Protective effects of nicorandil on cardiac function in rats with ischemic heart failure and its mechanism
-
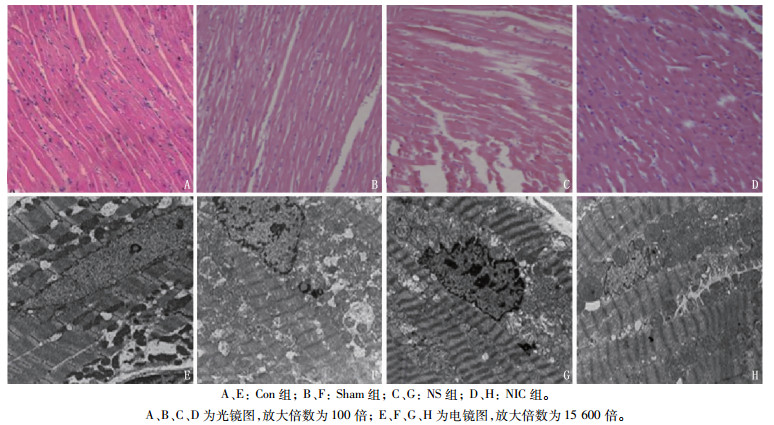
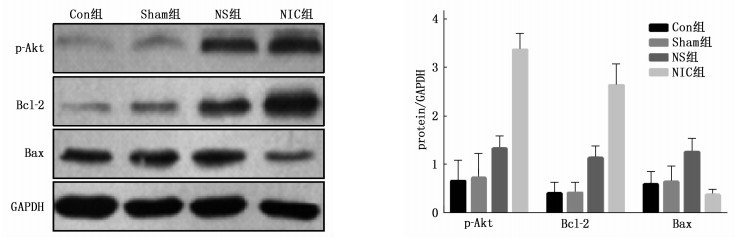
摘要:目的 探讨尼可地尔对缺血性心力衰竭大鼠心功能和左室重构的保护作用及相关机制。方法 将40只大鼠随机分为空白对照组(Con组)、尼可地尔组(NIC组)、生理盐水组(NS组)及假手术组(Sham组),每组10只,分别采取不同处理方式。记录各组大鼠体重、呼吸模式、活动量和毛色差异。术后8周所有大鼠行超声心动图检查。实验结束后对大鼠左心室前壁组织进行HE染色及电镜观察。检测心肌组织中p-Akt、Bcl-2、Bax蛋白的相对表达量。结果 与Con组及Sham组相比, NS组及NIC组左心室射血分数(LVEF)、速度最大值(E)/心房收缩心室充盈速度最大值(A)(E/A)降低, NS组LVEF下降最多,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。左心室舒张末期容积(LVEDV)则呈相反趋势, 3组间存在差异, NS组LVEDV最高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。NS组左心室收缩末期容积(LVESV)、左室舒张末期内径(LVIDd)和左室收缩末期内径(LVIDs)高于NIC组和Sham组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Sham组大鼠心肌细胞排列规则,横纹清晰; NS组心肌细胞排列紊乱,形状不规则,同时还表现出明显的纤维组织增生。Sham组、NIC组的左心室/体重比值(LVW/BW)和肺脏重量指数(Lungw/Bw)均低于NS组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与Con组及Sham组相比, NS组p-Akt、Bcl-2及Bax蛋白相对表达量增加,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。NIC组p-Akt、Bcl-2蛋白相对表达量高于NS组,但Bax蛋白表达量下降,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 尼可地尔可通过改善心功能和左室重塑对缺血性心力衰竭大鼠起到保护作用,这可能与抑制Bax蛋白表达有关。Abstract:Objective To investigate the protective effect of nicodil on cardiac function and left ventricular remodeling in ischemic heart failure rats and its related mechanism.Methods Forty rats were randomly divided into blank control group (Con group), nicodil group (NIC group), normal saline group (NS group) and Sham operation group (Sham group), with 10 rats in each group, and different treatment methods were adopted. The differences of body weight, respiratory pattern, activity and hair color were recorded. Echocardiography was performed in all rats 8 weeks after operation. After the experiment, the anterior wall tissue of the left ventricle of rats was observed by HE staining and electron microscopy. The relative expression levels of p-Akt, Bcl-2 protein and Bax in myocardial tissue were detected.Results Compared with Con group and Sham group, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and ratio of maximum velocity (E) to atrial contraction maximum ventricular filling velocity (A) (E/A) in NS group and NIC group were significantly decreased, and LVEF in NS group had the most decrease (P < 0.05). The left ventricular end-diastolicvolume (LVEDV) showed an opposite trend, with significant differences among the three groups, and the NS group had the highest LVEDV (P < 0.05). Left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVIDd) and left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVIDs) in NS group were significantly higher than those in NIC group and Sham group (P < 0.05). In the Sham group, the myocardial cells were arranged regularly and the transverse lines were clear; in the NS group, the myocardial cells were disordered and irregular in shape, and obvious fibrous tissue proliferation was also observed. However, compared with NS group, these abnormalities in NIC group were significantly reduced and myocardial fiber structure tended to be normal. The ratio of left ventricular weight (LVW) to body weight (LVW/BW) and lung mass index (Lungw/Bw) in Sham group and NIC group were significantly lower than those in NS group (P < 0.05). Compared with Con group and Sham group, the relative expression levels of p-Akt protein, Bcl-2 protein and Bax protein in NS group were significantly increased (P < 0.05). The relative expression levels of p-Akt protein and Bcl-2 protein in NIC group were significantly higher than those in NS group, but the expression level of Bax protein was significantly decreased (P < 0.05).Conclusion Nicorandil can protect rats with ischemic heart failure by improving cardiac function and left ventricular remodeling, which may be related to the inhibition of Bax protein expression.
-
Keywords:
- nicorandil /
- ischemic heart failure /
- left ventricular remodeling /
- cardiac function
-
近年来,初乳口腔免疫受到广泛关注,尤其是针对出生体质量低于1 500 g的极低出生体质量儿(VLBW)开展的相关治疗措施[1]。早产儿早期直接在口腔粘膜上放置少量初乳,可提供刺激免疫系统和促进肠道生长免疫的生长因子,可减少感染和新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎(NEC)的发生风险,提高VLBW的生存率,改善其长期预后[2]。目前,针对VLBW的相关护理实践研究较少[3]。因此,针对VLBW群体,基于护理实践的初乳口腔免疫干预值得进一步研究。本研究探讨初乳口腔免疫护理对VLBW生长发育的影响,以及初乳口腔免疫护理的积极影响,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
经南京医科大学伦理审查委员会同意,按照知情同意原则,于2019年7月—2020年6月从江苏省人民医院新生儿科收治的出生体质量低于1 500 g的早产儿中,招募69例VLBW纳入本研究,随机分为治疗组34例和对照组35例。纳入标准: ①出生体质量 < 1 500 g者。②出生后24 h内转入新生儿科病房者。③适于胎龄儿。排除标准: ①患严重紫绀型先天性心脏病、遗传代谢性疾病等者。②出生时存在严重先天性畸形,住院期间存在需要进行外科干预的疾病(如先天性肠道畸形、膈疝等)者。③母亲存在母乳喂养禁忌者。
治疗组早产儿在接受常规护理治疗的同时增加初乳口腔免疫护理。对照组早产儿给予常规治疗和护理,并给予初乳同等量生理盐水进行口腔按摩。
1.2 方法
早产儿出生后7 d内,乳母每日采用消毒的吸奶器或洁净的双手采集母乳,储存于一次性母乳专用储奶袋内,标明患儿姓名、床号、住院号、采集日期、时间、奶量,冷藏送至新生儿科。
初乳口腔免疫护理主要实施步骤: 从冰箱冷藏内取出奶袋,温奶器内放置5 min复温。洗手后带上无菌手套,使用1 mL注射器抽取0.2 mL母乳,去除注射器针头。使用负压吸引球清理患儿口腔内的分泌物,保持呼吸道通畅。将注射器沿患儿一侧嘴角送入口中,放于颊黏膜与牙龈之间,缓慢推注0.1mL初乳,持续时间大于20 s, 完成后移到患儿另侧颊黏膜与牙龈之间,向口腔内推注余下的0.1mL初乳,使用戴无菌手套的手按摩口腔内。初乳口腔免疫治疗每2 h进行1次,持续7 d。
口腔内按摩实施步骤: 治疗组和对照组都实施口腔内按摩。用两手指在宝宝脸颊两旁顺时针或逆时针按摩5 s。口周“米”字状按摩,嘴角两边、上嘴唇中间向下,下嘴唇中间向上、两上嘴角向下、两下嘴角向上,做“米”字状按摩。
1.3 观察指标
母亲的年龄、妊娠期并发症(妊娠期高血压、妊娠期糖尿病、绒毛膜羊膜炎)及产前激素水平、抗生素使用情况等资料通过电子病例系统查阅产科病例获得。早产儿的胎龄、出生体质量、性别、分娩方式、Apgar评分在转入新生儿科时记录。住院期间体格测量结果由经过培训的医生或护士统一测量记录,临床并发症以及住院天数、出院体质量、临床转归等资料在出院时由专人统一收集。
初乳口腔免疫护理相关实施方法经科内专家多次讨论,确定后对相关工作人员进行统一培训。早产儿相关临床资料由专人收集,及时审核以确保其完整性和准确性。体格测量的结果由经过统一培训的调查人员使用统一提供的测量工具进行测量。
1.4 数据分析
使用Epidata 3.1软件进行数据双轨录入,核对无误后采用软件进行统计分析。非正态分布的资料以P50(P25~P75)表示,正态分布资料以(x±s)表示,计数资料采用频数描述。组间差异比较,正态分布资料采用单因素方差(ANOVA)分析,非正态分布资料采用Mann-Whitney U检验。P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 研究对象一般情况
本次研究共纳入VLBW 69例,其中对照组35例,治疗组34例。治疗组男性早产儿20例(58.82%), 对照组男性早产儿19例(54.29%), 2组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗组小于28周早产儿6例(17.65%), 对照组8例(22.86%), 2组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。1 min Apgar评分10分早产儿对照组3例(8.57%), 治疗组4例(11.76%), 2组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 5 min Apgar评分10分早产儿对照组7例(20.00%), 治疗组6例(17.64%), 2组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗组和对照组在胎龄、剖宫产情况、超低出生体质量儿占比、出生身长、头围、体质量方面比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 2组VLBW一般情况比较[n(%)](x±s)一般情况 治疗组(n=34) 对照组(n=35) F/Z P 胎龄/周 29.22±1.67 29.91±1.45 3.336 0.072 男性 20(58.82) 19(54.29) -1.342 0.180 剖宫产占比 21(61.76) 27(77.14) -1.378 0.168 超低出生体质量儿 6(17.65) 8(22.86) 0.373 0.999 出生头围/cm 27.24±2.35 26.92±2.06 0.674 0.755 出生身长/cm 36.91±3.73 37.54±2.51 0.900 0.392 出生体质量/g 1 227.4±212.5 1 186.7±197.2 0.771 0.592 1 min Apgar评分/分 6.56±2.55 6.32±2.75 0.110 0.741 5 min Apgar评分/分 7.54±1.89 7.68±2.54 0.048 0.827 2.2 2组患儿治疗情况比较
2组开始经口喂养时间、开奶时间、使用有创和无创呼吸机治疗天数及住院时间比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。但治疗组达到全肠内营养时间显著短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 治疗组和对照组喂养情况[P50 (P25~P75)]d 类别 治疗组(n=34) 对照组(n=35) 开始经口喂养时间 7.00(4.00~12.00) 8.50(5.75~12.00) 达全肠内营养时间 41.50(32.00~55.80)* 43.00(29.00~55.00) 开奶时间 7.00(5.00~9.00) 8(5.00~12.00) 住院时间 51.00(42.50~60.00) 49.00(37.00~63.00) 有创呼吸机治疗时间 0(0~3.00) 0(0~2.25) 无创呼吸机治疗时间 5.00(3.00~7.00) 6(4.00~10.25) 与对照组比较, *P < 0.05。 2.3 2组患儿生长发育和临床结局比较
治疗组NEC、败血症及支气管发育不良的发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 2组视网膜病变、真菌感染、胆汁淤积、新生儿肺动脉高压、气胸、肝炎综合征、肺出血及抗生素使用时间的发生率比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。2组院内感染、真菌感染未见明显差异,但治疗组的院内感染情况好于对照组。见表 3。
表 3 2组临床结局情况比较[n(%)][P50(P25~P75)]临床结局 治疗组(n=34) 对照组(n=35) Z P 坏死性小肠结肠炎 0(0) 5(14.29) -2.272 0.023 支气管发育不良 14(41.18) 22(62.86) -2.039 0.041 败血症 0(0) 4(11.43) -2.016 0.044 院内感染 1(2.94) 6(17.14) -1.939 0.052 视网膜病变 2(5.88) 3(8.57) -0.428 0.669 真菌感染 0(0) 2(5.71) -1.404 0.160 抗生素使用时间/d 22(20, 24) 24(22, 25) 1.253 0.087 婴儿肝炎综合征 1(2.94) 2(5.71) -0.612 0.541 新生儿肺动脉高压 3(8.82) 1(2.86) -0.993 0.321 气胸 0(0) 1(2.86) -0.986 0.324 肺出血 0(0) 1(2.86) -0.986 0.324 治疗组平均每周体质量增加量高于对照组,且治疗组恢复出生体质量日龄早于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P=0.045, P=0.001)。治疗组的出院体质量为2 110(1 898~2 333) g, 对照组出院体质量为2 065(1 910~2 173) g, 参照早产儿Fenton生长曲线图[4], 以体质量作为评价标准,治疗组宫外生长发育迟滞发生率为44.11%(15/34), 低于对照组的68.57%(24/35), 差异有统计学意义(P=0.021)。见表 4。
表 4 2组生长发育情况比较生长发育 治疗组(n=34) 对照组(n=35) Z P 体质量增加/(g/w) 137.30(114.70~163.10) 125.40(101.50~133.30) -2.007 0.045 头围增加/(cm/w) 0.55(0.36~0.65) 0.56(0.37~0.73) -0.329 0.742 身长增加/(cm/w) 0.86(0.60~1.08) 0.78(0.55~1.27) -0.764 0.445 恢复出生体质量日龄/d 6.00(4.00~9.00) 10.00(8.00~14.00) -3.431 0.001 宫外生长发育迟滞/% 44.11 68.57 -2.306 0.021 3. 讨论
由于先天和后天适应性缺陷,早产儿尤其是VLBW的免疫系统发育极不成熟[5]。由于免疫系统缺陷发生感染是导致其死亡的重要原因[6]。相关研究[7]显示,迟发性败血症和NEC是导致VLBW死亡的重要原因。VLBW患儿因为出生时胃肠道在形态和功能上都不成熟,具有高度的通透性,其通常缺乏完善的微生物群或含有异常的微生物群[8]。长期的肠外营养会增加新生儿,尤其是VLBW晚发败血症等感染的风险。因此提高VLBW免疫功能可提高患儿生存率,降低迟发性败血症和NEC发生风险,减少死亡。研究[9]表明,初乳含有多种保护剂,其口咽给药安全,并可能与一些临床益处有关。得益于初乳中高浓度的免疫球蛋白A(IgA)、乳铁蛋白和其与肠道相关淋巴组织的相互作用,初乳口腔免疫治疗可以增强免疫系统功能[10]。然而,之前对于VLBW初乳口腔免疫治疗可以增强免疫系统功能的护理相关科学文献较少,部分临床研究样本量小,其中部分使用动物模型[11-12]替代人群研究,存在局限性。本研究针对于VLBW人群,以更全面地研究初乳口腔免疫护理对VLBW免疫系统及生长发育情况的全面影响。
本研究显示,在达到全肠内营养时间方面,治疗组显著短于对照组(P < 0.05), 这与RODRIGUEZ N A等[13]开展的研究结果相似。SEIGEL J K等[14]研究与本研究结果相一致,同时与孙勤[15]在江苏开展的早产儿初乳口腔免疫护理结果相近。ABD-ELGAWAD M等[16]研究也表明对VLBW开展初乳口腔免疫治疗能有效缩短相应治疗时间。初乳口腔免疫护理可缩短VLBW达到全肠内营养的时间,可能是由于在进行口腔涂抹的过程中,初乳附着于口咽部,初乳中的酶类和生长因子通过黏膜吸收,促进了早产儿的肠道运动和吸收功能的成熟[12]。
母乳是婴儿的第一免疫刺激物,具有完美的物种特异性营养[17]。本研究中,治疗组VLBW院内感染情况优于对照组,治疗组NEC、败血症及支气管肺发育不良的发生率均低于对照组(P < 0.005)。开展初乳口腔免疫治疗的VLBW血清学研究[18]结果显示,治疗组VLBW 15和30 d的IgA、IgM明显升高。研究[19]表明,初乳口腔免疫组被多方证实能缩短VLBW达全肠内营养时间,生命早期及时获得肠内营养能预防绒毛萎缩和营养吸收延迟,降低炎症、NEC和减少医院相关感染的护理风险发生。研究[20]表明,初乳口腔免疫还能提高VLBW唾液分泌IgA水平。初乳口腔免疫组VLBW达全肠内营养时间若较短,可改善细菌的定植和早产儿消化系统的发育,减少细胞因子的释放[21]。初乳口腔免疫对消化系统和免疫系统的共同促进,可能是因为加快VLBW的体质量增长速率,更快恢复VLBW出生体质量,降低宫外生长发育迟滞发生率。本研究由于纳入样本量有限以及未检测患儿免疫球蛋白水平、没有进行口腔细菌菌落分析等相关检验研究,存在一定局限性。在今后,将扩大研究样本量,开展更加全面具体的研究,以进一步探讨初乳口腔免疫护理对VLBW生长发育的全面影响。
综上所述,对VLBW开展每2 h一次的初乳口腔免疫护理,可缩短VLBW达到全肠内营养时间,同时有效减少早产儿NEC、败血症及BPD的发生风险,加快VLBW的体质量增长速率,更快恢复VLBW出生体质量,降低宫外生长发育迟滞发生率,从多方面改善患儿预后。
-
表 1 各组大鼠超声心动图指标水平比较(x±s)
指标 Con组(n=10) Sham组(n=10) NS组(n=10) NIC组(n=10) LVEF 72.60±9.00 68.30±9.40 48.90±7.40*#△ 59.50±8.40*# LVFS 42.60±7.80 39.50±7.40 26.50±11.90 34.40±6.20 E/A 2.16±0.40 2.02±0.20 0.98±0.21*#△ 1.33±0.31*# LVEDV 206.50±15.50 223.50±19.20 338.50±19.60*#△ 262.40±24.50 LVESV 66.90±10.20 72.60±9.70 118.50±28.20#△ 90.50±13.30 IVSd 1.32±0.30 1.36±0.20 1.52±0.20 1.38±0.20 LVIDd 6.29±0.80 6.59±0.70 8.04±0.80#△ 7.48±0.90 LVIDs 3.94±0.70 4.06±0.80 5.94±0.50#△ 4.83±0.30 LVEF: 左心室射血分数; LVFS: 左心室短轴收缩分数; E/A: 速度最大值(E)/心房收缩心室充盈速度最大值(A);
LVEDV: 左心室舒张末期容积; LVESV: 左心室收缩末期容积; IVSd: 室间隔舒张末期厚度; LVIDd: 左室舒张末期内径;
LVIDs: 左室收缩末期内径。与Con组比较, *P < 0.05; 与Sham组比较, #P < 0.05; 与NIC组比较, △P < 0.05。表 2 各组大鼠LVW/BW和LUNGW/BW比较
指标 Con组(n=10) Sham组(n=10) NS组(n=10) NIC组(n=10) LVW/BW 0.0028±0.005 0.0028±0.004* 0.003 6±0.002 0.002 7±0.005* LUNGW/BW 0.0041±0.008 0.0042±0.006* 0.006 4±0.003 0.004 0±0.002* LVW/BW: 左心室/体重比值; LUNGW/BW: 肺脏重量指数。与NS组比较, *P < 0.05。 -
[1] WANG X, PAN J, LIU D, et al. Nicorandil alleviates apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy through PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2019, 23(8): 5349-5359. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14413
[2] XIE J, JIANG M Y, LI L. Effect of nicorandil administration on preventing contrast-induced nephropathy: a meta-analysis[J]. Angiology, 2020, 71(5): 472-475. doi: 10.1177/0003319718785518
[3] GUO C Y, ZHANG Q, ZHU B Q, et al. Pharmaceutical cocrystals of nicorandil with enhanced chemical stability and sustained release[J]. Cryst Growth Des, 2020, 20(10): 6995-7005. doi: 10.1021/acs.cgd.0c01043
[4] HU K Q, WANG X Q, HU H Y, et al. Intracoronary application of nicorandil regulates the inflammatory response induced by percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(8): 4863-4870. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15169
[5] IRANIRAD L, HEJAZI S F, SADEGHI M S, et al. Efficacy of nicorandil treatment for prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in high-risk patients undergoing cardiac catheterization: a prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Cardiol J, 2017, 24(5): 502-507. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2017.0028
[6] LEE T M, LIN S Z, CHANG N C. Nicorandil regulates the macrophage skewing and ameliorates myofibroblasts by inhibition of RhoA/Rho-kinase signalling in infarcted rats[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(2): 1056-1069.
[7] YOSHIHISA A, SATO Y, WATANABE S, et al. Decreased cardiac mortality with nicorandil in patients with ischemic heart failure[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2017, 17(1): 141-145. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0577-3
[8] HE W K, SU Q, LIANG J B, et al. The protective effect of nicorandil on cardiomyocyte apoptosis after coronary microembolization by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in rats[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 496(4): 1296-1301. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.003
[9] FAN Z Y, LI Y, JI H H, et al. Efficacy of oral nicorandil to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with chronic renal dysfunction undergoing an elective coronary procedure[J]. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2019, 44(6): 1372-1382. doi: 10.1159/000503160
[10] GUPTA S, SINGH P, SHARMA B. Neuroprotective effects of nicorandil in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced vascular dementia[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2016, 25(11): 2717-2728. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.07.023
[11] BABIC V, PETITPAIN N, GUY C, et al. Nicorandil-induced ulcerations: a 10-year observational study of all cases spontaneously reported to the French pharmacovigilance network[J]. Int Wound J, 2018, 15(4): 508-518. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12845
[12] ZHANG X, YANG S C, ZHANG P, et al. Efficacy of nicorandil on the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with coronary heart disease undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Coron Artery Dis, 2020, 31(3): 284-288. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000826
[13] DONG Y F, CHEN Z Z, ZHAO Z, et al. Potential role of microRNA-7 in the anti-neuroinflammation effects of nicorandil in astrocytes induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2016, 13(1): 60-63. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0527-5
[14] LEE J M, KATO D, OI M, et al. Safety and efficacy of intracoronary nicorandil as hyperaemic agent for invasive physiological assessment: a patient-level pooled analysis[J]. EuroIntervention, 2016, 12(2): e208-e215. doi: 10.4244/EIJV12I2A34
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 贾庶捷,张倩落,李燕平,任健,杨海敏. 血必净注射液联合连续性肾替代疗法、白蛋白治疗肾综合征出血热的效果及对炎性因子、相关蛋白表达的影响. 临床医学研究与实践. 2024(02): 58-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 姜文娟,贺芬,任阳,张旭. 血清清蛋白联合动态动脉僵硬指数对急性缺血性脑卒中病人静脉溶栓后出血转化的预测价值. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志. 2023(05): 908-912 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 饶建锋,李珊. 流行性出血热患者血清CK-MB、IL-6、IL-10水平与病情程度、预后的关系研究. 中国医学创新. 2023(27): 137-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
