Effect of Hashimoto's thyroiditis on degree of necklymph node dissection and prognosis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
-
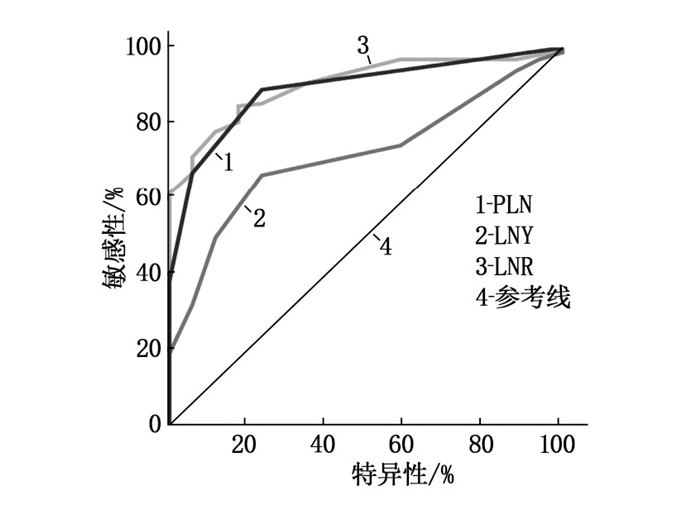
摘要:目的 探讨桥本甲状腺炎(HT)对甲状腺乳头状癌(PTC)患者颈淋巴结清扫程度及预后的影响。方法 回顾性分析2013年1月—2015年12月武汉市红十字会医院收治的180例行甲状腺全切除术联合中央区淋巴结清扫术的PTC患者的临床病理资料。根据术后HT诊断结果将患者分为PTC伴HT组(n=55)和PTC不伴HT组(n=125),手术后随访5年。根据初始治疗反应,依据2015年美国甲状腺协会指南进行动态危险度分层(DRS)。比较2组患者的临床病理特征和DRS;应用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评估转移性淋巴结数(PLN)、清扫淋巴结数(LNY)、转移性淋巴结比率(LNR)预测结构性复发/持续性疾病的价值及最佳界值点,并进一步通过Cox比例风险模型评估结构性复发/持续性疾病的风险因素。结果 2组患者颈中央区淋巴结转移差异无统计学意义(P=0.508),伴发HT并不能降低颈淋巴结转移的风险。PTC伴HT组LNY多于PTC不伴HT组,差异有统计学意义(P=0.001)。PTC伴HT组LNR显著较小(P=0.040),并与结构性复发/持续性疾病独立相关(OR=59.574,P=0.012)。在调整了其他临床病理因素后,HT本身与结构性复发/持续性疾病呈显著负相关(OR=0.064,P=0.032)。结论 无论淋巴结清扫达到何种程度,伴发HT是与PTC患者预后良好相关的独立因素。Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) on the degree of neck lymph node dissection and prognosis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC).Methods The clinical and pathological materials of 180 PTC patients underwent total thyroidectomy combined with central lymph node dissection in Wuhan City Red Cross Hospital from January 2013 to December 2015 were retrospectively analyzed. According to the postoperative HT diagnosis, the patients were divided into PTC combined with HT group (n=55) and PTC without HT group (n=125), and all the patients were followed up for 5 years after operation. According to the initial response to treatment, dynamic risk stratification (DRS) was performed according to the guidelines of the American Thyroid Association in 2015. The clinicopathological characteristics and DRS of the two groups were compared. The value and the best cut-off point of the number of positive lymph nodes (PLN), the number of lymph nodes yield (LNY) and lymph nodes ratio (LNR) in predicting structural relapse or persistent disease were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and the risk factors of structural relapse or persistent disease were further evaluated by Cox proportional hazards model.Results There was no significant difference in central cervical lymph node metastasis between the two groups (P=0.508), which suggested that complicating with HT was unable to reduce the risk of cervical lymph node metastasis. LNY in the PTC combined with HT group was significantly more than that in the PTC without HT group (P=0.001). LNR was significantly lower in the PTC with HT group (P=0.040), and was independently associated with structural relapse or persistent disease (OR=59.574, P=0.012). After adjusting for other clinicopathological factors, HT itself was negatively correlated with structural relapse or persistent disease (OR=0.064, P=0.032).Conclusion Regardless of the extent of lymph node dissection, HT is an independent prognostic factor for PTC patients.
-
目前,冠心病诊断的“金标准”是冠状动脉造影(CAG),临床中多依据CAG评估患者冠状动脉狭窄程度,并结合患者临床资料决定是否行介入治疗。但CAG难以对狭窄病变导致的心肌缺血情况进行评估,且受多种因素影响,导致其在评估冠状动脉狭窄程度上存在一定的局限性,特别是对于狭窄程度50%~70%的临界病变准确性较低[1]。临界病变治疗方案选择需结合斑块稳定性及是否导致心肌缺血来综合评估,明确斑块性质及血流动力学对治疗方案的选择尤为重要[2]。血管内超声(IVUS)及血流储备分数(FFR)是临界病变治疗方案选择的重要参考依据,其中IVUS是评估斑块稳定性的检查手段,而FFR是评估是否导致心肌缺血的检查手段[3-4]。本研究回顾性分析65例非ST段抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征(NSTE-ACS)患者临床资料,比较IUVS、FFR指导下的PCI对临界病变患者血浆脑钠肽(BNP)、超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)水平及主要不良心血管事件(MACE)的影响,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
回顾性分析2018年1月—2020年1月本院收治的65例行经皮冠状动脉介入(PCI)治疗的NSTE-ACS临界病变(冠状动脉狭窄50%~70%, 单支血管病变,直径≥2.5 mm)患者的临床资料,其中男40例,女25例,年龄55~75岁,平均(65.67±8.04)岁。纳入标准: ①患者均符合《非ST段抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征诊断和治疗指南(2016)》[5]中的相关诊断标准,且经CAG确诊为临界病变; ②可行PCI治疗者; ③患者或其家属知情。排除标准: ①合并严重心、肝、肾等脏器功能障碍者; ②合并弥漫性病变、左主干病变、多支血管病变等复杂病变者; ③存在PCI禁忌或IUVS、FFR检查禁忌者; ④ ST段抬高型急性心肌梗死者; ⑤既往PCI史者; ⑥合并恶性肿瘤者; ⑦预计生存期 < 1年者。根据PCI指导方式分为IVUS组33例和FFR组32例。
1.2 方法
依据Judkins法穿刺桡动脉或股动脉行CAG检查,根据患者病变部位获取全方位、多角度的造影图像,准确判断患者冠状动脉病变长度、部位、狭窄程度及血管壁状况。
IVUS组: CAG检查结束后,顺导丝置入超声导管于狭窄血管远端,以手动或自动方式缓慢(1 mm/s)回撤超声导管,超声导管前端探头获取、储存、分析血管横截面图像,并测定最小管腔面积(MLA),评估斑块性质。回撤过程中标记感兴趣重要血管解剖部位,以确定狭窄病变部位。根据MLA值及斑块性质确定PCI术中支架长度及直径。
FFR组: CAG检查结束及体外校正压力导丝完毕后,沿指引导管及导引针置入压力传感器于冠状动脉开口处,X线透视下确定压力传感器位置正确后校零,并送压力导丝进入冠状动脉病变部,将导丝上携带压力感受器置于距冠状动脉病变部远端2~3 cm处,前臂正中静脉持续泵注三磷酸腺苷(ATP), 直至冠状动脉微血管充血扩张至最大状态,动脉检测仪显示屏上即可显示FFR值,待FFR值稳定后取最小值作为最终结果。
1.3 观察指标
比较2组患者PCI情况及手术前后血浆BNP、hs-CRP水平。入院即刻和PCI术后7 d时抽取2组患者肘静脉血3 mL, 置于EDTA抗凝管, -70 ℃冷存待检。采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测待测样本中的BNP、hs-CRP水平,试剂盒购自上海酶联生物科技有限公司,严格按照试剂盒说明书进行操作。术后随访12个月,比较2组患者MACE发生情况。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0软件处理数据,计数资料以[n(%)]表示,组间差异采用Fisher确切概率分析检验; 正态分布的计量资料以(x±s)表示,组间差异采用独立样本t检验,组内治疗前后差异采用配对样本t检验。P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组患者基线资料比较
2组患者性别、年龄、体质量指数(BMI)、高血压史、高脂血症史、糖尿病史、吸烟史、心肌梗死史、心率、左室射血分数(LVEF)等基线资料比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2组患者基线资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]基线资料 IVUS组(n=33) FFR组(n=32) 男 21(63.64) 19(59.38) 女 12(36.36) 13(40.63) 年龄/岁 65.71±8.06 65.63±8.19 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 23.74±2.09 23.88±2.36 高血压 15(45.45) 14(43.75) 高脂血症 10(30.30) 11(34.38) 糖尿病 4(12.12) 3(9.38) 吸烟史 6(18.18) 7(21.88) 心肌梗死史 3(9.09) 2(6.25) 心率/(次/min) 87.76±8.95 89.31±9.42 左室射血分数/% 57.20±7.45 55.05±10.07 2.2 2组患者PCI情况比较
2组患者的病变部位、狭窄程度、病变血管直径、病变长度、支架植入率、支架植入数、PCI相关并发症等比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 2组患者PCI情况比较(x±s)[n(%)]指标 IVUS组(n=33) FFR组(n=32) 病变部位 左前降支 17(51.52) 20(62.50) 左回旋支 6(18.18) 4(12.50) 右冠状动脉 10(30.30) 8(25.00) 狭窄程度/% 62.61±5.05 60.26±7.51 病变血管直径/mm 3.58±0.74 3.31±0.55 病变长度/mm 20.23±6.83 21.51±7.01 支架植入 18(54.55) 12(37.50) 支架植入数/个 1.45±0.44 1.60±0.51 PCI相关并发症 3(9.09) 1(3.13) 2.3 2组患者手术前后血浆BNP、hs-CRP水平比较
2组患者入院即刻的血浆BNP、hs-CRP水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 2组患者术后7 d的血浆BNP、hs-CRP水平均低于入院即刻,且IVUS组低于FFR组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 3。
表 3 2组患者手术前后血浆BNP、hs-CRP水平比较(x±s)组别 时点 BNP/(ng/L) hs-CRP/(mg/L) IVUS组(n=33) 入院即刻 159.43±33.48 11.48±3.45 术后7 d 118.66±24.39*# 7.45±2.36*# FFR组(n=32) 入院即刻 161.38±35.35 11.69±3.34 术后7 d 133.52±28.89* 9.52±2.94* BNP: 脑钠肽; hs-CRP: 超敏C反应蛋白。
与入院即刻比较, *P < 0.05; 与FFR组比较, #P < 0.05。2.4 2组患者MACE发生情况比较
2组患者MACE发生情况及复发性心绞痛比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 见表 4。
表 4 2组患者MACE发生情况比较[n(%)]组别 IVUS组(n=33) FFR组(n=32) 靶血管血运重建 5(15.15) 3(9.38) 非致死性心肌梗死 1(3.03) 1(3.13) 心源性死亡 0 1(3.13) 复发性心绞痛 2(6.06) 3(9.38) MACE 6(18.18) 5(15.63) 心源性死亡采用Fisher确切概率分析;
复发性心绞痛不属于MACE; MACE: 主要不良心血管事件。3. 讨论
研究[7]显示,冠状动脉狭窄程度在50%~70%的临界病变通常是不会导致心肌缺血,但少数临界病变会引发心肌缺血甚至急性冠状动脉综合征,这些病变斑块稳定性较差,易破裂形成血栓。因此,病变稳定性对患者预后影响程度大于病变狭窄程度。目前,针对临界病变治疗策略存在较大分歧,研究[8]认为临界病变存在心肌缺血、心绞痛等证据时,主张行PCI治疗,若缺少心肌缺血证据时,则需行冠状动脉影像学检查以指导选择治疗方案。
CAG是冠心病诊断的“金标准”,但不能准确判断临界病变。IVUS、FFR技术的运用在较大程度上弥补了CAG不足,使临床医师对临界病变的斑块性质及血流动力学判断更为准确[9]。FFR是评估冠状动脉狭窄是否导致心肌缺血的重要方法,已被多个指南纳入并推荐作为指导、评估PCI的方法之一,特别对临界病变的血运重建治疗方案选择具有重要指导价值。FFR局限性是当患者处于急性心肌梗死、左心室肥厚、严重微循环障碍、冠状动脉痉挛、侧支循环等病理生理状态下时,难以评估病变血管的血流动力学,且活性药物存在一定不良反应[10]。IVUS可清晰显示冠状动脉管腔并精确定位病变部位,弥补CAG在狭窄程度、病变范围评估等方面的不足。国外研究[11]表明, IVUS指导临界病变血运重建标志为MLA≤4.0 mm2, 敏感度、特异度分别为88%、90%。本研究沿用此标准, MLA≤4.0 mm2的患者则行PCI治疗,反之则行药物治疗。
本研究结果表明, IVUS组及FFR组在病变部位、狭窄程度、病变血管直径、病变长度、支架植入率、支架植入数、PCI相关并发症等方面差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 提示2种技术均可准确反映临界病变冠状动脉情况,但IVUS组支架植入率相对更高。BNP是一种多肽类激素,心肌缺血、左心室容量和压力负荷增大时,血浆BNP水平会显著升高。BNP具有重要的病理生理学意义,可以促进排钠、排尿,具有较强的舒张血管作用,可对抗肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统(RAAS)的缩血管作用[12-13]。CRP是一种急性时相蛋白,其本身直接参与了炎症与动脉粥样硬化等心血管疾病过程,是心血管疾病最强有力的预示因子与危险因子。研究[14-15]证实hs-CRP与冠状动脉斑块稳定性密切相关。本研究中,2组患者入院时血浆BNP、hs-CRP均高于正常值,提示机体处于心肌缺血及高炎症状态,而2组术后7 d血浆BNP、hs-CRP均降低,且IVUS组降低程度更大,提示IVUS指导PCI治疗NSTE-ACS临界病变可改善患者心肌缺血、炎性反应。此外,术后随访12个月发现,2组患者MACE发生率无差异,表明IVUS指导PCI治疗NSTE-ACS临界病变患者的短期预后与FFR指导PCI治疗无异[16]。
综上所述, IVUS指导PCI治疗NSTE-ACS临界病变可改善患者血浆BNP、hs-CRP水平,且不会增高MACE发生风险。
-
表 1 2组患者临床病理特征(x±s)[n(%)]
变量 PTC伴HT组(n=55) PTC不伴HT组(n=125) t/χ2/Z P 年龄/岁 52.05±11.11 52.40±10.22 -0.203a 0.839 性别 女 51(92.73) 93(74.40) 8.018b 0.005 男 4(7.27) 32(25.60) FT3/(pmol/L) 4.88±0.77 4.86±0.71 0.143a 0.886 FT4/(pmol/L) 15.30±3.83 16.31±2.37 -1.696c 0.090 TSH/(mIU/L) 5.46±11.50 2.60±1.67 -2.036c 0.042 肿瘤直径/cm 1.19±0.35 1.18±0.26 -0.347c 0.728 多灶性 是 17(30.91) 37(29.60) 0.031b 0.860 否 38(69.09) 88(70.40) 甲状腺外侵犯 是 32(58.18) 23(18.40) 0.030b 0.863 否 23(41.82) 102(81.60) 中央区淋巴结转移 是 38(69.09) 80(64.00) 0.438b 0.508 否 17(30.91) 45(36.00) PLN/枚 1.11±0.94 1.26±1.16 -0.609c 0.543 LNY/枚 10.29±1.66 8.07±1.99 7.234a 0.001 LNR 0.10±0.08 0.13±0.12 -2.054c 0.040 a表示采用t检验, b表示采用χ2检验, c表示采用Mann-Whitney U检验。PTC: 甲状腺乳头状癌;
HT: 桥本甲状腺炎; PLN: 转移性淋巴结数; LNY: 清扫淋巴结数; LNR: 转移性淋巴结比率。表 2 2组患者动态风险分层[n(%)]
动态风险分层 PTC伴HT组(n=55) PTC不伴HT组(n=125) 反应良好 41(74.54) 90(72.00) 反应不确切 5(9.09) 17(13.60) 生化反应欠佳 6(10.91) 11(8.80) 结构反应欠佳 3(5.46) 7(5.60) PTC: 甲状腺乳头状癌; HT: 桥本甲状腺炎。 表 3 PTC患者结构性复发/持续性疾病危险因素的单因素和多因素Cox回归分析[n(%)]
变量 单因素分析 多因素分析 复发(n=17) 未复发(n=163) P B OR 95%CI P 年龄≥55岁 13(76.47) 69(42.33) 0.007a 2.884 17.878 3.890~82.172 0.001 女性 15(88.23) 129(79.14) 0.531b - - - - 肿瘤直径>1 cm 13(76.47) 82(50.31) 0.040a 0.679 1.972 0.621~6.261 0.249 多灶 14(82.35) 40(24.54) 0.001a -2.365 0.094 0.008~1.122 0.062 腺外侵犯 12(70.59) 91(55.83) 0.242a - - - - PLN>2枚 14(82.35) 17(10.43) 0.001b 2.187 8.908 1.250~63.478 0.029 LNY>11枚 7(41.18) 42(25.77) 0.249b - - - - LNR>0.4 15(88.23) 23(14.11) 0.001b 4.087 59.574 2.502~1 418.524 0.012 伴发HT 1(5.88) 54(33.13) 0.020a -2.754 0.064 0.005~0.784 0.032 a表示采用Pearson χ2检验, b表示采用Fisher检验。PTC: 甲状腺乳头状癌; HT: 桥本甲状腺炎;
PLN: 转移性淋巴结数; LNY: 清扫淋巴结数; LNR: 转移性淋巴结比率。 -
[1] CHEN Y K, LIN C L, CHANG Y J, et al. Cancer risk in patients with Graves'disease: a nationwide cohort study[J]. Thyroid, 2013, 23(7): 879-884. doi: 10.1089/thy.2012.0568
[2] 张玮婧, 张捷, 彭娟, 等. 桥本氏甲状腺炎与甲状腺乳头状癌的相关性分析[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2014, 19(7): 630-632. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCZL201407014.htm [3] LEE J H, KIM Y, CHOI J W, et al. The association between papillary thyroid carcinoma and histologically proven Hashimoto's thyroiditis: a meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2013, 168(3): 343-349. doi: 10.1530/EJE-12-0903
[4] DONANGELO I, WALTS A E, BRESEE C, et al. Lymphocytic thyroiditis is associated with increased number of benign cervical nodes and fewer central neck compartment metastatic lymph nodes in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Endocr Pract, 2016, 22(10): 1192-1198. doi: 10.4158/E151078.OR
[5] WANG P, WANG Y, MIAO C, et al. Defining a new tumor dimension in staging of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017, 24(6): 1551-1556. doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-5764-z
[6] HAUGEN B R, ALEXANDER E K, BIBLE K C, et al. 2015American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American thyroid association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2016, 26(1): 1-133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020
[7] 蔡永聪, 陈锦, 陈建超, 等. 细化分析甲状腺乳头状癌Ⅱ区淋巴结转移特点[J]. 中华内分泌外科杂志, 2016, 10(4): 287-290. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6090.2016.04.007 [8] 陆志峰, 冯尚勇, 顾学文, 等. 359例甲状腺癌患者临床特点及颈部淋巴结转移的相关因素[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2018, 22(21): 61-64. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201821019 [9] 周科, 潘俊峰, 龙斌斌, 等. 中央淋巴结清扫术治疗分化型甲状腺癌的临床疗效及预后分析[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2018, 22(3): 63-65. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201803017 [10] ZHU F, SHEN Y B, LI F Q, et al. The effects of Hashimoto thyroiditis on lymph node metastases in unifocal and multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective Chinese cohort study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2016, 95(6): e2674. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC4753890/
[11] QU N, ZHANG L, LIN D Z, et al. The impact of coexistent Hashimoto's thyroiditis on lymph node metastasis and prognosis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(6): 7685-7692. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4534-4
[12] QU H, SUN G R, LIU Y, et al. Clinical risk factors for central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Endocrinol(Oxf), 2015, 83(1): 124-132. doi: 10.1111/cen.12583
[13] KIM H S, CHOI Y J, YUN J S. Features of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in the presence and absence of lymphocytic thyroiditis[J]. Endocr Pathol, 2010, 21(3): 149-153. doi: 10.1007/s12022-010-9124-9
[14] HEATON C M, CHANG J L, ORLOFF L A. Prognostic implications of lymph node yield in central and lateral neck dissections for well-differentiated papillary thyroid car cinoma[J]. Thyroid, 2016, 26(3): 434-440. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0318
[15] HU J Q, WEN D, MA B, et al. The extent of lymph node yield in central neck dissection can be affected by preoperative and intraoperative assessment and alter the prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(3): 1017-1024. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2762
[16] 穆佳丽, 李昉璇, 魏玺, 等. 甲状腺乳头状癌淋巴结外软组织阳性的临床病理特征及超声表现[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2018, 40(4): 264-267. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.04.005 [17] 黄樱城, 李正江. 分化型甲状腺癌治疗管理和动态风险评估现状[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(5): 389-393. [18] MAHUL BA, STEPHEN E, FREDERICK LG, et al. AJCCcancer staging manual[M]. 8th ed. New York: Springer, 2016: 1-11.
[19] SUNG T Y, CHO J W, LEE Y M, et al. Dynamic risk stratification in stage I papillary thyroid cancer patients younger than 45 Years[J]. Thyroid, 2017, 27(11): 1400-1407. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0199
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 夏冬梅,石光顺,韩婷婷,金水. 血清半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂S在胃癌患者中的诊断价值. 实用临床医药杂志. 2025(02): 48-51 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 胡飞,张克昌,陈峰,童正喜,涂秀. 胃癌患者血清胃泌素释放肽前体、鳞癌相关抗原和糖类抗原72-4的变化及意义. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(12): 46-50 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
