Study on potential markers protein for diagnosis of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
-
摘要:目的 比较结核分枝杆菌标准株与休眠株蛋白质组差异表达情况,探讨结核潜伏性感染相关的诊断标志物。方法 选取结核分枝杆菌标准株H37Rv和由标准株诱导的潜伏性感染菌株模型(休眠株)的样本,每个样本各培养3皿。对2组样本中的菌株进行裂解并抽提蛋白,进行同位素标记相对和绝对定量(iTRAQ)检测与分析,获得标准株与休眠菌株中相关蛋白质组的表达数据,并利用蛋白富集、信号通路分析等生物信息学技术将差异蛋白进行分类,进一步确定参与能量代谢通路的相关蛋白。结果 所检测的187个蛋白质中,64个蛋白质具有差异性表达,其中40个蛋白质表达上调,24个蛋白质表达下调。P9WPC9蛋白在休眠菌株与标准株中表达量比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 P9WPC9蛋白主要参与细菌的能量代谢通路,可能成为结核潜伏性感染的潜在诊断标志物。
-
关键词:
- 结核分枝杆菌 /
- 蛋白质组学 /
- 同位素标记相对和绝对定量 /
- 潜伏性感染 /
- 诊断标志物
Abstract:Objective To compare differential expression of proteome in standard Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains and dormant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains so as to explore diagnostic markers related to latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.Methods The samples of standard Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain and latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection strain induced by standard strain (dormant strains) were selected, and each sample was cultured for three dishes. The strains of two sets of samples were cracked and proteins were extracted, isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) detection and quantitative analysis was performed, expression data of related proteome in standard strains and dormant strains were obtained, and bioinformatics techniques such as protein enrichment and signal pathway analysis were used to classify the differential proteins and further identify the related proteins involved in the energy metabolism pathway.Results A total of 64 proteins were differently expressed in the 187 detected proteins, of which 40 proteins were up-regulated and 24 proteins were down-regulated. Differently expressed proteins were mainly related to bacterial energy metabolism. P9WPC9 expression had a significant difference between dormant strains and standard strains.Conclusion P9WPC9 protein is mainly involved in the energy metabolism pathway of bacteria and may be a potential diagnostic marker for tuberculosis latent infection. -
结核病是由结核分枝杆菌感染所致,有潜伏期及活动期2种疾病状态[1-2], 潜伏性感染患者早期无明显症状[3], 因此早期发现和治疗潜伏性感染患者对控制结核病的传播意义重大。目前,检测结核潜伏性感染的方法仍不完善,结核菌素试验不能明确区分卡介苗接种者、非结核分枝杆菌感染者、结核潜伏性感染和活动性结核病者, γ-干扰素(IFN-γ)释放试验有局限性,亦不能鉴别潜伏性感染及活动性结核病[4]。因此,寻求结核潜伏性感染更为有效的诊断方法至关重要。潜伏性感染及活动性结核病患者中结核分枝杆菌蛋白表达差异,可作为潜伏性感染诊断的新思路。本研究通过同位素标记相对和绝对定量(iTRAQ)技术对结核分枝杆菌的休眠株及标准株进行蛋白质组差异表达筛选,并结合生物信息学技术进行分析,获得参与潜伏性感染菌株中直接与休眠相关的能量代谢通路中的蛋白P9WPC9, 从而为筛选出可用于结核潜伏性感染诊断的潜在标志物提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与试剂
选取结核分枝杆菌标准株H37Rv和由标准株诱导的潜伏性感染菌株模型(休眠株)各三皿,分别编号为sta1、sta2、sta3; dor1、dor2、dor3, 数量为1×107; 其中sta3和dor3因样本蛋白降解,所以未能检测出相关数据。试剂为蛋白酶抑制剂(protease inhibitor, 美国Calbiochem公司)、胰酶(trypsinPromega, 德国Merk公司)、乙腈(acetonitrile、超纯水,德国Fisher Chemical公司)、三氟乙酸(trifluoroacetic acid)、二硫苏糖醇(dithiothreitol)、三乙基碳酸氢铵(TEAB)、尿素、碘代乙酰胺(iodoacetamide)(三氟乙酸、二硫苏糖醇、TEAB、尿素、碘代乙酰胺均购自美国Sigma-Aldrich Sigma公司)。
1.2 实验方法
(1) 菌株造模。①标准菌种培养: 将结核分枝杆菌标准株H37Rv接种于提前配置好的中性罗氏培养基(珠海贝索生物技术有限公司)上,培养3~4周后将菌株转种于含0.2%甘油、10% ADC的7H9液体培养基(BI)上,并置于摇床中震荡培养,温度为37 ℃, 160转/min, 12~15 h待达到对数生长期即可(吸光度值约为0.4)。②休眠菌种模型构建: 取已经达到对数生长期的标准菌株进行研磨,研磨均匀后,按照菌株与培养基1∶ 100进行配液,加入亚甲蓝,终浓度为1.5 μg/mL。将此混合液制成菌悬液,吸取10 mL于15 mL试管中,上层气体与下层液体的体积比为1∶ 2, 封口胶密封后置于37 ℃恒温箱静止培养。培养12~15 d后,溶液中的亚甲蓝完全处于无色状态时,说明菌株已进入完全缺氧休眠状态。
(2) iTRAQ技术。①菌株样本蛋白抽提: 向不同菌株样本中分别加入4倍体积(尿素、1%蛋白酶抑制剂)裂解缓冲液,然后进行超声裂解。将裂解后的混合液至于4 ℃离心机中离心10 min, 转速为12 000 g。去除细胞碎片后,将上清液转移至新的离心管中,利用BCA试剂盒进行蛋白浓度测定。②样品及实验预判。③蛋白质经过还原及巯基封闭后,使用胰蛋白酶进行酶切。④肽段混合物分别使用4种不同的iTRAQ试剂进行标记,使用Strata X C18(Phenomenex)将胰酶酶解后肽段进行盐份祛除,待进行真空干燥及冷冻处理后,按照0.5 M TEAB将所获得的肽段全部进行溶解处理。根据iTRAQ操作说明书步骤,将肽段进行不同同位素的标记,样本分离信息及相关标记名称见表 1。⑤等量混合各种iTRAQ试剂标记的肽段。⑥混合样品的HPLC分级处理: 选取的色谱柱为Agilent 300 Extend C18, 长度250 mm, 内径4.6 mm, 粒径5 μm。在高pH值状态下,对已混合处理好的肽段进行反向高效液相色谱法(HPLC)分级。⑦相关质谱数据分析: 使用EASY-nLC 1200超高效液相系统对处理好的肽段进行分离,所有已处理好的肽段均使用液相色谱流动相A进行溶解,并将其注入NSI离子源中集中进行电离操作,然后进入Q Exactive HF-X质谱进行分析。⑧生物信息学分析: 使用Maxquant (v1.5.2.8)对二级质谱所获得的数据进行检索分析,相关参数设置的数据库为Mycobacterium_tuberculosis_Uniprot (6 529条序列),数据中的假阳性率(FDR)可通过添加反库计算方式进行优化,在数据库中添加常见污染库,以消除样本鉴定结果中污染蛋白的影响, iTRAQ-4plex参数为1%, 蛋白鉴定参数为1%, PSM鉴定的FDR参数为1%, 相关参数设置见表 2。
表 1 样本分离信息及相关标记名称样品编号 质谱同位素标签 dor 1 114 dor 2 115 sta 1 116 sta 2 117 表 2 质谱数据分析相关参数设置酶切方式 漏切位点数 肽段最小长度氨基酸残基/个 肽段最大修饰数 First search一级母离子质量误差容忍度 Main search一级母离子质量误差容忍度 二级碎片离子的质量误差容忍度 Trypsin/P 2 7 2 20 ppm 5 ppm 0.02 Da 2. 结果
2.1 蛋白鉴定
iTRAQ定量质谱分析共得到365 454张二级谱图。蛋白理论数据进行搜库及对比后共得到可利用有效谱图数量为5 624个,利用率为1.5%。通过谱图解析鉴定出518条肽段,其中514条肽段为特异性肽段,共鉴定出238个蛋白,其中187个可定量。
2.2 蛋白差异表达分析
通过iTRAQ质谱定量分析检测出肽段对应在每个样本中的定量值,每个蛋白会对应多个肽段,计算蛋白在每个样本中的定量值时,采用蛋白所对应特异性肽段的定量值中值作为该蛋白的定量值。对于每一次重复实验, 2个不同样本之间蛋白定量比值作为差异表达量(Ratio)。本项目分别进行了2次不同重复实验,可取2次重复Ratio值的平均值作为最终Ratio值。同时,可以取2次不同重复实验的Ratio值变异系数CV值作为最终CV值。当CV值<0.1时,差异表达量变化超过1.2作为显著上调的变化阈值,小于1/1.2作为显著下调的变化阈值。差异表达蛋白统计信息见表 3。
表 3 差异表达蛋白信息样本比对名称及类型 上调占比/% 下调占比/% dor/sta 40.0 24.0 2.3 基因的本体论(GO)分析
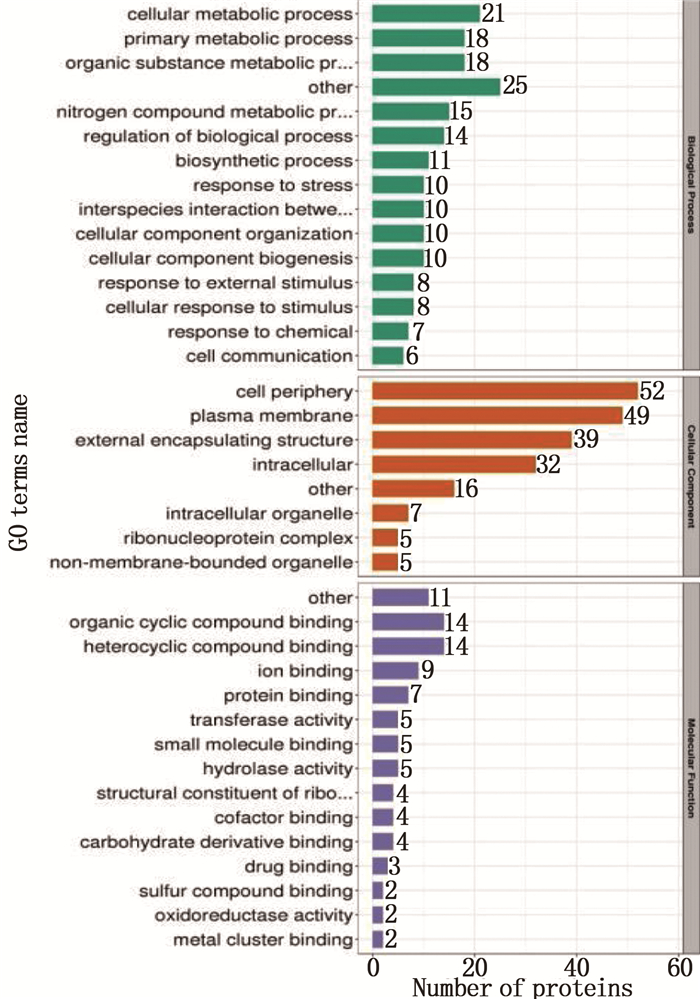
使用GO分析对差异表达的蛋白进行统计分析,通过数据库对比,找出标准株与休眠株中不同差异蛋白在不同信号通路中的功能,根据参与条款能量代谢途径的差异蛋白进行分析。差异表达蛋白在GO二级分类中统计分布见图 1。
2.4 同源蛋白簇分析(COG/KOG)功能分类
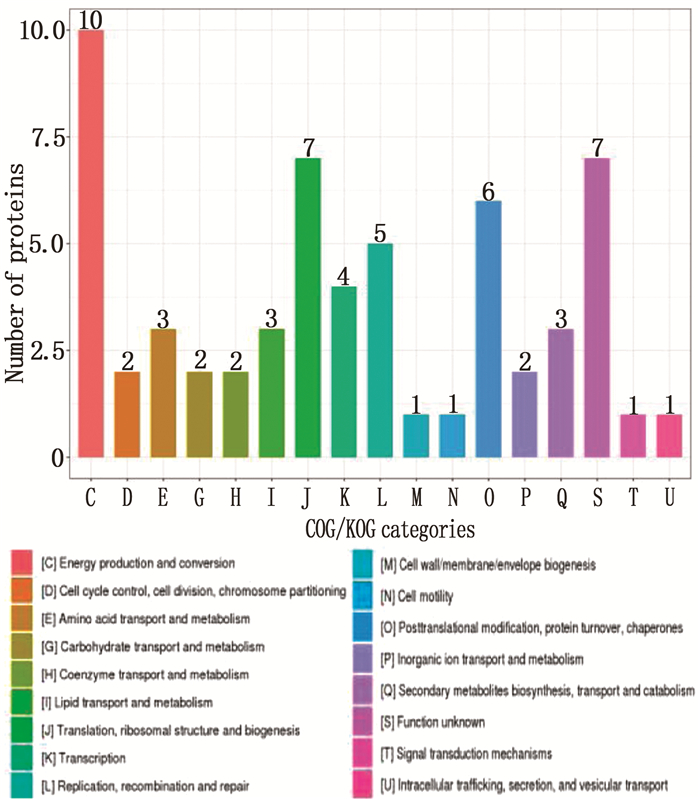
将所获得的质谱数据导入到数据库进行比对分析,通过数据库比对,找出标准株与休眠株中不同差异蛋白在不同信号通路中的功能,将差异蛋白进行COG/KOG功能分类统计(见图 2),发现不同生理状态下的结核杆菌菌株间,差异性表达的蛋白质同样与能量产生和转换、蛋白质翻译等关系。
2.5 差异蛋白互作网络分析
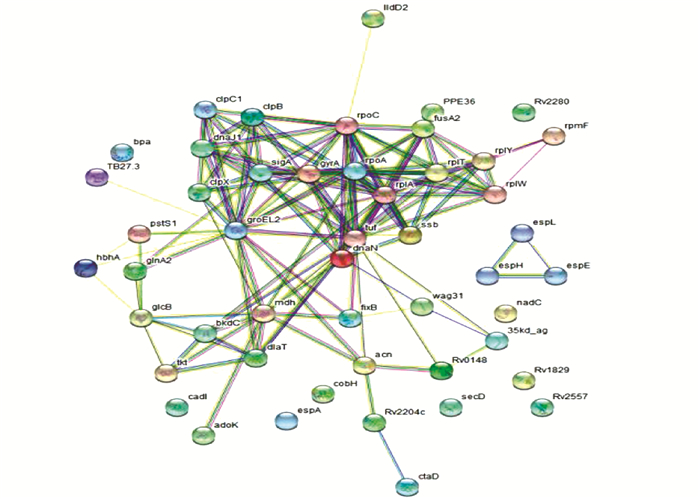
对结核分枝杆菌标准株H37Rv和诱导的潜伏性感染菌株样本中所获得表达差异的蛋白进行统一编码,将数据导入到STRING(v.10.5)蛋白网络互作数据库进行差异蛋白分析,按照参数confidence score>0.7 (high confidence)提取数据,从而分析标准株和潜伏性感染菌株中差异表达蛋白的相互作用网络。差异蛋白互作网络可通过R package“networkD3”工具构建展示,差异表达蛋白使用圆圈表示,图中标记的红颜色表示上调蛋白,蓝颜色表示下调蛋白。圆圈大小表示2种样本中差异表达蛋白及所对应的相互作用蛋白个数(圆圈越大说明与其互作的蛋白越多,圆圈越小说明与其互作的蛋白越少)。图中编号为C的部分为能量代谢相关通路蛋白,可通过差异蛋白的功能富集分析,清晰找出哪些差异蛋白参与了代谢调控潜伏性感染菌株能量代谢相关通路调节,从而进一步确定关键标志物蛋白。取排名前50个且互作关系最紧密的蛋白,最终通过数据库对比分析绘制出差异表达蛋白互作网络图,见图 3。
2.6 具有鉴别诊断价值的蛋白质及互作网络
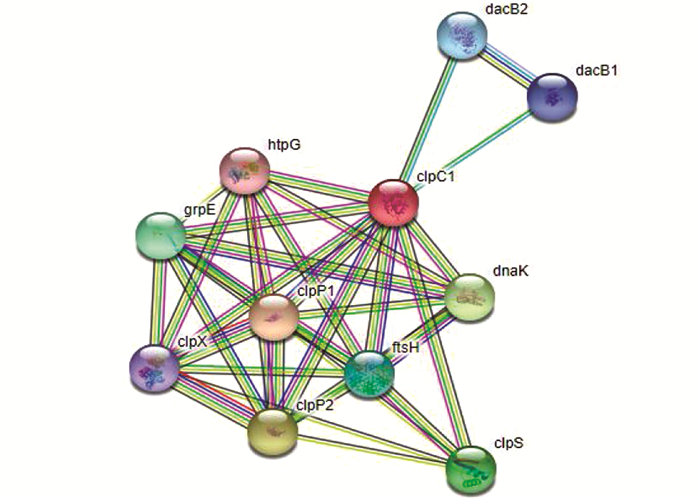
蛋白质组学差异表达结果以及生物信息学分析后得到详细蛋白及相关通路信息,见表 4。筛选出的P9WPC9(基因名称为ClpC1)是潜伏期肺结核具有潜在诊断价值的蛋白质。休眠菌株P9WPC9表达水平是标准结核杆菌菌株的2.2倍,其网络互作情况见图 4。
表 4 蛋白及相关通路信息通路分类 蛋白名称 比例数值 上调及下调 变异系数 基因名称 蛋白长度 [J]Translation,ribosomal structure and biogenesis Q53538 4.752 5 Up 0.001 3677 rpsL 13.849 P9WHC7 2.422 Up 0.090 0083 rplA 24.756 P9WNU1 3.099 5 Up 0.065 0105 dnaN 42.113 P9WGD5 1.334 Up 0.029 2354 ssb 17.353 [T]Signal transduction mechanisms P9WHP5 1.33 Up 0.077 4436 Rv2744c 29.258 [M]Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis P9WJC0 2.211 5 Up 0.000 6783 espK 73.909 [N]Cell motility P9WI01 1.463 Up 0.035 5434 PPE36 27.48 [U]Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport P9WGP1 1.847 5 Up 0.064 682 secD 60.266 [O]Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones P9WPD1 2.346 5 Up 0.033 8802 clpB 92.567 P9WPC9 2.197 5 Up 0.098 066 clpC1 93.551 P9WPB9 4.203 Up 0.021 4133 clpX 46.782 [C]Energy production and conversion P9WPV5 1.258 5 Up 0.058 4029 atpF 18.325 P9WK13 2.877 5 Up 0.050 5647 mdh 34.321 P9WIS7 1.619 Up 0.029 0303 dlaT 57.087 P9WP71 1.609 Up 0.093 8471 ctaD 63.672 O06159 1.212 5 Up 0.080 4124 bkdC 41.061 O53166 1.436 Up 0.091 922 acn 102.45 [G]Carbohydrate transport and metabolism P9WG25 1.349 Up 0.089 6961 tkt 75.588 3. 讨论
近年来,虽然医疗水平已有大幅提高,但结核病的诊断及治疗仍是严重的公共卫生问题[6-7]。耐药菌株的不断出现[8]以及糖尿病、免疫缺陷性疾病等合并结核感染更增加了结核病的防治难度。传统结核菌素试验无法明确区分卡介苗接种者、非结核分枝杆菌感染者、结核潜伏性感染者及结核病患者[9]; IFN-γ释放试验亦无法鉴别结核潜伏性感染及活动性结核病[10], 若患者伴有其他免疫缺陷性疾病[11-12], 则可会出现假阴性结果。因此寻求更加准确、有效的结核潜伏性感染诊断标志物至关重要。
从蛋白质组学分析结果中可知,所测差异蛋白主要与细胞能量代谢相关。进一步将差异蛋白进行COG/KOG功能分类统计,发现不同生理状态下结核杆菌菌株间,休眠株中P9WPC9表达上调2.2倍, P9WPC9为ATP依赖性Clp蛋白酶ATP结合亚基(基因名称为ClpC1), 可以将蛋白酶引导至特定的底物处,亦可在没有ClpP的情况下执行伴侣功能,在ClpP2存在的情况下降解抗σ-E因子RseA,从而调节能量代谢途径,其调控主要与能量产生和转换、蛋白质翻译等相关。
因此, P9WPC9有望成为结核潜伏性感染的潜在诊断性标志物。下一步可应用western-blot对P9WPC9蛋白质水平进行验证,应用实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)等技术观察ClpC1 mRNA水平的改变。研究潜伏性感染及活动性结核病患者P9WPC9表达的改变,从而进一步探讨P9WPC9在结核潜伏性感染诊断中的临床应用价值。
-
表 1 样本分离信息及相关标记名称
样品编号 质谱同位素标签 dor 1 114 dor 2 115 sta 1 116 sta 2 117 表 2 质谱数据分析相关参数设置
酶切方式 漏切位点数 肽段最小长度氨基酸残基/个 肽段最大修饰数 First search一级母离子质量误差容忍度 Main search一级母离子质量误差容忍度 二级碎片离子的质量误差容忍度 Trypsin/P 2 7 2 20 ppm 5 ppm 0.02 Da 表 3 差异表达蛋白信息
样本比对名称及类型 上调占比/% 下调占比/% dor/sta 40.0 24.0 表 4 蛋白及相关通路信息
通路分类 蛋白名称 比例数值 上调及下调 变异系数 基因名称 蛋白长度 [J]Translation,ribosomal structure and biogenesis Q53538 4.752 5 Up 0.001 3677 rpsL 13.849 P9WHC7 2.422 Up 0.090 0083 rplA 24.756 P9WNU1 3.099 5 Up 0.065 0105 dnaN 42.113 P9WGD5 1.334 Up 0.029 2354 ssb 17.353 [T]Signal transduction mechanisms P9WHP5 1.33 Up 0.077 4436 Rv2744c 29.258 [M]Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis P9WJC0 2.211 5 Up 0.000 6783 espK 73.909 [N]Cell motility P9WI01 1.463 Up 0.035 5434 PPE36 27.48 [U]Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport P9WGP1 1.847 5 Up 0.064 682 secD 60.266 [O]Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones P9WPD1 2.346 5 Up 0.033 8802 clpB 92.567 P9WPC9 2.197 5 Up 0.098 066 clpC1 93.551 P9WPB9 4.203 Up 0.021 4133 clpX 46.782 [C]Energy production and conversion P9WPV5 1.258 5 Up 0.058 4029 atpF 18.325 P9WK13 2.877 5 Up 0.050 5647 mdh 34.321 P9WIS7 1.619 Up 0.029 0303 dlaT 57.087 P9WP71 1.609 Up 0.093 8471 ctaD 63.672 O06159 1.212 5 Up 0.080 4124 bkdC 41.061 O53166 1.436 Up 0.091 922 acn 102.45 [G]Carbohydrate transport and metabolism P9WG25 1.349 Up 0.089 6961 tkt 75.588 -
[1] 朱小红, 胡颖君. 肺结核潜伏期和活动期外周血miR-29a和IFN-γ水平变化[J]. 现代诊断与治疗, 2019, 30(2): 302-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZD201902062.htm [2] SANTOS-PEREIRA A, MAGALHES C, PMM ARAUJO, et al. Evolutionary Genetics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and HIV-1: "The Tortoise and the Hare"[J]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9(1): 147. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010147
[3] LÓPEZ-AGUDELO V A, MENDUM T A, LAING E, et al. A systematic evaluation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Genome-Scale Metabolic Networks[J]. PLoS Comput Biol, 2020, 16(6): e1007533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007533
[4] KANG W L, WANG G R, WU M Y, et al. Interferon-gamma release assay is not appropriate for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis in high-burden tuberculosis settings: a retrospective multicenter investigation[J]. Chin Med J: Engl, 2018, 131(3): 268-275. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.223860
[5] 唐洁, 陈策, 查成, 等. 基于结核杆菌耐热抗原小分子多肽刺激人外周血T细胞产生TNF-α和IFN-γ鉴别肺结核和潜伏性结核感染[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(11): 1442-1447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2017.11.03 [6] XUAN W X, LU T T, WANG Z, et al. Diagnostic significance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis T-cell assays for active tuberculosis[J]. Chin Med J: Engl, 2017, 130(7): 811-816. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.202738
[7] BOEHME C C, NABETA P, HENOSTROZA G, et al. Operational feasibility of using loop-mediated isothermal amplification for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in microscopy centers of developing countries[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2007, 45(6): 1936-1940. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02352-06
[8] TORNHEIM J A, INTINI E, GUPTA A, et al. Clinical features associated with linezolid resistance among multidrug resistant tuberculosis patients at a tertiary care hospital in Mumbai, India[J]. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis, 2020, 20: 100175. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2020.100175
[9] 陈晶, 张裕娴, 芮勇宇. γ干扰素释放试验在结核病诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志, 2020, 20(3): 255-258. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KGHL202003004.htm [10] 张会强, 文政芳, 张冬杰, 等. IFN-γ及血清炎症因子水平变化与肺结核发病相关性及作用机制分析[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2019, 29(2): 184-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY201902006.htm [11] 莫胜林, 黄小红, 覃锦玉, 等. 艾滋病合并肺结核与单纯肺结核临床特征及胸部CT差异性研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2021, 19(4): 64-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2021.04.021 [12] 陆恩词, 朱颖蔚. 肺结核合并糖尿病患者T淋巴细胞亚群及红细胞免疫功能的变化及意义[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2017, 37(3): 648-649. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.03.055




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号