Correlations of plasma Alarin level with glucose and lipid metabolism and chronic inflammation in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients with obesity
-
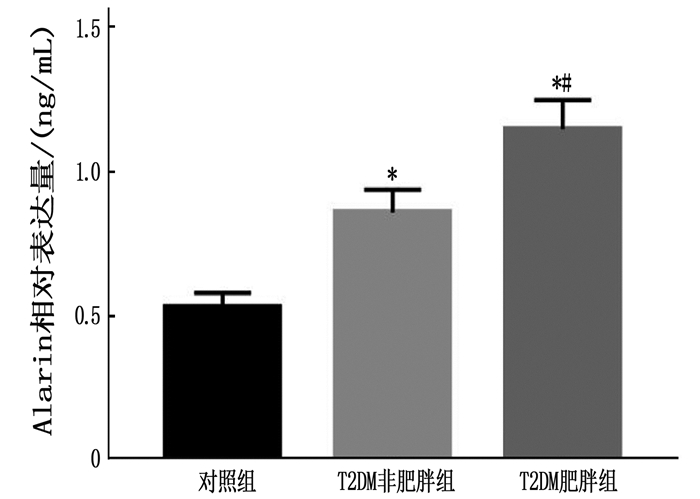
摘要:目的 探讨初诊2型糖尿病合并肥胖患者血浆Alarin水平与糖脂代谢及慢性炎症的相关性。方法 选取300例糖尿病患者为研究对象,根据肥胖情况分为T2DM肥胖组(n=128例)和T2DM非肥胖组(n=172),另选同期健康体检的100例健康人员为对照组。采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测各组血浆Alarin水平;比较各组空腹胰岛素(FINS)、餐后2 h胰岛素(2 hINS)、胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR)、血清糖化血红蛋白(HbAlc)、空腹血糖(FPG)、总胆固醇(TC)、三酰甘油(TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、血清白细胞介素6(IL-6)、C反应蛋白(CRP)及肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)水平。结果 T2DM肥胖组血浆Alarin水平高于T2DM非肥胖组和对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);T2DM非肥胖组血浆Alarin水平高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。T2DM肥胖组FINS、2 hINS及HOMA-IR水平高于T2DM非肥胖组和对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);T2DM非肥胖组FINS、2 hINS及HOMA-IR水平高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。T2DM肥胖组HbAlc、FPG、TC、TG、LDL-C水平高于T2DM非肥胖组和对照组,HDL-C水平低于T2DM非肥胖组和对照组(P < 0.05);T2DM非肥胖组HbAlc、FPG、TC、TG、LDL-C水平高于对照组,HDL-C水平低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。T2DM肥胖组CRP、IL-6和TNF-α水平高于T2DM非肥胖组和对照组,,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。T2DM非肥胖组CRP、IL-6和TNF-α水平高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Pearson相关性分析表明,T2DM患者血浆Alarin与FINS、2hINS、HOMA-IR、HbAlc、FPG、TC、TG、LDL-C、CRP、IL-6和TNF-α水平呈正相关,与HDL-C水平呈负相关(P < 0.05)。结论 初诊2型糖尿病患者血浆Alarin水平明显升高,且与肥胖、糖脂代谢紊乱、胰岛素抵抗以及慢性炎症反应密切相关,血浆Alarin水平随代谢异常危险因素的增加而增高。Abstract:Objective To explore the correlations of plasma Alarin level and lipid metabolism, chronic inflammation in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients with obesity.Methods A total of 300 patients with diabetes were selected as study subjects. According to the obesity situation, they were divided into T2DM obese group (n=128) and T2DM non-obese group (n=172). Another 100 healthy population who underwent physical examinations during the same period were selected as control group. Plasma Alarin levels were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Fasting insulin (FINS), 2 h postprandial insulin (2 hINS), insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) and serum glycosylated hemoglobin (HbAlc), fasting plasma glucose (FPG), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), serum interleukin 6 (IL-6) and C-reaction protein (CRP) and tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α) of different groups were compared.Results The plasma Alarin level of the T2DM obese group was significantly higher than that in the T2DM non-obese group and control group (P < 0.05), and was higher in the T2DM non-obese group than that in the control group (P < 0.05). The levels of FINS, 2 hINS and HOMA-IR in the T2DM obese group were significantly higher than those in the non-obese group and the control group, and were significantly higher in the T2DM non-obese group than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The levels of HbAlc, FPG, TC, TG and LDL-C in the T2DM obese group were significantly higher than those of the T2DM non-obese group and the control group, HDL-C level was significantly lower than that of the T2DM non-obese group and the control group (P < 0.05). The levels of HbAlc, FPG, TC, TG and LDL-C in the T2DM non-obese group were significantly higher than those of the control group, HDL-C level was significantly lower than the control group (P < 0.05). The levels of CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α in the T2DM obesity group were significantly higher than those in T2DM non-obesity group and control group, and were significantly higher in the T2DM non-obesity group than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that plasma Alarin was positively correlated with FINS, 2 hINS, HOMA-IR, HbAlc, FPG, TC, TG, LDL-C, CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α levels in T2DM patients (P < 0.05), and negatively correlated with HDL-C levels (P < 0.05).Conclusion The plasma Alarin level in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients is significantly increased, which is closely related to obesity, glucose and lipid metabolism disorder, insulin resistance and chronic inflammatory response. Plasma Alarin level is increased with the increase of risk factors of metabolic abnormalities.
-
Keywords:
- newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes /
- obesity /
- Alarin /
- glycolipid metabolism /
- inflammatory response
-
-
表 1 3组一般资料比较(x±s)
组别 男 女 年龄/岁 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 收缩压/mmHg 舒张压/mmHg 对照组(n=100) 41 59 65.40±1.35 20.10±1.30 126.00±9.00 76.00±4.00 T2DM非肥胖组(n=172) 76 96 66.70±1.21 22.50±1.50* 125.00±6.00 74.00±6.00 T2DM肥胖组(n=128) 53 75 67.30±1.73 30.70±1.60*# 127.00±8.00 75.00±5.00 与对照组比较, * P<0.05; 与T2DM非肥胖组比较, #P<0.05。 表 2 各组胰岛功能水平比较(x±s)
组别 n FINS/(mU/L) 2 hINS/(mU/L) HOMA-IR 对照组 100 4.51±0.79 8.03±1.25 1.08±0.13 T2DM非肥胖组 172 8.69±1.01* 16.41±2.57* 4.11±0.72* T2DM肥胖组 128 12.36±1.87*# 22.34±2.95*# 6.56±1.62*# FINS: 空腹胰岛素; 2 hINS: 餐后2 h胰岛素; HOMA-IR: 胰岛素抵抗指数。
与对照组比较, * P<0.05; 与T2DM非肥胖组比较, #P<0.05。表 3 各组糖脂代谢水平比较(x±s)
组别 n HbAlc/% FPG/(mmol/L) TC/(mmol/L) TG/(mmol/L) LDL-C/(mmol/L) HDL-C/(mmol/L) 对照组 100 5.03±0.24 4.65±0.41 4.19±0.31 1.06±0.11 2.38±0.25 1.54±0.16 T2DM非肥胖组 172 9.37±1.26* 8.48±0.82* 5.06±0.37* 2.03±0.24* 3.26±0.33* 1.23±0.23* T2DM肥胖组 128 11.23±1.59*# 9.47±0.93*# 5.34±0.39*# 2.64±0.29*# 3.87±0.37*# 1.12±0.26*# HbAlc: 糖化血红蛋白; FPG: 空腹血糖; TC: 总胆固醇; TG: 三酰甘油; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; HDL-C: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇。
与对照组比较, * P<0.05; 与T2DM非肥胖组比较, #P<0.05。表 4 各组炎性因子水平比较(x±s)
组别 n CRP/(mg/L) IL-6/(ng/L) TNF-α/(ng/L) 对照组 100 2.48±0.26 6.72±0.69 31.34±2.17 T2DM非肥胖组 172 5.46±1.33* 9.75±1.05* 49.56±2.68* T2DM肥胖组 128 9.18±1.59*# 15.21±2.04*# 69.47±5.56*# IL-6: 白细胞介素-6; CRP: C反应蛋白; TNF-α: 肿瘤坏死因子-α。与对照组比较, * P<0.05; 与T2DM非肥胖组比较, #P<0.05。 表 5 血浆Alarin与胰岛功能、糖脂代谢及炎性因子水平的相关性分析
指标 血浆Alarin r P 空腹胰岛素 0.608 <0.001 餐后2 h胰岛素 0.643 <0.001 胰岛素抵抗指数 0.597 <0.001 糖化血红蛋白 0.554 <0.001 空腹血糖 0.612 <0.001 总胆固醇 0.701 <0.001 三酰甘油 0.527 <0.001 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 0.614 <0.001 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 -0.503 <0.001 C反应蛋白 0.574 <0.001 白细胞介素-6 0.609 <0.001 肿瘤坏死因子-α 0.598 <0.001 -
[1] 郭哲, 宁金月, 王玉沙. 2型糖尿病患者BMI与HbAlc、胰岛素抵抗及肾损害指标的相关性分析[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2020, 35(2): 297-300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2020.02.031 [2] WEI X, GU N, FENG N, et al. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase exerts a hypoglycemic effect by improving β cell function via inhibition of β cell apoptosis in db/db mice[J]. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem, 2018, 33(1): 1494-1500. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1477138
[3] HU W, FAN X, ZHOU B, et al. Circulating alarin concentrations are high in patients with type 2 diabetes and increased by glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment: an Consort-compliant study[J]. Medicine: Baltimore, 2019, 98(28): e16428. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016428
[4] FANG X, ZHANG T, YANG M, et al. High circulating alarin levels are associated with presence of metabolic syndrome[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 51(5): 2041-2051. doi: 10.1159/000495823
[5] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2021, 37(4): 311-398. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20210304-00142 [6] LI M, HE Q, CHEN Y, et al. Xuezhikang capsule for type 2 diabetes with hyperlipemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trails[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2015, 2015: 468520. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC4515518?pdf=render
[7] CIGROVSKI BERKOVIC M, VIROVIC-JUKIC L, BILIC-CURCIC I, et al. Post-transplant diabetes mellitus and preexisting liver disease-a bidirectional relationship affecting treatment and management[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(21): 2740-2757. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2740
[8] ZHANG C, HE X, SHENG Y, et al. Allicin regulates energy homeostasis through brown adipose tissue[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(5): 101113. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101113
[9] HUANG J Y, CHIANG M T, CHAU L Y. Adipose overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 does not protect against high fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e55369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055369
[10] LI Y, LIU B, LI Y, et al. Epicardial fat tissue in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2019, 18(1): 3. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0807-3
[11] PARK S, SON H K, CHANG H C, et al. Effects of Cabbage-Apple Juice Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum EM on Lipid Profile Improvement and Obesity Amelioration in Rats[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(4): 1135. doi: 10.3390/nu12041135
[12] OHLSSON B, ROTH B, LARSSON E, et al. Calprotectin in serum and zonulin in serum and feces are elevated after introduction of a diet with lower carbohydrate content and higher fiber, fat and protein contents[J]. Biomed Rep, 2017, 6(4): 411-422. doi: 10.3892/br.2017.865
[13] JUSZCZAK F, CARON N, MATHEW A V, et al. Critical Role for AMPK in Metabolic Disease-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(21): 7994. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217994
[14] EBERHARD N, MAYER C, SANTIC R, et al. Distribution of alarin immunoreactivity in the mouse brain[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2012, 46(1): 18-32. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9546-y
[15] MIKÓA, BALLA P, TENK J, et al. Thermoregulatory effect of alarin, a new member of the galanin peptide family[J]. Temperature: Austin, 2014, 1(1): 51-56. doi: 10.4161/temp.29790
[16] 谢芳, 李强, 赵爱国, 等. 外周血LncRNA-p3134表达水平在妊娠期糖尿病诊断中的价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(20): 106-110. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20211287 [17] EL-ASRAR M A, ELBARBARY N S, ISMAIL E A, et al. Serum YKL-40 in young patients with β-thalassemia major: Relation to hepatitis C virus infection, liver stiffness by transient elastography and cardiovascular complications[J]. Blood Cells Mol Dis, 2016, 56(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2015.09.006
[18] 刘建丽, 刘力铭, 杨晓莹. 3种胰岛自身抗体与1型糖尿病患儿并发肾损害的关系研究[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(21): 119-123. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20212482 -
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 刘龙富. 乙肝肝硬化患者CT肝脏体积与病理分级及临床分期和终末期肝病模型评分的关系分析. 中国实用乡村医生杂志. 2022(05): 60-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘芳,季良,姜海燕,陈男男,陈志赫,杜宁. 肝爽颗粒联合富马酸替诺福韦二吡呋酯片对乙型病毒性肝炎肝硬化患者APRI、FIB-4的影响. 医学信息. 2021(05): 104-106+110 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王箭焱,张慧,吕婕,陈灵,陈述. 奥曲肽联合一贯煎合猪苓汤治疗肝肾阴虚型肝肾综合征临床研究. 基层医学论坛. 2021(25): 3680-3682 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张国顺,王志源,李盛楠,孟冬梅,方正亚,刘斌,袁聚祥. 核苷类抗病毒药物联合前列地尔治疗HBV感染失代偿期肝硬化患者难治性腹水的临床疗效及对肝肾功能的影响. 中国老年学杂志. 2020(08): 1624-1627 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 程崇勇. 奥曲肽联合白蛋白治疗肝硬化合并肝肾综合征的临床观察. 临床研究. 2020(09): 77-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘建,胡红波,廖宗敏. 术后醋酸奥曲肽应用对妇科肿瘤术后淋巴液及肠道功能恢复的影响. 中国医药科学. 2020(09): 69-71+75 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
