Value of serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9, endothelial cell specific molecule 1 and C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in diagnosis and evaluating prognosis of colorectal cancer
-
摘要:目的 分析血清糖类抗原19-9(CA19-9)、内皮细胞特异性分子1(ESM-1)及C反应蛋白与白蛋白比率(CRP/ALB)对结直肠癌的诊断价值及与临床病理特征和生存时间的关系。方法 选取86例结直肠癌患者为结直肠癌组, 50例同期结直肠良性病变患者为良性病变组, 50例体检健康者为对照组。检测3组血清CA19-9、ESM-1及CRP/ALB; 随访结直肠癌术后患者生存情况; 分析CA19-9、ESM-1、CRP/ALB对结直肠癌的诊断效能及与临床病理特征、生存时间的关系; 分析患者预后危险因素。结果 结直肠癌组血清CA19-9、ESM-1水平高于良性病变组、对照组, 差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 结直肠癌组CRP/ALB高于良性病变组,且良性病变组高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。CA19-9、ESM-1及CRP/ALB联合诊断结直肠癌的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.961, 敏感度为94.18%, 特异度为85.75%。CA19-9与淋巴结转移、远处转移相关(P < 0.05); ESM-1与TNM分期、远处转移相关(P < 0.05); CRP/ALB与肿瘤分化程度、TNM分期、淋巴结转移及远处转移相关(P < 0.05)。CA19-9、ESM-1、CRP/ALB高水平患者中位生存时间分别短于CA19-9、ESM-1、CRP/ALB低水平患者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。分化程度、TNM分期、远处转移、CA19-9、ESM-1、CRP/ALB为结直肠癌预后影响因素(P < 0.05)。结论 血清CA19-9、ESM-1及CRP/ALB联合检测对结直肠癌具有较高的诊断效能,且均与结直肠癌的发生发展密切相关,并影响患者预后。
-
关键词:
- 结直肠癌 /
- 糖类抗原19-9 /
- 内皮细胞特异性分子1 /
- C反应蛋白与白蛋白比率
Abstract:Objective To analyze the diagnostic value of serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), endothelial cell specific molecule 1 (ESM-1) and ratio of C-reactive protein (CRP) to albumin (ALB) in colorectal cancer and their relationships with clinicopathological features and survival time.Methods Eighty-six patients with colorectal cancer were selected as colorectal cancer group, 50 patients with concurrent colorectal benign lesions were selected as benign lesion group, and 50 healthy subjects were selected as control group. Serum CA19-9, ESM-1 and CRP/ALB in three groups were detected; postoperative survival of colorectal cancer patients were followed up; diagnostic efficacy of CA19-9, ESM-1, CRP/ALB in colorectal cancer and their relationships with clinicopathological features and survival time were analyzed; prognostic risk factors were analyzed.Results Serum CA19-9 and ESM-1 levels in the colorectal cancer group were significantly higher than those in the benign lesion group and control group (P < 0.05); the CRP/ALB in the colorectal cancer group was significantly higher than that in the benign lesion group, and was significantly higher in the benign lesion group than that in the control group (P < 0.05). The area under curve (AUC) of combined diagnosis of CA19-9, ESM-1 and CRP/ALB for colorectal cancer was 0.961, the sensitivity was 94.18%, and the specificity was 85.75%. CA19-9 was correlated with lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis (P < 0.05); ESM-1 was correlated with TNM stage and distant metastasis (P < 0.05); CRP/ALB was correlated with tumor differentiation, TNM stage, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis (P < 0.05). The median survival time of patients with high levels of CA19-9, ESM-1 and CRP/ALB was significantly shorter than that of patients with low levels (P < 0.05). The degree of differentiation, TNM stage, distant metastasis, CA19-9, ESM-1 and CRP/ALB were prognostic influencing factors for colorectal cancer (P < 0.05).Conclusion The joint detection of serum CA19-9, ESM-1 and CRP/ALB has a high diagnostic efficiency for colorectal cancer. They are all closely related to the occurrence and development of colorectal cancer, and affect the prognosis of patients. -
慢性肾脏病(CKD)在全球的发病率为8%~16%[1], 心血管疾病(CVD)与CKD密切相关,是CKD患者主要死亡原因。左心室肥厚(LVH)是CKD患者常见的心血管并发症[2], 与患者死亡及其他心血管事件的发生密切相关[3-4], 因此需要早期识别并干预。炎症是LVH常见的危险因素[5], 研究[6-8]发现由血常规衍生的新型炎症指标如中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR)、血小板与淋巴细胞比值(PLR)、红细胞分布宽度与心血管事件密切相关,并证实了其在LVH中的意义。
全身免疫炎症指数(SII)是基于中性粒细胞、血小板和淋巴细胞的综合指标,能反映机体内炎症和免疫平衡状态,是一种新型的炎症标志物,对肿瘤、肝硬化有预后预测价值[9-10], 但对LVH的评估价值研究较少。本研究探讨慢性肾脏病(CKD) 非透析患者LVH发生情况及危险因素,分析SII对CKD患者LVH的评估价值。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2019—2020年在苏州大学附属第一医院肾内科住院并根据KDIGO指南诊断为CKD的非透析患者196例(CKD组),其中男117例(CKD男性组),女79例(CKD女性组)。纳入标准: 18~89岁者; 数据完整的CKD患者。排除标准: 已进入透析(包括血液透析和腹膜透析) 者; 合并急性感染性疾病者; 合并肝硬化、急性心力衰竭、恶性肿瘤、血液系统疾病者。随机选取40例同期健康体检者为对照组。
1.2 方法
收集所有入组患者的性别、年龄、体质量指数(BMI)、收缩压(SBP)、舒张压(DBP)、平均动脉压(MBP)、脉压(PP)。采集CKD患者空腹静脉血2 mL送至苏州大学附属第一医院检验科进行检测。
1.3 观察指标
检测血常规、生化全套、超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)等指标,并进行如下计算: NLR=中性粒细胞计数/淋巴细胞计数; PLR=血小板计数/淋巴细胞计数; 淋巴细胞与单核细胞比值(LMR)=淋巴细胞计数/与单核细胞计数; 全身免疫炎症指数(SII)=血小板计数×(中性粒细胞计数/淋巴细胞计数)。
心脏彩色多普勒超声检查由心脏超声专职医生操作。根据美国超声心动图协会推荐的测量方法,取胸骨旁长轴切面,测量左房内径(LAD)、左心室舒张末内径(LVEDD)、左室舒张期后壁厚度(LVPWT)、室间隔厚度(IVST)、相对室壁厚度(RWT)、左室射血分数(EF)等。各参数均测量3个心动周期,取平均值。LVH诊断标准: 参照Devereux公式计算。左心室质量指数(LVMI)(g/m2)=心室质量(LVM)/体表面积。LVM(g)=0.8×1.04×[(LVEDD+IVST+LVPWT)3-(LVEDd)3]+0.6; 体表面积=0.006 1×身高(cm)+0.012 8×体质量(kg)-0.152 9; 诊断标准: 男性LVMI>115 g/m2, 女性LVMI>95 g/m2。估算肾小球滤过率(eGFR): 将血清肌酐(SCr)代入CKD-EPI公式计算得出。
1.4 统计学分析
应用SPSS 23.0软件进行统计分析。连续变量用(x±s)表示,分类变量用[n(%)]表示。正态分布资料组间比较采用t检验,非正态分布资料组间比较采用非参数检验。分类数据组间比较采用卡方检验。LVMI与各指标间的相关性采用Pearson相关分析或Spearsman相关性分析。采用单因素和多因素Logistic回归分析LVH的独立危险因素。定义检验水准为0.05, P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 临床特征
CKD男性组和CKD女性组的中位LVMI分别是104.83、99.72 g/m2。与健康对照组相比, CKD患者无论男女, SBP、PP、NLR、SII、LVM、LVMI均较高,而LMR、Hb、ALB较低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 1、表 2。
表 1 CKD组与对照组临床指标比较(x±s)[M(P25, P75)]指标 CKD男性组(n=117) CKD女性组(n=79) 对照组(n=40) 年龄/岁 57.50(46.00, 66.00) 55.50(43.00, 67.50) 54.00(47.25, 63.00) 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 24.03(22.15, 27.16)# 22.68(20.79, 26.13) 22.98(21.22, 26.37) 收缩压/mmHg 139.50(129.75, 153.00)* 138.00(124.00, 153.50)* 124.50(115.00, 135.00) 舒张压/mmHg 81.93±10.42 78.70±11.67 79.30±12.78 平均动脉压/mmHg 101.72±10.10* 98.23±12.14 95.41±15.12 脉压/mmHg 57.75(47.00, 68.00)* 58.25(46.50, 68.75)* 45.50(40.00, 54.50) 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值 2.83(1.95, 4.23)* 2.95(2.02, 4.56)* 1.71(1.37, 2.04) 淋巴细胞与单核细胞比值 2.87(2.26, 4.00)* 2.95(1.98, 4.27)* 4.77(3.85, 5.74) 血小板与淋巴细胞比值 113.23(89.84, 147.02) 116.35(93.69, 155.52) 111.05(85.49, 136.19) 全身免疫炎症指数/(×1012/L) 472.92(303.26, 663.45)* 430.50(309.39, 577.46)* 310.06(263.65, 404.09) 血红蛋白/(g/L) 121.50(96.00, 138.00)*# 108.00(87.00, 122.00)* 138.50(129.25, 153.25) 红细胞分布宽度/% 12.80(12.10, 13.40) 12.95(12.40, 13.60) 12.50(12.03, 13.20) 血小板/(×1012/L) 195.25±61.87 206.62±70.29 199.56±63.49 碱性磷酸酶/(U/L) 64.70(54.30, 82.30) 59.95(45.75, 85.10) 61.35(50.30, 71.68) 白蛋白/(g/L) 38.45(34.10, 41.70)* 38.45(34.5, 42.00)* 43.75(42.75, 46.48) 尿素氮/(mmol/L) 11.20(7.70, 22.80)* 12.30(5.90, 21.45)* 5.45(4.60, 6.18) 血清肌酐/(μmol/L) 201.00(129.30, 393.30)* 201.05(83.05, 383.00)* 62.00(52.98, 71.40) 尿酸/(μmol/L) 438.90(373.20, 519.50)*# 399.65(326.40, 491.15)* 337.70(275.73, 389.25) 血糖/(mmol/L) 4.88(4.39, 5.39) 4.84(4.41, 5.74) 4.89(4.49, 5.39) 总胆固醇/(mmol/L) 4.42(3.83, 5.15)# 4.94(4.275, 5.85) 4.80(4.29, 5.54) 甘油三酯/(mmol/L) 1.47(1.08, 2.24)* 1.51(1.15, 2.36)* 1.20(0.82, 1.44) 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) 0.97(0.79, 1.14)* 1.22(0.97, 1.45)* 1.26(1.06, 1.56) 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) 2.53(1.79, 3.33) 2.66(2.00, 3.31) 3.01(2.39, 3.38) 钙/(mmol/L) 2.21(2.11, 2.32) 2.21(2.13, 2.33) - 磷/(mmol/L) 1.25(1.06, 1.53) 1.35(1.20, 1.54) - 超敏C反应蛋白/(mg/L) 1.35(0.47, 2.95)* 0.98(0.35, 3.29)* 1.72(1.44, 2.84) eGFR/[mL/(min·1.73 m2)] 29.08(12.60, 52.05)* 23.65(11.14, 72.50)* 105.03(98.91, 118.54) eGFR: 估算肾小球滤过率。与对照组比较, *P<0.05; 与CKD女性组比较, #P<0.05。 表 2 CKD组与对照组心脏超声指标比较[M(P25, P75)][n(%)]指标 CKD男性组(n=117) CKD女性组(n=79) 对照组(n=40) 左房内径/mm 38.00(35.00, 42.00)* 38.00(33.50, 41.50)* 34.00(32.00, 38.00) 室间隔厚度/mm 10.00(9.00, 11.00)*# 9.00(9.00, 10.00)* 9.00(8.00, 9.00) 左心室舒张末内径/mm 51.00(47.00, 54.00)*# 47.50(44.00, 51.00) 46.00(43.25, 49.00) 左室舒张期后壁厚度/mm 10.00(9.00, 10.00)* 9.00(8.50, 10.00)* 9.00(8.00, 9.75) 左心室质量/g 181.98(153.42, 213.18)*# 153.09(127.73, 175.61)* 135.79(109.44, 164.13) 左心室质量指数/(g/m2) 104.90(83.20, 120.84)* 95.87(84.23, 114.70)* 79.61(69.89, 95.13) 相对室壁厚度/mm 0.39(0.36, 0.42) 0.38(0.36, 0.41) 0.37(0.35, 0.40) EF值/% 65.00(61.00, 69.00)* 67.00(63.00, 69.00) 67.00(65.00, 69.00) 左心室肥厚 37(31.62) 40(50.63) - EF: 射血分数。与对照组比较, *P<0.05; 与CKD女性组比较, #P<0.05。 2.2 CKD患者LVH发生情况
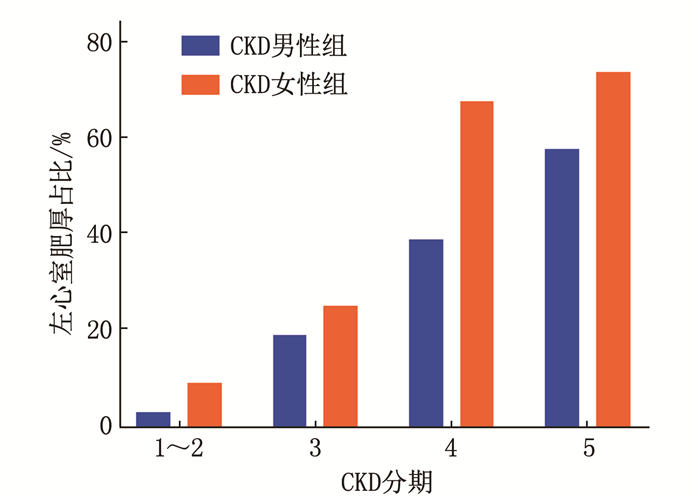
196例患者中有77例诊断为LVH, LVH发生率为39.29%。CKD男性组和CKD女性组中LVH的占比分别为31.62%(37/117)、50.63%(40/79), 2组差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。随着eGFR的降低,无论是男性还是女性, LVH的占比逐渐升高,见图 1。
2.3 LVMI与临床指标的相关性分析
CKD男性组患者LVMI与SBP、PP、PLR、SII、RDW、尿素氮(UN)、SCr、磷(P)呈正相关(P<0.05), 与Hb、ALB、TC、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、钙(Ca)、eGFR呈负相关(P<0.05)。CKD女性组患者LVMI与年龄、SBP、PP、红细胞分布宽度(RDW)、UN、SCr、UA呈正相关(P<0.05), 与Hb、PLT、TC、HDL-C、LDL-C、Ca、eGFR呈负相关(P<0.05)。见表 3。
表 3 LVMI与临床指标的相关性分析自变量 CKD男性组(n=117) CKD女性组(n=79) r P r P 年龄/岁 0.109 0.242 0.482 < 0.001 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 0.053 0.570 -0.074 0.516 收缩压/mmHg 0.411 < 0.001 0.366 0.001 舒张压/mmHg -0.130 0.163 -0.139 0.221 平均动脉压/mmHg 0.131 0.158 0.101 0.377 脉压/mmHg 0.477 < 0.001 0.509 < 0.001 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值 -0.003 0.978 -0.093 0.415 淋巴细胞与单核细胞比值 0.086 0.357 0.129 0.258 血小板与淋巴细胞比值 0.277 0.002 0.024 0.834 全身免疫炎症指数/(×1012/L) 0.284 0.002 -0.050 0.659 血红蛋白/(g/L) -0.635 < 0.001 -0.625 < 0.001 红细胞分布宽度/% 0.373 < 0.001 0.318 0.004 血小板/(×1012/L) -0.106 0.255 -0.394 < 0.001 碱性磷酸酶/(U/L) 0.046 0.619 0.177 0.119 白蛋白/(g/L) -0.204 0.027 -0.083 0.469 尿素氮/(mmol/L) 0.537 < 0.001 0.576 < 0.001 血清肌酐/(μmol/L) 0.615 < 0.001 0.585 < 0.001 尿酸/(μmol/L) 0.007 0.944 0.413 < 0.001 血糖/(mmol/L) 0.030 0.748 -0.085 0.457 总胆固醇/(mmol/L) -0.264 0.004 -0.246 0.029 甘油三酯/(mmol/L) -0.097 0.299 0.108 0.342 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) -0.260 0.005 -0.336 0.002 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) -0.226 0.014 -0.330 0.003 钙/(mmol/L) -0.377 < 0.001 -0.257 0.022 磷/(mmol/L) 0.415 < 0.001 0.213 0.059 超敏C反应蛋白/(mg/L) -0.064 0.496 0.021 0.853 eGFR/[mL/(min·1.73 m2)] -0.398 < 0.001 -0.487 < 0.001 eGFR: 估算肾小球滤过率。 2.4 LVH影响因素分析
在CKD男性组患者中, SBP、PP、PLR、SII、RDW、UN、SCr、P是其发生LVH的危险因素,而Hb、TC、HDL-C、Ca、eGFR是其保护因素。将单因素分析有意义的变量纳入多因素回归分析,结果显示SBP及SII值越高, Hb越低,患者发生LVH的风险越高。在CKD女性组患者中,年龄、SBP、PP、RDW、UN、SCr、UA是患者发生LVH的危险因素,而Hb、PLT、TC、HDL-C、LDL-C、eGFR则是其保护因素。将单因素分析有意义的变量纳入多因素回归分析,结果显示年龄及UA值越高, Hb越低,患者发生LVH的风险越高。见表 4、表 5。
表 4 影响CKD男性组患者LVH的Logistic回归分析自变量 单因素Logistic回归分析 多因素Logistic回归分析 OR(95%CI) P OR(95%CI) P 年龄/岁 1.010(0.984~1.036) 0.461 - - 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 1.063(0.946~1.194) 0.306 - - 收缩压/mmHg 1.056(1.025~1.087) < 0.001 1.033(1.001~1.066) 0.043 舒张压/mmHg 0.992(0.955~1.030) 0.662 - - 平均动脉压/mmHg 1.037(0.996~1.080) 0.079 - - 脉压/mmHg 1.057(1.028~1.087) < 0.001 - - 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值 1.142(0.888~1.467) 0.300 - - 淋巴细胞与单核细胞比值 1.169(0.867~1.574) 0.305 - - 血小板与淋巴细胞比值 1.013(1.005~1.022) 0.003 - - 全身免疫炎症指数/(×1012/L) 1.002(1.001~1.004) 0.001 1.002(1.001~1.004) 0.009 血红蛋白/(g/L) 0.959(0.942~0.976) < 0.001 0.962(0.943~0.981) < 0.001 红细胞分布宽度/% 1.822(1.235~2.687) 0.003 - - 血小板/(×1012/L) 0.999(0.993~1.005) 0.744 - - 碱性磷酸酶/(U/L) 1.017(0.999~1.034) 0.066 - - 白蛋白/(g/L) 0.955(0.897~1.017) 0.151 - - 尿素氮/(mmol/L) 1.073(1.032~1.115) < 0.001 - - 血清肌酐/(μmol/L) 1.004(1.002~1.006) < 0.001 - - 尿酸/(μmol/L) 1.002(0.999~1.006) 0.223 - - 血糖/(mmol/L) 1.141(0.879~1.481) 0.320 - - 总胆固醇/(mmol/L) 0.669(0.461~0.970) 0.034 - - 甘油三酯/(mmol/L) 0.746(0.500~1.114) 0.152 - - 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) 0.179(0.039~0.821) 0.027 - - 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) 0.724(0.491~1.067) 0.103 - - 钙/(mmol/L) 0.005(0~0.100) 0.001 - - 磷/(mmol/L) 4.238(1.609~11.166) 0.003 - - 超敏C反应蛋白/(mg/L) 1.019(0.898~1.157) 0.769 - - eGFR/[mL/(min·1.73 m2)] 0.973(0.956~0.990) 0.002 - - eGFR: 估算肾小球滤过率。 表 5 影响CKD女性组患者LVH的Logistic回归分析自变量 单因素Logistic回归分析 多因素Logistic回归分析 OR(95%CI) P OR(95%CI) P 年龄/岁 1.068(1.031~1.107) < 0.001 1.064(1.019~1.111) 0.005 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 1.005(0.909~1.111) 0.919 - - 收缩压/mmHg 1.032(1.006~1.059) 0.017 - - 舒张压/mmHg 0.970(0.932~1.009) 0.133 - - 平均动脉压/mmHg 1.006(0.970~1.043) 0.761 - - 脉压/mmHg 1.068(1.029~1.108) 0.001 - - 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值 0.929(0.731~1.181) 0.548 - - 淋巴细胞与单核细胞比值 1.044(0.795~1.371) 0.756 - - 血小板与淋巴细胞比值 0.998(0.990~1.005) 0.543 - - 全身免疫炎症指数/(×1012/L) 1.000(0.999~1.001) 0.923 - - 血红蛋白/(g/L) 0.942(0.916~0.969) < 0.001 0.953(0.926~0.982) 0.002 红细胞分布宽度/% 1.593(1.041~2.439) 0.032 - - 血小板/(×1012/L) 0.986(0.977~0.994) 0.001 - - 碱性磷酸酶/(U/L) 1.013(0.995~1.032) 0.150 - - 白蛋白/(g/L) 0.999(0.938~1.064) 0.974 - - 尿素氮/(mmol/L) 1.095(1.036~1.157) 0.001 - - 血清肌酐/(μmol/L) 1.004(1.002~1.007) 0.001 - - 尿酸/(μmol/L) 1.006(1.002~1.011) 0.004 1.006(1.001~1.012) 0.031 血糖/(mmol/L) 0.735(0.507~1.064) 0.102 - - 总胆固醇/(mmol/L) 0.578(0.372~0.898) 0.015 - - 甘油三酯/(mmol/L) 0.957(0.664~1.380) 0.814 - - 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) 0.148(0.035~0.618) 0.009 - - 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇/(mmol/L) 0.457(0.262~0.795) 0.006 - - 钙/(mmol/L) 0.056(0.002~1.288) 0.072 - - 磷/(mmol/L) 4.108(0.965~7.482) 0.056 - - 超敏C反应蛋白/(mg/L) 1.027(0.916~1.152) 0.650 - - eGFR/(mL/min/1.73 m2) 0.970(0.954~0.986) < 0.001 - - eGFR: 估算肾小球滤过率。 3. 讨论
心血管事件的发生随着肾功能减退逐渐增加[11], 合并CVD的CKD患者病死率远高于普通CKD患者。心血管事件包括冠心病、心力衰竭、心室肥厚等。LVH作为CKD患者心脏病变的重要特征,在CKD患者中普遍存在[12], 且与上述心血管事件及全因死亡密切相关[3-4]。CKD患者较高LVH患病率的原因除了高血压、糖尿病等因素外,炎症可能在LVH的发展过程中具有重要作用。研究[6-8]发现NLR、PLR、RDW等新型炎症指标与LVH密切相关,但是反映机体炎症和免疫平衡状态的指标SII是否与LVH有更密切关联的研究较少。
本研究中, CKD患者LVH患病率为39.29%, 与男性相比,女性患病率更高,与侯凡凡等[13]调查结果一致。造成这种现象的原因可能为绝经后女性体内激素水平变化相关。既往研究[14-15]表明,雌激素可通过改善脂质代谢、抗氧化等多种途径对心血管发生具有保护作用。本研究中,女性中位年龄为55.50岁,考虑其高LVH患病率可能与该类女性雌激素水平较低有关。此外,本研究发现,随着eGFR的降低,无论男性还是女性, LVH的患病率逐渐升高,与既往研究[2]结果相符。高血压患者同时存在压力、容量负荷, 2种负荷均可增加心肌细胞容积、改变胶原蛋白基质的成分,最终引起肥厚[16-17]。CKD患者由于肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统(RAAS)及交感神经系统激活等因素,往往合并有难以控制的高血压。本研究发现, SBP是男性CKD患者的危险因素,但未观察到血压独立于其他因素与女性患者LVH之间的关系,可能与本研究中女性患者样本量相对较少、血压控制程度相对较好有关。
炎症因子不仅可影响血管内皮功能,诱导趋化因子表达,引起炎性细胞的聚集和浸润,导致炎性损伤; 还可直接导致细胞增殖、凋亡,调节细胞外间质的合成和降解,从而参与心脏重构[5]。此外,氧化应激也是参与LVH发生发展的重要原因之一[18], 炎症与氧化应激过程相互影响,共同促进LVH的发生。CKD患者体内处于微炎症状态,本研究中,与对照组相比, CKD组患者NLR、SII等反映炎症状态的指标水平较高。行LVH危险因素分析提示, SII是男性患者LVH的独立危险因素。众多炎症指标中,仅SII与LVH发生独立相关,而与由血常规检测获得的其他炎症指标,如NLR、LMR、PLR、RDW则未发现与LVH发生的独立相关性,显示SII更能够全面地反映机体内炎症和免疫平衡状态,对LVH的发生影响更大。女性CKD患者多因素分析未发现炎症指标与LVH的关系密切,可能与女性患者样本较少有关; 此外,有研究[19]显示,血管紧张素受体阻滞剂(ARB)类药物可减少炎症因子产生,本研究中因未记录患者用药种类,也有可能影响研究结果。
Hb降低是LVMI增加主要的危险因素[20]。贫血不仅会加重心肌缺血,还会降低血液的粘滞度,导致静脉回心血量增多,使机体处于慢性容量超载的状态,而心脏容量负荷增加也是导致心室肥厚的重要因素之一。此外,低Hb浓度可能导致内皮来源的舒张因子(一氧化氮)的可用性提高,从而导致血管扩张和心输出量增加[21]。本研究中,无论女性还是男性, Hb降低均是CKD患者LVH发生的危险因素。机体处于炎症状态时,肝脏合成铁调素增加,影响机体铁释放,从而加重了患者贫血的程度,因此炎症在贫血对LVH的影响上也具有重要的作用。研究[22]显示,在使用促红细胞生成素纠正贫血后,患者LVH有所逆转,且心功能也得到改善,因而纠正CKD患者的贫血对防治LVH有重要意义。
综上所述, LVH在CKD患者中普遍存在,且女性患者较高。贫血是所有CKD患者LVH的危险因素。新型炎症指标SII是男性患者LVH的危险因素,而在女性患者中未发现SII与LVH具有相关性。由血常规衍生出的SII,在临床中获取简单,经济适用,有望成为早期干预并延缓LVH发生的指标。本研究为单中心横断面研究,样本量相对较少、未记录患者用药情况,因此SII对于LVH的评估价值还需进一步验证。此外, SII对于CKD患者远期预后也有待进一步研究。
-
表 1 3组基线资料比较(x±s)
组别 性别 年龄/岁 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 男 女 结直肠癌组(n=86) 48 38 61.14±7.32 23.55±2.44 良性病变组(n=50) 27 23 59.30±8.26 24.22±2.30 对照组(n=50) 26 24 59.40±7.71 23.89±2.40 表 2 3组CA19-9、ESM-1、CRP/ALB比较(x±s)
组别 n CA19-9/(U/mL) ESM-1/(pg/mL) CRP/ALB 结直肠癌组 86 26.53±4.12*# 30.27±4.30*# 0.11±0.02*# 良性病变组 50 21.94±4.18 25.21±3.51 0.08±0.01* 对照组 50 21.93±3.73 22.95±4.24 0.06±0.01 CA19-9: 糖类抗原19-9; ESM-1: 内皮细胞特异性分子1;
CRP/ALB: C反应蛋白与白蛋白比率。与对照组比较, *P < 0.05;
与良性病变组比较, #P < 0.05。表 3 CA19-9、ESM-1和CRP/ALB对结直肠癌的诊断价值
变量 AUC 标准误 P 渐进95%CI 截断值 上限 下限 CA19-9 0.784 0.041 < 0.001 0.703 0.865 24.03 ESM-1 0.826 0.035 < 0.001 0.758 0.894 28.49 CRP/ALB 0.923 0.022 < 0.001 0.879 0.966 0.10 三者联合 0.961 0.015 < 0.001 0.932 0.990 - CA19-9: 糖类抗原19-9; ESM-1: 内皮细胞特异性分子1; CRP/ALB: C反应蛋白与白蛋白比率。 表 4 不同临床病理特征患者CA19-9、ESM-1、CRP/ALB比较[n(%)]
项目 n CA19-9 χ2 P ESM-1 χ2 P CRP/ALB χ2 P 高水平(n=41) 低水平(n=45) 高水平(n=41) 低水平(n=45) 高水平(n=36) 低水平(n=50) 肿瘤原发部位 0.896 0.344 0.259 0.611 0.170 0.680 结肠 36 15(36.59) 21(46.67) 16(39.02) 20(44.44) 16(44.44) 20(40.00) 直肠 50 26(63.41) 24(53.33) 25(60.98) 25(55.56) 20(55.56) 30(60.00) 肿瘤直径cm 1.766 0.184 3.103 0.078 2.692 0.101 < 5 cm 46 25(60.98) 21(46.67) 26(63.41) 20(44.44) 23(63.89) 23(46.00) ≥5 cm 40 16(39.02) 24(53.33) 15(36.59) 25(55.56) 13(36.11) 27(54.00) 肿瘤分化程度 0.032 0.857 0.032 0.857 8.653 0.003 高/中分化 76 36(87.80) 40(88.89) 37(90.24) 39(86.67) 27(75.00) 49(98.00)* 低/未分化 10 5(12.20) 5(11.11) 4(9.76) 6(13.33) 9(25.00) 1(2.00)* TNM分期 1.013 0.314 7.743 0.005 10.433 0.001 Ⅰ~Ⅱ 53 23(56.10) 30(66.67) 19(46.34) 34(75.56)* 15(41.67) 38(76.00)* Ⅲ~Ⅳ 33 18(43.90) 15(33.33) 22(53.66) 11(24.44)* 21(58.33) 12(24.00)* 淋巴结转移 10.995 0.001 3.688 0.055 20.861 0.010 有 27 20(48.78) 7(15.56)* 17(41.46) 10(22.22) 21(58.33) 6(12.00)* 无 59 21(51.22) 38(84.44)* 24(58.54) 35(77.78) 15(41.67) 44(88.00)* 远处转移 9.700 0.002 6.399 0.011 9.260 0.002 有 14 12(29.27) 2(4.44)* 11(26.83) 3(6.67)* 11(30.56) 3(6.00)* 无 72 29(70.73) 43(95.56)* 30(73.17) 42(93.33)* 25(69.44) 47(94.00)* 病理类型 0.529 0.971 2.132 0.344 5.101 0.078 腺癌 73 36(87.80) 37(82.22) 37(90.24) 36(80.00) 27(75.00) 46(92.00) 神经内分泌肿瘤 8 3(7.32) 5(11.11) 3(7.32) 5(11.11) 5(13.89) 3(6.00) 黏膜内癌 5 2(4.88) 3(6.67) 1(2.44) 4(8.89) 4(11.11) 1(2.00) CA19-9: 糖类抗原19-9; ESM-1: 内皮细胞特异性分子1; CRP/ALB: C反应蛋白与白蛋白比率。与高水平比较, *P < 0.05。 表 5 CA19-9、ESM-1、CRP/ALB与病理特征的关系
病理特征 CA19-9 ESM-1 CRP/ALB 95%CI P 95%CI P 95%CI P 分化程度 0.658~1.237 0.613 0.705~1.328 0.547 1.409~3.391 0.001 TNM分期 0.798~1.365 0.536 1.780~3.704 < 0.001 1.613~2.612 < 0.001 淋巴结转移 1.529~2.419 < 0.001 0.605~1.178 0.492 1.869~2.820 < 0.001 远处转移 2.272~3.538 < 0.001 2.210~3.245 < 0.001 3.306~5.791 < 0.001 CA19-9: 糖类抗原19-9; ESM-1: 内皮细胞特异性分子1; CRP/ALB: C反应蛋白与白蛋白比率。 表 6 患者预后COX回归分析
变量 β SE Wald OR 95%CI P 肿瘤直径 0.062 0.128 0.235 1.064 0.828~1.367 0.628 分化程度 1.087 0.106 105.159 2.965 2.409~3.650 < 0.001 TNM分期 1.248 0.123 102.948 3.483 2.737~4.433 < 0.001 淋巴结转移 0.047 0.119 0.156 1.048 0.830~1.323 0.693 远处转移 0.928 0.136 46.561 2.529 1.938~3.302 < 0.001 CA19-9 0.875 0.114 58.912 2.399 1.919~2.999 < 0.001 ESM-1 1.356 0.248 29.896 3.881 2.387~6.310 < 0.001 CRP/ALB 1.132 0.196 33.357 3.102 2.112~4.555 < 0.001 CA19-9: 糖类抗原19-9; ESM-1: 内皮细胞特异性分子1; CRP/ALB: C反应蛋白与白蛋白比率。 -
[1] WONG S H, YU J. Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer: mechanisms of action and clinical applications[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16(11): 690-704. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0209-8
[2] WANG G, FU S, LI D C, et al. Expression and clinical significance of serum NT5E protein in patients with colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2019, 24(4): 461-468. doi: 10.3233/CBM-182207
[3] FAHRMANN J F, SCHMIDT C M, MAO X Y, et al. Lead-time trajectory of CA19-9 as an anchor marker for pancreatic cancer early detection[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(4): 1373-1383, e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.11.052
[4] 李世龙, 张宝, 宋扬, 等. 血清ESM-1和CEA及CA199检测对结直肠癌诊断价值探讨[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2019, 26(15): 1119-1123. [5] 余中林, 周业江. 基于CRP的炎症指标与进展期胃癌预后的相关性分析[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2020, 36(5): 618-624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.05.019 [6] 田山, 曹英豪, 廖斐, 等. 术前C反应蛋白与前白蛋白比值预测结直肠癌患者术后预后的价值[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2021, 41(3): 195-199. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311367-20200811-00481 [7] 乔乐乐, 王公平, 周博, 等. 胃癌患者术前CRP/Alb比与淋巴结转移相关性的研究[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2017, 14(5): 210-213. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2017.05.246 [8] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会《中国结直肠癌诊疗规范(年版)》专家组. 中国结直肠癌诊疗规范(2017年版)[J]. 中华临床医师杂志: 电子版, 2018, 12(1): 3-23. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2018.01.003 [9] YAMASHITA S, PASSOT G, ALOIA T A, et al. Prognostic value of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in patients undergoing resection of biliary tract cancer[J]. Br J Surg, 2017, 104(3): 267-277. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10415
[10] 张辉, 姚士伟, 崔培林, 等. 66例血清CA19-9异常高值患者的病因分析[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58(35): 78-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2018.35.021 [11] LI C, GENG H, JI L H, et al. ESM-1: a novel tumor biomaker and its research advances[J]. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem, 2019, 19(14): 1687-1694. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666190705151542
[12] SHEN Y J, WANG H G, LI W D, et al. Prognostic significance of the CRP/Alb and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratios in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing TACE and RFA[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2019, 33(9): e22999.
[13] WU T T, MO Y L, WU C T. Prognostic values of CEA, CA19-9, and CA72-4 in patients with stages Ⅰ-Ⅲ colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2020, 13(7): 1608-1614.
[14] HIDAKA E, MAEDA C, NAKAHARA K, et al. High serum CA19-9 concentration predicts poor prognosis in elderly patients with stage Ⅳ colorectal cancer[J]. Gastrointest Tumors, 2018, 5(3/4): 117-124.
[15] LU G J, SHAO C J, ZHANG Y, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic values of endothelial-cell-specific molecule-1 with malignant pleural effusions in patients with non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(30): 49217-49223. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17455
[16] 李伟娟. 血清P53、ESM-1水平与胃癌晚期化疗患者预后的相关性[J]. 临床医学, 2021, 41(5): 38-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBED202105015.htm [17] YANG W E, HSIEH M J, LIN C W, et al. Plasma levels of endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 as a potential biomarker of oral cancer progression[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2017, 14(11): 1094-1100. doi: 10.7150/ijms.20414
[18] 裴家强, 游波, 游凯, 等. PET/CT联合血清HE4、ESM-1在肺癌诊断中的应用价值[J]. 河北医药, 2020, 42(14): 2125-2128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBYZ202014010.htm [19] 李锐, 李晓丽. 甲状腺癌患者癌组织中CD34、增殖细胞核抗原和内皮细胞特异分子-1的表达及意义[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2018, 38(16): 3881-3883. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.16.017 [20] 罗宝洋, 杨勇, 段云飞, 等. 术前C反应蛋白和清蛋白比值对可切除胰腺癌患者预后的影响[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2018, 5(9): 712-717. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?dbid=WF_QK&id=PeriodicalPaper_zhwk201809014 [21] 张璐, 张莉, 李昌平. CD64指数和可溶性髓系细胞触发受体1对结肠癌术后感染的诊断价值[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2019, 29(14): 2162-2166. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZHYY201914021.htm [22] LIU Z Q, JIN K Z, GUO M, et al. Prognostic value of the CRP/alb ratio, a novel inflammation-based score in pancreatic cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017, 24(2): 561-568. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5579-3
[23] 张大为, 张桂铭, 刘勇. 局部进展期肾癌术前CRP/Alb比值对预后的价值[J]. 青岛大学学报: 医学版, 2020, 56(4): 413-416. [24] 郭信伟, 冀胜军, 周绍兵, 等. 治疗前血液炎性标志物对食管鳞癌患者放化疗疗效及预后的影响[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2019(3): 202-207. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?dbid=WF_QK&id=PeriodicalPaper_zhfsyxyfhzz98201903009 [25] 赵晓慧, 李爽. SEPT9基因甲基化、生长分化因子15、糖类抗原199与结直肠癌患者临床病理特征和预后的关系[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(24): 52-56. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20213287 [26] 魏智民, 孙玉发, 李刚, 等. 癌症相关性炎症与肿瘤微环境相关研究进展[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2018, 45(21): 1117-1121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2018.21.767 -
期刊类型引用(23)
1. 邓玉珍. 健身气功八段锦锻炼结合睡眠干预对改善冠心病行冠状动脉介入术患者生活质量的效果观察. 心血管病防治知识. 2024(03): 68-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王妍蝶,时贤君,秦庆祝. 认知行为干预结合健康教育对提高冠心病行经皮冠状动脉介入术后患者自我管理能力的效果. 慢性病学杂志. 2024(07): 1017-1020 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘翠琴,郭小燕. 基于运动疗法的康复护理对风湿性心脏病瓣膜置换患者术后的影响. 心血管病防治知识. 2024(10): 135-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 余媛媛,贺泽霞,张永佳,兰富霞,徐英. 4C干预模式对老年经皮冠状动脉介入术后患者的影响. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(16): 68-71 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 梁夷凤. 冠心病患者PCI术后应用基于5E理念的综合康复护理的效果分析. 中外医疗. 2023(23): 155-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 吴伟,高鹃. 双心护理模式对冠心病经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者心理健康状况和护理满意度的影响观察. 基层医学论坛. 2022(03): 87-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 吴张平. 早期心脏康复训练对PCI术后患者的影响. 继续医学教育. 2022(05): 125-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 牛杜娟,尚雯,张红. 以FTS理论为指导的系统化护理模式对PCI术后患者心功能的影响. 保健医学研究与实践. 2022(07): 82-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王琳,张亚铮,袁媛. 基于CSMS量表和CQQC的5E康复护理在冠心病PCI术后患者康复中的应用效果. 河北医药. 2022(14): 2228-2231 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘娟,刘芳,张静. 临床护理路径在冠状动脉搭桥术患者术后康复中的应用效果研究. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志. 2022(11): 4-6+13 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 贾艳静,王新宙. 优质护理应用于老年冠心病患者护理中对患者生活质量和疗效的影响. 中国药物与临床. 2021(08): 1409-1411 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 邹蓉蓉,李天兰,吴莉玫,尹艳华. 优化康复护理流程对PCl术后患者心肺功能以及预后的影响分析. 心血管病防治知识. 2021(04): 59-61+64 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 宋敏. 整体化康复护理措施在冠心病患者中的应用. 黑龙江中医药. 2021(01): 294-295 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 张善婷,冯俊,刘洋. 冠心病患者PCI介入治疗中的护患沟通对治疗依从性的影响. 河北医药. 2021(11): 1743-1746 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 胥加艳,郭晓鑫. 5E护理在冠心病病人PCI术后康复中的应用研究. 循证护理. 2021(08): 1108-1111 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 郭秀蝶,郑雅娟,林晨芳,吴群,张亚真. 评判性思维护理对缺铁性贫血伴缺血性心脏病患者贫血及心功能的影响. 心血管病防治知识. 2021(32): 26-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 柯晓玲,吴娟娟. 早期康复护理对老年心血管病患者的效果观察. 心血管病防治知识(学术版). 2020(14): 68-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 孙婧,李萍. 冠心病患者的系统性心肺康复护理. 实用临床医药杂志. 2020(14): 122-125 .  本站查看
本站查看
19. 陈燕华,张苗. 慢性肾脏病合并冠心病患者冠状动脉介入术后行血液透析护理研究. 山西医药杂志. 2020(18): 2548-2549 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 刘姝娉. 过渡期康复护理措施对老年心血管疾病患者功能恢复及预后的影响. 心血管病防治知识. 2020(24): 70-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 郑燕,常莉,刘桂玲,刘晚霞. 常规护理联合心脏康复护理对冠心病介入治疗后心功能的改善作用. 贵州医药. 2020(10): 1662-1663 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 张书明. 探讨冠心病冠状动脉介入术患者心脏康复护理模式的建立对促进患者术后恢复的意义. 心血管病防治知识. 2020(31): 58-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 聂志鑫. 时机理论下的家庭护理对经皮冠状动脉性心脏病介入治疗后患者预后和生活质量的影响. 中西医结合护理(中英文). 2020(11): 59-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
