Value of preoperative prognostic nutrition index in predicting prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients initially undergoing radical operation
-
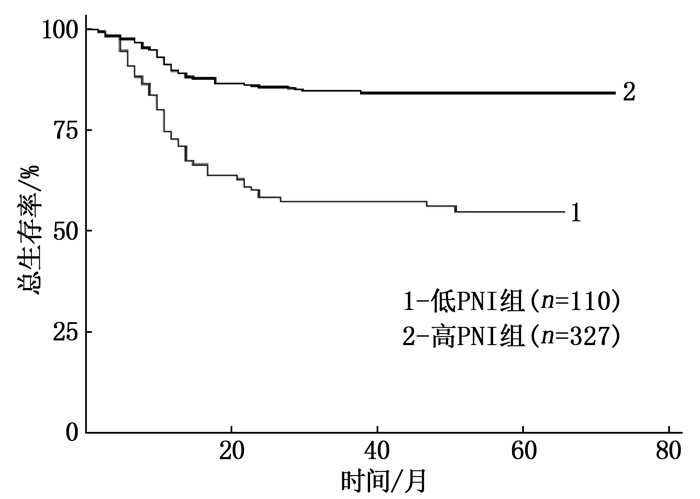
摘要:目的 探讨术前预后营养指数(PNI)对首次行根治性手术的口腔鳞状细胞癌(OSCC)患者预后的预测价值。方法 回顾性分析2015年1月—2017年10月上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院首次行根治性手术的437例OSCC患者的临床和随访资料。根据术前1周的血常规检查结果计算PNI。通过受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线计算约登(Youden)指数,将Youden指数最大值所对应的PNI作为预测OSCC预后的最佳临界值。分析术前PNI与临床病理特征的关系。采用Kaplan-Meier生存曲线和Cox回归模型分析PNI对OSCC患者预后的影响。结果 患者术前PNI的平均值为(49.93±5.60),最佳临界值为46.23。术前PNI与年龄(P < 0.001)、T分期(P < 0.001)、TNM分期(P=0.013)有相关性。高PNI组患者3年总生存率为84.7%,高于低PNI组的57.3%,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。多因素分析结果显示,年龄>60岁(HR=2.211,95% CI为1.390~3.518,P=0.001)、TNM分期为Ⅲ期和Ⅳ期(HR=3.911,95% CI为2.561~6.221,P < 0.001)、PNI≤46.23(HR=2.554,95% CI为1.707~3.821,P < 0.001)是OSCC患者术后预后较差的独立危险因素。结论 术前低PNI是影响OSCC患者预后的独立危险因素,对OSCC的预后评估具有一定的指导意义。Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of postoperative prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in predicting prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) patients initially undergoing radical operation.Methods Clinical and follow-up materials of 437 OSCC patients initially undergoing radical operation in the Ninth People's Hospital Affiliated to Medical School of Shanghai Jiaotong University from January 2015 to October 2017 were retrospectively analyzed. PNI was calculated according to the blood routine results one week before surgery. The Youden index was calculated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and PNI with the maximum Youden index was selected as the optimal critical value for predicting the prognosis of OSCC. The relationship between preoperative PNI and clinical characteristics was analyzed. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox regression analysis were conducted to analyze the influence of PNI on prognosis of patients with OSCC.Results The mean value of preoperative PNI was (49.93±5.60) and the optimal critical value of PNI was 46.23. Preoperative PNI was associated with age (P < 0.001), T staging (P < 0.001) and TNM staging (P=0.013). The 3-year survival rate of patients in the high PNI group was 84.7%, which was significantly higher than 57.3% in the low PNI group (P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that aged over 60 years old (HR=2.211, 95% CI, 1.390 to 3.518, P=0.001), stage Ⅲ and Ⅳ of TNM (HR=3.911, 95% CI, 2.561 to 6.221, P < 0.001) and PNI ≤46.23 (HR=2.554, 95% CI, 1.707 to 3.821, P < 0.001) were the independent risk factors of prognosis in patients with OSCC.Conclusion Preoperative low PNI is an independent risk factor for the prognosis of patients with OSCC, which has a certain guiding significance for the prognosis evaluation of OSCC.
-
妊娠期糖尿病是孕产妇较为常见的并发症之一,也是导致不良妊娠结局的重要原因之一[1-2]。因此,在临床实践中有效预测并及时干预妊娠期糖尿病对改善患者预后具有重要意义[3]。研究[4]表明,多种因素与妊娠期糖尿病的发生显著相关,主要包括妊娠期葡萄糖代谢异常、胰岛素抵抗以及胰岛素分泌异常。甲状腺功能减退可能会影响血液中葡萄糖和脂肪酸水平,但目前关于甲状腺功能减退与妊娠期糖尿病的相关性及其预测模型的研究相对较少[5]。研究[6]显示,随着甲状腺功能减退,生长激素水平会升高,而长期高水平的生长激素会导致胰岛素受体敏感性下降。本研究建立个体化预测甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病风险的Nomogram模型,为临床诊断提供参考。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
本研究采用前瞻性研究设计,选取2021年1—12月在本院诊断并治疗的甲状腺功能减退孕产妇160例作为研究对象。患者年龄为21~31岁,平均(25.66±2.59)岁; 孕周为22~30周,平均(26.54±2.91)周; 孕次为0~3次,平均(1.26±0.32)次; 产次为0~2次,平均为(1.09±0.12)次。其中,合并妊娠期糖尿病患者(观察组)85例,血糖正常患者(对照组)75例。所有患者均签署知情同意书。本研究经伦理委员会论证通过。
纳入标准: ①妊娠期糖尿病诊断标准者, 在孕期24~28周,进行75 g口服葡萄糖耐量试验(OGTT), 其空腹血糖或1 h后血糖或2 h后血糖异常[7]; ②年龄40岁以下者; ③经B超确定怀孕者; ④孕期诊断甲状腺功能减退(甲减),入组时表现为甲状腺功能水平异常降低者。排除标准: ①感染性疾病者; ②肿瘤患者; ③精神疾病者; ④孕前糖尿病者; ⑤经临床评估有心、脑、肾、胎盘等受损者。
1.2 方法
所有患者入组后均进行静脉采血4 mL, 15 000 r/min离心15 min后,取上清液。采用全自动生化仪对患者的空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)进行检测,采用化学发光法对患者的甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体(TPOAb)、血清游离四碘甲腺原氨酸(FT4)、游离三碘甲腺原氨酸(FT3)和促甲状腺激素(TSH)水平进行检测。胰岛素抵抗水平: 通过胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR)、胰岛β细胞功能指数(HOMA-β)进行评估。HOMA-IR=空腹胰岛素含量×空腹血糖含量/22.5。HOMA-β= 20×空腹胰岛素/(空腹血糖含量-3.5)。
记录所有患者的孕次、产次、孕前摄入碘含量、接受教育年限、自然流产史和孕期合并症等情况。
1.3 观察指标
比较2组患者的孕次、产次、接受教育年限、自然流产史、孕前空腹血糖、HbA1c、TPOAb、FT4、FT3以及TSH水平。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 26.0软件进行数据分析,所有计量资料均符合正态分布,采用(x±s)表示,行独立样本t检验,计量资料采用[n(%)]表示,行卡方检验。采用多因素Logistic分析法筛选妊娠期糖尿病发病的影响因素。采用Nomogram模型预测甲状腺功能减退患者发生妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评估Nomogram模型对甲状腺功能减退患者发生妊娠期糖尿病风险的预测价值。P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 妊娠期糖尿病的单因素分析
观察组患者年龄、孕次、产次、孕前体质量指数、孕前TPOAb、孕前HOMA-IR和孕前HOMA-β高于对照组,孕前FT4、孕前FT3、孕前TSH低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 妊娠期糖尿病的单因素分析(x±s)指标 观察组(n=85) 对照组(n=75) t P 年龄/岁 27.38±3.16 22.49±3.72 8.898 < 0.001 孕次/次 2.75±0.82 1.54±0.22 13.081 < 0.001 产次/次 2.06±0.37 1.08±0.27 19.284 < 0.001 孕前体质量指数/(kg/m2) 25.44±1.84 24.03±1.17 5.851 < 0.001 接受教育年限/年 13.65±3.32 13.68±2.81 0.062 0.951 自然流产次数/次 1.21±0.78 1.22±0.67 0.087 0.931 孕前空腹血糖/(mmol/L) 6.08±1.36 6.11±1.09 0.155 0.877 孕前HbA1c/% 6.17±1.02 6.27±1.47 0.494 0.622 孕前TPOAb/(IU/mL) 421.39±22.98 218.94±23.85 54.504 < 0.001 孕前FT4/(ng/dL) 0.34±0.11 0.45±0.02 5.101 < 0.001 孕前FT3/(pg/mL) 1.65±0.12 2.47±0.33 12.456 < 0.001 孕前TSH/(mIU/mL) 0.29±0.01 2.99±1.87 11.184 < 0.001 孕前HOMA-IR 2.24±0.23 1.02±0.77 13.211 < 0.001 孕前HOMA-β 115.66±3.89 69.14±3.11 83.962 < 0.001 HbA1c: 糖化血红蛋白; TPOAb: 甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体; FT4: 游离四碘甲腺原氨酸; FT3: 游离三碘甲腺原氨酸; TSH: 促甲状腺激素; HOMA-IR: 胰岛素抵抗指数; HOMA-β: 胰岛β细胞功能指数。 2.2 妊娠期糖尿病的多因素分析
多因素分析显示,较高的年龄、孕次、产次、孕前体质量指数、孕前TPOAb、孕前HOMA-IR、孕前HOMA-β以及较低的孕前FT4、孕前FT3、孕前TSH是甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素(P < 0.05), 见表 2、表 3。
表 2 赋值表指标 赋值 年龄/岁 实际值 孕次/次 实际值 产次/次 实际值 孕前体质量指数/(kg/m2) 实际值 孕前TPOAb/(IU/mL) 实际值 孕前FT4/(ng/dL) 实际值 孕前FT3/(pg/mL) 实际值 孕前TSH/(mIU/mL) 实际值 孕前HOMA-IR 实际值 孕前HOMA-β 实际值 表 3 妊娠期糖尿病的多因素分析因素 β S. E. Wald P OR 95%CI 年龄 1.018 2.361 1.322 0.001 1.019 1.009~1.926 孕次 1.062 3.269 1.333 0.002 1.632 1.331~2.320 产次 0.369 4.139 1.691 < 0.001 1.089 1.002~2.065 孕前体质量指数 1.302 2.541 1.025 < 0.001 1.002 1.001~1.568 孕前TPOAb 1.022 2.521 1.002 < 0.001 1.259 1.023~1.599 孕前FT4 1.262 3.251 1.332 < 0.001 0.541 0.023~0.947 孕前FT3 1.003 4.110 1.741 < 0.001 0.225 0.200~0.521 孕前TSH 1.047 5.119 1.025 < 0.001 0.210 0.025~0.574 孕前HOMA-IR 1.552 6.521 1.302 < 0.001 1.336 1.098~1.521 孕前HOMA-β 1.669 4.201 1.587 < 0.001 1.417 1.052~1.977 2.3 Nomogram模型预测甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素
Nomogram模型预测显示,较高的年龄(28~31岁)、孕次(2次以上)、产次(1次以上)、孕前体质量指数(24 kg/m2以上)、孕前TPOAb(>421.33 IU/mL)、孕前HOMA-IR(>2.21)、孕前HOMA-β(>115.66), 较低的孕前FT4(<0.33 ng/dL)、孕前FT3(<1.65 pg/mL)、孕前TSH(<0.26 mIU/mL)均是甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素。见图 1。
2.4 ROC曲线分析
ROC曲线分析显示, Nomogram模型预测甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的曲线下面积为0.785, 预测效能较好,见图 2。
3. 讨论
妊娠期糖尿病是临床上较为常见的妊娠期并发症之一,可对孕产妇和新生儿健康构成严重威胁[8]。研究[9]表明,妊娠期糖尿病与多种不良妊娠结局显著相关。产后,特别是在产后3~6年内,超重或肥胖的风险显著增加。不合理的孕期膳食、高龄、不良孕产史、高体质量指数和分娩巨大儿都是导致妊娠期糖尿病发生的危险因素[10]。在该病的进展过程中,随着孕期对葡萄糖需求量的增加,机体的胰岛素抵抗和分泌异常成为引起代谢异常的影响因素[11]。在孕期女性代谢异常发生时,其激素水平也显著波动,并成为其代谢异常的危险因素。内分泌异常主要包括性激素和生长激素水平异常。当甲状腺功能异常时,机体促性腺激素和促性腺激素释放激素的分泌量过高,会对婴幼儿产生严重影响。同时,在长期促性腺激素和促性腺激素释放激素过高的刺激下,机体代谢能力发生显著变化,胰岛素敏感性显著降低,可增加机体糖尿病发生风险[12-13]。在甲状腺功能减退孕妇的健康教育中,临床营养师通常建议加强营养指导,必要时及时检测孕妇甲状腺功能和血糖水平,并在整个孕期适当补充甲状腺素,以有效预防妊娠期糖尿病的发生[14]。
随着年龄增长,机体甲状腺功能和胰岛素分泌功能可能会出现显著退化[15]。随着孕次和产次增加,患者机体受到性激素波动影响也随之升高,而机体性激素波动水平异常是临床上影响患者发生妊娠期胰岛素功能异常和胰岛素分泌异常的重要因素[16]。在性激素过度影响下,机体下丘脑性激素轴的功能发生显著偏差,对糖脂代谢调控功能显著降低,其也是导致机体妊娠期糖尿病发生的重要危险因素[17]。本研究结果显示,在Nomogram模型预测中得出的截断值可作为临床预测甲状腺功能低下孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的重要参考[18]。随着机体甲状腺功能降低,胰岛细胞和多种蛋白质合成细胞的能力以及新陈代谢功能发生显著改变。同时,在炎性反应和多种代谢产物的应激作用下,局部病灶部位的微循环障碍风险逐渐升高,这也是孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的重要危险因素。但妊娠期糖尿病的发生受遗传因素的影响较大,不同地区、不同人种的遗传基因多态性也是造成其妊娠期糖尿病发生的重要影响因素。本研究仍存在局限性: 研究中模型的验证存在一定单一性,需要结合多种因素进行多中心分析,后续还需开展多中心、大样本研究进一步验证。
综上所述,风险预测Nomogram模型在个体化预测甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病方面具有一定优势,其可作为临床诊断的参考工具之一。
-
表 1 OSCC患者PNI与临床病理特征的关系
临床病理特征 n 低PNI组(n=110) 高PNI组(n=327) χ2 P 性别 男 289 71 218 0.165 0.684 女 148 39 109 年龄 ≤60岁 187 30 157 14.462 < 0.001 >60岁 250 80 170 T分期 T1、T2期 365 79 286 14.638 < 0.001 T3、T4期 72 31 41 肿瘤部位 舌 169 37 132 6.469 0.167 牙龈 183 56 127 口底 20 3 17 颊黏膜 53 10 43 硬腭 12 4 8 淋巴结转移 否 279 64 215 2.042 0.153 是 158 46 112 TNM分期 Ⅰ、Ⅱ期 243 50 193 6.137 0.013 Ⅲ、Ⅳ期 194 60 134 组织学分类 高分化 57 17 40 0.801 0.670 中分化 369 90 279 低分化 11 3 8 OSCC: 口腔鳞状细胞癌; PNI: 预后营养指数。 表 2 OSCC患者术后OS相关影响因素的单因素分析
变量 HR(95%CI) P 性别 男 1 0.756 女 1.067(0.710~1.603) 年龄 ≤60岁 1 < 0.001 >60岁 2.548(1.621~4.004) 肿瘤部位 颊黏膜 1 0.175 口底 0.478(0.138~1.650) 舌 0.605(0.326~1.120) 牙龈 0.929(0.523~1.653) 硬腭 0.264(0.035~2.002) T分期 T1、T2期 1 < 0.001 T3、T4期 3.342(2.216~5.039) 淋巴结转移 否 1 < 0.001 是 2.762(1.861~4.100) TNM分期 Ⅰ、Ⅱ期 1 < 0.001 Ⅲ、Ⅳ期 4.127(2.654~6.416) PNI >46.23 1 < 0.001 ≤46.23 3.334(2.255~4.930) OSCC: 口腔鳞状细胞癌; OS: 总生存期; HR: 风险比例; CI: 可信区间; PNI: 预后营养指数。 -
[1] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
[2] CHEN F, LIN L S, YAN L J, et al. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts the prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a large-sample prospective study[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 75(6): 1275-1282. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.11.022
[3] SCHWAM Z G, JUDSON B L. Improved prognosis for patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Analysis of the National Cancer Database 1998-2006[J]. Oral Oncol, 2016, 52: 45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.10.012
[4] LEUNG J S, SETO A, LI G K. Association between preoperative nutritional status and postoperative outcome in head and neck cancer patients[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2017, 69(3): 464-469. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2017.1285406
[5] DANAN D, SHONKA D C JR, SELMAN Y, et al. Prognostic value of albumin in patients with head and neck cancer[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(7): 1567-1571. doi: 10.1002/lary.25877
[6] RIGHINI C A, TIMI N, JUNET P, et al. Assessment of nutritional status at the time of diagnosis in patients treated for head and neck cancer[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2013, 130(1): 8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2012.10.001
[7] KONO T, SAKAMOTO K, SHINDEN S, et al. Pre-therapeutic nutritional assessment for predicting severe adverse events in patients with head and neck cancer treated by radiotherapy[J]. Clin Nutr, 2017, 36(6): 1681-1685. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.10.021
[8] ONODERA T, GOSEKI N, KOSAKI G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients[J]. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi, 1984, 85(9): 1001-1005. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6438478
[9] LEE J Y, KIM H I, KIM Y N, et al. Clinical significance of the prognostic nutritional index for predicting short-and long-term surgical outcomes after gastrectomy: a retrospective analysis of 7781 gastric cancer patients[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2016, 95(18): e3539. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003539
[10] HONG Y M, YOON K T, HWANG T H, et al. Pretreatment peripheral neutrophils, lymphocytes and monocytes predict long-term survival in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 937. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07105-8
[11] LUVIÁN-MORALES J, GONZÁLEZ-TREJO S, CARRILLO J F, et al. Association of the prognostic nutritional index and overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer: a STROBE compliant retrospective cohort study[J]. Cancer Med, 2019, 8(7): 3379-3388. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2212
[12] WANG J, LIU Y, MI X, et al. The prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) for advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with platinum-based chemotherapeutics[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2020, 9(3): 967-978. doi: 10.21037/apm.2020.04.31
[13] XUE Y B, ZHOU X, XUE L, et al. The role of pretreatment prognostic nutritional index in esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(11): 19655-19662. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28565
[14] WU X, JIANG Y, GE H, et al. Predictive value of prognostic nutritional index in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oral Dis, 2020, 26(5): 903-911. doi: 10.1111/odi.13318
[15] ZHANG H D, SHANG X B, REN P, et al. The predictive value of a preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index and prognostic nutritional index in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(2): 1794-1802. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27052
[16] SEEBACHER V, GRIMM C, REINTHALLER A, et al. The value of serum albumin as a novel independent marker for prognosis in patients with endometrial cancer[J]. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2013, 171(1): 101-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.07.044
[17] MIURA K, HAMANAKA K, KOIZUMI T, et al. Clinical significance of preoperative serum albumin level for prognosis in surgically resected patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Comparative study of normal lung, emphysema, and pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Lung Cancer, 2017, 111: 88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.07.003
[18] BORST J, AHRENDS T, BABAŁA N, et al. CD4+ T cell help in cancer immunology and immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2018, 18(10): 635-647. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0044-0
[19] DUNN G P, BRUCE A T, IKEDA H, et al. Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape[J]. Nat Immunol, 2002, 3(11): 991-998. doi: 10.1038/ni1102-991
[20] TIAN C, SONG W, TIAN X, et al. Prognostic significance of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2018, 48(5): e12917. doi: 10.1111/eci.12917
[21] TAN D W, FU Y, TONG W D, et al. Prognostic significance of lymphocyte to monocyte ratio in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Int J Surg, 2018, 55: 128-138. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.05.030




 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
