Regularity of acupoint selection of acupuncture and moxibustion in treatment of constipation predominant irritable bowel syndrome
-
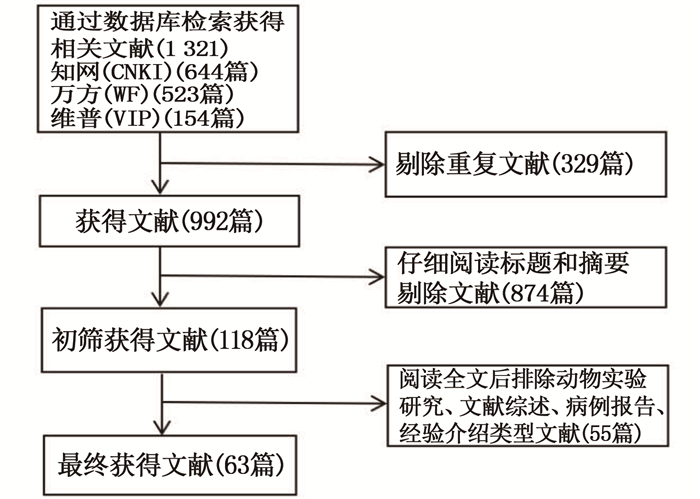
摘要:目的 探讨针灸治疗便秘型肠易激综合征(IBS-C)的取穴规律。方法 检索中国知网数据库、万方数据库、维普数据库和PubMed、Cochrane Library、Web of Science数据库2004年1月1日—2021年8月15日有关针灸治疗IBS-C的临床随机对照试验文献。对IBS-C针灸治疗的穴位处方进行梳理统计并建立数据库,运用IBM SPSS 26.0和Climentine 12.0对针灸处方进行聚类和关联分析。结果 共纳入63篇文献,涉及针灸处方63个、穴位40个,其中高频穴位有天枢、足三里、上巨虚、大肠俞、中脘。使用频率最高的经络是足阳明胃经; 穴位主要集中在双下肢与胸腹部; 最常用的特定穴为下合穴; 天枢、足三里在IBS-C针灸治疗中具有重要地位。结论 针灸治疗IBS-C遵循以循经取穴为主、辨证取穴为辅的原则,且具有特定穴治疗这一特点。Abstract:Objective To analyze point selection rules of acupoint selection of acupuncture and moxibustion for treatment of constipation predominant irritable bowel syndrome(IBS-C).Methods Clinical research literatures on acupuncture and moxibustion in treatment of IBS-C from January 1, 2004 to August 15, 2021 in China National Knowledge Resource Database, Chinese academic journal database, Chinese Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP), PubMed, Cochrane Library and Web of Science were retrieved. Acupoint prescriptions for IBS-C by acupuncture and moxibustion treatment were searched to establish a database, and IBM SPSS26.0 and Climentine 12.0 were used to perform luster and correlation analysis.Results A total of 63 documents were included, involving 63 acupuncture prescriptions and 40 acupuncture points. Among them, the high-frequency acupoints were Tianshu, Zusanli, Shangjuxu, Dachangshu, and Zhongwan. The most frequently used meridian was the Foot-Yangming Stomach Meridian; the acupoints were mainly concentrated in the lower limbs, chest and abdomen; the most commonly used specific acupoint was the He-sea point. Tianshu and Zusanli played important roles in the treatment of IBS-C.Conclusion Acupuncture and moxibustion treatment for IBS-C follows the principles of selecting acupoints along the meridian as the main point, and syndrome differentiation as supplemented principle, and has the characteristic of specific acupoint treatment.
-
放射治疗是复发性鼻咽癌治疗的重要手段之一,约60%以上的复发性鼻咽癌采用放射治疗后能提高临床疗效及生存率[1]。尽管放射治疗设备有所更新,放射治疗技术如调强放疗、适行放疗等取得了进步,但仍需避免或减少放疗不良反应的发生[2-4]。本研究选取99例均为确诊复发性鼻咽癌放疗的患者为研究对象,探讨中医辨证治疗对血液、放射性皮肤损伤和放疗后症候反应的影响,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2007年5月—2013年4月南部战区总医院收治的99例复发性鼻咽癌患者为研究对象,采用随机数字表法分为观察组(52例)和对照组(47例)。观察组女24例,男28例; 年龄31~69岁,平均(48.32±6.22)岁; 肺热壅盛型16例,气阴两虚型19例,痰凝血瘀型17例。对照女21例,男26例; 年龄32~65岁,平均(47.12±5.96)岁; 肺热壅盛型15例,气阴两虚型17例,痰凝血瘀型15例。2组基本资料(年龄、性别、中医辨证分型)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。纳入标准: 全部患者均经PET/CT或头颈部MRI确诊,存在可测量的肿瘤复发病灶; 患者预计生存期>6个月。排除标准: 合并神经系统疾病,肝、肾功能不全者; 有其他肿瘤手术史、放化疗史者; 哺乳期、妊娠期妇女。本研究经医学伦理委员会评审通过,患者知情并自愿签署知情同意书。
1.2 方法
观察组实施放射治疗。以高能X线三野照射(1.8~2 Gy/F, 5 F/W)在模拟机下定位,范围为原发病灶及区域淋巴结引流区的照射总量为40~60 Gy。校正放射野2周1次。中医辨证用药: 肺热壅盛型患者采用清热泻肺汤加减,其中组方包括百部12 g, 桑白皮15 g, 胆南星6 g, 黄芩12 g, 蝉蜕12 g, 苍术9 g, 连翘12 g, 辛夷花12 g, 苍耳子12 g, 桔梗12 g, 细辛3 g, 北杏仁15 g, 白芷12 g, 蒲公英12 g, 随症加减; 气阴两虚型患者采用生脉散合增液汤加减,组方包括人参9 g, 生地15 g, 麦冬30 g, 菖蒲6 g, 玄参30 g, 远志12 g, 赤芍12 g, 随症加减; 痰凝血瘀型患者采用柴胡疏肝散合通窍活血加减,组方包括柴胡12 g, 半夏12 g, 郁金12 g, 白芍12 g, 青皮12 g, 皂角刺12 g, 丹参12 g, 枳壳12 g, 川芎9 g, 大枣12 g, 茯苓18 g, 桃仁12 g, 牡蛎18 g, 海藻18 g, 浙贝母18 g, 随症加减。对照组放疗方法同观察组。
1.3 观察指标
1.3.1 骨髓抑制
分别于放疗前1 d、放疗结束后4周检测血红蛋白(Hb)、白细胞计数(WBC)、血小板(PLT)。骨髓抑制分级标准采用世界卫生组织(WHO)毒副作用分级标准[5]进行评定, 分为0~Ⅳ度。
1.3.2 放射性皮肤损伤程度
根据皮肤放射损伤评分标准量表(RTOG)[6]对放射性皮肤损伤程度进行评价。0度为皮肤无变化; 1度为出现轻度皮肤红斑、干性脱发、滤泡,出汗减少,患者生活质量不受影响,痛苦小; 2度为出现明显皮肤红斑、湿性斑状皮炎和中度水肿; 3度为出现融合性湿性皮炎和凹陷性水肿; 4度为皮肤坏死,合并溃疡出血,甚至被迫终止放疗。
1.3.3 症候指标
口腔黏膜炎、胃肠道反应、口干症、张口受限等。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 23.0软件进行统计分析,计量资料行t检验,以(x±s)表示,计数资料行χ2检验,以[n(%)]表示, P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组血液检测指标水平比较
观察组治疗前后血液检测指标水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。对照组治疗前后血液检测指标水平比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。观察组血液检测指标水平高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01), 见表 1。
表 1 2组血液检测指标水平比较(x±s)组别 n 时点 Hb/(g/L) WBC/(×109/L) PLT/(×109/L) 观察组 52 治疗前 137.60±23.24 4.74±0.94 216.90±31.80 治疗后 132.58±20.13# 4.44±1.24# 210.73±29.21# 对照组 47 治疗前 132.67±29.36 4.77±1.09 217.46±35.84 治疗后 122.56±28.24* 3.59±1.00* 180.37±25.69* Hb: 血红蛋白; WBC: 白细胞计数; PLT: 血小板。与治疗前比较, *P < 0.05; 与对照组比较, #P < 0.05。 2.2 2组放射性皮肤损伤比较
观察组1度皮肤损伤16例, 2度皮肤损伤18例, 3度皮肤损伤15例, 4度皮肤损伤3例; 对照组1度皮肤损伤5例, 2度皮肤损伤19例, 3度皮肤损伤17例, 4度皮肤损伤6例。观察组皮肤损伤患者占比与对照组比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。观察组平均治愈时间(7.78±2.32) d, 对照组为(13.73±3.16) d。观察组皮肤损伤平均治愈时间短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
2.3 2组放疗后症候发生情况比较
放疗后,观察组口腔黏膜炎、胃肠道反应、口干症、张口受限发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 2组放疗后症候反应发生情况比较[n(%)]组别 n 口腔黏膜炎 胃肠道反应 口干症 张口受限 观察组 52 30(57.7)* 31(59.6)* 27(51.9)* 33(63.5)* 对照组 47 37(78.7) 38(80.9) 42(89.4) 39(83.0) 与对照组比较, *P < 0.05。 3. 讨论
鼻咽癌是中国南部各地区头颈部较常见的恶性肿瘤,放射治疗是鼻咽癌的主要治疗手段之一[7]。复发性鼻咽癌患者需加大放射剂量才能提高疗效,随着常规照射剂量的增加,患者皮肤、颞颌关节、腮腺、脊髓等组织会出现损伤,并会表现出骨髓抑制、放射性皮炎、张口受限、黏膜反应、口干症、消化道反应等毒副作用,从而降低患者对放疗的耐受性和依从性,甚至延长放疗疗程或导致治疗终止[8]。
鼻咽癌在中医学中属于“失荣”“上石疽”“鼻渊”等范畴,中医学认为,放射线属于火热之毒邪,作用于人体后可引起经脉痹阻、阴液亏虚,肌肤筋骨失去濡养,表现为吞咽困难、口干咽燥、张口受限、皮肤损伤等。此外,肿瘤患者均有一定程度的正气虚损,接受放疗时,火热毒邪攻伐机体,导致体内热毒之邪积聚,邪气过剩,耗气伤阴。“精气夺则体更虚”,加之癌毒附着,脾胃之功能受损加剧,气血生化不足,造成气阴两虚、气血损伤,临床表现为纳差、恶心、呕吐等胃肠道反应,也可能出现贫血、血小板减少、白细胞下降等骨髓抑制表现[9]。中医辨证论治过程中对患者治疗期间出现的有关症候、系统整体状态和功能溯本求源,发现鼻咽癌患者以肺热壅盛、痰凝血瘀和气阴两虚3种证型为主,因此基本治疗原则应以清泻肺热、化痰活血、益气养阴为主[10]。
中医辨证治疗能够提高鼻咽癌患者的机体免疫功能,减轻放疗毒性反应。研究[11]发现,黄芪注射液能够减轻肿瘤放化疗的毒副作用,保护骨髓,防止白细胞下降。林冯杰等[12]研究显示,参麦注射液能显著减轻晚期鼻咽癌患者放射性皮肤损伤。本研究结果显示,观察组血液检测指标水平高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01); 观察组皮肤损伤平均治愈时间短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 观察组口腔黏膜炎、胃肠道反应、口干症、张口受限发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。以上结果提示,中医辨证治疗能够在复发性鼻咽癌放疗过程中起到减毒作用。但目前对中医药放疗的减毒机制尚不明确,研究应从细胞分子生物学机制上继续深入探讨,同时还需设计更先进的试验方法以观察中医药对放疗减毒作用的影响。
-
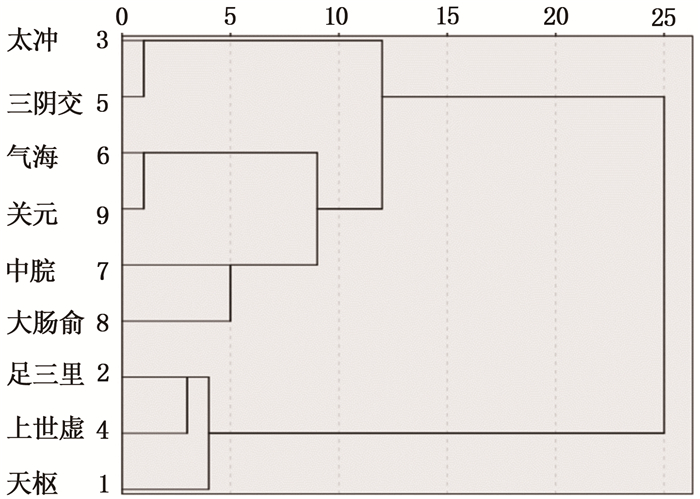
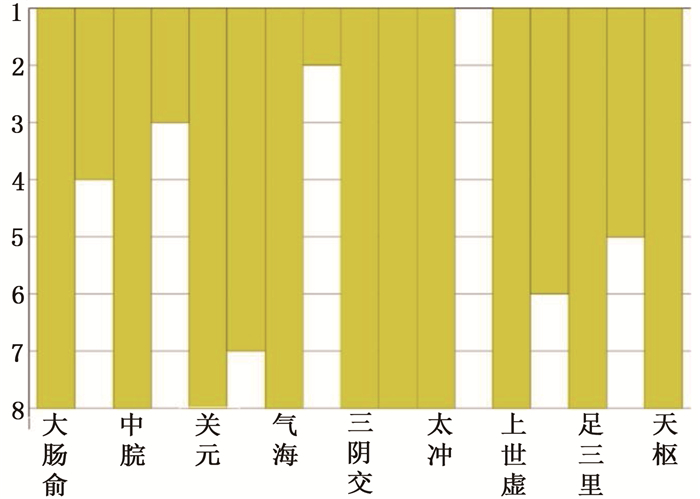
表 1 63个IBS-C针灸处方中频数>10次的穴位统计
序号 穴位 频数/次 频率/% 1 天枢 48 76.19 2 足三里 43 68.25 3 上巨虚 37 58.73 4 大肠俞 23 36.51 5 中脘 18 28.57 6 三阴交 14 22.22 7 太冲 14 22.22 8 气海 12 19.05 9 关元 12 19.05 表 2 IBS-C针灸处方的穴位归经频数统计
序号 归经 频数/次 频率/% 归经穴位及穴位频数 1 足阳明胃经 138 43.81 天枢(48)、足三里(43)、上巨虚(37)、下巨虚(4)、滑肉门(2)、外陵(2)、丰隆(1)、内庭(1) 2 任脉 57 18.10 中脘(18)、气海(12)、关元(12)、神阙(10)、下脘(3)、上脘(1)、膻中(1) 3 足太阳膀胱经 34 10.79 大肠俞(23)、肺俞(6)、肝俞(2)、肾俞(1)、脾俞(2) 4 足太阴脾经 26 8.25 三阴交(14)、大横(4)、公孙(3)、腹结(3)、阴陵泉(2) 5 足厥阴肝经 18 5.71 太冲(14)、期门(2)、行间(2) 6 督脉 17 5.40 百会(9)、印堂(7)、神庭(1) 7 手少阳三焦经 8 2.54 支沟(8) 8 手厥阴心包经 6 1.90 内关(6) 9 手阳明大肠经 4 1.27 曲池(2)、合谷(2) 10 经外奇穴 3 0.95 四神聪(2)、华佗夹脊穴(1) 11 足少阳胆经 2 0.63 阳陵泉(2) 12 足少阴肾经 2 0.63 太溪(1)、照海(1) 穴位总频数为315次。 表 3 IBS-C针灸处方的穴位所属部位频数统计
序号 部位 频数/次 频率/% 归经穴位 1 下肢部 125 39.68 足三里(43)、上巨虚(37)、太冲(14)、三阴交(14)、下巨虚(4)、公孙(3)、行间(2)、阳陵泉(2)、太溪(1)、丰隆(1)、照海(1)、内庭(1)、阴陵泉(2) 2 胸腹部 118 37.46 天枢(48)、中脘(18)、关元(12)、气海(12)、神阙(10)、大横(4)、下脘(3)、腹结(3)、滑肉门(2)、外陵(2)、膻中(1)、期门(2)、上脘(1) 3 背部 35 11.11 大肠俞(23)、肺俞(6)、肝俞(2)、脾俞(2)、华佗夹脊穴(1)、肾俞(1) 4 头部 19 6.03 百会(9)、印堂(7)、四神聪(2)、神庭(1) 5 上肢部 18 5.08 支沟(8)、内关(6)、曲池(2)、合谷(2) 穴位总频数为315次。 表 4 IBS-C针灸处方的特定穴统计
序号 特定穴 频数/次 频率/% 用穴数 穴位 1 下合穴 86 27.39 4 足三里(43)、上巨虚(37)、下巨虚(4)、阳陵泉(2) 2 五腧穴 75 23.89 9 足三里(43)、太冲(14)、支沟(8)、阴陵泉(2)、行间(2)、曲池(2)、阳陵泉(2)、太溪(1)、内庭(1) 3 募穴 71 22.61 5 天枢(48)、中脘(18)、期门(2)、关元(2)、膻中(1) 4 背俞穴 34 10.83 5 大肠俞(23)、肺俞(6)、肝俞(2)、脾俞(2)、肾俞(1) 5 八会穴 21 6.69 3 中脘(18)、阳陵泉(2)、膻中(1) 6 原穴 17 5.41 3 太冲(14)、合谷(2)、太溪(1) 7 络穴 10 3.18 3 内关(6)、公孙(3)、丰隆(1) 特定穴总频数为314次。 表 5 IBS-C的腧穴使用关联性分析
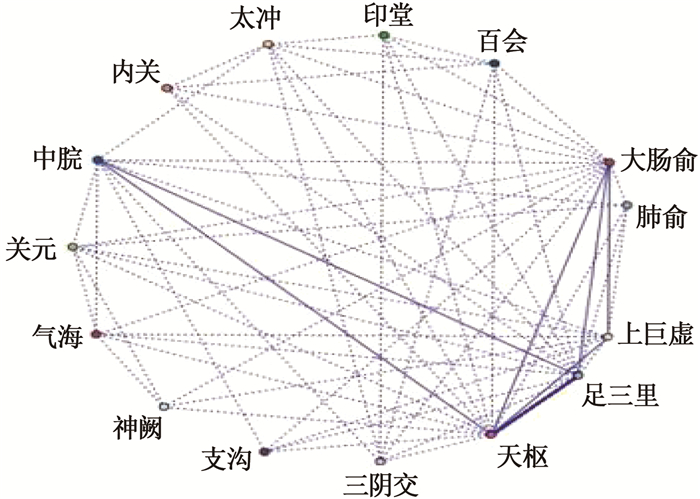
前项 后项 支持度/% 置信度/% 大肠俞-足三里 天枢 31.667 94.737 大肠俞 天枢 38.333 91.304 上巨虚-足三里 天枢 51.667 90.323 上巨虚 天枢 60.000 88.889 上巨虚-天枢 足三里 53.333 87.500 上巨虚 足三里 60.000 80.111 足三里 天枢 70.000 85.714 大肠俞-天枢 足三里 35.000 85.714 大肠俞 足三里 38.333 82.609 最小支持度设为30%, 最小置信度设为80%。 -
[1] 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠功能性疾病协作组, 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠动力学组. 2020年中国肠易激综合征专家共识意见[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2020, 40(12): 803-818. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311367-20201116-00660 [2] BRIAN E A, FERMIN M, LIN C, et al. Bowel disorders[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(5): 1393-1407. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27144627
[3] XIONG L S, CHEN M H, CHEN H X, et al. A population-based epidemiologic study of irritable bowel syndrome in South China: stratified randomized study by cluster sampling[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2004, 19(11): 1217-1224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01939.x
[4] 杨倩, 王小天, 杜姚, 等. 便秘型肠易激综合征药物治疗研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2015, 17(6): 5-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB201506001.htm [5] ZHENG H, CHEN R, ZHAO X, et al. Comparison between the effects of acupuncture relative to other controls on irritable bowel syndrome: a meta-analysis[J]. Pain Res Manag, 2019, 2019: 2871505. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31814859
[6] 韩亚飞, 王允亮, 李军祥. 腹泻型肠易激综合征发病机制及中药干预研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2018, 20(1): 114-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB201801036.htm [7] TANG B Z, ZHANG J L, YANG Z G, et al. Moxibustion for diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2016, 2016: 5105108. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4884811/pdf/ECAM2016-5105108.pdf
[8] MA X P, HONG J, AN C P, et al. Acupuncture-moxibustion in treating irritable bowel syndrome: how does it work[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(20): 6044-6054. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6044
[9] 刘新光. 肠易激综合征与罗马Ⅲ诊断标准[J]. 胃肠病学, 2006, 11(12): 736-738. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2006.12.010 [10] DOUGLAS A D. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: history, pathophysiology, clinical features, and rome Ⅳ[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(6): 1262-1279. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.032
[11] 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠动力学组. 肠易激综合征诊断和治疗的共识意见(2007, 长沙)[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2008, 28(1): 38-40. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0254-1432.2008.01.011 [12] 中华中医药学会脾胃病分会. 肠易激综合征中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J]. 中医杂志, 2017, 58(18): 1614-1620. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ201718024.htm [13] 沈雪勇. 经络腧穴学[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2016: 16-191. [14] 孙建梅, 李慧, 田耀洲. 便秘型肠易激综合征中西医机制研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2017, 19(3): 94-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB201703029.htm [15] 张浩, 车文文, 张静莎, 等. 针刺治疗便秘腧穴配伍规律文献研究[J]. 中医杂志, 2019, 60(19): 1692-1696. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ201919015.htm [16] 秦庆广, 王海萍, 刘坤, 等. 针刺天枢对正常、便秘和腹泻模型大鼠不同肠段运动功能的双向调节效应[J]. 世界中医药, 2013, 8(3): 245-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJZA201303004.htm [17] 冉国平, 刘嘉颖, 杨大业, 等. 电针足三里对肠易激综合征腹泻型大鼠炎性损伤的机制研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2019, 39(3): 342-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXJ201903017.htm [18] 朱文莲, 李滢, 杨帅, 等. 同神经节段不同穴位对肠易激综合征效应机制的比较研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2013, 28(11): 3224-3227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201311024.htm [19] 韩捷, 顾亚娇, 赵文霞, 等. 基于脑肠轴理论的俞募配穴法治疗气滞血瘀型功能性消化不良的临床观察[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育, 2017, 15(14): 115-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2017.14.052 [20] 王超, 王巧民, 宋继中, 等. 肠易激综合征患者精神心理因素对生活质量、睡眠质量以及症状严重程度的影响[J]. 胃肠病学, 2016, 21(1): 34-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2016.01.008 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 赵蕾,魏岚,费晓璐. 血糖间隙对药物保守治疗脑卒中患者症状性颅内出血的预测价值. 国际老年医学杂志. 2024(04): 414-418 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 廖青玲. 血清CK-MB、MYO、cTnI、NT-proBNP联合检测在急性心肌梗死早期诊断中应用价值. 黑龙江医学. 2024(15): 1844-1846 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韩佳玉,徐明星. 基于循证理念的延续护理对老年心血管疾病患者介入术后再发主要心血管不良事件的影响. 中国医药导报. 2023(10): 170-173+193 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘亚楠,张逸,吴慧. 司美格鲁肽对2型糖尿病患者心血管危险因素的影响. 糖尿病新世界. 2023(10): 73-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张俊峰,苏绍红. 急性心肌梗死主要不良心血管事件的血清指标预测研究. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(23): 31-36+42 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
