Effects of Toll like receptor 4 and hepatocyte growth factor expression levels on prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after radical resection
-
摘要:目的 探讨术前血清Toll样受体4(TLR4)、肝细胞生长因子(HGF)表达水平对肝细胞癌患者切除术后预后的影响。方法 选取78例肝细胞癌患者作为研究对象,均接受肝细胞癌切除术治疗并随访1年,依据随访1年时预后情况(带瘤生存或无瘤生存)将患者分为预后不良组与预后良好组。记录并比较2组患者的基线资料,术前检测患者的血清TLR4、HGF水平,并分析术前血清TLR4、HGF水平对肝细胞癌患者肝细胞癌切除术后预后的影响。结果 随访1年时,预后不良患者16例,占20.51%(16/78);预后不良组患者血清甲胎蛋白(AFP)、α-L-岩藻糖苷酶(AFU)、TLR4、HGF水平均高于预后良好组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);2组基线资料及其他实验室指标水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,术前血清AFP、AFU、TLR4和HGF高水平是肝细胞癌患者术后预后不良的危险因素(OR>1,P<0.05);受试者工作特征曲线显示,术前血清TLR4、HGF水平单独及联合检测预测肝细胞癌患者术后预后的曲线下面积均>0.70,具有一定的预测价值;TLR4、HGF的cut-off值分别取13.629、0.608 ng/mL时,可获得最佳预测价值。结论 肝细胞癌患者肝细胞癌切除术后预后可能受术前血清TLR4、HGF水平的影响。Abstract:Objective To explore effects of serum Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) expression levels on prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after radical resection.Methods A total of 78 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were selected as research subjects, and all received hepatocellular carcinoma resection and were followed up for 1 year. The patients were divided into poor prognosis group and good prognosis group according to the prognosis of patients at 1 year of follow-up (according to the conditions of patients surviving with or without tumors). The baseline data questionnaire of patients was recorded and compared. Serum TLR4 and HGF levels of patients were detected before surgery, and the effects of serum TLR4 and HGF levels on the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatocellular carcinoma resection were analyzed.Results At one year of follow-up after liver radical resection, 16 patients had poor prognosis, accounting for 20.51% (16/78); the serum levels of Serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), α-L-fucosidase (AFU), TLR4 and HGF of patients in the poor prognosis group were higher than those in the good prognosis group (P < 0.05); there were no significant differences in baseline data and other laboratory indicators between the two groups (P > 0.05); Logistic regression analysis results showed that high preoperative serum levels of AFP, AFU, TLR4 and HGF were risk factors for poor prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after liver radical resection (OR > 1, P < 0.05); the receiver operating characteristic curve showed that the AUC of preoperative serum levels of TLR4 and HGF alone and their combination in predicting the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after liver radical resection were all over 0.70, which had certain predictive value; when the cut-off values of each index were 13.629 ng/mL and 0.608 ng/mL respectively, the best predictive value could be obtained.Conclusion The prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after liver radical resection may be affected by the preoperative serum levels of TLR4 and HGF.
-
-
表 1 2组患者基线资料和实验室指标结果比较(x±s)[n(%)][M(P25, P75)]
指标 预后不良组(n=16) 预后良好组(n=62) χ2/t/Z/U P 年龄/岁 52.00(49.00, 55.00) 51.00(49.00, 53.50) 0.702 0.483 性别 男 15(93.75) 51(82.26) 0.558 0.455 女 1(6.25) 11(17.74) 高血压病 有 4(25.00) 10(16.13) 0.211 0.646 无 12(75.00) 52(83.87) 糖尿病 有 3(18.75) 4(6.45) 1.090 0.297 无 13(81.25) 58(93.55) 大量饮酒史 有 11(68.75) 36(58.06) 0.606 0.436 无 5(31.25) 26(41.94) 病灶最大径/cm 3.00±0.55 3.24±1.10 0.793 0.428 TNM分期 Ⅱ期 5(31.25) 38(61.29) 1.876 0.061 Ⅲ期 11(68.75) 24(38.71) 手术时间/h 10.00±2.30 9.38±2.34 0.826 0.409 术中出血量/mL 1 256.00(1 163.50, 1 297.00) 1 310.00(1 232.00, 1 393.00) 1.395 0.163 ALT/(U/L) 77.17±4.65 76.81±4.65 0.260 0.795 AST/(U/L) 58.74±3.55 58.36±3.66 0.368 0.713 AFP/(ng/mL) 513.60±48.16 438.21±58.83 3.924 <0.001 AFU/(μmol/L) 526.65±52.79 487.73±43.67 2.371 0.018 TLR4/(ng/mL) 15.72±3.48 11.66±2.75 3.693 <0.001 HGF/(ng/mL) 0.68±0.19 0.46±0.16 3.766 <0.001 ALT: 谷丙转氨酶; AST: 谷草转氨酶; AFP: 甲胎蛋白; AFU: α-L-岩藻糖苷酶; TLR4: Toll样受体4; HGF: 肝细胞生长因子。 表 2 自变量类型与赋值情况
自变量 变量类型 赋值 TNM分期 分类变量 1=Ⅲ期,0=Ⅱ期 AFP 连续变量 - AFU 连续变量 - TLR4 连续变量 - HGF 连续变量 - AFP: 甲胎蛋白; AFU: α-L-岩藻糖苷酶;
TLR4: Toll样受体4; HGF: 肝细胞生长因子。表 3 前血清TLR4、HGF水平对肝细胞癌患者术后预后影响的回归分析
相关因素 β 标准误 Wald P OR 95%置信区间 TNM分期 1.510 1.191 1.607 0.205 4.526 0.438~46.724 AFP 0.026 0.012 4.690 0.030 1.026 1.002~1.050 AFU 0.022 0.011 4.007 0.045 1.022 1.000~1.043 TLR4 0.472 0.230 4.213 0.040 1.603 1.022~2.515 HGF 8.054 3.834 4.412 0.036 3 146.129 1.713~5 776 642.632 常量 -36.585 9.840 13.823 <0.001 - - AFP: 甲胎蛋白; AFU: α-L-岩藻糖苷酶; TLR4: Toll样受体4; HGF: 肝细胞生长因子。 表 4 术前血清TLR4、HGF单独及联合对肝细胞癌患者术后预后的预测价值
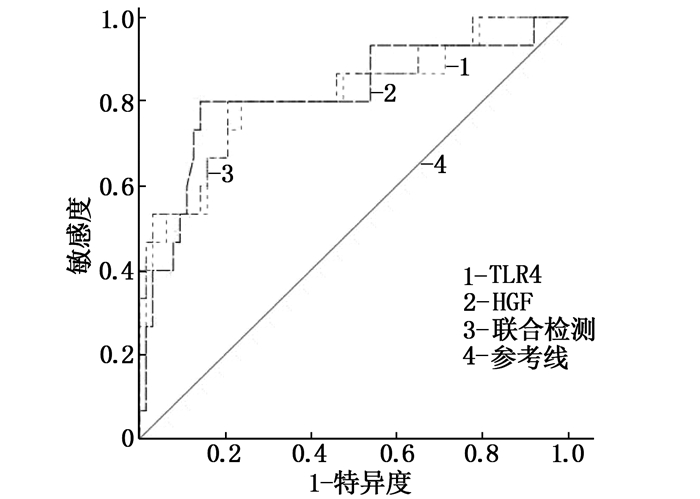
项目 AUC cut-off值 AUC的95%置信区间 P 特异度 敏感度 约登指数 TLR4 0.808 13.629 ng/mL 0.672~0.945 <0.001 0.762 0.733 0.495 HGF 0.814 0.608 ng/mL 0.676~0.953 <0.001 0.857 0.800 0.657 联合 0.822 - 0.691~0.953 <0.001 0.794 0.800 0.594 TLR4: Toll样受体4; HGF: 肝细胞生长因子; AUC: 曲线下面积。 -
[1] RODRÍGUEZ-PERÁLVAREZ M, CRESPO G, MAIRA T D, et al. Incidence and prognostic impact of cancer after liver transplantation[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73(1): 276-277. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168827820310576
[2] 吕少诚, 潘冰, 李立新, 等. 原发性肝癌肝移植患者预后评价及相关影响因素分析[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2019, 25(7): 493-496. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.2019.07.003 [3] KUSUHARA Y, DAIZUMOTO K, KAWAI K, et al. Low expression of toll-like receptor 4 is associated with poor prognosis in bladder cancer[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39(2): 703-711. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13166
[4] 李建华, 韩玲. 血清HGF、CA199、CA724联合检测在胆管癌诊断及复发预测中的价值[J]. 实用癌症杂志, 2020, 35(5): 745-748. doi: 10.3969/j.isn.1001-5930.2020.05.013 [5] 陈孝平, 汪建平, 赵继宗. 外科学[M]. 9版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018: 418-420. [6] 贾户亮, 钦伦秀. 肝细胞癌术后复发的预测与预防策略[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2016, 24(5): 330-334. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.05.004 [7] LAI Q, VITALE A, IESARI S, et al. Intention-to-treat survival benefit of liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular cancer[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(6): 1910-1919. doi: 10.1002/hep.29342
[8] 张达利, 冯丹妮, 张利娟, 等. 肝细胞癌患者肝移植术后复发的危险因素及预后分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(9): 1985-1989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.09.015 [9] 郁淼, 秦兵, 胡道军, 等. 血清甲胎蛋白、高尔基体蛋白73、α-L-岩藻糖苷酶、血清铁蛋白联合检测在原发性肝癌早期诊断中的价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2020, 24(20): 37-39, 43. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.202020010 [10] BONIN S, PARASCANDOLO A, AVERSA C, et al. Reduced expression of α-L-Fucosidase-1(FUCA-1) predicts recurrence and shorter cancer specific survival in luminal B LN+ breast cancer patients[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(20): 15228-15238. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24445
[11] 周东晓, 马英杰, 杨丽, 等. Toll样受体4在乙型肝炎相关性肝癌患者外周血CD14+单核细胞表面的表达及意义[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2018, 47(4): 143-146. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YXYZ201804037.htm [12] 万波, 母齐鸣, 贺伟. 肝细胞癌术后血清AFP、CA19-9、HGF水平对预后状况的影响[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2020, 27(1): 114-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJMY202001026.htm [13] 刘开才, 吕维富, 周春泽, 等. 肝细胞肝癌肝动脉化学栓塞术后血清脂多糖、toll样受体4和肠道微生态改变[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2018, 38(11): 780-782. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2018.11.011 [14] 洪淑贞, 梁海英, 黄彩彩. 高迁移率族蛋白B1和toll样受体4在宫颈癌组织中的表达及相关性分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2019, 34(6): 1379-1382. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFYB201906057.htm [15] 王敬, 陈冠男, 吕琪, 等. 高迁移率族蛋白B1、Toll样受体4在脓毒症大鼠心肌组织中表达及意义[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2018, 38(12): 2962-2964. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.12.059 [16] 孙雪东, 严一核, 褚韦韦, 等. 高迁移率族蛋白B1/Toll样受体4信号通路在脓毒症大鼠致急性肺损伤中的作用研究[J]. 中华危重症医学杂志: 电子版, 2020, 13(6): 419-426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWZD202006005.htm [17] KATAOKA H, KAWAGUCHI M, FUKUSHIMA T, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitors (HAI-1 and HAI-2): Emerging key players in epithelial integrity and cancer[J]. Pathol Int, 2018, 68(3): 145-158. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040199161410_0fa4.html
[18] MATSUMOTO K, UMITSU M, DE SILVA D M, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor/MET in cancer progression and biomarker discovery[J]. Cancer Sci, 2017, 108(3): 296-307. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5378267/pdf/CAS-108-296.pdf
[19] 庄晓苹, 林琼琼, 季剑乐, 等. 乳腺癌中SyK、HGF表达的相关性及预后的关系[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2019, 48(5): 126-129. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YXYZ201905034.htm [20] 庄晓苹, 谭晓, 朱暐, 等. SyK和HGF在乳腺癌中表达及临床意义[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2016, 45(11): 145-148. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YXYZ201611039.htm [21] 虞小亭, 刘正人, 谢熠, 等. 肝细胞生长因子在乳腺癌新辅助化疗前后的变化及其临床意义[J]. 中华普外科手术学杂志: 电子版, 2021, 15(3): 306-309. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHPW202103022.htm -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 杨维泽,梁爱群,李斌飞,舒惠萍,陈维纯,罗小平,李素英,赖紫霞. 标准化防护流程在心脏直视手术患者术中压疮预防中的应用. 齐鲁护理杂志. 2020(04): 63-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李怡昉,田赛严,甄晓星. 低温体外循环开胸心脏术后老年ICU住院患者压疮事件影响因素分析. 首都食品与医药. 2020(13): 28 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张丽,张玲玲,耿冉,汪静怡. 体外循环手术术中急性压力性损伤的对因循证预防. 护理实践与研究. 2020(16): 120-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 朱琳. 手术室急性压力性损伤形成的危险因素分析. 感染、炎症、修复. 2020(03): 167-170 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
