Relationships of serum endothelin 1, nitric oxide and C-reactive protein levels with restenosis in patients with lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans after stent implantation
-
摘要:目的
探讨血清内皮素-1(ET-1)、一氧化氮(NO)及C反应蛋白(CRP)水平与下肢动脉硬化闭塞症(ASO)患者支架植入术后再狭窄的关系。
方法回顾性分析行支架植入术治疗的173例ASO患者的临床资料,根据术后1个月是否出现再狭窄将其分为再狭窄组22例和未狭窄组151例。比较2组患者的临床资料,分析再狭窄的危险因素,并采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析血清ET-1、NO、CRP水平对ASO患者支架植入术后再狭窄的诊断价值。
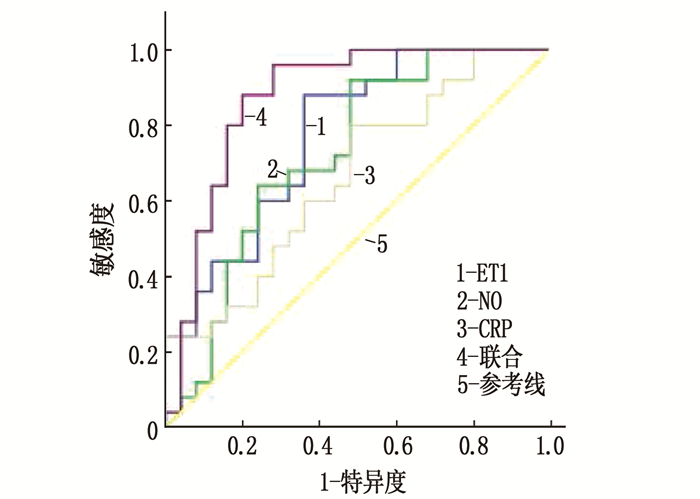
结果再狭窄组吸烟、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、ET-1、NO、CRP水平高于未狭窄组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 多因素Logistic回归分析显示,吸烟、HbA1c≥6%、ET-1≥60 g/L、NO≥32 μmol/L、CRP≥20 mg/L为ASO患者支架植入术后再狭窄的独立危险因素(P < 0.05); ROC曲线显示,血清ET-1、NO、CRP联合诊断ASO患者支架植入术后再狭窄的曲线下面积大于单独检测,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论ASO支架植入术后再狭窄患者血清ET-1、NO、CRP水平高表达,可能参与术后再狭窄的发生发展。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo study the relationships of serum endothelin 1 (ET-1), nitric oxide (NO) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels with restenosis in patients with lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans (ASO) after stent implantation.
MethodsA retrospective analysis was performed on the clinical data of 173 patients with ASO treated with stent implantation. The patients were divided into restenosis group (n=22) and non-stenosis group (n=151) according to the presence or absence of restenosis at one month after operation. The clinical data of the two groups were compared, and the risk factors were analyzed. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyze the value of serum ET-1, NO and CRP levels in the diagnosis of restenosis in patients with ASO after stent implantation.
ResultsThe proportion of patients with smoking history, levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), ET-1, NO and CRP in the restenosis group were higher than those in the non-stenosis group (P < 0.05). Logistic multivariate regression analysis showed that smoking and HbA1c≥6%, ET-1≥60 g/L, NO≥32 μmol/L and CRP≥20 mg/L were independent risk factors for restenosis after STENT implantation in ASO patients (P < 0.05). ROC curve showed that the area under the curve of combined diagnosis of serum ET-1, NO and CRP levels for restenosis in patients with ASO after stent implantation was higher than that of single detection (P < 0.05).
ConclusionSerum ET-1, NO and CRP levels are higher in ASO patients with restenosis after stent implantation, which indicates that these indicators may be involved in the occurrence and development of restenosis.
-
在人口老龄化和代谢危险因素的双重压力下,中国居民的心血管疾病风险持续增加,心肌梗死患者的病死率亦逐渐上升[1]。心肌梗死是指心肌缺血性坏死,通常是在冠状动脉病变的基础上发生冠状动脉血供减少或中断,心肌细胞因严重且持续的缺血缺氧而发生坏死[2]。心肌细胞的死亡会引发一系列免疫炎症反应,这些免疫炎症反应介导的受损心肌修复在梗死后心室重构、心功能和患者结局等方面起着关键作用[3]。急性心肌梗死的诊断主要依据临床表现、血清生物学标志物和心电图,其中临床常用的生物学标志物包括肌红蛋白、肌酸激酶-MB、心肌肌钙蛋白I和心肌肌钙蛋白T[4-5]。然而,这些标志物水平在心力衰竭、肾衰竭和甲状腺疾病患者中也同样升高,故结合多组学平台探寻更多特异性的生物学标志物非常必要[6-7]。外周血单个核细胞(PBMCs)包括T细胞、B细胞、单核细胞、树突状细胞和自然杀伤细胞,在免疫应答、免疫监测和免疫治疗中发挥着重要作用[8]。本研究基于PBMCs分析心肌梗死和梗死恢复过程中潜在的关键基因和生物学改变,旨在为心肌梗死的诊断、评估、管理和预后分析提供新的见解。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 数据集获取
从GEO数据库中下载关于心肌梗死PBMCs的转录组测序芯片数据集GSE59867[9-10], 芯片注释平台为GPL6244, 芯片信息为Affymetrix Human Gene 1.0 ST Array。该数据集收集了111例ST段抬高型心肌梗死(STEMI)患者入院、出院、心肌梗死后1个月、心肌梗死后6个月时的外周血样本数据。对照组为46例无心肌梗死病史的稳定型冠心病患者。基于芯片注释平台对数据集进行基因名转换,用于后续共表达网络的构建。
1.2 加权基因共表达网络分析(WGCNA)
通过WGCNA R包筛选与心肌梗死有关的易感基因模块[11]。WGCNA是一种常用的生物信息学方法,可以识别具有相似表达模式的基因模块,分析基因模块与样本表型之间的关系,绘制基因模块中的调控网络,识别关键模块和调控基因[12-13]。首先,选取数据集中方差变异程度最高的前3 000个基因构建共表达网络; 其次,利用R函数pickSoftThreshold计算软阈值1~20; 然后,对这些基因进行层次聚类和动态树切割来划分模块,并合并相似的模块(阈值为0.25); 最后,计算模块与疾病之间的Spearman相关系数,进而确定易感基因模块。为了探讨所选模块的潜在生物学功能,通过ClusterProfiler R包对模块中的基因进行基因本体论(GO)分析和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)通路分析[14]。GO分析包括生物过程(BP)、分子功能(MF)和细胞成分(CC)。通过Ggplot2 R包进行结果展示。
1.3 基因差异分析和转录因子预测
使用Limma R包进行基因差异分析[15]。差异表达基因(DEGs)的筛选标准为矫正后P < 0.05, |log2(倍数变化)|>0.5。基于ClusterProfiler R包对DEGs进行GO分析和KEGG通路分析, P < 0.05表示显著富集。对上述易感基因模块和DEGs进行交集分析,通过ChEA3数据库对交集基因进行转录因子预测。ChEA3是一种转录因子富集分析工具,整合了多个数据库,如ENCODE、GTEx、ARCHS4等数据库[16]。由于ChEA3数据库并未对预测结果可靠度进行严格划分,参考相关研究[16-17]结论,本研究对平均排名分≤30分的共同转录因子进行结果展示。基于STRING数据库构建交集基因的蛋白相互作用网络,并将交互评分>0.4分的数据导入Cytoscape 3.8.2软件进行可视化处理[18-19]。
1.4 关键基因的确定和受试者工作特征(ROC) 曲线分析
LASSO回归分析是常用的筛选变量的压缩估计方法,通过构造惩罚函数获得较为精炼的模型,使得其压缩一些回归系数,同时设定一些回归系数为0,因此保留了子集收缩的优点,是一种处理具有复共线性数据的有偏估计,常被用于协变量筛选[20]。基于glmnet R包对交集基因中存在蛋白相互作用的基因进行LASSO回归分析,进一步筛选关键基因[21]。采用10倍交叉验证法选择惩罚项(λ), 并选择最小二项偏差在1个标准误差内的最简单模型的λ值(lambda.1se)。通过pROC R包对关键基因进行ROC曲线分析,计算曲线下面积(AUC), 评估关键基因对心肌梗死的诊断价值[22]。
1.5 基因集富集分析(GSEA)和外部数据集验证
根据每个关键基因的表达量将数据集划分为高表达组和低表达组,通过GSEA探讨高表达组和低表达组之间潜在的生物学功能变化,将特征基因集作为预先定义的基因集。作为一种常见的生物信息学方法, GSEA可评估一个预先定义的基因集的基因在与表型相关度排序的基因表中的分布趋势,从而判断其对表型的影响[23]。从GEO数据库中选取另一个数据集GSE123342, 将其用于验证关键基因的表达。GSE123342数据集包括急性心肌梗死(65例)、梗死后30 d(64例)、梗死后1年(37例)、稳定型冠心病(22例)样本数据以及4例技术重复样本数据。
2. 结果
2.1 易感基因模块的确定
根据无标度网络原理,选取10作为共表达网络的软阈值,见图 1A。通过层次聚类和动态树切割,将前3 000个基因划分为15个基因模块,见图 1B。剔除聚类失败的灰色模块,棕色模块的总体表达与心肌梗死的相关性最高(r=0.4), 且与出院至心肌梗死后6个月的演变过程呈负相关(r=-0.33), 见图 1C。棕色模块中的共表达基因伴随着心肌梗死的发生呈现高表达趋势,而在心肌梗死恢复过程中则呈现低表达趋势。由此提示,棕色模块可能是易感基因模块,其中包含243个基因,即ABHD5、ACER3、ACP3、ACSL1、ADAM17、ADAM9、ADM、AHR、ALCAM、ALDH2、ALPK1、ANKRD50、ANO5、AQP9、ARHGAP24、ARHGAP29、ARRDC4、ASPH、ATP6V0A1、ATP6V1A、B3GNT5、BACH1、BLVRB、BST1、C3AR1、C5、C9orf72、CALCRL、CAPG、CAPZA2、CARD6、CASP1、CASP5、CCDC88A、CCR2、CD14、CD163、CD1D、CD33、CD36、CD63、CLEC1A、CLEC4A、CLEC4D、CLEC4E、CLEC7A、CLMN、CNTLN、CPED1、CPM、CPNE8、CPVL、CR1、CR1L、CREG1、CRISPLD2、CSTA、CTNNA1、CTSH、CYBRD1、CYP1B1、CYP1B1-AS1、DACH1、DDIAS、DOCK4、DOCK5、DRAM1、DSC2、DSE、DUSP6、EDNRB、ENTPD1、ERLIN1、EVI5、F5、FAM114A1、FAM13A、FAM151B、FAM20A、FAM198B、FAR2、FBN2、FBP1、FCGR2A、FGD4、FGD6、FLT3、FLVCR2、FMO5、FPR1、FPR2、FRRS1、FUCA1、FUCA2、GAPT、GAS2L3、GCA、GIMAP8、GLT1D1、GPAT3、GPR141、HAL、HGF、HMGB2、HNMT、HORMAD1、HP、HPSE、IDH1、IFNGR1、IL13RA1、IL15、IL18、IMPA2、IRAK3、JAK2、KCNJ15、KCNJ2、KIF13A、KLHL8、KYNU、LHFPL2、LILRA5、LIN7A、LIPN、LMNB1、LPCAT2、LRMDA、LRRK2、LTA4H、LY86、LYVE1、MAP3K20、MCEMP1、ME1、METTL7A、METTL7B、MFSD1、MGST1、MGST2、MILR1、MNDA、 MOSPD2、MS4A4A、MSRB1、MTARC1、MYOF、NAAA、NAIP、NETO2、NLN、NLRC4、NPL、OLFML2B、P2RX7、P2RY13、PGD、PIP4P2、PLA2G4A、PLBD1、PLD1、PLIN2、PLSCR1、PPARG、PPT1、PRRG4、PSTPIP2、PYGL、QPCT、RAB39A、RALB、RBP7、RGL1、RNASE2、RNASE6、RNF141、RNF217、RRAGD、S100A12、S100A9、S100Z、SAT2、SEMA3C、SEPTIN10、SERPINB1、SERPINB2、SESTD1、SGMS2、SH3PXD2B、SHTN1、SIPA1L2、SIRPD、SLC15A2、SLC1A3、SLC22A15、SLC22A4、SLC26A8、SLC31A1、SLC36A4、SLC7A7、SLC8A1、SLITRK4、SMAD1、SMPDL3A、SNX10、SOD2、SORT1、SPATA6、ST3GAL6、ST6GALNAC3、STEAP4、SULT1B1、TASL、TBC1D12、TCN2、TDRD9、TFEC、TGFBI、TLR1、TLR2、TLR4、TLR5、TLR6、TLR7、TLR8、TM6SF1、TMEM144、TMEM167A、TMTC2、TNFAIP6、TNFSF13B、TPST1、TSPO、UBE2D1、UGGT2、VNN2、VNN3、WASF1、WDFY3、WLS、ZC3H12C、ZFYVE16、ZNF438。
棕色模块GO分析最显著的结果分别是骨髓白细胞激活(BP)、囊泡(CC)和模式识别受体活性(MF), 见图 1D; KEGG分析结果则主要为感染、免疫炎症等相关生物学过程的改变,包括Toll样受体信号通路等,见图 1E。
2.2 基因差异分析
进一步对数据集进行基因差异分析,根据筛选标准共得到142个DEGs(图 2A), 其中上调的DEGs有77个,下调的DEGs有65个,见表 1。BP分析结果主要包括免疫反应、免疫系统过程和免疫效应过程, CC分析结果包括分泌颗粒、分泌小泡和细胞质小泡部分等, MF分析结果主要包括信号受体活性、分子传感器活性和碳水化合物结合,见图 2B。KEGG分析提示,这些DEGs主要涉及免疫、炎症和感染的相关生物学改变,见图 2C。DEGs与上述棕色模块存在35个交集基因,见图 2D。基于ChEA3数据库对35个交集基因进行共同转录因子预测,其中平均排名分≤30分的共同转录因子分别是CREB5、MTF1、NFE4、SPI1、ZNF467、NFE2、TFEC、MXD1、NR1H3、BORCS8MEF2B、NFIL3和CEBPE, 见表 2。构建蛋白互作网络,其中有18个基因存在蛋白质相互作用,见图 2E。
表 1 差异基因与交集基因上调DEGs 下调DEGs 与棕色模块交集的DEGs ACSL1、ADM、AQP9、ASGR2、BLVRB、BST1、CCR1、CCR2、CD14、CD163、CES1、CES1P1、CR1、CYP1B1、CYP27A1、DSC2、DYSF、ECRP、EGR1、EGR2、FAM20A、FAM20C、FLVCR2、FMN1、FOLR3、FPR1、FPR2、FAM198B、GPR162、HLX、HP、IFITM3、IL1R2、KCNJ15、LILRA3、LILRA5、LILRB4、LRP1、MAFB、MCEMP1、MERTK、MIR21、MS4A4A、MTARC1、NFE2、NRG1、PADI2、PLB1、PLBD1、PPARG、QPCT、RNASE1、RNASE2、S100A12、S100A9、SASH1、SERPINB10、SERPINB2、SH3PXD2B、SIGLEC16、SIGLEC9、SLED1、SOCS3、ST14、STAB 1、STEAP4、TBC1D2、TCN2、TDRD9、TMEM150B、TMEM176A、TMEM176B、TNFAIP6、TREM1、TRIB1、TSPO、VSIG4 ARAP2、BIRC3、C12orf75、CD160、CD3G、CENPK、CEP78、CLC、CLEC2D、CPA3、DTHD1、EPB41L4A、FAM169A、FCRL6、FGFBP2、GBP4、GNLY、HRH4、IL18RAP、JAKMIP2、KLRA1P、KLRC1、KLRC3、KLRC4-KLRK1、KLRD1、KLRF1、KLRG1、KPNA5、MIR29A、MS4A3、MYBL1、MYO6、ODF2L、PDGFD、PRSS23、RNU5A-1、RORA、SAMD3、SCARNA9、SH2D1A、SLC4A4、SLCO4C1、SNORA16B、SNORA20、SNORA75、SNORD20、SNORD28、SNORD30、SNORD45C、SNORD50A、SNORD54、SNORD58A、SNORD59A、SNORD59B、SNORD61、SNORD81、SNORD82、SYTL2、TARP、TBC1D19、TFDP2、TGFBR3、VPS13A、ZNF675、ZNF737 ACSL1、ADM、AQP9、BLVRB、BST1、CCR2、CD14、CD163、CR1、CYP1B1、DSC2、FAM20A、FLVCR2、FPR1、FPR2、FAM198B、HP、KCNJ15、LILRA5、MCEMP1、MS4A4A、MTARC1、PLBD1、PPARG、QPCT、RNASE2、S100A12、S100A9、SERPINB2、SH3PXD2B、STEAP4、TCN2、TDRD9、TNFAIP6、TSPO 表 2 共同转录因子预测结果(平均排名分≤30分)排名 转录因子 平均得分/分 转录因子数据库计算方法与得分 重叠基因 1 CREB5 7.667 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 5分; Enrichr Queries, 14分; GTEx Coexpression, 4分 CR1、STEAP4、TNFAIP6、ACSL1、AQP9、FPR1、MCEMP1、ADM、FPR2、LILRA5、BST1、QPCT、PLBD1、CYP1B1、CD14、S100A9、CCR2 2 MTF1 8.500 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 6分; GTEx Coexpression, 11分 CR1、SERPINB2、TNFAIP6、ACSL1、AQP9、FPR1、FPR2、LILRA5、BST1、PLBD1、CYP1B1、FLVCR2、CD14、S100A9 3 NFE4 9.000 GTEx Coexpression, 9分 BST1、CR1、AQP9、FPR1、PLBD1、MCEMP1、FPR2、LILRA5、CCR2 4 SPI1 9.667 Literature ChIP-seq, 5分; ARCHS4 Coexpression, 11分; ENCODE ChIP-seq, 8分; Enrichr Queries, 11分; ReMap ChIP-seq, 5分; GTEx Coexpression, 18分 CD163、CR1、STEAP4、SERPINB2、ACSL1、AQP9、FPR1、TDRD9、MCEMP1、FPR2、RNASE2、LILRA5、MS4A4A、BST1、QPCT、PLBD1、CYP1B1、CD14、S100A9、CCR2 5 ZNF467 19.333 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 18分; Enrichr Queries, 30分; GTEx Coexpression, 10分 CR1、AQP9、FPR1、MCEMP1、ADM、FPR2、LILRA5、BST1、PLBD1、CYP1B1、BLVRB、CD14、S100A9、CCR2 6 NFE2 21.000 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 16分; ENCODE ChIP-seq, 78分; Enrichr Queries, 1分; ReMap ChIP-seq, 8分; GTEx Coexpression, 2分 CR1、SERPINB2、AQP9、FPR1、MCEMP1、ADM、FPR2、RNASE2、LILRA5、BST1、TCN2、QPCT、PLBD1、S100A12、BLVRB、TSPO、CYP1B1、PPARG、CD14、S100A9、CCR2 7 TFEC 21.667 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 21分; Enrichr Queries, 4分; GTEx Coexpression, 40分 CD163、CR1、SERPINB2、TNFAIP6、ACSL1、AQP9、FPR1、MS4A4A、BST1、TCN2、FLVCR2、PPARG、CD14、S100A9、CCR2 8 MXD1 23.000 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 4分; Enrichr Queries, 9分; GTEx Coexpression, 56分 CR1、SERPINB2、STEAP4、ACSL1、AQP9、FPR1、ADM、FPR2、LILRA5、BST1、PLBD1、CYP1B1、CD14、S100A9 9 NR1H3 26.600 Literature ChIP-seq, 10分; ARCHS4 Coexpression, 17分; Enrichr Queries, 10分; ReMap ChIP-seq, 36分; GTEx Coexpression, 60分 CD163、STEAP4、TCN2、ACSL1、FLVCR2、CYP1B1、PPARG、ADM、CD14、S100A9、MS4A4A 10 BORCS8MEF2B 29.000 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 29分 AQP9、FPR1、TSPO、FPR2、S100A9、LILRA5 11 NFIL3 30.000 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 1分; Enrichr Queries, 21分; GTEx Coexpression, 68分 CR1、TNFAIP6、ACSL1、AQP9、FPR1、ADM、FPR2、LILRA5、MS4A4A、BST1、CYP1B1、PLBD1、CD14、S100A9 12 CEBPE 30.000 ARCHS4 Coexpression, 31分; Enrichr Queries, 12分; GTEx Coexpression, 47分 BST1、FPR1、PLBD1、ADM、MCEMP1、FPR2、CD14、RNASE2、S100A9、CCR2、LILRA5 计算方法包括ARCHS4 Coexpression、ENCODE ChIP-seq、Enrichr Queries、GTEx Coexpression、Literature ChIP-seq、ReMap ChIP-seq; 平均得分为各计算方法得分之和除以计算方法数量所得之商。 2.3 关键基因的确定
对18个存在蛋白相互作用的基因进一步行LASSO回归分析,这些基因不同惩罚参数值所对应的系数见图 3A。本研究选取最小二项偏差在1个标准误差内的λ值(lambda.1se, 6个基因),该λ值提供更精简的模型,见图 3B。ROC曲线分析显示, CD163、RNASE2、HP、FAM20A、MCEMP1和FAM198B基因表达水平对心肌梗死的发生均具有良好的诊断价值, AUC分别为0.831、0.798、0.775、0763、0.866和0.829, 见图 3C。与对照组稳定型冠心病患者相比,这些关键基因的表达水平在入院时心肌梗死患者中显著上升,并在出院时、心肌梗死后1个月、心肌梗死后6个月逐步下降,见图 3D。
2.4 GSEA结果和验证
GSEA结果提示,这些关键基因涉及的生物学改变主要与糖脂代谢、活性氧、免疫炎症等有关,见图 4。这些基因在外部数据集中大多也存在差异表达。基于外部验证数据集GSE123342, 本研究同样发现,与稳定型冠心病相比, HP、FAM198B、CD163、FAM20A、MCEMP1表达水平在急性心肌梗死发生时显著上升,而RNASE2仅表现出上升趋势,见图 5。
3. 讨论
本研究基于PBMCs转录组学的变化探讨心肌梗死及梗死恢复过程中可能存在的生物学改变和潜在标志物, WGCNA和DEGs分析结果显示,心肌梗死过程伴随着免疫炎症紊乱。基于LASSO分析,本研究从上述2种分析方法得到的共同基因中鉴定出6个关键基因,即 CD163、RNASE2、HP、FAM20A、MCEMP1和FAM198B。ROC曲线分析结果提示,这些关键基因对心肌梗死的发生均具有较高的诊断价值。本研究还发现,在梗死恢复过程中,这些基因的表达呈现明显下降趋势。GSEA分析结果表明,这些关键基因涉及的生物学改变主要与糖脂代谢、活性氧、免疫炎症等有关。
CD163分子是Ⅰ型膜蛋白,蛋白表达限于单核细胞/巨噬细胞系, CD163抗原特异性释放机制可能在炎症调节过程中起重要作用。在动脉粥样硬化过程中, CD163+巨噬细胞能促进血管生成和增加血管通透性,并伴随炎症反应;此外,破裂的冠状动脉斑块中 CD163 的表达增加了心肌梗死和冠心病发生风险[24]。 RNASE2 编码的蛋白质是非分泌型核糖核酸酶,属于胰核糖核酸酶家族[25]。 FAM20A 是激酶编码基因家族的成员,本身不具有激酶活性,通过与家族成员 FAM20C 形成复合物,增强 FAM20C 的激酶活性,从而使分泌通路内的蛋白磷酸化[26]。 MCEMP1 又称 C19ORF59 , 可编码表达于肥大细胞、巨噬细胞等的跨膜蛋白[27]。研究[27]表明, MCEMP1 基因可能是卒中诊断和预后评估的新生物标志物。生物信息学研究[28-29]提示, RNASE2、FAM20A和 MCEMP1 可能是心肌梗死的关键基因,然而这些基因在心肌梗死及梗死恢复过程中的具体作用机制有待进一步研究。HP基因编码一种前蛋白,经处理后产生α链和β链,结合为四聚体产生触珠蛋白,其基因型与急性心肌梗死的发病风险密切相关,并且能决定心肌梗死面积[30-31]。 FAM198B(GASK1B) 是目前未知功能的新基因,可能编码定位在高尔基体上的膜结合糖蛋白,被认为参与癌症的转移与进展[32]。本研究分析结果显示, FAM198B 可能是心肌梗死和反映心肌梗死恢复的关键基因。
本研究尚存在一定局限性: 首先,本研究基于GEO数据库中下载的心肌梗死患者PBMCs的测序数据集进行分析,还需要进一步开展分子生物学实验来验证这些基因在心肌梗死中的表达及其可能的生物学机制; 其次,本研究仅分析了现有的样本数据,未来还需基于更大的样本规模和更详细的样本类型进一步深入研究; 最后,由于缺乏临床资料,本研究未分析这些关键基因的表达与心肌梗死患者年龄、性别、射血分数等临床指标的相关性。
综上所述,本研究基于PBMCs确定了6个可能与心肌梗死密切相关的关键基因,即 CD163、RNASE2、HP、FAM20A、MCEMP1和FAM198B, 为心肌梗死的诊断、评估、管理和预后分析提供了新的思路。
-
表 1 再狭窄组和未狭窄组临床资料比较[n(%)](x±s)
指标 再狭窄组(n=22) 未狭窄组(n=151) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 55.43±7.26 54.87±7.20 0.340 0.734 性别 男 13(59.09) 80(52.98) 0.288 0.591 女 9(40.91) 71(47.02) BMI/(kg/m2) 22.80±4.03 22.91±4.06 0.119 0.906 SBP/mmHg 131.15±20.69 128.52±19.07 0.598 0.551 DBP/mmHg 82.44±15.19 79.60±14.22 0.868 0.387 吸烟 15(68.18) 49(32.45) 10.518 0.001 高血压 10(45.45) 70(46.61) 0.006 0.937 高脂血症 8(36.36) 43(28.48) 0.575 0.448 HbA1c/% 8.90±2.04 5.33±1.86 8.308 < 0.001 TC/(mmol/L) 5.11±1.03 5.02±0.95 0.411 0.682 TG/(mmol/L) 2.03±0.14 1.99±0.10 1.658 0.099 LDL-C/(mmol/L) 3.04±0.22 2.98±0.18 1.418 0.158 ET-1/(ng/L) 68.52±10.33 55.26±7.31 7.503 < 0.001 NO/(μmol/L) 37.90±7.22 30.60±4.52 6.486 < 0.001 CRP/(mg/L) 25.68±6.41 14.62±3.25 12.811 < 0.001 BMI: 体质量指数; SBP: 收缩压; DBP: 舒张压; HbA1c: 糖化血红蛋白; TC: 总胆固醇; TG: 甘油三酯; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; ET-1: 内皮素-1; NO: 一氧化氮; CRP: C反应蛋白。 表 2 支架植入术后再狭窄的多因素分析
变量 β SE Wald χ2 P OR 95%CI 吸烟 0.335 0.112 8.947 0.003 1.398 1.122~1.741 HbA1c 0.345 0.126 7.497 0.006 1.412 1.103~1.808 ET-1 0.401 0.110 13.289 < 0.001 1.493 1.204~1.853 NO 0.405 0.106 14.598 < 0.001 1.499 1.218~1.846 CRP 0.392 0.114 11.824 < 0.001 1.480 1.184~1.850 HbA1c: 糖化血红蛋白; ET-1: 内皮素-1; NO: 一氧化氮; CRP: C反应蛋白。 -
[1] 张丹, 刘明, 郝清智, 等. 下肢动脉硬化闭塞症支架内再狭窄的腔内治疗研究进展[J]. 山东医药, 2019, 59(7): 98-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2019.07.027 [2] 马强, 王慰敏, 庞宏刚, 等. 血清可溶性髓系细胞触发受体1水平与下肢动脉硬化闭塞症患者支架植入术后再狭窄的关系研究[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2019, 27(2): 38-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2019.02.009 [3] JIANG X L, JU S, CHEN B, et al. Application and value of excimer laser ablation in the treatment of lower limb atherosclerotic obliterans[J]. Chin Med J, 2021, 101(14): 1026-1030. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/350847394_Application_and_value_of_excimer_laser_ablation_in_the_treatment_of_lower_limb_atherosclerotic_obliterans
[4] 侯俊杰, 李大勇, 李世征, 等. 加味阳和汤治疗寒凝血瘀证下肢动脉硬化闭塞症的临床疗效及对血清ET-1、NO水平变化的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2019, 37(9): 47-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS201909010.htm [5] LI Y, HAO Y F, WANG T, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen may improve vascular endothelial function in patients undergoing coronary stent implantation[J]. Undersea hyperbaric med, 2019, 46(2): 145-152. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/tech-docs/paper/1216630
[6] 唐欣, 李丰华, 秦陆兵. 冠心病患者内皮素-1水平与PCI术后支架内再狭窄的相关性[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2018, 10(2): 227-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2018.02.28 [7] 张金李, 韩鹏, 王曜宇. 养心通脉汤治疗冠脉支架植入术后再狭窄疗效及对患者血清肿瘤坏死因子-α和C反应蛋白的影响[J]. 陕西中医, 2019, 40(5): 572-575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2019.05.008 [8] 刘昌伟. 下肢动脉硬化性闭塞症治疗指南[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2008, 28(11): 923-924. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2208.2008.11.006 [9] 卢庆威, 王军, 王刚, 等. 基于数据库数据分析下肢动脉硬化闭塞症患者腔内介入术治疗后支架内再狭窄的危险因素[J]. 山东医药, 2020, 60(30): 80-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2020.30.021 [10] LU R, GAO Y, YU C W, et al. Therapeutic effect and follow-up analysis of drug-coated balloon in the treatment of lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans[J]. Journal of Qiqihar Medical University, 2019, 40(5): 541-544.
[11] 孙波, 章旭, 张杰峰, 等. 2型糖尿病下肢动脉硬化闭塞症患者血清VCAM-1与支架植入术后再狭窄的相关性[J]. 中国医刊, 2020, 55(4): 406-409. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1070.2020.04.018 [12] 肖永生, 杨柳, 刘一东. 下肢动脉硬化闭塞症介入后人内皮素-1和一氧化氮及动态变化及预测再狭窄的价值[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2019, 36(8): 1487-1487. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9030.2019.08.046 [13] KüP A, TOPRAK C, BAYAM E, et al. Serum endocan levels predict drug-eluting stent restenosis in patients with stable angina pectoris[J]. Acta Cardiol Sin, 2020, 36(2): 111-117. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32201461/
[14] 曾仲衍, 李嘉宏, 黄敏捷, 等. 下肢动脉硬化闭塞经介入治疗后再狭窄的危险因素分析[J]. 福建医药杂志, 2020, 42(2): 51-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2600.2020.02.015 [15] 黄燕妮, 袁燕萍, 肖雪梅. 血清超敏C反应蛋白对颈动脉支架植入术后再狭窄的预测价值研究[J]. 临床输血与检验, 2019, 21(2): 190-193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2587.2019.02.022 [16] 周欣峰, 戚韶红, 周俊文, 等. 血清sTREM-1对下肢动脉硬化闭塞症支架植入术后血管再狭窄的预测价值[J]. 山东医药, 2020, 60(10): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2020.10.005 [17] 张波, 刘亚民, 吴佳庆, 等. 下肢闭塞性动脉硬化患者经皮腔内血管成形术结合血管内支架成形术后发生支架内再狭窄的影响因素[J]. 血管与腔内血管外科杂志, 2021, 7(2): 140-144. [18] 卢晓操, 王晓琳. 影响冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病支架植入术后冠脉支架再狭窄相关因素的Logistic回归分析[J]. 河北医学, 2020, 26(2): 205-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6233.2020.02.008 [19] QIU S, SUN J. lncRNAMALAT1 expression in patients with coronary atherosclerosis and its predictive value for instent restenosis[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20(6): 1-1. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33082861/
[20] 安彩霞, 房辉, 杨岳, 等. 血清高迁移率族蛋白B1水平与2型糖尿病下肢动脉硬化闭塞症患者支架植入术后再狭窄的相关性观察[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2019, 27(6): 429-433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTL201906006.htm -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 于琪力,葛雪,刘丽. 冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病患者心力衰竭危险因素分析. 新乡医学院学报. 2024(06): 560-565 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙宁,李飞. 心肌梗死患者血清miR-34a-5p和C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白-9水平及其与心肌重构的相关性. 检验医学与临床. 2024(19): 2785-2789 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
