Correlation between cerebral state index and end-tidal concentration of sevoflurane in children with cerebral palsy undergoing adjustment surgery
-
摘要:目的 探讨脑状态指数(CSI)与呼气末七氟醚浓度(CETSev)在脑瘫患儿七氟醚全身麻醉期间的相关性。方法 选择80例择期下肢调整手术的脑瘫患儿,采用七氟醚全身麻醉和常规监测,持续监测CETSev和CSI。于诱导前(T0)、喉罩置入后(T1)和CETSev 0.8%(T2)、CETSev 1.2%(T3)、CETSev 1.6%(T4)、CETSev 2.0%(T5)、CETSev 2.4%(T6)、CETSev 2.8%(T7)时,以及停吸七氟醚(T8)和下降期CETSev 1.4%(T9)、CETSev 1.2%(T10)、CETSev 1.0%(T11)、CETSev 0.8%(T12)、CETSev 0.6%(T13)、CETSev 0.4%(T14)和喉罩拔除前(T15)、喉罩拔除后(T16)时,记录CETSev和CSI值。分析CETSev和CSI的相关性。结果 在CETSev上升期(T0~T7),T2~T7的CSI低于T0,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);CSI与CETSev呈负相关(r=-0.890,P < 0.001)。在CETSev下降期(T8~T16),T9~T16的CSI高于T8,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);CSI与CETSev呈负相关(r=-0.889,P < 0.001)。结论 在脑瘫调整手术患儿CETSev的上升期和下降期,CSI与CETSev均呈显著负相关,故可通过CSI指导全身麻醉期间的七氟醚精准用药。Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation between cerebral state index (CSI) and end-tidal concentration of sevoflurane (CETSev) in children with cerebral palsy during sevoflurane general anesthesia.Methods Eighty children with cerebral palsy for selective lower limb adjustment surgery were selected. Sevoflurane general anesthesia and routine monitoring were performed, and CETSev as well as CSI were continuously monitored. Before induction (T0), after laryngeal mask implantation (T1), CETSev 0.8% (T2), CETSev 1.2% (T3), CETSev 1.6% (T4), CETSev 2.0%(T5), CETSev 2.4% (T6), CETSev 2.8% (T7), stop taking sevoflurane (T8) and declining stages including CETSev 1.4% (T9), CETSev 1.2%(T10), CETSev 1.0% (T11), CETSev 0.8% (T12), CETSev 0.6% (T13), CETSev 0.4% (T14), before (T15) and after (T16) laryngeal mask removal, the values of CETSev and CSI were recorded. The correlation between CETSev and CSI introduction was analyzed.Results During the rising period of CETSev (T0 to T7), the CSI of T2 to T7 was significantly lower than that of T0 (P < 0.05); CSI was negatively correlated with CETSev (r=-0.890, P < 0.001). During the decreasing period of CETSev (T8 to T16), CSI values of T9 to T16 were significantly higher than that of T8 (P < 0.05); CSI was negatively correlated with CETSev (r=-0.889, P < 0.001).Conclusion There is a significant negative correlation between CSI and CETSev in the rising and descending period of CETSev in children with cerebral palsy undergoing palsy adjustment surgery. Therefore, CSI can be used to guide the accurate use of sevoflurane during general anesthesia.
-
Keywords:
- sevoflurane /
- cerebral state index /
- cerebral palsy /
- children /
- concentration
-
脑瘫(CP)是发育期大脑的非进行性损伤所导致的一种运动功能障碍[1]。为了改善脑瘫患儿运动功能障碍,恢复自主协调运动,其通常需要接受多次下肢肌力肌张力调整手术,因而需要反复接受全身麻醉(简称全麻)。七氟醚吸入麻醉有利于改善调整手术中的肌张力。有关脑电麻醉深度监测参数与脑瘫患儿吸入麻醉药的相关性研究已有报道[2-4], 通常采用吸入麻醉药的呼气末浓度维持几个固定值并在固定值稳定3~15 min后监测脑电参数,但尚未见实时、连续、全程监测的相关报道。此外,脑状态指数(CSI)作为脑电监测麻醉深度的技术之一,逐渐应用于临床。本研究探讨脑瘫患儿下肢调整手术全麻期间呼气末七氟醚浓度(CETSev)逐步增加(上升期)以及逐步减少(下降期)过程中, CSI与CETSev的相关性,同时观察CSI与七氟醚最低肺泡有效浓度(MAC-Sev)的相关性,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
本研究为前瞻性研究,选取2018年1月—2020年1月本院收治的脑瘫痉挛型运动障碍拟行下肢调整手术患儿80例,性别不限,年龄4~9岁,美国麻醉医师协会(ASA)分级Ⅰ~Ⅱ级,无癫痫发作或智力障碍。本研究纳入的80例患儿,男53例,女27例; 年龄(6.7±2.2)岁,身高(110.6±14.6) cm, 体质量(20.4±7.3) kg。本研究已获本院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 方法
患儿术前均未用药,入室后连接监护仪(Drager Infinity Delta XL, 德国)监测心率(HR)、收缩压(SBP)、舒张压(DBP), 监测患儿CSI (NW-9002S, 中国)和CETSev和MAC-Sev (Drager Primus, 德国)。
麻醉诱导通过静脉注射阿托品0.01 mg/kg、咪唑安定0.1 mg/kg、舒芬太尼0.2 μg/kg、异丙酚2 mg/kg、罗库溴铵0.6 mg/kg, 根据患儿体质量置入合适的喉罩并行机械通气,采用容量控制通气模式,呼吸参数设置为潮气量(Vt)6~8 mL/kg[5-6], 呼吸频率(RR)15~25次/min, 维持术中呼气末二氧化碳分压35~45 mmHg。确定喉罩无漏气后,开始使用七氟醚(恒瑞医药,凯特力)。将七氟醚挥发罐调至8 %, 流量为2 L/min。当CETSev达到1.8%, 同时静脉泵注瑞芬太尼0.2~0.3 μg/(kg·min), 开始手术[7]。术中麻醉维持,当CETSev达到2.8%并维持10 min后,调节七氟醚挥发罐输出浓度以维持CSI 40的麻醉深度,继续静脉泵注瑞芬太尼0.2~0.3 μg/(kg·min), 必要时追加罗库溴铵0.3 mg/kg。手术结束时,关闭七氟醚挥发罐,停止静脉泵注瑞芬太尼,追加舒芬太尼0.1 μg/kg。待患儿自主呼吸恢复良好,出现呛咳、吞咽反射即在严密监测下拔除喉罩。
1.3 观察指标
各项监测参数采集分为2个阶段: CETSev的上升期和下降期。上升期的观察时点为: 诱导前(T0)、喉罩置入后(T1)、CETSev 0.8% (T2)、CETSev 1.2% (T3)、CETSev 1.6% (T4)、CETSev 2.0% (T5)、CETSev 2.4% (T6)、CETSev 2.8% (T7)。下降期的观察时点为: 关闭挥发罐时(T8)、CETSev 1.4% (T9)、CETSev 1.2% (T10)、CETSev 1.0% (T11)、CETSev 0.8% (T12)、CETSev 0.6% (T13)、CETSev 0.4% (T14)、喉罩拔除前(T15)、喉罩拔除后(T16)。观察及记录指标为: CETSev、CSI、MAC-Sev以及HR、SBP、DBP。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 26.0统计软件进行数据分析,正态分布计量资料以(x±s)表示,采用重复测量方差分析,应用Pearson相关系数来衡量相关性。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 CETSev上升期不同时点的监测变量
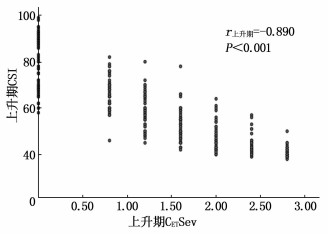
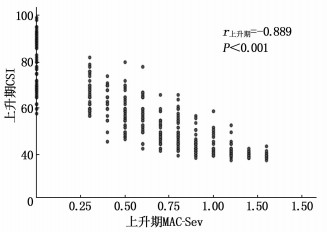
80例患儿手术时间(45.1±17.3) min, 复苏时间(22.1±4.8) min。在CETSev上升期,与T0时相比, T2 ~T7的CSI降低,差异有统计意义(P < 0.01), 见表 1。CSI与CETSev的Pearson相关系数r上升期=-0.890(P < 0.001), 见图 1。CSI与MAC-Sev的Pearson相关系数r上升期=-0.889(P < 0.001), 见图 2。
表 1 80例患儿CETSev上升期不同时点的监测变量(x±s)指标 T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 CETSev/% 0 0 0.8 1.2 1.6 2.0 2.4 2.8 CSI 90.5±2.8 70.2±5.1** 65.7±6.4** 58.0±6.7** 50.8±6.6** 45.7±5.2** 42.7±3.5** 40.5±1.7** MAC-Sev 0 0 0.3±0** 0.5±0.1** 0.7±0.1** 0.9±0.1** 1.0±0.1** 1.2±0.8** HR/(次/min) 109.0±13.0 107.0±12.0* 105.0±12.0** 101.0±12.0** 101.0±14.0** 103.0±13.0** 104.0±14.0** 100.0±14.0** SBP/mmHg 114.0±11.0 109.0±10.0** 106.0±9.0** 102.0±11.0** 101.0±12.0** 104.0±13.0** 103.0±11.0** 101.0±11.0* * DBP/mmHg 67.0±10.0 63.0±9.0** 61.0±8.0** 58.0±9.0** 57.0±9.0** 59.0±10.0** 59.0±9.0** 56.0±10.0** CETSev: 呼气末七氟醚浓度; CSI: 脑状态指数; MAC-Sev: 七氟醚最低肺泡有效浓度; HR: 心率; SBP: 收缩压; DBP: 舒张压。与T0比较, * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01。 2.2 CETSev下降期不同时点的监测
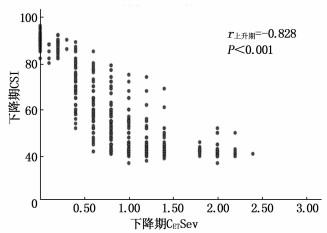
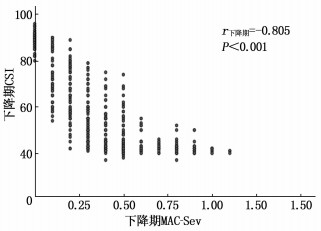
在CETSev下降期,与T8相比, T9~T16的CSI增高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01), 见表 2。CSI与CETSev的Pearson相关系数r下降期=-0.828(P < 0.001), 见图 3。CSI与MAC-Sev的Pearson相关系数r下降期=-0.805(P < 0.001), 见图 4。
表 2 80例患儿CETSev下降期不同时点的监测(x±s)指标 T8 T9 T10 T11 T12 T13 T14 T15 T16 CETSev/% 2.0±0.1 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2±0.1 0 CSI 42.1±2.4 43.5±4.4** 44.5±5.8** 47.4±7.8** 52.2±9.0** 60.4±8.9** 70.3±8.3** 87.8±2.6** 90.1±2.1** MAC-Sev 0.9±0.1 0.6±0.1 0.5±0.1 0.4±0.1 0.3±0.1 0.2±0 0.1±0 0.1±0 0 HR/(次/min) 97.0±11.0 97.0±11.0 97.0±12.0 97.0±12.0 98.0±13.0 99.0±13.0 104.0±11.0* 112.0±10.0* 110.0±12.0* SBP/mmHg 102.0±9.0 103.0±8.0 103.0±8.0 104.0±9.0** 105.0±9.0** 107.0±9.0** 110.0±8.0** 115.0±8.0** 113.0±8.0** DBP/mmHg 57.0±9.0 58.0±9.0 58.0±8.0 58.0±8.0 59.0±8.0* 62.0±9.0** 64.0±9.0** 68.0±8.0** 66.0±8.0** CETSev: 呼气末七氟醚浓度; CSI: 脑状态指数; MAC-Sev: 七氟醚最低肺泡有效浓度; HR: 心率; SBP: 收缩压; DBP: 舒张压。与T8比较, * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01。 2.3 CETSev在0.8%、1.2%和2.0%时各时期CSI值
CETSev在0.8%、1.2%和2.0%时,上升期的CSI值分别为(65.7±6.4)、(58.0±6.7)和(45.7±5.2); 而下降期的CSI分别为(52.2±9.0)、(44.5±5.8)和(42.1±2.4)。
3. 讨论
CSI是与脑电双频指数(BIS)类似的采用单导联脑电图(EEG)的麻醉深度监测指数。尽管两者对于原始EEG的处理算法不同,但是2种指数都以0(等电位EEG)~100(完全清醒)的无量纲数字表示。全麻期间, BIS和CSI都推荐在40~60之间作为合适的麻醉深度。CSI是将EEG信号通过EEG的时域分析(爆发抑制比率)和频域分析(α比率、β比率和α-β比率)而派生出来的4个子参数而获得[8]。CSI因其与BIS反映麻醉催眠深度的一致性[9], 以及反应速度较快,能作为单板机使用的便利性[10], 已成为常被选用的麻醉深度脑电监测指标。本研究在麻醉诱导置入喉罩后才开始吸入七氟醚,并且实时同步监测CSI值的变化。由此可以避免麻醉诱导和置入喉罩等操作而影响脑电信号的采集质量,也有利于观察CSI值随着CETSev和MAC-Sev改变的及时反应。
随着七氟醚浓度的增加或降低,所对应的CSI值变化并不一致,本研究将麻醉过程分为CETSev上升期和下降期。本研究显示,在CETSev上升期, CSI与CETSev的相关系数r上升期=-0.890(P < 0.001); CETSev下降期CSI与CETSev的相关系数为r下降期=-0.828 (P < 0.001)。尽管下降期的相关系数略低于上升期的相关系数,但仍然表现出CSI与CETSev的显著负相关性。两者都能反映出七氟醚的麻醉催眠深度。此外, CSI与MAC-Sev的相关系数在七氟醚上升期和下降期分别为: r上升期=-0.889 (P < 0.001)和r下降期=-0.805 (P < 0.001)。尽管两者也有显著相关性,但由于MAC值的变化观察范围比较狭窄,不便于临床应用和记忆。本研究还显示,在相同的CETSev时,上升期与下降期所对应的CSI值是不同的。对于同样的CETSev, CETSev上升期CSI值较高,在CETSev下降期CSI值较低。在麻醉维持期间,即处于稳态阶段的T8时, CSI (42.1±2.4)或CETSev (2.0±0.1)可以作为麻醉维持的目标值,即达到了适宜麻醉深度。在麻醉恢复至T15时, CSI (87.8±2.6)或CETSev (0.2±0.1)可以作为患儿苏醒恢复的目标值,此时即可平稳拔出喉罩。
本研究的脑瘫患儿均无严重的脑意识功能障碍,所以围术期并未表现出明显的吸入麻醉敏感或麻醉恢复延迟的现象。遗憾的是本研究未能有同类下肢手术的健康患儿进行比较。相关研究[11-14]提示,与健康患儿相比,脑瘫患儿在同等的吸入麻醉药浓度时,脑电BIS值较低,由此可能导致麻醉药使用过多、麻醉过深及麻醉复苏延迟的现象。所以通过脑电直接监测指导吸入麻醉药,可以减少或避免此类不良现象的发生。
综上所述,在脑瘫患儿手术吸入全麻过程中可以通过CSI指导七氟醚精准用药,提高脑瘫患儿七氟醚麻醉的可控性和安全性。
-
表 1 80例患儿CETSev上升期不同时点的监测变量(x±s)
指标 T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 CETSev/% 0 0 0.8 1.2 1.6 2.0 2.4 2.8 CSI 90.5±2.8 70.2±5.1** 65.7±6.4** 58.0±6.7** 50.8±6.6** 45.7±5.2** 42.7±3.5** 40.5±1.7** MAC-Sev 0 0 0.3±0** 0.5±0.1** 0.7±0.1** 0.9±0.1** 1.0±0.1** 1.2±0.8** HR/(次/min) 109.0±13.0 107.0±12.0* 105.0±12.0** 101.0±12.0** 101.0±14.0** 103.0±13.0** 104.0±14.0** 100.0±14.0** SBP/mmHg 114.0±11.0 109.0±10.0** 106.0±9.0** 102.0±11.0** 101.0±12.0** 104.0±13.0** 103.0±11.0** 101.0±11.0* * DBP/mmHg 67.0±10.0 63.0±9.0** 61.0±8.0** 58.0±9.0** 57.0±9.0** 59.0±10.0** 59.0±9.0** 56.0±10.0** CETSev: 呼气末七氟醚浓度; CSI: 脑状态指数; MAC-Sev: 七氟醚最低肺泡有效浓度; HR: 心率; SBP: 收缩压; DBP: 舒张压。与T0比较, * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01。 表 2 80例患儿CETSev下降期不同时点的监测(x±s)
指标 T8 T9 T10 T11 T12 T13 T14 T15 T16 CETSev/% 2.0±0.1 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2±0.1 0 CSI 42.1±2.4 43.5±4.4** 44.5±5.8** 47.4±7.8** 52.2±9.0** 60.4±8.9** 70.3±8.3** 87.8±2.6** 90.1±2.1** MAC-Sev 0.9±0.1 0.6±0.1 0.5±0.1 0.4±0.1 0.3±0.1 0.2±0 0.1±0 0.1±0 0 HR/(次/min) 97.0±11.0 97.0±11.0 97.0±12.0 97.0±12.0 98.0±13.0 99.0±13.0 104.0±11.0* 112.0±10.0* 110.0±12.0* SBP/mmHg 102.0±9.0 103.0±8.0 103.0±8.0 104.0±9.0** 105.0±9.0** 107.0±9.0** 110.0±8.0** 115.0±8.0** 113.0±8.0** DBP/mmHg 57.0±9.0 58.0±9.0 58.0±8.0 58.0±8.0 59.0±8.0* 62.0±9.0** 64.0±9.0** 68.0±8.0** 66.0±8.0** CETSev: 呼气末七氟醚浓度; CSI: 脑状态指数; MAC-Sev: 七氟醚最低肺泡有效浓度; HR: 心率; SBP: 收缩压; DBP: 舒张压。与T8比较, * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01。 -
[1] WONGPRASARTSUK P, STEVENS J. Cerebral palsy and anaesthesia[J]. Pediatr Anesth, 2002, 12(4): 296-303. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2002.00635.x
[2] MELLO S S, SARAIVA R A. Electroneourophysiological changes in anesthesia with sevoflurane: comparative study between healthy and cerebral palsy patients[J]. Rev Bras Anestesiol, 2003, 53(2): 150-159. doi: 10.1590/S0034-70942003000200002
[3] 赵泽宇, 程庆, 张蓉, 等. 脑状态指数与脑电双频指数在脑性瘫痪患儿七氟醚麻醉中镇静水平的相关性[J]. 中国医药导报, 2015, 12(34): 90-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY201534025.htm [4] CHO S H, KIM S S, HYUN D M, et al. Comparison between cerebral state index and bispectral index during desflurane anesthesia[J]. Korean J Anesthesiol, 2018, 71(6): 447-452. doi: 10.4097/kja.d.17.00084
[5] 吴坤, 谷春红, 王师建. 压力控制通气和容量控制通气在小儿喉罩全麻腹腔镜手术中的应用[J]. 中国医疗器械信息, 2018, 24(10): 118-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGQX201810059.htm [6] 徐莉, 侯立功, 王江涛, 等. 不同潮气量机械通气治疗小儿急性肺损伤所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征的临床观察[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2019, 47(1): 98-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYS201901034.htm [7] 张国华, 孙莉. 不同阿片类药物对意识消失时异丙酚用量及大脑皮质抑制速度和抑制程度的影响[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2015, 44(3): 63-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYZ201503020.htm [8] HAN D W, LINARES-PERDOMO O J, LEE J S, et al. Comparison between cerebral state index and bispectral index as measures of electroencephalographic effects of sevoflurane using combined sigmoidal E(max) model[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2011, 32(10): 1208-1214. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.99
[9] NISHIYAMA T. Cerebral state index vs. bispectral index during sevoflurane-nitrous oxide anaesthesia[J]. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2009, 26(8): 638-642. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328324e946
[10] ANDERSON R E, JAKOBSSON J G. Cerebral state monitor, a new small handheld EEG monitor for determining depth of anaesthesia: a clinical comparison with the bispectral index during day-surgery[J]. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2006, 23(3): 208-212. doi: 10.1017/S0265021505002206
[11] SUDHAKARAN R, MAKKAR J, JAIN D, et al. Comparison of bispectral index and end-tidal anaesthetic concentration monitoring on recovery profile of desflurane in patients undergoing lumbar spine surgery[J]. Indian journal of anaesthesia, 2018, 62(7): 516. doi: 10.4103/ija.IJA_172_18
[12] KIP G, ONAL P, OZTAS N. Comparison of bispectral index values and depth of sedation during deep sedation using sevoflurane anesthesia in healthy children versus children with cerebral palsy[J]. Niger J Clin Pract, 2019, 22(6): 801. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_553_18
[13] DA C, SRÂNGELO, DOMINGUES D L T. Regressão da anestesia geral em pacientes com paralisia cerebral: estudo comparativo utilizando o índice bispectral[J]. Revista Brasileira De Anestesiologia, 2006, 56(5): 431-442.
[14] WASS C T, WARNER M E, WORRELL G A, et al. Effect of general anesthesia in patients with cerebral palsy at the turn of the new millennium: a population-based study evaluating perioperative outcome and brief overview of anesthetic implications of this coexisting disease[J]. J Child Neurol, 2012, 27(7): 859-866.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王玲玲,李桂婷,胡玉翠. 七氟醚吸入麻醉与静吸复合麻醉在小儿脑瘫手术中的麻醉效果对比研究. 系统医学. 2024(09): 134-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 董芳,王亚男. 脑状态指数对子宫全切术患者地氟醚全麻苏醒期意识水平的监测价值. 新疆医科大学学报. 2023(09): 1199-1205 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号