Etiology and prognostic indicators of pediatric acute liver failure
-
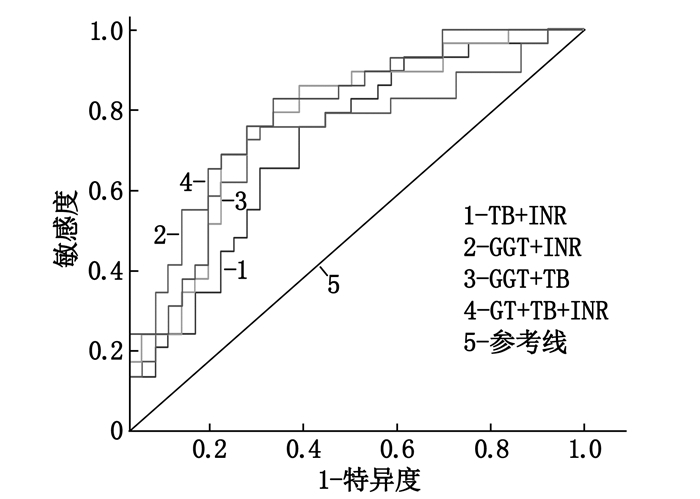
摘要:目的 分析儿童急性肝衰竭(PALF)的病因及预后指标。方法 回顾性分析64例PALF患儿的临床资料,根据预后的不同将患儿分为死亡组和存活组,比较2组患儿的年龄、性别、生化指标和儿童终末期肝病模型(PELD)评分。结果 本研究PALF患儿的最常见病因为遗传代谢疾病(18例),此后依次为感染因素(13例)、药物毒副作用与中毒(8例)、血液系统疾病(4例)、自身免疫性肝病(2例)、缺血性肝病(1例),另有18例患儿病因不明;死亡组患儿总胆红素(TB)、国际标准化比值(INR)、PELD评分水平高于存活组,γ-谷氨酰转肽酶(GGT)水平低于存活组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析显示,GGT、TB、INR三者联合的曲线下面积为0.793(95% CI为0.684~0.903),诊断PALF预后的敏感度为0.828,特异度为0.626。结论 遗传代谢疾病是PALF的主要病因,PALF患儿出现TB、INR升高和GGT降低时提示预后不良,需尽早完善评估并及时选择合适的治疗方案。Abstract:Objective To analyze the etiology and the prognostic indicators of pediatric acute liver failure (PALF).Methods A retrospective study was performed on the data of 64 patients with PALF. The patients were then divided into survival group and death group based on their prognosis. Age, gender, biochemical indicators and pediatric of end-stage liver disease (PELD) were compared between the two groups.Results The common causes of PALF were identified as genetic and metabolic diseases (18 cases), followed by infectious diseases (13 cases), drug adverse reations and toxicity(8 cases), hematopathy (4 cases), immunologic liver diseases (2 cases), ischemic liver disease (1 case), and unclear causes (18 cases). The levels of total bilirubin (TB), international standardized ratio (INR) and PELD score in the death group were higher than those in the survival group, and the level of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) in the death group was lower than that in the survival group (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed that the combined area under the curve of GGT, TB and INR in combination was 0.793 (95%CI, 0.684 to 0.903), and the prognostic sensitivity and specificity of PALF diagnosis were 0.828 and 0.626, respectively.Conclusion Inherited metabolic disorders are the most common known cause of PALF. For patients with PALF, higher levels of TB, INR and lower level of GGT may indicate a poor prognosis.
-
-
表 1 存活组和死亡组患儿的临床资料比较[M(P25, P75)][n(%)]
指标 存活组(n=35) 死亡组(n=29) Z/χ2 P 年龄/月 16.00(7.00, 64.00) 36.00 (6.00, 96.00) 1.569 0.123 性别 男 14(40.00) 16(55.17) 1.466 0.226 女 21(60.00) 13(44.83) TB/(μmol/L) 114.81(69.21, 180.42) 174.62(120.33, 248.82) -2.124 0.034 DB/(μmol/L) 99.53(47.64, 149.82) 125.56(78.05, 178.31) -1.369 0.171 ALT/(U/L) 648.04(98.92, 2 000.10) 322.10(92.12, 3 019.25) -0.040 0.968 AST/(U/L) 640.04(186.02, 2 064.21) 580.11(193.14, 3 695.25) -0.330 0.741 Alb/(g/L) 31.93(26.24, 37.15) 30.65(23.18, 36.58) -0.487 0.663 INR 2.35(1.99, 5.04) 4.65(2.48, 5.86) -2.327 0.020 TBA/(μmol/L) 173.81(94.03, 302.70) 143.28(68.75, 253.80) -1.328 0.184 GGT/(U/L) 87.00(65.00, 215.00) 57.00(31.50, 161.00) -2.954 0.003 Cr/(μmol/L) 18.20(15.11, 32.00) 22.10(13.05, 77.99) -0.996 0.319 PELD评分/分 20.40(18.20, 33.30) 30.60(24.70, 39.00) -2.387 0.017 TB: 总胆红素; DB: 直接胆红素; ALT: 丙氨酸转氨酶; AST: 天冬氨酸转氨酶; Alb: 白蛋白; INR: 国际化标准比值; TBA: 总胆汁酸; GGT: γ-谷氨酰转肽酶; Cr: 肌酐; PELD: 儿童终末期肝病模型。 表 2 相关指标的ROC曲线分析结果
指标 曲线下面积 标准误 95%CI TB 0.655 0.070 0.519~0.792 INR 0.680 0.069 0.545~0.814 GGT 0.716 0.067 0.585~0.847 TB联合INR 0.716 0.064 0.591~0.842 GGT联合INR 0.744 0.064 0.618~0.870 GGT联合TB 0.775 0.059 0.660~0.891 GGT、TB、INR联合 0.793 0.056 0.684~0.903 TB: 血清总胆红素; INR: 国际标准化比值; GGT: γ-谷氨酰转肽酶。 表 3 相关指标对PALF预后的诊断价值
指标 截断值 敏感度 特异度 Youden指数 阳性似然比 阴性似然比 TB 171.55 0.586 0.743 0.329 2.28 0.56 INR 2.84 0.724 0.686 0.410 2.30 0.40 GGT 47.00 0.886 0.586 0.472 5.13 0.47 GGT、TB、INR联合 - 0.828 0.626 0.513 2.63 0.25 TB: 血清总胆红素; INR: 国际标准化比值; GGT: γ-谷氨酰转肽酶。 -
[1] LEE W M, SQUIRES R H, NYBERG S L, et al. Acute liver failure: Summary of a workshop[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 47(4): 1401-1415.
[2] CIOCCA M, RAMONET M, CUARTEROLO M, et al. Prognostic factors in paediatric acute liver failure[J]. Arch Dis Child, 2008, 93(1): 48-51. doi: 10.1136/adc.2006.115113
[3] DHAWAN A. Acute liver failure in children and adolescents[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2012, 36(3): 278-283. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2012.03.022
[4] KAMATH P S, WIESNER R H, MALINCHOC M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2001, 33(2): 464-470. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.22172
[5] NEWLAND C D. Acute Liver Failure[J]. Pediatr Ann, 2016, 45(12): e433-e438.
[6] HEGARTY R, HADZIC N, GISSEN P, et al. Inherited metabolic disorders presenting as acute liver failure in newborns and young children: King's College Hospital experience[J]. Eur J Pediatr, 2015, 174(10): 1387-1392. doi: 10.1007/s00431-015-2540-6
[7] DIAS C F, MOINHO R, FERREIRA S, et al. Acute liver failure related to inherited metabolic diseases in young children[J]. An Pediatr (Barc), 2018, 88(2): 69-74. doi: 10.1016/j.anpedi.2017.02.012
[8] WANG J S, TAN N, DHAWAN A. Significance of low or normal serum gamma glutamyl transferase level in infants with idiopathic neonatal hepatitis[J]. Eur J Pediatr, 2006, 165(11): 795-801. doi: 10.1007/s00431-006-0175-3
[9] 徐惠敏, 兰小勤, 纪雅丽. 肝功能衰竭合并肝硬化患者血清γ-谷氨酰转肽酶与前白蛋白水平的相关性[J]. 中国肝脏病杂志: 电子版, 2018, 10(3): 90-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZBZ201803023.htm [10] LU F T, WU J F, HSU H Y, et al. gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase level as a screening marker among diverse etiologies of infantile intrahepatic cholestasis[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2014, 59(6): 695-701. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000538
[11] ABUDUXIKUER K, CHEN R, WANG Z L, et al. Risk factors associated with mortality in neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency (NICCD) and clinical implications[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2019, 19(1): 18-25. doi: 10.1186/s12887-018-1383-5
[12] OSWARI H, WIDJAJA R K, ROHSISWATMO R, et al. Prognostic value of biochemical liver parameters in neonatal sepsis-associated cholestasis[J]. J Paediatr Child Health, 2013, 49(1): E6-E11. doi: 10.1111/jpc.12053
[13] CHEN H L, WU S H, HSU S H, et al. Jaundice revisited: recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of inherited cholestatic liver diseases[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2018, 25(1): 75-87. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0475-8
[14] ZHANG J, YANG Y, GONG J Y, et al. Low-GGT intrahepatic cholestasis associated with biallelic USP53 variants: Clinical, histological and ultrastructural characterization[J]. Liver Int, 2020, 40(5): 1142-1150. doi: 10.1111/liv.14422
[15] 姜涛, 欧阳文献, 谭艳芳, 等. 儿童急性肝衰竭120例病因和预后分析[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2020, 35(6): 422-425. [16] 苗敏, 钱素云. 儿童急性肝衰竭流行病学研究进展及预后因素分析[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2018, 27(11): 1302-1307. [17] LÓPEZ-VELÁZQUEZ J A, CHÁVEZ-TAPIA N C, PONCIANO-RODRÍGUEZ G, et al. Bilirubin alone as a biomarker for short-term mortality in acute-on-chronic liver failure: an important prognostic indicator[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2013, 13(1): 98-104. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/24378272
[18] 苗敏, 钱素云. 儿童急性肝衰竭病因及转归相关因素分析[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2019, 34(19): 1462-1466. [19] 罗兰, 刘萍萍, 隆彩霞, 等. 重症儿童急性肝衰竭预后的相关因素[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2019, 34(18): 1390-1393.




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号