Value of pulmonary artery compliance in acute respiratory distress syndrome
-
摘要:目的 检测急性呼吸窘迫综合征(ARDS)患者肺动脉顺应性及右心功能,探讨肺动脉顺应性与右心功能及ARDS短期预后的关系。方法 选取同期135例ARDS患者(观察组)及46例健康体检者(对照组)为研究对象,根据30 d预后情况分为死亡组89例、生存组46例。检测受试者肺动脉收缩压(PASP),计算房间隔缺损面积指数(ASD-AI)、肺动脉顺应性指数(PACI),并以PACI作为评价肺动脉顺应性的指标;检测受试者每搏输出量(RVSV)等右心功能指标;分析PACI与右心功能的相关性;比较不同预后情况患者的PASP、ASD-AI、PACI水平;分析PACI对ARDS患者近期预后的预测价值。结果 观察组患者PASP、ASD-AI、心室舒张末期容积(RVEDV)、动脉血二氧化碳分压[pa(CO2)]水平均高于对照组,PACI、右心室射血分数(RVEF)、心室收缩末期容积(RVESV)、平均动脉压(MAP)、动脉血氧分压[pa(O2)]、氧合指数[pa(O2)/FiO2]水平均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。ARDS患者PACI与RVEF、RVESV及pa(O2)/FiO2呈正相关(P < 0.05),与RVEDV呈负相关(P < 0.05)。死亡组患者PASP、ASD-AI水平高于生存组,PACI、pa(O2)/FiO2水平低于生存组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线显示,PACI对ARDS短期预后诊断的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.844,敏感性为70.8%,特异性为80.4%。结论 ARDS患者肺动脉顺应性和右心功能下降,PACI与右心功能存在一定相关性,PACI在ARDS患者近期预后中能够起到较好的预测作用。Abstract:Objective To detect pulmonary artery compliance and right heart function in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and to explore the relationships between pulmonary artery compliance and right heart function as well as short-term prognosis of ARDS.Methods A total of 135 ARDS patients (observation group) and 46 healthy subjects (control group) were selected as subjects. According to the prognosis of 30 days, they were divided into death group (n=89) and survival group (n=46). Pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) was measured, atrial septal defect area index (ASD-AI) and pulmonary arterial compliance index (PACI) were calculated, and PACI was used as indicators to evaluate the compliance of pulmonary artery; stroke volume (RVSV) and other indicators of right heart function were measured; the correlation between PACI and right heart function was analyzed; the levels of PASP, ASD-AI and PACI in patients with different prognosis were compared; the value of PACI in predicting short-term prognosis ARDS of patients was analyzed.Results PASP, ASD-AI, right ventricular end-diastolic volume (RVEDV) and arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide[pa(CO2)] in the observation group were significantly higher, and PACI, right ventricular ejection fraction (RVEF), right ventricular end-systolic volume (RVESV), mean arterial pressure (MAP), arterial partial pressure of oxygen[pa(O2)] and oxygenation index[pa(O2) to FiO2] were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). In ARDS patients, PACI was positively correlated with RVEF, RVESV and pa(O2)/FiO2 (P < 0.05), and negatively correlated with RVEDV (P < 0.05). PASP and ASD-AI levels in the death group were significantly higher, PACI and pa(O2)/FiO2 levels were significantly lower than those in the survival group (P < 0.05). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve showed that the area under the curve (AUC) of PACI for the short-term prognosis of ARDS was 0.844, the sensitivity was 70.8%, and the specificity was 80.4%.Conclusion In ARDS patients, pulmonary artery compliance and right heart function both decrease. PACI has a certain correlation with right heart function, and PACI can play a role in predicting the short-term prognosis of ARDS patients.
-
急性呼吸窘迫综合征(ARDS)是一种呈肺容积减少、肺顺应性降低等生理特征的疾病,病因复杂,治疗难度较大,病死率高,严重危害人们生活质量和身心健康[1-2]。ARDS患者不仅存在肺泡病变,也存在肺循环异常,其中以肺动脉高压为基本特征之一,严重者可导致右心衰竭[3]。正压机械通气虽为ARDS目前主要治疗手段之一,但治疗过程中易增加肺循环阻力,进而引起急性肺动脉高压,甚至造成右心衰竭[4]。目前,临床评价右心功能方法尚不完备,因此探讨评估右心功能的可靠指标对ARDS患者临床诊治大有裨益。研究[5]显示,肺动脉顺应性是反映肺循环状态的重要指标,而肺血管结构和机能状态是决定左心前负荷和右心后负荷的主要因素,故其还可反映大小动脉血管结构和机能状态。此外, ARDS患者右室功能障碍与预后关系密切,右心衰竭还可对预后造成不利影响,但关于三者在ARDS中的相互关系尚不明确[6]。基于此,本研究以肺动脉顺应性作为主要检查指标,探究其与ARDS患者右心功能及短期预后间的关系,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2017年6月—2019年6月收治的135例ARDS患者作为观察组,其中男76例,女59例,平均年龄(58.31±8.24)岁,根据30 d预后情况分为死亡组89例、生存组46例。选取同期健康体检者46例为对照组,其中男25例,女21例,平均年龄(56.16±6.87)岁。纳入标准: ①患者均符合中华医学会呼吸学会制定的ARDS诊断标准[7]; ②年龄≥18岁者; ③急性起病,明确诊断ARDS时间<24 h, 氧合指数[pa(O2)/FiO2]≤200 mmHg者,胸部X摄片为双肺斑片状阴影,肺动脉嵌顿压<18 mmHg者。排除标准: ①临床资料不全者; ②合并严重心、肺、肝、肾功能不全者; ③妊娠期、肿瘤终末期、自身免疫性疾病者。所有受试者知情同意并签订知情同意书。
1.2 方法
肺动脉顺应性相关指标检测: 所有入组患者检查前均给予纯氧吸入30 min, 并完成动脉血气检查,包括酸碱度(pH值)、平均动脉压(MAP)、动脉血二氧化碳分压[pa(CO2)]、动脉血氧分压[pa(O2)]、pa(O2)/FiO2, 然后在ARDS患者确诊24 h内进行超声检查,检查前保证患者充分镇静,采用GE Vivid 7彩色多普勒超声诊断仪,频率1.7~3.4 MHz, 自然组织谐波功能。二维超声测量房间隔缺损最大径(DL)及最小径(DS), 并计算房间隔缺损面积指数(ASD-AI)=(DL/2)×(DS/2)×π/体面积(BSA); 多普勒超声测量房间隔跨缺损最大分流速度,依据公式将ASD-AI化为肺动脉顺应性指数(PACI)=分流压差(PGASD)/ASD-AI。测定肱动脉压为体循环压(Ps), 得肺动脉收缩压(PASP)(mmHg)=Ps-PGASD。
右心功能检测: 采用西门子3.0T Verio超导型磁共振扫描仪、32通道心脏相控阵线圈及呼吸门控、心电门控。应用心脏电影成像序列,右心室二腔心、四腔心及短轴位电影CMR图像则采用二维快速稳态进动采集序列。扫描右心室基底段至心尖段在内的心室短轴、长轴以及四腔心层面。扫描结束后将MRI数据传入后处理工作站(Argus, Syngo; 西门子公司),载入全部基底段至心尖段心室短轴电影图像,选取心室舒张/收缩末期图像,手动描绘右心室舒张/收缩末期所有图像的心内/外膜,记录右心室射血分数(RVEF)、心室舒张末期容积(RVEDV)、心室收缩末期容积(RVESV)和每搏输出量(RVSV)等心功能指标。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 21.0软件进行统计学分析,计量资料采用(x±s)描述,组间比较采用t检验。计数资料比较采用χ2检验。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析PACI对ARDS短期预后的诊断价值。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 观察组和对照组患者肺动脉顺应性、右心功能及一般资料比较
2组患者年龄、性别、pH值、RVSV水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 观察组患者PASP、ASD-AI、RVEDV、pa(CO2)水平均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05), PACI、RVEF、RVESV、MAP、pa(O2)、pa(O2)/FiO2水平均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 观察组和对照组肺动脉顺应性、右心功能及一般资料比较(x±s)指标 观察组(n=135) 对照组(n=46) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 58.31±8.24 56.16±6.87 1.590 0.113 性别 男 76 25 0.053 0.818 女 59 21 PASP/mmHg 86.54±26.81 56.14±23.10 6.868 <0.001 ASD-AI/(cm2/m2) 2.69±1.10 1.86±0.62 4.856 <0.001 PACI/(mmHg×10-4) 1.29±0.45 2.06±0.91 7.519 <0.001 RVEF/% 37.98±10.55 49.06±11.57 6.001 <0.001 RVEDV/mL 76.40±20.48 63.59±18.37 3.757 <0.001 RVESV/mL 41.64±10.00 52.48±13.51 5.778 <0.001 RVSV/mL 35.09±11.73 35.51±10.48 0.215 0.830 pH值 7.32±0.06 7.34±0.07 1.869 0.063 MAP/mmHg 63.72±11.58 79.65±10.58 8.231 <0.001 pa(CO2)/mmHg 51.25±5.36 40.52±5.32 11.748 <0.001 pa(O2)/mmHg 78.35±10.42 90.35±10.35 6.757 <0.001 pa(O2)/FiO2/mmHg 168.61±45.86 452.86±50.47 34.134 <0.001 PASP: 肺动脉收缩压; ASD-AI: 房间隔缺损面积指数; PACI: 肺动脉顺应指数; RVEF: 右心室射血分数;
RVEDV: 心室舒张末期容积; RVESV: 心室收缩末期容积; RVSV: 每搏输出量; pH值: 酸碱度; MAP: 平均动脉压;
pa(CO2): 动脉血二氧化碳分压; pa(O2): 动脉血氧分压; pa(O2)/FiO2: 氧合指数。2.2 ARDS患者肺动脉顺应性与右心功能相关性分析
ARDS患者PACI与右心功能指标RVEF、RVESV及pa(O2)/FiO2呈正相关(r=0.510、0.612、0.524, P<0.05); PACI与RVEDV呈负相关(r=-0.547, P<0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 ARDS患者肺动脉顺应性与右心功能指标 PACI r P RVEF 0.510 0.010 RVEDV -0.547 0.003 RVESV 0.612 <0.001 RVSV 0.311 0.106 pa(O2)/FiO2 0.524 0.008 PACI: 肺动脉顺应指数; RVEF: 右心室射血分数;
RVEDV: 心室舒张末期容积; RVESV: 心室收缩末期容积;
RVSV: 每搏输出量; pa(O2)/FiO2: 氧合指数。2.3 不同近期预后情况ARDS患者PASP、ASD-AI、PACI水平比较
根据ARDS患者近期预后结果进行分组,死亡组患者PASP、ASD-AI水平高于生存组, PACI、pa(O2)/FiO2水平低于生存组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 3。
表 3 不同近期预后结果ARDS患者PASP、ASD-AI、PACI水平比较(x±s)指标 生存组(n=46) 死亡组(n=89) PASP/mmHg 64.86±27.59 97.87±35.64* ASD-AI/(cm2/m2) 1.83±0.55 3.14±1.04* PACI/(mmHg×10-4) 1.65±0.41 1.10±0.35* pa(O2)/FiO2/mmHg 178.75±20.61 134.28±25.43* PASP: 肺动脉收缩压; ASD-AI: 房间隔缺损面积指数;
PACI: 肺动脉顺应指数; pa(O2)/FiO2: 氧合指数。
与生存组比较, * P<0.05。2.4 PACI对ARDS患者近期预后的诊断价值
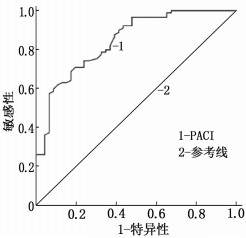
ROC曲线结果显示,肺动脉顺应性对ARDS患者短期预后诊断的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.844, 敏感性为70.8%, 特异性为80.4%, 95%可信区间(CI)为0.776~0.913, 见图 1。
3. 讨论
临床研究[8]认为,肺泡上皮、肺毛细血管内皮通透性异常增加是引起ARDS基本病理生理改变的主要原因,同时存在肺泡水肿或塌陷,造成通气与血流比例严重失调,尤以肺内分流异常增加最为显著,最终可引起严重低氧血症。ARDS对肺循环也会造成不利影响,肺血管痉挛和肺微小血栓形成引发肺动脉高压,并进一步导致急性肺源性心脏病(ACP)[9]。随着对ARDS病理生理研究的深入,机械通气策略不断改进,病死率有所控制但仍居高不下[10-11]。研究[12]显示,初期检测的pa(O2)/FiO2尚不可作为判断ARDS预后的关键指标,故寻找能对ARDS预后进行判断的指标尤为重要。
肺动脉顺应性是影响室间隔缺损合并肺动脉高压的重要环节。正常情况下,肺循环是一个低阻力、低压力、高容量的系统,肺血管中血流量增加时则其被动扩张,以保持压力不变,而增加至正常值3倍以上时,则肺血管进行主动调节[13]。研究[14]显示,内皮依赖的缩血管反应增强及舒张反应减弱是导致血管张力增高的主要原因,进而发生的肺血管重构与肺动脉顺应性下降又进一步促进肺动脉阻力增高。肺动脉顺应性与肺动脉高压的关系已有较多研究,肺动脉高压即为ARDS患者的突出病理生理改变,因此探究肺动脉顺应性在ARDS中的作用具有意义[15]。正常情况下,人心脏左右室收缩是同步的,左室压力高于右室压力[16]。ARDS患者由于本身病变及高呼吸末正压急性同期,导致右心后负荷急剧增加及收缩延迟,进而使收缩末期跨室间隔压力梯度逆转,如超声心动图显示室间隔变平甚至凸向左室[17]。研究[18]证实,经3 d机械通气后, ARDS患者出现急性右心室扩张。以往为保持ARDS患者血碳酸正常,应用大潮气量(13 mL/kg)导致ACP发生率升高,相应病死率也有所上升[19]。而应用小潮气量可限制肺拉伸,不仅能显著降低患者病死率,还可保护右心功能[20]。因此,临床治疗中应注意保护ARDS患者的右心功能,以改善预后。本研究对ARSD患者PACI变化进行观察分析,结果显示, ARDS患者PASP、ASD-AI、RVEDV、pa(CO2)水平均显著高于对照组, PACI、RVEF、RVESV、MAP、pa(O2)、pa(O2)/FiO2水平均显著低于对照组,提示ARDS患者肺动脉顺应性下降,影响收缩压恢复,而且房间隔缺损也影响左向右分流量,两者呈正相关,进而导致右心系统容量负荷明显增加,进一步加重ARDS病变。PACI与右心功能相关性分析结果显示, ARDS患者PACI与右心功能指标RVEF、RVESV及pa(O2)/FiO2呈正相关,与RVEDV呈负相关,提示肺动脉顺应性与右心功能相关,肺动脉顺应性与右心功能正相关。此外,本研究结果还显示,生存组患者PASP、ASD-AI水平显著低于死亡组, PACI水平显著高于死亡组,可见预后较好患者的肺动脉高压进程相对较慢,提示可通过检测上述3项指标来预测患者的预后情况。ROC结果显示, PACI对ARDS患者短期预后的诊断的AUC为0.844, 敏感度为70.8%, 特异性为80.4%, 95%CI为0.776~0.913, 提示PACI能够较好判断ARDS患者预后,可作为ARDS潜在预后判断指标。
综上所述, ARDS患者PACI降低,右心功能下降,两者有一定相关性,且PACI能够较好判断ARDS患者短期预后情况。但本研究样本量较小,纳入对象仅限本地区,且未结合患者右心功能恢复情况,研究结果存在局限性,后续研究将不断完善,并深入探讨可判断患者远期预后的可靠指标。
-
表 1 观察组和对照组肺动脉顺应性、右心功能及一般资料比较(x±s)
指标 观察组(n=135) 对照组(n=46) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 58.31±8.24 56.16±6.87 1.590 0.113 性别 男 76 25 0.053 0.818 女 59 21 PASP/mmHg 86.54±26.81 56.14±23.10 6.868 <0.001 ASD-AI/(cm2/m2) 2.69±1.10 1.86±0.62 4.856 <0.001 PACI/(mmHg×10-4) 1.29±0.45 2.06±0.91 7.519 <0.001 RVEF/% 37.98±10.55 49.06±11.57 6.001 <0.001 RVEDV/mL 76.40±20.48 63.59±18.37 3.757 <0.001 RVESV/mL 41.64±10.00 52.48±13.51 5.778 <0.001 RVSV/mL 35.09±11.73 35.51±10.48 0.215 0.830 pH值 7.32±0.06 7.34±0.07 1.869 0.063 MAP/mmHg 63.72±11.58 79.65±10.58 8.231 <0.001 pa(CO2)/mmHg 51.25±5.36 40.52±5.32 11.748 <0.001 pa(O2)/mmHg 78.35±10.42 90.35±10.35 6.757 <0.001 pa(O2)/FiO2/mmHg 168.61±45.86 452.86±50.47 34.134 <0.001 PASP: 肺动脉收缩压; ASD-AI: 房间隔缺损面积指数; PACI: 肺动脉顺应指数; RVEF: 右心室射血分数;
RVEDV: 心室舒张末期容积; RVESV: 心室收缩末期容积; RVSV: 每搏输出量; pH值: 酸碱度; MAP: 平均动脉压;
pa(CO2): 动脉血二氧化碳分压; pa(O2): 动脉血氧分压; pa(O2)/FiO2: 氧合指数。表 2 ARDS患者肺动脉顺应性与右心功能
指标 PACI r P RVEF 0.510 0.010 RVEDV -0.547 0.003 RVESV 0.612 <0.001 RVSV 0.311 0.106 pa(O2)/FiO2 0.524 0.008 PACI: 肺动脉顺应指数; RVEF: 右心室射血分数;
RVEDV: 心室舒张末期容积; RVESV: 心室收缩末期容积;
RVSV: 每搏输出量; pa(O2)/FiO2: 氧合指数。表 3 不同近期预后结果ARDS患者PASP、ASD-AI、PACI水平比较(x±s)
指标 生存组(n=46) 死亡组(n=89) PASP/mmHg 64.86±27.59 97.87±35.64* ASD-AI/(cm2/m2) 1.83±0.55 3.14±1.04* PACI/(mmHg×10-4) 1.65±0.41 1.10±0.35* pa(O2)/FiO2/mmHg 178.75±20.61 134.28±25.43* PASP: 肺动脉收缩压; ASD-AI: 房间隔缺损面积指数;
PACI: 肺动脉顺应指数; pa(O2)/FiO2: 氧合指数。
与生存组比较, * P<0.05。 -
[1] 何园, 张硌, 刘慧莹, 等. 巨噬细胞对急性肺损伤后炎症的消解与组织修复的研究进展[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2018, 17(4): 430-434. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHW201804033.htm [2] LOPES-PACHECO M, ROBBA C, ROCCO P R M, et al. Current understanding of the therapeutic benefits of mesenchymal stem cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2020, 36(1): 83-102. doi: 10.1007/s10565-019-09493-5
[3] FU S, THANGAVEL S, IVANOVA V. Cardiac dysfunction in acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Crit Care Nurs Q, 2019, 42(4): 448-458. doi: 10.1097/CNQ.0000000000000284
[4] 颜卫峰, 陈喆, 史淑静, 等. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征应用有创-无创序贯性机械通气治疗的效果及时机分析[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2019, 48(24): 3018-3020. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2019.24.002 [5] 林锦乐, 傅萱, 曾世永, 等. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者血清Clara细胞蛋白16表达及与肺顺应性关系[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2018, 32(3): 265-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZD201803017.htm [6] REPESSÉX, VIEILLARD-BARON A. Right heart function during acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2017, 5(14): 295. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.06.66
[7] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会. 急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征的诊断标准(草案)[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2000, 23(4): 203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHJH200004005.htm [8] 刘鸿飞, 崔颖. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者血管外肺水指数和肺血管通透性指数变化对其预后的影响[J]. 内科急危重症杂志, 2018, 24(3): 261-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKJW201803028.htm [9] 李佳清, 袁彩云, 缪红军. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征患儿的右心保护通气策略[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2019, 26(6): 412-414. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4912.2019.06.003 [10] 陈利红, 张蕾, 刘红娟, 等. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者肺死腔分数与患者死亡风险关系探讨[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2018, 23(9): 1642-1645. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2018.09.022 [11] 朱勇, 李吉明, 高冉冉, 等. 前列地尔对感染性休克并急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者呼吸功能、炎性反应、免疫调节及近期预后的影响[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2018, 26(10): 41-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2018.10.010 [12] 贾子毅, 刘晓伟, 刘志. 机械通气氧合指数对ARDS患者预后评估的价值: 附228例回顾性分析[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2017, 29(1): 45-50. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.01.010 [13] 李欢, 吉训恋. 前列地尔对慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并肺动脉高压患者肺血管顺应性和血管内皮功能的影响[J]. 中国医药, 2020, 15(12): 1849-1853. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYG202012008.htm [14] 张臣, 陈辉, 赵蕾, 等. 磁共振相位对比法评价老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者肺动脉血流及右心功能[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2019, 38(5): 542-546. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2019.05.017 [15] PRICE L C, WORT S J. Pulmonary hypertension in ARDS: inflammation matters![J]. Thorax, 2017, 72(5): 396-397. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209199
[16] 张小花, 姜志荣, 孙安华, 等. 实时三维超声心动图和二维斑点追踪技术对冠心病患者左心室收缩同步性的评价[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2016, 32(10): 901-904. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2016.10.014 [17] 夏炳杰, 施善阳. PiCCO监测对SAP合并ARDS患者心功能心脏前后负荷及血管外肺水的观察作用[J]. 河北医学, 2016, 22(5): 766-768. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6233.2016.05.024 [18] PATERNOT A, REPESSÉX, VIEILLARD-BARON A. Rationale and description of right ventricle-protective ventilation in ARDS[J]. Respir Care, 2016, 61(10): 1391-1396. doi: 10.4187/respcare.04943
[19] BEITLER J R, SANDS S A, LORING S H, et al. Quantifying unintended exposure to high tidal volumes from breath stacking dyssynchrony in ARDS: the BREATHE criteria[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2016, 42(9): 1427-1436. doi: 10.1007/s00134-016-4423-3
[20] 黄莉, 黎明, 陈娟, 等. 肺保护通气策略对小儿急性呼吸窘迫综合征心肺功能的影响及存活者随访的研究[J]. 贵州医药, 2018, 42(8): 950-952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2018.08.014 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 韩虎,袁军,李建国. 血管外肺水指数结合血乳酸清除率、APACHEⅡ评分对ARDS患者近期预后不良的预测价值. 重庆医学. 2023(03): 321-325+332 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
