Expression of miR-1180 in non-small cell lung cancer and its clinical significance
-
摘要:目的 探讨微小RNA-1180(miR-1180)在非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者血清及组织中的表达情况,并分析其与临床病理特征的关系及对疾病诊断、预后评估的价值。方法 选取NSCLC患者72例,另选取同期接受治疗的良性肺部疾病患者50例为研究对象。收集NSCLC患者、良性肺部疾病患者的空腹静脉血,另收集NSCLC患者手术切除的癌组织和癌旁组织。采用实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)检测血清及组织中的miR-1180的相对表达量。所有NSCLC患者均进行为期5年的随访,并统计其生存情况。结果 NSCLC患者血清miR-1180的相对表达量高于良性肺部疾病患者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 癌组织中miR-1180的相对表达量高于癌旁组织,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。NSCLC患者血清及组织中miR-1180的相对表达量与性别、年龄、吸烟史、病理类型无关(P > 0.05), 与肿瘤大小、TNM分期、淋巴结转移以及分化程度有关(P < 0.05)。血清miR-1180对NSCLC的辅助诊断价值较高,曲线下面积(AUC)为0.747, 95%CI为0.580~0.914, 准确度为0.754。miR-1180高表达患者的5年生存率低于miR-1180低表达患者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 miR-1180在NSCLC的血清和癌组织中均呈异常高表达,且其表达水平与肿瘤的恶性进展密切相关。miR-1180可作为NSCLC疾病诊断和预后评估的新型生物标志物。Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression of miR-1180 in serum and tissues of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and to analyze its relationship with clinicopathological characteristics and its value for disease diagnosis and prognostic evaluation.Methods Seventy-two patients with NSCLC and 50 patients with benign lung disease who received treatment at the same period were selected as the study subjects. Fasting venous blood of NSCLC patients and those with benign lung diseases was collected, and the cancer tissues and adjacent tissues were collected from NSCLC patients. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction(qRT-PCR)was used to detect the relative expression of miR-1180 in serum and tissues. All patients with NSCLC were followed up for 5 years, and their survival status was counted.Results The relative expression levels of miR-1180 in serum of the NSCLC patients were significantly higher than those in patients with the benign lung diseases (P < 0.05); the relative expression of miR-1180 in the cancer tissues was significantly higher than that in the adjacent tissues (P < 0.05). The relative expression of miR-1180 in serum and tissues of NSCLC patients was not correlated with gender, age, smoking history and pathological type (P > 0.05), but was related to tumor size, TNM stage, lymph node metastasis and degree of differentiation (P < 0.05). Serum miR-1180 had a high value in the auxiliary diagnosis of NSCLC, the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.747, the 95%CI was 0.580~0.914, and the accuracy was 0.754. The 5-year survival rate of patients with miR-1180 high expression was significantly lower than that of patients with low expression of miR-1180 (P < 0.05).Conclusion MiR-1180 is abnormally highly expressed in serum and cancer tissues of NSCLC, and its expression level is closely related to the malignant progression of tumors. MiR-1180 can be used as a new biomarker for diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of NSCLC.
-
Keywords:
- non-small cell lung cancer /
- miR-1180 /
- diagnosis /
- prognosis /
- biomarkers /
- survival rate
-
冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病(CHD)在中国已成为仅次于脑卒中的第二大心血管病[1-2]。经桡动脉冠状动脉介入治疗(TRI)为CHD患者首选治疗方式。TRI术中心肌损伤、术后桡动脉并发症与年龄呈正相关[3-4]。缺血预处理(IPC)是通过袖带周期性加减压来刺激机体组织产生血管生长因子及抗损伤因子,提高组织耐受缺血缺氧能力,减少TRI相关并发症[5-6]。目前,临床多采用水银血压计或缺血预适应训练仪对患者术前进行200 mmHg高压力IPC[7-8], 效果方面双侧优于单侧[9], 上肢优于下肢[10], 5个循环优于3个循环[11]。但水银血压计全程需护士对袖带手动加压、减压与补压,常因操作不及时影响患者的舒适与IPC效果; 缺血预适应训练仪缺乏针对性,且自动补压感知精度在10~20 mmHg, 血压不高者在200 mmHg高压力的IPC期间舒适性较差。本研究观察应用双气道、双气泵、双换能器设计的定制智能血压计在IPC中的应用效果,旨在为临床提供高效、个性化的指导意见。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2020年2月—2023年2月行择期TRI治疗的老年CHD患者459例,随机分成A组、B组和C组,每组153例。其中,A组有3例患者不能耐受IPC,中途退出,最终纳入150例,其余456例患者均顺利配合完成本研究。纳入标准: ①年龄≥60岁者; ②择期行TRI者; ③双上肢健全无外伤者; ④双侧肱动脉收缩压均 < 140 mmHg者; ⑤凝血指标正常者。排除标准: ①符合急诊再灌注治疗指征[12]行急诊冠状动脉介入或溶栓治疗者; ②心、肾功能不全者; ③ Killip Ⅳ级者; ④不能耐受IPC者; ⑤恶性肿瘤者。本研究通过南京市第一医院伦理委员会审查,所有患者均知情同意。3组患者基线资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 3组患者一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]组别 年龄/岁 女性 高血压 糖尿病 血脂异常 收缩压/mmHg 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 病变血管支数 单支 双支 3支 A组(n=150) 70.10±6.52 49(32.67) 107(71.33) 60(40.00) 77(51.33) 118.90±10.22 24.17±3.24 27(18.00) 58(38.67) 65(43.33) B组(n=153) 70.31±6.12 50(32.68) 112(73.20) 69(45.10) 74(48.37) 119.13±10.58 24.24±3.36 35(22.87) 63(41.18) 55(35.95) C组(n=153) 69.05±5.68 36(23.53) 106(69.28) 50(32.67) 81(52.94) 118.55±10.15 24.14±3.05 33(21.57) 58(37.91) 62(40.52) 1.2 方法
成立IPC小组: IPC小组有主治医师2名,负责桡动脉B超; 副主任护师2名,担任组长; 主管护师8名。所有组员均顺利通过≥3次小组线下培训与考核。所有IPC操作均需2人在场进行,以确保数据的真实性。
A组: 护士使用同一台深圳力上松RIP双臂缺血预适应训练仪对患者双上肢进行IPC, 选择标准训练,调节IPC压力为200 mmHg(自动补压感知精度为10 mmHg)后一键运行,持续压迫5 min后袖带放气,间隔5 min后再重复上述循环,共计5次,术前1 d上午、下午及术前1~2 h各进行1次IPC。IPC期间需监测患者心率、血压等生命体征,如果患者不能耐受IPC, 即刻终止IPC。
B组: 护士使用2台深圳力上松RIP单臂缺血预适应训练仪先分别测量患者双上肢血压,然后选择标准训练,调节IPC压力高于测压处肱动脉收缩压50 mmHg[13-14]后一键运行, IPC时间、周期、频次、监测要点均同A组。
C组: 护士使用2台定制智能血压计(ZL201921841348.8、永康YK-BPA3)对患者双上肢进行IPC, 将袖带缠绕于双上肢后按启动键,智能血压计自动按照内置程序一键运行。先测量血压后,机器自动周期性加压、补压(感知精度为1 mmHg)压迫, IPC压力、时间、周期、频次、监测要点均同B组。
1.3 观察指标
① 手部发绀时间: IPC期间患者中指指尖与手掌末端出现发绀的时间。②麻木评分: 采用麻木视觉模拟评分进行评估,无麻木为0分,轻度麻木为1~3分,中度麻木为4~6分,重度麻木为7~9分[15]。③上臂皮下出血点。④操作时间: IPC期间护士缠绕双上肢袖带与操作仪器进行测压与设置模式、参数时间之和。⑤术中心绞痛、ST段偏移>1 mm发生情况及心率。⑥手部肿胀: 术后将患者腕横纹以下手部浸入装满水的容器中,使用同一力辰TD50002A电子分析天平测量溢出水的质量,评估手部肿胀程度[16]。⑦疼痛评分: 采用疼痛数字评分法,无痛为0分,轻度疼痛为1~3分,中度疼痛为4~6分,重度疼痛为7~10分。⑧桡动脉狭窄: 超声提示桡动脉内径前后减少15%即为桡动脉狭窄[17]。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 27.0软件进行数据分析,正态分布的计量资料用(x±s)表示,采用方差分析,组间比较行t检验; 非正态分布的计量资料用[M(P25, P75)]表示; 计数资料用[n(%)]表示,采用χ2检验。检验水准α=0.05。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 3组手部发绀、麻木、上臂皮下出血点发生情况及护士操作时间
IPC期间, B组、C组患者手部发绀时间晚于A组,麻木评分、上臂皮下出血点发生率低于A组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。A组、C组护士操作时间短于B组,且C组短于A组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 3组手部发绀时间、麻木时间、上臂皮下出血点发生率及护士操作时间比较(x±s)[M(P25, P75)][n(%)]组别 手部出现发绀时间/s 麻木评分/分 上臂皮下出血点 护士操作时间/s 中指指尖 手掌末端 A组(n=150) 79.73±5.34 115.62±9.12 7.00(6.00,7.00) 59(39.33) 32.36±5.96# B组(n=153) 97.31±6.05* 157.76±10.01* 5.00(5.00,6.00)* 27(17.64)* 86.53±6.14 C组(n=153) 96.86±5.85* 155.69±9.79* 6.00(5.00,6.00)* 30(19.61)* 21.63±5.68*# 与A组比较, *P < 0.05; 与B组比较, #P < 0.05。 2.2 3组术中心绞痛、ST段偏移>1 mm发生情况及心率
术中, A组、C组患者术中心绞痛、ST段偏移>1 mm发生率和心率低于B组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 3。
表 3 3组术中心绞痛、ST段偏移>1 mm发生情况及心率比较(x±s)[n(%)]组别 心绞痛 ST段偏移>1 mm 心率/(次/min) IPC前 术中 A组(n=150) 44(29.33)* 29(19.33)* 79.76±12.85 74.49±10.37* B组(n=153) 69(45.10) 51(33.33) 78.42±11.41 77.06±11.29 C组(n=153) 41(26.80)* 31(20.26)* 77.78±11.97 73.90±11.38* 与B组比较, *P < 0.05。 2.3 3组术后手部肿胀、疼痛评分与出院前桡动脉狭窄比较
A组、C组患者术后手部肿胀、疼痛评分低于B组,出院前桡动脉狭窄率低于B组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 4。
表 4 3组术后手部肿胀、疼痛评分与出院前桡动脉狭窄比较(x±s)[M(P25, P75)][n(%)]组别 手部肿胀/g 疼痛评分/分 桡动脉狭窄 术前 术后 A组(n=150) 255.67±31.75 262.33±33.45* 3.00(2.00, 4.00)* 31(20.67)* B组(n=153) 258.84±33.09 272.53±32.71 4.00(4.00, 5.00) 58(37.91) C组(n=153) 255.41±33.14 260.30±33.22* 3.00(3.00, 4.00)* 28(18.30)* 与B组比较, *P < 0.05。 3. 讨论
IPC是一种经济、有效、无创的保护心肌措施,近年来已被广泛应用于TRI术前,可有效提高患者术中组织耐受缺血缺氧能力[13]。老年人群的血压差异较大,双侧肱动脉收缩压差值在15 mmHg以内[18]。本研究中, A组有3例患者因不能耐受200 mmHg高压力的IPC退出研究,提示双侧200 mmHg高压力的IPC缺乏针对性,而既往研究[19]证实袖带压力高于收缩压50 mmHg即可有效阻断肱动脉血流。压力过高会增加患者肢体发绀、麻木等血液循环障碍与毛细血管损伤,压力过低会降低IPC效果。本研究结果表明, IPC期间B组、C组患者手部发绀时间、麻木评分、上臂皮下出血点发生率均优于A组。分析原因, B组、C组患者收缩压相对较低, IPC压力仅高于双侧收缩压50 mmHg, 远低于A组的200 mmHg, 低压力IPC减轻了手部、前臂静脉回流与微循环障碍、组织缺血缺氧,延缓患者中指指尖至手掌末端发绀时间,且手部神经较为丰富,从而降低了麻木感; A组高压力的IPC会造成神经组织损伤,进一步增加患者麻木感,也会造成微循环障碍与压迫处皮下组织、毛细血管、皮肤损伤[20], 增加上臂皮下出血点发生率。本研究结果亦表明, A组、C组护士操作时间短于B组,这是因为B组护士IPC前需要先测量双侧肱动脉血压,等待时间相对较长,之后还需要根据所测收缩压设置相应的IPC压力,相对比较耗时[21]; A组、C组省去了护士测压与等待时间。C组护士操作时间短于A组,这是因为A组护士IPC前需要先缠绕双侧袖带,再选择标准训练、调节IPC压力为200 mmHg后启动仪器一键运行,而C组护士IPC前仅需将袖带缠绕好后,按启动键一键运行即可。
老年CHD患者常伴有心绞痛、ST段偏移>1 mm, 在病变血管球囊扩张或支架释放的过程中,冠状动脉前向血流减少或中断会进一步加重患者的心肌缺血,导致心肌耗氧增加,心率增快。本研究结果显示, A组、C组患者术中心绞痛、ST段偏移>1 mm发生率及心率均优于B组,与张慧等[7]研究结果相似。这是因为C组定制智能血压计采用脉搏波技术,无创血压测量更精确,与有创无显著差异[22], 压力监测管道与充放气、补压管道为双通道设计, IPC期间压力减少1 mmHg即可感知并自动充气补压; A组、B组缺血预适应训练仪采用示波法、单通道设计,血压测量精确度低于水银血压计,比有创压更低,误差最高可达11.65 mmHg[23], IPC期间压力减少10 mmHg才充气补压。因此, B组IPC期间并不能充分阻断肱动脉血流,导致机体组织不能产生足够多的抗损伤因子,使心肌细胞耐受缺血缺氧能力不足; 而A组、C组分别以高、低压力阻断肱动脉血流,促使机体分泌应激性体液介质能力高于B组,在降低心肌细胞对氧需求与敏感性的同时,减轻了TRI术中的心肌缺血,可保护心肌[24-25]。
老年CHD患者常合并高血脂、糖尿病等疾病,血液循环相对较慢,术后桡动脉压迫期间会进一步减缓血流速度,从而加重患者手部的肿胀与疼痛,甚至桡动脉狭窄或闭塞。研究[6, 26]多以中指指围评估患者手部肿胀程度,测量时存在人为误差。通过高精度显示屏电子分析天平对整只手部溢水量进行测量,可更加直观、精确反映整只手部肿胀程度。本研究结果显示, A组、C组患者术后手部肿胀、疼痛评分均优于B组,与既往研究[6]结果相似。这是因为A组、C组IPC期间压力能充分阻断肱动脉血流,而B组不能。只有在充分压力IPC的1~2 h后机体组织才可分泌大量内源性保护因子,增强外周血管组织的防御与修复能力,加快外周动静脉血流速度[27-28], 从而减轻TRI术后桡动脉压迫期间因循环障碍引起的手部肿胀。此外, IPC后由于外周毛细血管通透性与密度增加,减轻了术后桡动脉压迫处因缺血缺氧引起的局部神经损伤,并延缓神经传导,进一步减轻了患者疼痛。本研究结果显示, A组、C组患者出院前桡动脉狭窄率均优于B组,与相关研究[17]结果相似。这是因为A组、C组由于IPC期间充分阻断了肱动脉血流,促使机体应激性产生足够的血管生长因子及抗损伤因子,术后使桡动脉内膜组织细胞对氧需求降低,桡动脉内膜增殖得到抑制; 此外,内源性组织保护因子足量释放也促使了桡动脉血管扩张,加之外周动脉血流的加速冲刷,有效减少了桡动脉的狭窄[17]。
综上所述,术前应用定制智能血压计针对性地实施高于双侧肱动脉收缩压50 mmHg的IPC, 在减少工作量的情况下, IPC效果与200 mmHg高压力相当,提高了患者舒适性,减少了毛细血管损伤。但本研究存在局限,本研究病例相对较少,后续将扩大样本量并结合B超优化IPC袖带压力,以期进一步提高患者舒适性。
-
表 1 NSCLC患者血清及组织中miR-1180的相对表达量与一般资料及临床病理特征的关系(x±s)
临床病理参数 n 血清miR-1180 t P 组织miR-1180 t P 性别 0.350 0.727 0.163 0.871 男 48 2.14±0.72 2.66±0.75 女 24 2.08±0.61 2.63±0.71 年龄 0.667 0.507 0.625 0.534 < 60岁 33 2.06±0.63 2.59±0.70 ≥60岁 39 2.17±0.75 2.70±0.78 吸烟史 0.766 0.446 0.569 0.571 有 52 2.16±0.73 2.68±0.75 无 20 2.02±0.59 2.57±0.69 病理类型 0.124 0.902 1.079 0.284 腺癌 42 2.13±0.69 2.73±0.78 鳞癌 30 2.11±0.65 2.54±0.67 肿瘤大小 3.342 0.001 7.059 < 0.001 < 3 cm 40 1.89±0.56 2.08±0.57 ≥3 cm 32 2.41±0.76 3.36±0.89 TNM分期 4.195 0.000 7.051 < 0.001 Ⅰ、Ⅱ期 44 1.87±0.57 2.13±0.61 Ⅲ期 28 2.52±0.74 3.47±0.88 淋巴结转移 2.702 0.009 4.755 < 0.001 有 32 2.36±0.73 3.09±0.77 无 40 1.93±0.62 2.30±0.64 分化程度 3.028 0.003 3.894 < 0.001 低分化 24 2.46±0.72 3.12±0.81 中高分化 48 1.95±0.65 2.42±0.67 表 2 血清miR-1180相对表达对NSCLC的诊断价值分析结果
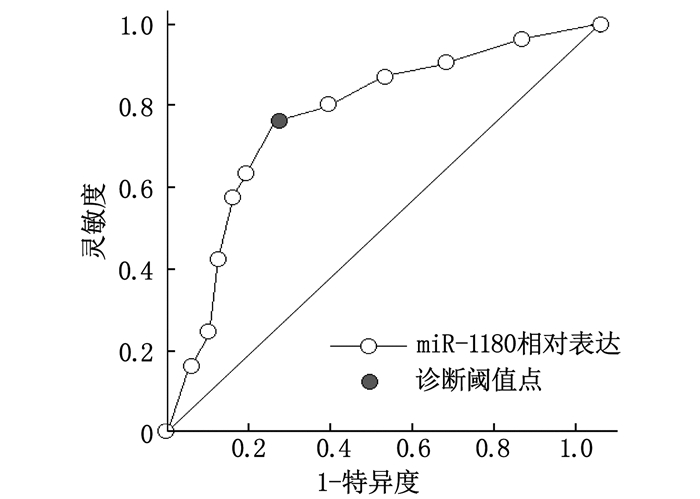
指标 AUC(95%CI) 阈值 灵敏度 特异度 约登指数 准确度 miR-1180相对表达 0.747(0.580~0.914) 1.60 0.764 0.740 0.504 0.754 表 3 NSCLC患者组织miR-1180高、低表达组的Kaplan-Meier生存期资料及比较[n(%)]
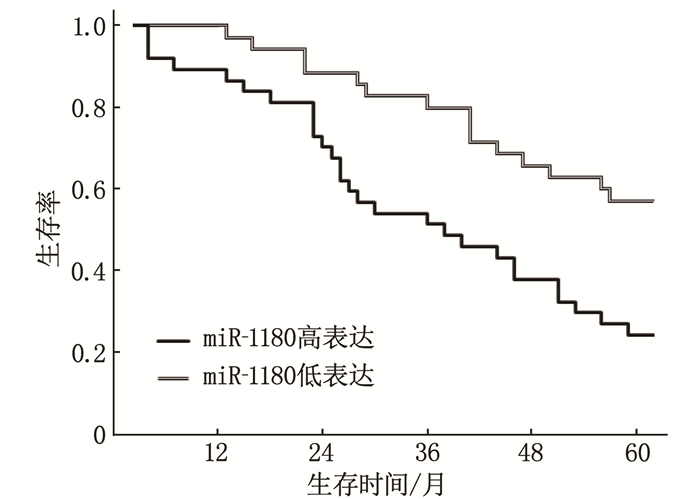
组别 n 3年生存 5年生存 中位生存期/月 miR-1180高表达组 37 19(51.35) 9(24.32) 36 miR-1180低表达组 35 28(80.00) 20(57.14)* — 与miR-1180高表达组比较, *P < 0.05。 -
[1] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
[2] DING N, ZHOU N, LI Q L, et al. Analysis of middle-and long-term efficacy of thoracoscope-assisted segmental resection of the lung on non-small cell lung cancer in the early stage[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15(3): 3662-3668.
[3] BICA-POP C, COJOCNEANU-PETRIC R, MAGDO L, et al. Overview upon miR-21 in lung cancer: focus on NSCLC[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2018, 75(19): 3539-3551. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2877-x
[4] KANG M, LI Y, ZHAO Y, et al. miR-33a inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting CAND1 in lung cancer[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2018, 20(4): 457-466. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1730-2
[5] ZHU D Y, GAO W X, ZHANG Z M. microRNA-1180 is associated with growth and apoptosis in prostate cancer via TNF receptor associated factor 1 expression regulation and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway activation[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15(4): 4775-4780.
[6] 余斌, 丁佑铭, 廖晓锋. 基于生物信息学的肝细胞癌组织miR-1180表达与临床意义分析[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2018, 27(7): 862-869. [7] 陈万青, 李贺, 孙可欣, 等. 2014年中国恶性肿瘤发病和死亡分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2018, 40(1): 5-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHLU201501001.htm [8] 孙可欣, 郑荣寿, 张思维, 等. 2015年中国分地区恶性肿瘤发病和死亡分析[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2019, 28(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHLU201901001.htm [9] 陈秀红, 李坤, 靳爽, 等. 非小细胞肺癌中卵巢肿瘤泛素异肽酶1与程序性死亡受体-1配体的表达相关性[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(23): 31-36. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20213152 [10] DETTERBECK F C, BOFFA D J, KIM A W, et al. The eighth edition lung cancer stage classification[J]. Chest, 2017, 151(1): 193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.10.010
[11] 李思佳, 宋新宇, 李文新. 肺癌干细胞的研究进展[J]. 巴楚医学, 2020, 3(1): 100-103, 111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BMJJ202001024.htm [12] 中华医学会, 中华医学会肿瘤学分会, 中华医学会杂志社. 中华医学会肺癌临床诊疗指南(2018版)[J]. 肿瘤研究与临床, 2018, 30(12): 793-824. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-9801.2018.12.001 [13] CHU G C W, LAZARE K, SULLIVAN F. Serum and blood based biomarkers for lung cancer screening: a systematic review[J]. BMC Cancer, 2018, 18(1): 181. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4024-3
[14] 黄成军, 关菁, 覃丽华. 微小RNA-1180对肝癌细胞侵袭迁移和TGF-β信号通路的影响[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2019, 24(11): 989-993. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2019.11.006 [15] GU L, ZHANG J Q, SHI M M, et al. The effects of miRNA-1180 on suppression of pancreatic cancer[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2017, 9(6): 2798-2806.
[16] GU Z W, HE Y F, WANG W J, et al. miR-1180 from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induces glycolysis and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer cells by upregulating the Wnt signaling pathway[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2019, 20(3): 219-237. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1800190
[17] GE Q Q, WANG C H, CHEN Z, et al. The suppressive effects of miR-1180-5p on the proliferation and tumorigenicity of bladder cancer cells[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2017, 32(1): 77-86.
[18] CHEN E G, ZHANG J S, XU S, et al. Long non-coding RNA DGCR5 is involved in the regulation of proliferation, migration and invasion of lung cancer by targeting miR-1180[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2017, 7(7): 1463-1475.
[19] CHEN M B, HUANG X M, LI L, et al. A regulatory axis of circ_0008193/miR-1180-3p/TRIM62 suppresses proliferation, migration, invasion, and Warburg effect in lung adenocarcinoma cells under hypoxia[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2020, 26: e922900.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 万建平,周强. 经直肠超声造影检查联合血清前列腺特异性抗原检测对前列腺癌的诊断及预后预测价值. 癌症进展. 2025(02): 236-239 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王安勇,高余杰,黄学东,张衡,朱杰. 尿道前列腺切除术联合经尿道膀胱取石治疗老年前列腺增生伴膀胱结石的疗效及预后. 中国临床医生杂志. 2024(03): 290-294 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 潘宗森,王慧. 经尿道前列腺钬激光剜除术在大体积良性前列腺增生中的应用效果. 浙江创伤外科. 2024(03): 538-541 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 黄登辉,周广臣. 前列腺特异性抗原灰区患者前列腺穿刺活检结果的相关影响因素分析. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(15): 77-81 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
