Correlations between levels of serum cholyglycine, soluble growth stimulating gene 2 and viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis B
-
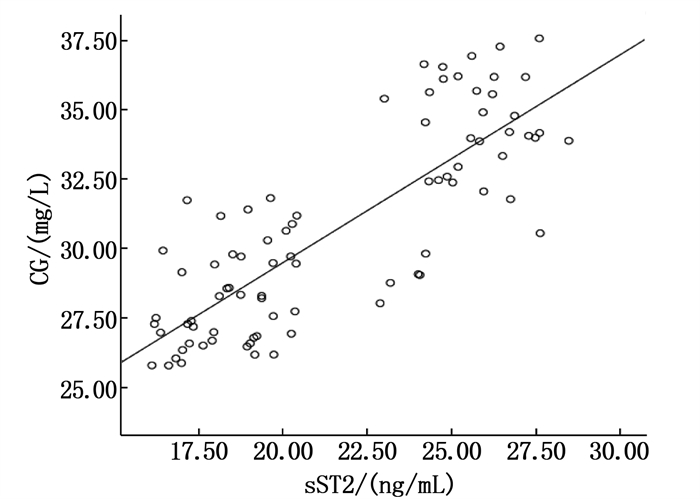
摘要:目的 探讨血清甘胆酸(CG)、可溶性生长刺激表达基因2蛋白(sST2)水平与慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者病毒载量的相关性。方法 选择2019年3月—2020年3月在本院接受抗病毒治疗的83例CHB患者,根据就诊时的乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)-DNA病毒载量将患者分为高病毒载量组(n=32)、低病毒载量组(n=21)以及阴性组(n=30)。测定并比较3组血清CG、sST2水平,分析血清CG、sST2水平与CHB患者病毒载量的关系。结果 高病毒载量组总胆红素(TBIL)、直接胆红素(DBIL)、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、谷氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、CG、sST2水平高于低病毒载量组、阴性组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。经Kendall's tau-b相关评价结果显示,TBIL、DBIL、AST、ALT、CG、sST2表达与CHB患者病毒载量呈显著正相关(Kendall's tau-b=0.485、0.476、0.523、0.624、0.665、0.598,P均 < 0.001)。一般线性双变量Pearson直线相关性分析检验结果显示,CHB患者血清CG、sST2表达呈显著正相关(r=0.818,P < 0.001)。结论 CHB患者血清CG、sST2水平与病毒载量相关,可能是促进患者病情进一步进展的重要原因。Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlations between levels of serum cholyglycine (CG), soluble growth stimulating gene 2 (sST2) and the viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).Methods A total of 83 CHB patients with antiviral treatment in authors'hospital from March 2019 to March 2020 were selected, and they were divided into high viral load group (n=32), low viral load group (n=21) and negative group (n=30) according to viral load of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-DNA at visit. Serum CG and sST2 levels were measured and compared in the three groups, and the relationships between levels of serum CG, sST2 and the viral load in patients with CHB were analyzed.Results Levels of total bilirubin (TBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), glutamate aminotransferase (ALT), CG and sST2 in the high viral load group were significantly higher than those in the low viral load group and the negative group (P < 0.05). Kendall's tau-b relevant evaluation showed that the expressions of TBIL, DBIL, AST, ALT, CG and sST2 were positively correlated with the viral load in CHB patients (Kendall's tau-b=0.485, 0.476, 0.523, 0.624, 0.665, 0.598, P < 0.001). General linear bivariate Pearson linear correlation analysis showed that there was a positive correlation between the expressions of serum CG and sST2 in patients with CHB (r=0.818, P < 0.001).Conclusion The levels of serum CG and sST2 in patients with CHB are related to the viral load, which may be an important reason to promote the further progress of the disease.
-
-
表 1 3组患者基线资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
基线资料 高病毒载量组(n=32) 低病毒载量组(n=21) 阴性组(n=30) 性别 男 18(56.25) 12(57.14) 16(53.33) 女 14(43.75) 9(42.86) 14(46.67) 年龄/岁 40.72±3.25 40.15±3.66 40.38±2.74 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 21.89±0.47 22.12±0.51 21.95±0.43 病程/年 5.08±0.84 5.11±0.63 4.98±0.72 TBIL/(μmol/L) 23.88±1.72 22.11±1.40* 21.19±1.97* DBIL/(μmol/L) 7.96±1.37 7.08±0.81* 6.79±0.67* AST/(U/L) 163.87±11.12 151.90±7.40* 147.16±5.78* ALT/(U/L) 246.64±12.59 217.55±11.50* 211.95±9.66* CG/(mg/L) 34.53±1.79 29.02±1.96* 27.97±2.18* sST2/(ng/mL) 25.88±1.28 18.73±1.19* 19.04±2.47* TBIL: 总胆红素; DBIL: 直接胆红素; AST: 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶; ALT: 谷氨酸氨基转移酶; CG: 甘胆酸; sST2: 可溶性生长刺激表达基因2蛋白。与高病毒载量组比较, *P < 0.05。 -
[1] CHEN T, WANG J, QIU H, et al. Different interventional criteria for chronic hepatitis B pregnant women with HBeAg(+) or HBeAg(-): Epidemiological data from Shaanxi, China[J]. Medicine: Baltimore, 2018, 97(27): e11406. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011406
[2] 孔媛媛, 魏巍, 单姗, 等. 乙型肝炎肝硬化患者的临床特征与抗病毒治疗模式变化[J]. 肝脏, 2020, 25(2): 123-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZUAN202002011.htm [3] 周洁, 杨梅, 赵琦, 等. 526例慢性乙肝患者不同病期HBV-DNA载量与外周血TBi、TBA、ALB、ALP变化分析[J]. 贵州医药, 2019, 43(9): 1377-1378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2019.09.010 [4] 赵蓉, 石亚玲, 江笑文, 等. 血清甘胆酸检测在肝脏疾病诊断中的临床意义[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2019, 16(13): 1823-1825, 1828. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2019.13.009 [5] 林兰意, 姜绍文, 莫瑞东, 等. 血清sST2在慢性HBV感染者中的表达及其与病情严重程度相关性的研究[J]. 肝脏, 2017, 22(11): 987-990. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2017.11.006 [6] 中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2016, 19(3): 389-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GBSY201603038.htm [7] KIM T H, LEE E J, CHOI J H, et al. Identification of novel susceptibility loci associated with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(7): e0199094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199094
[8] 陈旭东, 陈佳, 金炜, 等. 血清胆汁酸对不同病因所致肝硬化的诊断价值[J]. 肝脏, 2019, 24(2): 150-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2019.02.013 [9] JIANG S W, WANG P, XIANG X G, et al. Serum soluble ST2 is a promising prognostic biomarker in HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2017, 16(2): 181-188. doi: 10.1016/S1499-3872(16)60185-6
[10] 郭雯佳, 贾亚男, 周琪, 等. 血清甘胆酸对肝病的诊断价值探讨[J]. 重庆医学, 2019, 48(1): 140-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2019.01.036 [11] 夏小梅, 朱云波, 尹小青, 等. 血清甘胆酸检测在慢性肝炎诊断中的临床意义[J]. 湖南师范大学学报: 医学版, 2018, 15(4): 154-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-016X.2018.04.049 [12] PETRICK J L, FLORIO A A, KOSHIOL J, et al. Prediagnostic concentrations of circulating bile acids and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: REVEAL-HBV and HCV studies[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 147(10): 2743-2753. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33051
[13] 段丽. 血清甘胆酸联合铜蓝蛋白测定对肝硬化患者肝细胞损害程度的评价[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2020, 27(4): 653-657. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJMY202004026.htm [14] 李章勇, 林应标, 夏川, 等. 肝纤维化指标联合AFP、GGT检测在肝病诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中国医药导报, 2019, 16(7): 153-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY201907039.htm [15] XIE L, LIAO G, CHEN H, et al. Elevated expression of serum soluble ST2 in clinical relapse after stopping long-term Nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy for chronic hepatitis B[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2019, 19(1): 640. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4261-3
[16] 李劲, 骆仲榆, 陈刘镇, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染患者血清IL-33、sST2、MCP-1水平变化及其临床意义[J]. 中国医药导报, 2019, 16(17): 125-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY201917030.htm [17] GRIESENAUER B, PACZESNY S. The ST2/IL-33 axis in immune cells during inflammatory diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 475. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00475
[18] SHEN Z, YANG H, YANG S, et al. Hepatitis B virus persistence in mice reveals IL-21 and IL-33 as regulators of viral clearance[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 2119. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02304-7
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 牛绍迁,杨魏东,冯灵,张晓瑶,周琼蓉. 老年卒中后睡眠障碍的影响因素及药物与非药物治疗研究进展. 保健医学研究与实践. 2024(03): 134-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 史哲宇,黄慧丽,朱少炳,朱路文. 近5年血府逐瘀汤在神经系统疾病中的应用及作用机制研究进展. 中医药学报. 2024(11): 109-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张雯,江丽杰,赵海河. 《医林改错》中活血化瘀类方剂治疗中风的研究进展. 中国中医基础医学杂志. 2023(06): 1036-1039 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高娟,张则甫. 血府逐瘀汤联合康复训练对脑卒中后偏瘫足下垂患者下肢肌张力恢复及体感诱发电位的影响. 中国民族医药杂志. 2023(11): 8-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 孙晓. 血府逐瘀胶囊辅治脑卒中后抑郁临床观察. 实用中医药杂志. 2023(12): 2418-2420 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 乔煦,吴广,王钰. 养心方对缺血性脑卒中后睡眠障碍患者睡眠质量及血清5-HT、BDNF水平的影响. 中医药信息. 2022(02): 60-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 路琦,张永全. 中西医治疗脑卒中后失眠的研究进展. 大众科技. 2022(02): 106-109+113 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 贾军. 清肺化痰逐瘀汤治疗冠心病临床观察. 光明中医. 2022(08): 1423-1425 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 沈晓桦,卢根娣,蒋国静,胡丽,谈晓红. 引阳入阴推拿对剖宫产后心脾两虚证产妇睡眠障碍及负性情绪的影响. 实用临床医药杂志. 2022(09): 54-58 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 陈素银. 血府逐瘀汤对缺血性脑卒中患者血清细胞因子水平和脑血流的影响. 光明中医. 2022(13): 2357-2359 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 徐梦圆,孙平,杨言府. 血府逐瘀汤联合小剂量奥氮平治疗脑卒中后睡眠障碍30例临床观察. 中国民族民间医药. 2022(23): 113-115+118 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
