak longitudinal strain (GPLS), global peak circumferential strain (GPCS) and LVEF detection changes in the study group were analyzed. Speckle-tracking imaging curve and longitudinal strain bull eye diagram were observed in two groups.Results The A value of the study group before and after PCI was significantly higher, and the E/A and LVEF of the study group were significantly lower than that of the control group (P < 0.01); LVEF after PCI was significantly higher than that before PCI (P < 0.01); the GPRS of the study group before and after PCI was significantly lower, and the GPLS and GPCS of the study group were significantly higher than that of the control group (P < 0.01). GPRS in the study group after PCI was significantly higher, and GPLS and GPCS were significantly lower than before (P < 0.01). GPRS, GPLS and GPCS in the study group were correlated with LVEF (r=-0.722, -0.545, -0.667, P < 0.05). Before PCI, the shape and amplitude of motion curve of each segment of STI curve were inconsistent, and the contour was irregular and obviously separated. The STI curve after PCI showed that the shape and amplitude of motion curve of each segment were basically consistent, and the curve had tended to be normal; in the control group, the contour of strain curve was regular, the peak time was unified, and the peak and trough were consistent.Conclusion Ultrasound speckle tracking technique can effectively evaluate left ventricular systolic function in patients with coronary heart disease after PCI, and has the advantages of repeatable tracking, convenience and painless.
-
近年来,高危产妇因妊娠高血压综合征、前置胎盘、胎盘早剥等多种因素,面临术中及术后高出血风险[1-2]。四川省凉山彝族自治州地理位置偏远,教育水平相对较低,医疗资源有限,许多彝族产妇缺乏必要的产前检查,导致高危因素难以被及时发现和控制。剖宫产术是解决难产、高危妊娠等问题的重要手段[3]。在剖宫产术中,一旦出血过多,不仅危及产妇生命安全,也可能对胎儿的健康造成威胁[4]。然而,对于高出血风险的彝族产妇而言,如何有效管理术中及术后的血液容量成为棘手的问题。传统的异体输血虽然能够迅速补充血容量,但存在免疫排斥、疾病传播等潜在风险,尤其在凉山彝族地区,由于艾滋病和结核病等传染性疾病的高发,这些风险更为显著[5]。回收式自体输血(IOCS)作为一种新型的血液管理技术,通过收集患者自身的失血并进行处理后再回输,能够避免异体输血带来的诸多风险[6-7], 其在减少异体输血需求、降低输血相关并发症发生率等方面具有显著优势[8]。本研究选取100例高出血风险产妇作为研究对象,探究IOCS在高出血风险产妇剖宫产术中的应用效果,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2021年1月—2024年1月在凉山州第一人民医院接受治疗的100例高出血风险产妇为研究对象。纳入标准: ①年龄20~45岁,美国麻醉医师协会(ASA)分级Ⅰ~Ⅱ级,彝族产妇; ②择期或急诊剖宫产手术者; ③术中出血量2级以上者; ④产妇及其家属对本研究内容详细了解并签署同意书。排除标准: ① ASA分级Ⅲ级以上,合并内科或外科疾病者; ② Rh阴性产妇; ③有镰状细胞贫血、地中海贫血、血小板及凝血功能异常的产妇; ④中途因自身原因退出研究者。本研究通过本院伦理委员会审批。依据输血方式不同,将自体输血50例作为观察组,异体输血50例作为对照组。2组患者年龄、体质量、孕次、产次、孕周等基线资料比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 2组基线资料比较(x ±s)组别 n 年龄/岁 体质量/kg 孕次/次 产次/次 孕周/周 对照组 50 32.12±3.88 66.18±8.33 3.32±1.19 2.98±0.96 37.17±1.05 观察组 50 31.90±3.95 66.75±6.33 3.70±1.33 3.04±1.16 37.04±1.46 1.2 方法
患者术前常规禁食、禁饮,不用术前药物。入室后常规监测,开放2条外周静脉,予复方氯化钠输入。进行桡动脉Allen试验,并于局麻下行桡动脉穿刺置管,监测有创动脉血压。
麻醉方案根据产妇术前病情决定, ASA分级Ⅰ~Ⅱ级产妇采用腰3~4节段腰硬联合阻滞,等比重罗哌卡因15 mg蛛网膜下腔麻醉。对于紧急剖宫产或者拒绝行椎管内麻醉的产妇,采用气管内插管全麻,诱导方案为: 丙泊酚2 mg/kg, 瑞芬太尼0.5~1.0 μg/kg, 罗库溴铵0.6~1.0 mg/kg, 待胎儿取出后,追加咪达唑仑2 mg, 舒芬太尼0.3 μg/kg, 而后采用丙泊酚、瑞芬太尼静脉泵注维持麻醉,根据情况间断给予肌松药罗库溴铵。
术前准备BM-8200B型自体血液回收机及白细胞滤器,正确安置管路,设备自检通过。配置50 U/mL肝素液,对所有的管路和储血罐用抗凝液(200 mL)进行预冲洗。准备2套吸引装置,一套吸引羊水、胎粪、胎脂及胎盘血,另一套待胎盘娩出后再进行自体血回收,最大程度地减少羊水和胎儿血液成分混入; 抗凝液速度为60滴/min(应根据出血量调整),严格遵守无菌操作原则。术中当贮血量达800 mL时,立即进行第1次血液的分离、洗涤、离心,洗涤盐水不少于2 000 mL, 回输患者前使用白细胞滤器再次进行过滤。而后根据贮血量情况进行后续的血液回收、回输操作。若失血量>30%血容量时,根据血气分析及凝血指标检测结果,补充输入相应血液制品。对于术前存在出血高危因素、不规则抗体阳性或稀有血型的患者,应提前备血。经过白细胞滤器过滤后的自体血从外周静脉通道输注,先用0.9%生理盐水冲洗输血器后再输注。
术中血液回收禁忌: ①血液流出血管外超过6 h; ②怀疑流出的血液被细菌、粪便、消毒液污染; ③怀疑流出的血液含有癌细胞; ④流出的血液严重溶血。注意事项: 尽量避免组织碎屑吸入储血罐阻塞管道或滤器; 避免非等渗溶液、消毒液、含钙溶液、外用止血剂等吸入储血罐。
1.3 观察指标
本研究对2组患者临床指标、血常规、凝血功能及术后不良反应进行评估。
1.3.1 临床指标:
记录患者术中出血量、术中输血量(包括自体血回输量、红细胞悬液、血浆、血小板等成分输血)、血费、总费用、手术时长及住院时间。
1.3.2 血常规
记录患者开始输血即刻(T1)、输血结束(T2)及术后24 h(T3)血常规指标。通过自动化血液分析仪检测血红蛋白(Hb)、红细胞压积(Hct)及血小板(Plt)。
1.3.3 凝血功能
记录患者T1、T2及T3凝血功能指标。采用凝血分析仪检测凝血酶原时间(PT)、凝血酶时间(TT)、活化部分凝血活酶时间(APTT)、纤维蛋白原(Fib)、D-二聚体(D-D)。
1.3.4 炎症因子
测定患者输血前、输血后48 h炎症因子水平,取患者肘静脉血,采用免疫荧光层析法检测患者血清降钙素原(PCT)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)。
1.3.5 不良反应
记录患者术后输血不良反应,包括过敏反应、感染、低血压,并统计总不良反应发生率。
1.4 统计学处理
将统计数据录入Excel表格中,采用SPSS 22.0软件进行分析计算。对于符合正态分布的计量数据资料采用(x ±s)表示, 比较行t检验; 对于不符合正态分布的偏态计量数据资料,使用中位数表示,采用非参数分析、秩和检验; 计数数据资料用[n(%)]表示,比较行χ2检验, P < 0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组产妇临床指标比较
观察组术中失血量、术中输血量、血费、总费用、手术时间及住院时间少于或短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 2组产妇临床指标比较(x ±s)[M(P25, P75)]组别 n 术中失血量/mL 术中输血量/mL 血费/元人民币 总费用/元人民币 手术时间/min 住院时间/d 对照组 50 1 578.00±891.98 1 039.00±728.24 4 982.10(1 588, 19 585) 22 159.21±8 785.91 118.54±20.73 10.40±5.22 观察组 50 1 082.00±487.26* 718.82±445.50* 1 054.38(0, 10 507)* 17 503.82±4 148.35* 95.02±24.86* 8.36±2.47* 与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。 2.2 2组产妇血常规指标比较
T1时, 2组产妇血常规指标比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。T2、T3时, 2组Hct比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 观察组Hb、Plt均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 3。
表 3 2组产妇血常规指标比较(x ±s)指标 时点 对照组(n=50) 观察组(n=50) Hb/(g/L) T1 113.82±11.41 113.78±13.49 T2 93.52±8.41 103.34±12.85* T3 89.66±8.55 96.36±11.20* Hct/% T1 36.74±3.48 36.52±3.51 T2 29.58±2.75 30.37±2.81 T3 29.82±2.53 30.12±3.31 Plt/(×109/L) T1 218.84±33.12 219.60±34.57 T2 143.06±20.94 164.00±31.11* T3 151.56±14.87 179.16±36.21* T1: 开始输血即刻; T2: 输血结束; T3: 术后24 h;
Hb: 血红蛋白; Hct: 红细胞压积; Plt: 血小板。
与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。2.3 2组产妇凝血功能指标比较
T1时, 2组产妇凝血功能指标比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。T2、T3时, 2组D-D比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 观察组PT、TT、APTT均短于对照组, Fib高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 4。
表 4 2组产妇凝血功能指标比较(x ±s)指标 时点 对照组(n=50) 观察组(n=50) PT/s T1 10.06±0.36 10.04±0.32 T2 11.53±0.86 10.56±0.81* T3 11.26±0.76 10.19±0.38* TT/s T1 15.16±0.82 15.36±0.93 T2 19.30±1.49 17.83±1.44* T3 18.49±0.72 16.96±1.22* APTT/s T1 27.21±1.91 27.39±2.25 T2 32.47±2.18 30.12±3.17* T3 32.35±1.98 30.36±2.74* Fib/(g/L) T1 4.54±0.46 4.37±0.61 T2 2.54±0.36 2.81±0.61* T3 3.62±0.91 4.21±1.42* D-D/(mg/L) T1 1.63±0.44 1.66±0.87 T2 11.60±2.24 11.17±8.01 T3 4.03±0.99 4.02±1.96 PT: 凝血酶原时间; TT: 凝血酶时间; APTT: 活化部分
凝血活酶时间; Fib: 纤维蛋白原; D-D: D-二聚体。
与对照组比较, * P<0.05。2.4 2组产妇炎症因子比较
输血前, 2组产妇PCT、IL-6比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。输血后48 h, 观察组PCT、IL-6均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 5。
表 5 2组产妇炎症因子比较(x ±s)组别 n PCT/(pg/mL) IL-6/(ng/L) 输血前 输血后48 h 输血前 输血后48 h 对照组 50 3.74±1.13 16.44±5.13 66.78±6.89 121.64±18.37 观察组 50 3.87±1.01 7.62±2.75* 65.64±7.05 85.44±10.62* PCT: 降钙素原; IL-6: 白细胞介素-6。与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。 2.5 2组产妇不良反应比较
观察组过敏反应、感染及低血压发生人数均低于对照组,但2组产妇总不良反应发生率比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 见表 6。
表 6 2组产妇不良反应比较[n(%)]组别 n 过敏反应 感染 低血压 合计 对照组 50 4(8.00) 1(2.00) 1(2.00) 6(12.00) 观察组 50 2(4.00) 0 0 2(4.00) 3. 讨论
剖宫产术是常见的分娩方式之一, IOCS是通过收集患者自身的失血,经过处理后再回输给患者的方法[9-10]。与传统的异体输血相比,回收式自体输血具有减轻输血反应、减少输血相关疾病传播风险、节约血源等多重优势。在高出血风险的剖宫产术中,回收式自体输血的应用显得尤为重要[11-12]。
本研究结果表明,观察组术中失血量、术中输血量、血费、总费用、手术时间及住院时间均显著低于对照组。分析其原因为自体输血能够减少异体血的输注需求,从而降低了与异体输血相关的各种成本,包括血费、储存费用等。患者的整体健康状态、凝血功能、手术前的准备也会影响术中出血量。自体输血患者因为更好的术前准备和更严格的筛选标准而表现出较低的出血量。自体输血通常在术前或术中某个阶段进行,而异体输血可能在整个手术过程中根据需要多次进行。张薇等[13]研究表明,回收式自体输血能够显著减少术中失血量和输血量,降低手术成本,缩短术后恢复时间。
本研究T2、T3时, 2组Hct无显著差异,观察组Hb、Plt均显著高于对照组。分析其原因为IOCS能够及时补充产妇在手术过程中失去的血液成分,有助于维持血红蛋白和血小板的稳定水平。而对照组由于输注异体血,可能存在免疫排斥反应或输血反应,影响了血常规指标的恢复。Hct作为反映红细胞数量和血液浓缩程度的指标,其变化可能受到术中出血量、补液量、血浆容量以及红细胞生成和破坏等多种因素的影响。李刚等[14]研究也支持了这一观点,发现自体输血能够有效维持血常规指标的稳定,减少输血反应的发生。
本研究结果表明T2、T3时, 2组D-D无显著差异,观察组PT、TT、APTT均显著短于对照组, Fib显著高于对照组。分析其原因为D-D作为反映凝血功能状态的指标,其变化可能受到凝血系统激活、纤维蛋白溶解以及炎症反应等多种因素的影响。手术过程中, 2组产妇都会受到手术创伤、麻醉药物等因素的影响,导致凝血系统的激活和纤维蛋白溶解过程的变化,使得2组产妇D-D水平无显著差异。自体红细胞与患者自身的血浆和其他凝血成分更为匹配,减少了因不匹配或免疫反应导致的凝血障碍。此外,自体输血避免了异体输血可能引起的免疫反应,如抗体形成或补体激活,这些反应可能会间接影响凝血系统的正常功能。同时,手术刺激、失血后的代偿性反应以及肝脏的急性时相反应等都可能促进Fib的合成和释放。此外,由于自体输血减少了异体输血可能引起的免疫反应,患者的整体凝血状态可能更加稳定,有利于Fib水平的维持或升高。相关研究[15]表明,自体输血在维持凝血功能方面优于异体输血。本研究输血后48 h, 观察组PCT、IL-6均显著低于对照组,这是因为异体输血会引发免疫反应,包括白细胞和血小板抗原的抗体反应,这可能导致炎症介质的释放,如IL-6等细胞因子。而自体输血则完全避免了这种免疫反应,因为输注的是患者自己的血液成分。同时,异体输血中的血液成分与患者自身存在差异,导致患者体内产生炎症反应,进而影响PCT和IL-6等炎症指标的水平。然而, PCT和IL-6的比较可能受到多种干扰因素的影响,包括手术愈合进程、手术持续时间长短以及是否为急诊手术等。这些因素都可能对炎症反应产生影响,从而影响PCT和IL-6的水平。因此,仍需深入探究并控制这些潜在的干扰因素,以确保结果的准确性和可靠性。
观察组过敏反应、感染及低血压发生人数均低于对照组,但2组产妇总不良反应发生率无显著差异。分析其原因为IOCS避免了异体输血时可能发生的免疫排斥反应,从而降低了过敏反应的风险。同时,由于自体血不含有外来病原体,感染的风险也相应减少。此外, IOCS能够更好地维持患者血压稳定,减少了低血压的发生。但在异体输血中,虽然存在免疫排斥和感染等风险,但通过严格的血液筛选、交叉配血和无菌操作等措施,也可以在一定程度上降低风险。
综上所述, IOCS在高出血风险产妇剖宫产术中的应用具有显著优势,能够减少术中失血量、输血量及相关费用,维持血常规和凝血功能的稳定,改善输血后炎症反应,降低输血相关的不良反应发生率。
-
表 1 研究组PCI术前、术后与对照组的心脏超声指标对比(x ±s)
组别 n 时点 LVDs/cm LVDd/cm A/(cm/s) E/(cm/s) E/A LVEF/% 对照组 51 - 3.05±0.85 4.80±0.85 57.52±13.52 62.12±12.65 1.16±0.40 67.02±6.85 研究组 51 术前 3.10±0.56 4.92±0.65 73.52±16.52# 63.25±12.52 0.80±0.30# 47.52±5.65# 术后 3.08±0.52 4.88±0.58 71.30±15.65# 62.18±14.52 0.83±0.32# 58.65±6.52**# LVDs: 左心室收缩末内径; LVDd: 室心室舒张末内径; A: 舒张晚期峰值血流速度; E: 二尖瓣口舒张早期峰值血流速度;
LVEF: 左心室射血分数。与术前比较, **P < 0.01; 与对照组比较, #P < 0.01。表 2 研究组PCI术前、术后与对照组的GPRS、GPLS、GPCS对比(x ±s)
组别 n 时点 GPRS GPLS GPCS 对照组 51 - 35.15±7.52 -24.12±5.68 -27.52±5.65 研究组 51 术前 18.88±6.52# -12.85±5.65# -15.85±5.05# 术后 25.32±6.65**# -16.52±5.60**# -20.00±5.42**# GPRS: 整体径向应变峰值; GPLS: 整体纵向应变峰值; GPCS: 整体环向应变峰值。
与术前比较, **P < 0.01; 与对照组比较, #P < 0.01。表 3 研究组GPRS、GPLS、GPCS与LVEF检测变化相关性
整体应变指标 r P值 GPRS 0.722 0.023 GPLS -0.545 0.018 GPCS -0.667 0.016 LVEF: 左心室射血分数; GPRS: 整体径向应变峰值;
GPLS: 整体纵向应变峰值; GPCS: 整体环向应变峰值。 -
[1] 李艳红, 龚晓萍, 穆玉明, 等. 三维超声斑点追踪技术对冠状动脉多支重度狭窄的诊断价值[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2018, 27(12): 1020-1024. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2018.12.002 [2] 李文, 邵宏增, 章蓉, 等. 三维超声斑点追踪技术评价不同程度左前降支冠状动脉狭窄心肌应变[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2018, 28(3): 404-408. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201803016.htm [3] RUSINARU D, BOHBOT Y, RINGLE A, et al. Impact of low stroke volume on mortality in patients with severe aortic Stenosis and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39(21): 1992-1999. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy123
[4] 李静, 朱芳, 丁明岩, 等. 三维斑点追踪技术对冠心病患者左心室重构的评估价值[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2020, 20(1): 104-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-816x.2020.01.026 [5] 丁歆, 曹衡玉. 超声斑点追踪技术对评估2型糖尿病患者心脏收缩功能的影响[J]. 中国现代医生, 2019, 57(27): 22-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYS201927007.htm [6] 厉玉彬, 王丽丽, 许玲. 超声斑点追踪成像技术在诊断冠心病患者左室心肌收缩功能的临床价值[J]. 中国社区医师, 2020, 36(14): 93-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYS202014057.htm [7] 麦兴盛, 吴参伟. 全容积三维超声评估冠心病患者左心功能的价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2019, 23(8): 57-60. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201908016 [8] 彭玲, 朱芳, 丁明岩, 等. 三维斑点追踪技术评价冠状动脉病变严重程度[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2019, 35(5): 677-681. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201905013.htm [9] 张建鑫, 张平洋, 马小五, 等. 三维面积应变参数预测冠心病患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后心功能改善的价值[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2019, 39(10): 2252-2258. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2019.10.023 [10] 张姝, 赵洪震, 兰海峰. 彩色多普勒超声检测动脉内中膜厚度、血管舒张功能在预测冠心病发生中的价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2019, 23(6): 17-20. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201906004 [11] 许继梅, 马芳, 冯俊, 等. 斑点追踪超声心动图评价冠心病病人左心室收缩功能的研究[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2018, 43(9): 1204-1207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BANG201809028.htm [12] 高磊, 刘昕, 傅群峰, 等. 实时三维斑点追踪成像评价PCI术后左心室收缩功能的临床研究[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2019, 40(12): 1442-1446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBYX201912022.htm




 下载:
下载:



 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
