Relationships between expressions of serum neuregulin 1, microRNA-221-3p and cognitive function in patients with refractory epilepsy
-
摘要:目的 探讨难治性癫痫患者血清神经调节蛋白1(NRG1)、microRNA-221-3p(miR-221-3p)表达水平与认知功能障碍(CD)的关系。方法 选取64例难治性癫痫患者(难治性癫痫组)和58例抗癫痫药物控制良好患者(药物控制良好组)作为研究对象,另选取同期本院70例健康体检者纳入对照组。采用蒙特利尔认知评估量表(MoCA)评估难治性癫痫患者的认知功能受损程度,并根据MoCA总分将难治性癫痫患者分为CD组40例和非CD组24例。采用实时荧光定量PCR法检测血清miR-221-3p水平,采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测血清NRG1水平,并采用Pearson相关性分析探讨miR-221-3p、NRG1水平与MoCA总分的相关性,采用多因素Logistic回归分析探讨难治性癫痫患者发生CD的影响因素。结果 难治性癫痫组血清miR-221-3p、NRG1水平高于对照组、药物控制良好组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);CD组血清miR-221-3p、NRG1水平高于非CD组,MoCA总分、空间与执行能力评分、语言评分、延迟记忆评分、计算力与定向评分低于非CD组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Pearson相关性分析显示,难治性癫痫CD患者血清miR-221-3p、NRG1水平均与MoCA总分呈负相关(P < 0.05)。Logistic回归分析显示,NRG1、miR-221-3p均为难治性癫痫患者发生CD的影响因素(P < 0.05)。结论 难治性癫痫合并CD患者血清miR-221-3p、NRG1水平较高,且miR-221-3p、NRG1均与难治性癫痫患者CD进程密切相关。
-
关键词:
- 难治性癫痫 /
- 神经调节蛋白1 /
- microRNA-221-3p /
- 认知功能 /
- 相关性
Abstract:Objective To explore the relationships between serum levels of microRNA-221-3p (miR-221-3p), neuregulin 1 (NRG1) and cognitive dysfunction (CD) in patients with refractory epilepsy.Methods A total of 64 patients with refractory epilepsy (refractory epilepsy group) and 58 patients with well-controlled anti-epileptic drugs (anti-epileptic drugs well-controlled group) were selected as research objects. During the same period, 70 healthy patients in the same hospital were selected as control group. Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MoCA) was used to evaluate the degree of cognitive impairment in patients with refractory epilepsy, and the patients with refractory epilepsy were divided into CD group (40 cases) and non-CD group (24 cases) according to the MoCA total score. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR method was used to detect the serum level of miR-221-3p, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the serum level of NRG1, Pearson method was used to analyze the correlations between miR-221-3p, NRG1 levels and the total score of MoCA, multivariate Logistic regression was used to analyze the independent risk factors affecting the development of CD in patients with refractory epilepsy.Results Compared with the control group and the anti-epileptic drugs well-controlled group, the serum miR-221-3p and NRG1 levels in the refractory epilepsy group were higher (P < 0.05); compared with the non-CD group, the serum miR-221-3p and NRG1 levels in the CD group were higher, and the MoCA total score, spatial and executive ability score, language score, delayed memory score, computing power and orientation score were lower (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that the serum levels of miR-221-3p and NRG1 were negatively correlated with the total score of MoCA(P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that NRG1 and miR-221-3p were risk factors for CD in patients with refractory epilepsy (P < 0.05).Conclusion The patients with refractory epilepsy and CD have relatively higher levels of serum miR-221-3p and NRG1, and they are closely related to the progression of CD in patients with refractory epilepsy.-
Keywords:
- refractory epilepsy /
- neuregulin 1 /
- microRNA-221-3p /
- cognitive function /
- correlation
-
卵巢囊肿是一种常见且多发的女性生殖系统肿瘤,临床多见于育龄女性,相关统计学调查[1-2]显示,卵巢囊肿约占妇科良性肿瘤的25%。卵巢囊肿蒂扭转发病率约占卵巢囊肿的10%, 患者临床症状主要表现为呕吐、恶心、腹部骤然疼痛,甚至出现休克等危急症状[3-4]。该病常发于妊娠早期、产后或体位忽然变动时,其诊断易与外科急腹症混淆,常常错过最佳治疗时期[5-6]。因此,在早期对卵巢囊肿蒂扭转患者有效诊断可预防疾病进展、改善预后。超声用于临床筛查囊肿病灶具有易操作、无创、诊断效果较好等优点,经腹超声和经阴道超声是目前用于诊断卵巢囊肿的主要声像学方法[7]。本研究选取本院43例卵巢囊肿蒂扭转患者作为研究对象,应用经阴道超声和腹超声对其进行诊断检查,并以病理诊断结果作为金标准,分析卵巢囊肿蒂扭转患者经阴道彩超诊断的临床价值,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取本院2012年2月—2018年2月收治的卵巢囊肿蒂扭转患者43例为研究对象,年龄28~50岁,平均(35.20±1.60)岁; 病程2~24 h, 平均(10.10±3.50) h。所有患者有性生活史,临床症状主要有腹痛剧烈、恶心、呕吐等,并伴随阴道流血甚至休克。纳入标准: ①符合人民卫生出版社《妇产科学》(第8版)[8]中关于卵巢囊肿蒂扭转诊断标准者; ②年龄22~50岁; ③既往有卵巢囊肿病史者; ④接受经腹超声以及经阴道超声2种超声检查者; ⑤接受病理检查确诊者。排除标准: ①肠扭转、阑尾炎、肠套叠等非妇科急腹症者; ②外伤者。
1.2 检查方法
所有患者经腹部超声和阴道超声检查,选用GE公司生产型号为E8和Logiq-7彩色多普勒超声诊断仪进行检查。
阴道超声检查: 调节探头频率为5~9 MHz, 检查前嘱咐患者将膀胱尽量排空,检查时在检查床上平躺,取截石位,然后检查医师在检查探头上涂抹适当的耦合剂,并将一个无菌避孕套套在探头上,之后经患者阴道缓慢放入,最终将探头放置于阴道后穹窿,然后多角度多方位扫描检查卵巢,重点观察囊内透声关系、囊肿大小、所处位置等,并详细观察扭转蒂形态、大小、回声状况以及其与囊肿的关系。
腹部超声检查: 调节探头频率为3~5 NHz, 检查前嘱咐患者使膀胱尽量保持充盈状态,检查时取仰卧位,检查医师在其腹部横向或纵向进行多方位、多角度进行扫描检查,观察囊肿大小、所处位置以及囊壁和子宫的联系,找出扭转蒂部位,并详细观察其与囊肿的关系。
1.3 观察指标
患者经阴道超声和腹超声检查后经病理确诊,并以病理诊断结果为金标准。选取2位资历较深的主治医师对患者观察指标、声像图进行记录和评估,评估结果即为诊断意见,同时将诊断意见与病理结果对照,比较2种超声检查方法对腹腔囊肿检查的准确率以及对囊肿蒂扭转的诊断效果。
1.4 统计学处理
本次实验数据应用SPSS 19.0软件包进行处理,患者病程、年龄等计量资料以(±s)表示,行t检验。患者超声检查结果等计数资料以[n(%)]表示,进行χ2检验。P < 0.05表明差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 超声检查结果比较
经阴道超声和经腹超声检查均发现患者有大小不一囊实性或囊性包块,其大小为2 cm×3 cm~15 cm×21 cm。经阴道超声提示,患者囊壁厚薄不均,包块边界清晰,部分患者囊内可见分隔光带,回声显著,部分患者囊内有斑点状、团块状、浮点状弱回声; 扭转蒂血管超声表现为斑点状、漩涡状、麻花状; 腹部肿块仅少数和腹壁粘连,移动性较好。7例可探及动静脉频谱, 13例可探及动脉频谱, 23例未探及扭转蒂血流信号,见图 1。经腹超声可见单纯实性肿块或无回声肿块或混合型回声肿块,肿块直径在50 mm以上,内部透射度较差多位于单侧下腹部或中腹部,大部分患者盆腔提示少量游离性暗区,见图 2。
2.2 手术结果比较
43例患者经手术确认后发现,卵巢囊肿均存在不同程度的蒂扭转,其中扭转最多者为5周,且大部分由于扭转较为严重已经发生缺血坏死,扭转最小者为90°。阴道超声检查准确率为93.02%, 较腹部超声检查准确率的67.44%显著更高(P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2种超声检查方法对卵巢囊肿蒂扭转诊断效果比较[n(%)]检查方法 n 检查准确 手术相符 经腹超声 43 29(67.44) 29(67.44) 经阴道超声 43 40(93.02)* 40(93.02)* 与经腹超声比较, *P < 0.05。 2.3 病理检查结果比较
将术中留取病理标本送检后证实, 43例患者有2例卵巢巧克力囊肿, 3例黄体囊肿, 4例输卵管系膜囊肿, 5例囊性畸胎瘤, 14例滤泡囊肿, 15例浆液性囊腺瘤,与阴道超声检查结果基本一致,见表 2。
表 2 阴道超声检查结果和病理结果比较[n(%)]类型 阴道超声检查结果 病理结果 卵巢巧克力囊肿 1(2.33) 2(4.65) 黄体囊肿 3(6.98) 3(6.98) 输卵管系膜囊肿 5(11.63) 4(9.30) 囊性畸胎瘤 4(9.30) 5(11.63) 滤泡囊肿 13(30.23) 14(32.56) 浆液性囊腺瘤 16(37.21) 15(34.88) 2种检查方法均有少数患者被误诊为输卵管积水扭转、异位妊娠破裂、黄体囊肿破裂等。经阴道超声检查的误诊率和漏诊率分别为4.65%和2.33%, 经腹超声检查的误诊率和漏诊率分别为18.60%和13.95%, 2组比较经阴道超声误诊率和漏诊率显著低于经腹超声(P < 0.05), 见表 3。
表 3 2种超声检查方法对卵巢囊肿蒂扭转诊断效果比较[n(%)]检查方法 n 检查准确 误诊 漏诊 经腹超声 43 29(67.44) 8(18.60) 6(13.95) 经阴道超声 43 40(93.02)* 2(4.65)* 1(2.33)* 与经腹超声比较, *P < 0.05。 3. 讨论
卵巢囊肿属于卵巢良性肿瘤中的一种,在育龄女性中发生率较高,其发病机制非常复杂,主要是由于卵巢结构、组织具有多能性,同时和泌尿系统距离较近,部分肾组织在其胚胎发生时期容易误入卵巢[9-10]。卵巢囊肿蒂内含有骨盆漏斗韧带、卵巢固有韧带以及输卵管,患者发生急性扭转后突发性下腹剧痛,刀割样持续性痛,并伴随呕吐、恶心甚至休克等[11-12]。该病在发病时由于急性缺血而导致囊肿坏死,甚至引发腹腔感染和卵巢破裂,严重危害患者生命健康[13-14]。因此及时正确的临床诊断和治疗显得尤为重要。
超声检查由于易操作、无创、诊断效果较好等优点在临床广泛应用于检查卵巢囊肿蒂扭转,医师可以根据不同回声特征有效评估不同组织间界面特点以及形态,而彩超的应用则能更好地观察囊肿声影、位置、大小等[15]。临床主要采取经阴道超声和经腹超声诊断卵巢囊肿蒂扭转,经腹超声探查范围较广,可更为完整地显示卵巢囊肿形态,但该超声检查方法容易受到腹壁脂肪和肠道气体的影响,使得检查图像的分辨率较低,漏诊和误诊率也较高[16-17]。
经阴道超声与经腹超声比较其探查范围较为局限,但其距离病灶较近,图像分辨率较高; 同时,由于检查探头直接放置在阴道穹窿处,距离盆腔器官较近,对子宫、卵巢等发病部位的具体表现观察更为清楚,对蒂扭转部位的血流以及微小结构显示也更为清楚[18]。
本研究通过比较经阴道超声和经腹超声对卵巢囊肿蒂扭转的诊断结果发现,2种超声诊断方法的准确率均较高,说明超声检查的应用在诊断卵巢囊肿蒂扭转中均具有一定的临床应用价值。而经阴道超声检查准确率较腹部超声检查准确率更高,说明经阴道超声在诊断卵巢囊肿蒂扭转中更为灵敏,具有更高的临床价值。同时,经阴道超声检查的误诊率和漏诊率显著低于经腹超声检查,进一步证实经阴道超声检查的临床应用价值。此外,经阴道超声图像提示,患者囊壁厚薄不均,包块边界清晰,部分患者囊内可见分隔光带,回声显著,部分患者囊内提示斑点状、团块状、浮点状弱回声; 扭转蒂血管超声表现为斑点状、漩涡状、麻花状; 腹部肿块仅少数和腹壁粘连,移动性较好。经腹超声可见单纯实性肿块或无回声肿块或混合型回声肿块,肿块直径在50 mm以上,内部透射度较差多位于单侧下腹部或中腹部; 大部分患者盆腔提示少量游离性暗区,提示经腹超声适用于诊断大蒂或巨大蒂扭转病灶,而经阴道超声适用于诊断偏小或中度蒂扭转病灶。
综上所述,经阴道超声检查诊断卵巢囊肿蒂扭转具有较好的临床价值,其距离病灶近、探头频率高,可有效发现病灶,诊断更为方便、准确。同时,由于其回声特征显著,适用于诊断偏小或中度蒂扭转病灶。
-
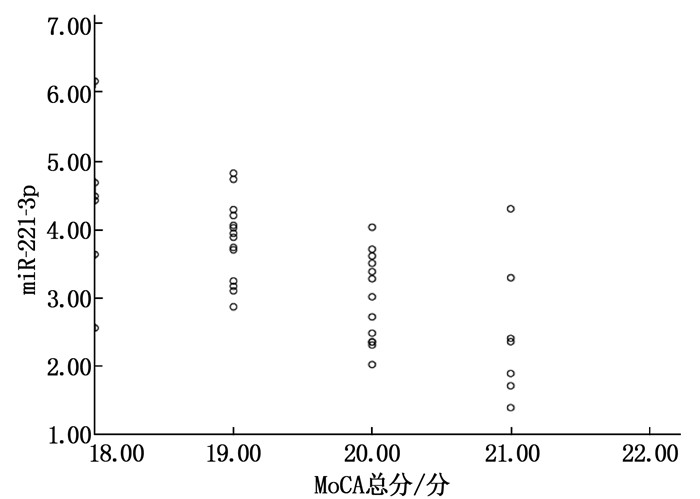
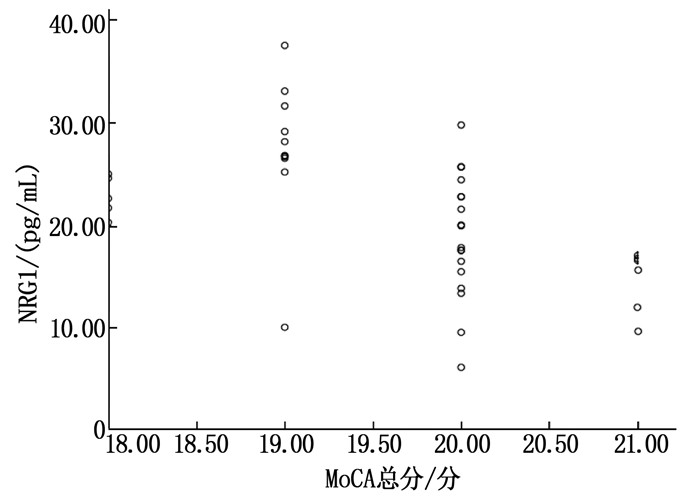
表 1 3组血清NRG1、miR-221-3p水平比较(x±s)
组别 n miR-221-3p NRG1/(pg/mL) 难治性癫痫组 64 3.07±0.86 16.43±4.32 药物控制良好组 58 1.10±0.29* 6.03±1.89* 对照组 70 1.02±0.25* 5.56±1.39* miR-221-3p: microRNA-221-3p; NRG1: 神经调节蛋白1。与难治性癫痫组比较, *P < 0.05。 表 2 CD组与非CD组血清NRG1、miR-221-3p水平比较(x±s)
组别 n miR-221-3p NRG1/(pg/mL) CD组 40 3.29±0.89 21.39±6.29 非CD组 24 1.64±0.45* 15.68±4.92* miR-221-3p: microRNA-221-3p; NRG1: 神经调节蛋白1。与CD组比较, * P < 0.05。 表 3 CD组与非CD组MoCA评分比较(x±s)
分 项目 CD组(n=40) 非CD组(n=24) 空间与执行能力评分 2.98±0.21 4.52±0.26* 语言评分 2.84±0.33 3.89±0.25* 延迟记忆评分 2.17±0.75 4.71±0.56* 注意与集中评分 4.65±0.94 5.01±1.12 命名评分 2.96±0.28 3.05±0.35 抽象思维评分 1.97±0.29 2.08±0.31 计算力与定向评分 3.01±0.35 5.31±0.37* 总分 20.20±0.72 28.75±1.24* MoCA: 蒙特利尔认知评估量表。与CD组比较, * P < 0.05。 表 4 难治性癫痫患者发生CD影响因素的Logistic回归分析
自变量 B SE wald P OR 95%CI miR-221-3p 0.744 0.209 12.667 < 0.001 2.104 1.396~3.169 NRG1 -0.601 0.212 8.049 < 0.001 0.548 0.362~0.830 MoCA总分 0.070 0.254 0.077 0.781 1.073 0.652~1.765 miR-221-3p: microRNA-221-3p; NRG1: 神经调节蛋白1; MoCA: 蒙特利尔认知评估量表。 -
[1] 赵午骏, 黎瀚, 王彬, 等. 非编码RNA在癫痫发病机制中的研究进展[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2021, 54(1): 48-54. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113694-20200422-00290 [2] 李蓉, 汪雨萱, 黎玉丹, 等. 抗癫痫药物临床评价指标研究进展[J]. 卒中与神经疾病, 2020, 27(4): 552-556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0478.2020.04.035 [3] 张彩彩, 莫业和, 刘友斌, 等. 硫化氢/3-巯基丙酮酸转硫酶在癫痫患者颞叶中的表达[J]. 临床神经病学杂志, 2019, 32(2): 131-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1648.2019.02.026 [4] 陈波. miR-146a通过靶向TRIB3调节癫痫大鼠海马神经元凋亡及炎症反应[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志, 2020, 28(7): 422-428. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYSJ202007008.htm [5] LANG Y, LI Y, YU H, et al. HOTAIR drives autophagy in midbrain dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra Compacta in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease by elevating NPTX2 via miR-221-3p binding[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2020, 12(9): 7660-7678. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/341328815_HOTAIR_drives_autophagy_in_midbrain_dopaminergic_neurons_in_the_substantia_nigra_compacta_in_a_mouse_model_of_Parkinson
[6] 杨振栋, 张云美, 于亚峰. 神经调节因子1对老年C57BL/6J小鼠听皮层的保护作用[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2018, 17(15): 2501-2504. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2018.15.012 [7] ROBERT S, FISHER J, HELEN CROSS, 等. 2016年国际抗癫痫联盟癫痫发作分类的更新及介绍[J]. 癫痫杂志, 2017, 3(1): 60-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXZA201701013.htm [8] CAMERON J, WORRALL-CARTER L, PAGE K, et al. Screening for mild cognitive impairment in patients with heart failure: Montreal cognitive assessment versus mini mental state exam[J]. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs, 2013, 12(3): 252-260. doi: 10.1177/1474515111435606
[9] 孔德燕, 罗杰峰, 石胜良, 等. 药物难治性癫痫患者认知功能损害影响因素的研究[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志, 2020, 28(4): 251-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYSJ202004014.htm [10] TITZE-DE-ALMEIDA S S, SOTO-SÁNCHEZ C, FERNANDEZ E, et al. The promise and challenges of developing miRNA-based therapeutics for parkinson's disease[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(4): 841-864. doi: 10.3390/cells9040841
[11] 李秀翠, 赵成, 邵华, 等. 乳腺癌组织中Bmi-1、miR-221-3P的表达及意义[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58(41): 22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2018.41.006 [12] 范迎春, 李锋, 朱孟霞, 等. 血清25(OH)D3、miR-221水平与冠状动脉病变程度、内皮功能的关系[J]. 重庆医学, 2019, 48(8): 1339-1343. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2019.08.020 [13] 范崇桂, 张燕平, 付国惠, 等. 微小RNA-221靶向凋亡蛋白酶活化因子1对神经胶质瘤细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2020, 37(3): 548-550. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9030.2020.03.045 [14] QUERO L, TIADEN A N, HANSER E, et al. miR-221-3p drives the shift of M2-macrophages to a pro-inflammatory function by suppressing JAK3/STAT3 activation[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 3087. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/338848808_miR-221-3p_Drives_the_Shift_of_M2-Macrophages_to_a_Pro-Inflammatory_Function_by_Suppressing_JAK3STAT3_Activation
[15] ZHANG K, LIANG Y, FENG Y, et al. Decreased epithelial and sputum miR-221-3p associates with airway eosinophilic inflammation and CXCL17 expression in asthma[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2018, 315(2): L253-L264. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00567.2017
[16] 徐义勇, 刘金莲, 朱丽娟, 等. 温胆汤含药血清对谷氨酸环境下星型胶质细胞凋亡及NRG1、ErbB4表达的影响[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2019, 35(2): 7-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYL201902002.htm [17] 陈彦霖, 陈诚, 李泽平, 等. NRG1/ErbB4信号通路与精神疾病关联的研究进展[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2020, 30(15): 44-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2020.15.008 [18] YOO J Y, KIM H B, YOO S Y, et al. Neuregulin 1/ErbB4 signaling attenuates neuronal cell damage under oxygen-glucose deprivation in primary hippocampal neurons[J]. Anat Cell Biol, 2019, 52(4): 462-468. doi: 10.5115/acb.19.210
[19] HEI Y, CHEN R, MAO X, et al. Neuregulin1 attenuates cognitive deficits and hippocampal CA1 neuronal apoptosis partly via ErbB4 receptor in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2019, 365: 141-149. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.02.046
[20] WU L, RAMIREZ S H, ANDREWS A M, et al. Neuregulin1-β decreases interleukin-1β-induced RhoA activation, myosin light chain phosphorylation, and endothelial hyperpermeability[J]. J Neurochem, 2016, 136(2): 250-257. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13374
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 钱新民,丁兆生,李佟,徐春丽,张万权,周芳. 奥沙西泮联合度洛西汀治疗抑郁症的临床效果. 临床合理用药. 2024(08): 71-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴书清,黄蕾,王丽君,秦艳,孙英,闵凌峰,刘异凡,刘彦. 光电容积脉搏波描记法对重症患者合并阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征的诊断价值. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(11): 1-5 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 原改兰,罗少亚,张兵兵. 分析NSCLC患者血清学指标与OSAS之间的相关性. 罕少疾病杂志. 2024(08): 45-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 胡佩瑞,张亚倩,阎妍,陈玺. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者HIF-1a、IGF-1及HGF的表达与意义. 分子诊断与治疗杂志. 2023(06): 939-942 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 朱淑芹,邓旭,魏吉林,刘治国. 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值、胱抑素C在2型糖尿病周围神经病变中的诊断价值. 国际检验医学杂志. 2023(14): 1709-1712 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 孙雅琪. 睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征筛查中动态心电图推导呼吸曲线技术的应用效果. 中国医疗器械信息. 2022(22): 58-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
