Infection of human papillomavirus and gene subtypes distribution in 56 434 female patients
-
摘要:目的 分析江苏省扬州市某医院女性人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)阳性感染情况,为扬州地区HPV防控策略的制订和疫苗的选用提供参考依据。方法 选取2018年1月—2020年12月江苏省扬州市妇幼保健院56 434例就诊女性的宫颈上皮脱落细胞标本,采用基因扩增及导流杂交技术对37种HPV亚型进行分型检测。结果 共检出HPV阳性样本12 900份,检出率为22.86%(12 900/56 434),其中单一感染(以高危型HPV亚型感染为主)占77.35%、多重感染(以高危型HPV亚型感染+低危型HPV亚型感染为主)占22.65%;36种HPV基因亚型被检出,检出率居前5位的高危型HPV亚型为HPV52、HPV16、HPV58、HPV53和HPV51;26~35岁女性的HPV感染检出率最高(25.07%),其次为36~45岁女性(24.45%)和46~55岁女性(20.96%)。结论 2018—2020年江苏省扬州市妇幼保健院就诊女性HPV感染以单一型感染、高危型感染为主,其中以HPV52、HPV16、HPV58、HPV53和HPV51基因亚型多见,扬州地区女性预防接种宜选用针对亚型中包含这5种亚型的HPV疫苗。Abstract:Objective To investigate the positive infection of human papillomavirus (HPV) in a hospital in Yangzhou of Jiangsu Province, and provide references for HPV prevention and control strategy as well as selection of vaccine.Methods The cervical epithelial cell samples from 56 434 women from January 2018 to December 2020 were selected, and 37 HPV subtypes were tested by gene amplification and diversion hybrid.Results A total of 12 900 HPV positive samples were detected, with a positive rate of 22.86%(12 900/56 434), among which single infection(mainly high-risk HPV subtypes infection) accounted for 77.35%, and multiple infections(mainly high-risk and low-risk HPV subtypes infection) for 22.65%. A total of 36 subtypes of HPV were detected, HPV 52, HPV16, HPV58, HPV53 and HPV51 ranked the top five in detection rate. The detection rate of HPV infection was the highest in women aged 26 to 35 (25.07%), followed by women aged 36 to 45 (24.45%) and women aged 46 to 55 (20.96%).Conclusion HPV positive Females in Yangzhou Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital of Jiangsu Province from 2018 to 2020 are mainly infected by single and high risk subtypes, HPV 52, HPV16, HPV58, HPV53 and HPV 51 gene subtypes are commonly seen. Therefore, HPV vaccines for these 5 subtypes should be selected for women in Yangzhou.
-
Keywords:
- human papillomavirus /
- genotyping /
- subtype /
- vaccine /
- infection
-
宫颈癌是全球范围内女性健康的重要威胁之一,发病率和病死率均较高,被列为女性第4大常见癌症[1]。人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)持续感染是造成宫颈癌的主要原因,宫颈癌患者的HPV感染率可高达99.7%[2]。相关研究[3]认为,持续性HPV感染易发展为癌前病变或宫颈癌,故宫颈癌的防控主要依赖于宫颈癌筛查和HPV疫苗接种。目前中国已批准上市的HPV疫苗有3种,即二价疫苗、四价疫苗和九价疫苗,这3种疫苗对HPV感染的预防效果及针对性尚有待继续深入研究。本研究对56 434例就诊女性进行HPV分型检测,旨在了解本地区女性HPV感染现状与亚型分布特点,从而为今后本地区HPV疫苗类型的选用和研发提供参考依据。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集2018年1月—2020年12月在江苏省扬州市妇幼保健院就诊的56 434例女性的宫颈上皮脱落细胞标本,就诊女性均自愿接受HPV筛查(含宫颈癌疫苗接种门诊接种前自愿行HPV检查者579例)。纳入标准: ①有性生活史且未注射HPV疫苗者; ②近期未接受宫颈侵入性诊疗、未使用过激素类药物者; ③未处于月经期、妊娠期、哺乳期者; ④ 3 d内未使用阴道内药物或阴道冲洗且24 h内未有性行为者。排除生殖道结构畸形者后,对纳入的研究对象进行宫颈上皮脱落细胞HPV分型筛查。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 样本采集
宫颈脱落细胞采样工作由妇科医生完成,采样步骤和样品保存方法参照HPV分型检测盒说明书。
1.2.2 检测方法
宫颈脱落细胞病毒基因亚型检测采用HPV核酸扩增分型检测试剂盒(凯普生物技术有限公司)、HHM-2基因扩增仪和凯普医用核酸分子快速杂交仪(凯普公司)进行,严格按照试剂盒说明书操作和判读结果。每份标本可一次性同时检测36种HPV亚型,包括18种高危型HPV亚型(HPV16、HPV18、HPV31、HPV33、HPV35、HPV39、HPV45、HPV51、HPV52、HPV53、HPV56、HPV58、HPV59、HPV66、HPV68、HPV26、HPV73和HPV82)和18种低危型HPV亚型[HPV6、HPV11、HPV42、HPV43、HPV44、HPV81(CP8304)、HPV34、HPV40、HPV54、HPV55、HPV61、HPV67、HPV69、HPV70、HPV71、HPV72、HPV83、HPV84]。2种或2种以上亚型阳性为多重感染。
1.3 统计学分析
使用Excel软件和SPSS 20.0软件对数据进行整理和统计学分析,计数资料以例和百分率(%)表示,比较采用卡方检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 HPV感染总体情况
56 434例就诊女性中, 2018、2019、2020年进行HPV检查者依次为19 853、19 423、17 158例,年龄为20~79岁。最终共检出HPV阳性样本12 900份,总阳性率为22.86%(12 900/56 434),其中单一感染(以高危型HPV亚型感染为主)占77.35%(9 978/12 900), 多重感染(以高危型HPV亚型感染+低危型HPV亚型感染为主)占22.65%(2 922/12 900)。
2.2 2018—2020年HPV亚型检出情况
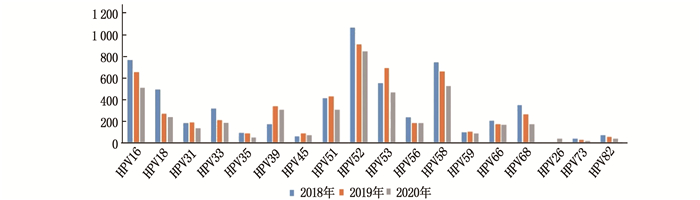
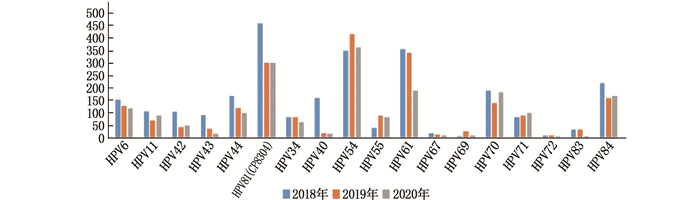
本研究中有36种HPV基因亚型被检出,其中高危型HPV亚型合计检出15 567项次,低危型HPV亚型合计检出6 563项次(多重感染者的各HPV亚型均分别计数),高危型HPV亚型的检出率高于低危型HPV亚型,差异有统计学意义(χ2=77.678, P<0.001)。高危型HPV亚型中,检出率居前5位的分别为HPV52(18.16%)、HPV16(12.44%)、HPV58(12.42%)、HPV53(10.96%)和HPV51(7.43%); 低危型HPV亚型中,检出率居前5位的分别为HPV54(17.19%)、HPV81(CP8304)(16.15%)、HPV61(13.44%)、HPV84(8.30%)和HPV70(7.76%)。见图 1、图 2、表 1。
表 1 2018年—2020年HPV基因亚型分布项次 类型 HPV亚型 2018年 2019年 2020年 合计 占比/% 高危型 HPV16 769 653 514 1 936 12.44 HPV18 495 268 241 1 004 6.45 HPV31 180 191 137 508 3.26 HPV33 316 212 189 717 4.61 HPV35 95 89 50 234 1.50 HPV39 170 339 310 819 5.26 HPV45 58 91 72 221 1.42 HPV51 417 430 310 1 157 7.43 HPV52 1 068 912 847 2 827 18.16 HPV53 549 691 466 1 706 10.96 HPV56 233 184 184 601 3.86 HPV58 745 662 526 1 933 12.42 HPV59 99 104 88 291 1.87 HPV66 208 170 165 543 3.49 HPV68 354 263 174 791 5.08 HPV26 0 0 41 41 0.26 HPV73 40 24 8 72 0.46 HPV82 69 56 41 166 1.07 合计 5 865 5 339 4 363 15 567 100.00 低危型 HPV6 150 127 116 393 5.99 HPV11 106 69 88 263 4.01 HPV42 105 43 48 196 2.99 HPV43 91 35 14 140 2.13 HPV44 167 120 98 385 5.87 HPV81(CP8304) 457 302 301 1 060 16.15 HPV34 84 82 62 228 3.47 HPV40 159 17 14 190 2.90 HPV54 349 417 362 1 128 17.19 HPV55 38 87 83 208 3.17 HPV61 356 339 187 882 13.44 HPV67 17 11 9 37 0.56 HPV69 8 25 4 37 0.56 HPV70 187 139 183 509 7.76 HPV71 82 89 100 271 4.13 HPV72 4 10 2 16 0.24 HPV83 34 34 7 75 1.14 HPV84 220 159 166 545 8.30 合计 2 614 2 105 1 844 6 563 100.00 多重感染者的各HPV亚型均分别计数。 2.3 不同年龄段女性HPV感染检出情况
将56 434例女性按照年龄的不同分成≤25岁组、26~35岁组、36~45岁组、46~55岁组、>55岁组,其中26~35岁组女性的HPV感染检出率最高(25.07%), 感染HPV亚型的总项次也最多,其次为36~45岁组和46~55岁组。见表 2。
表 2 不同年龄段女性的HPV感染检出情况组别 n HPV亚型/项次 HPV感染/例 感染检出率/% 低危型 高危型 合计 ≤25岁组 2 400 156 697 853 429 17.88 26~35岁组 17 917 2 168 5 300 7 468 4 492 25.07 36~45岁组 15 623 2 037 4 123 6 160 3 820 24.45 46~55岁组 14 439 1 717 3 680 5 397 3 026 20.96 >55岁组 6 055 485 1 767 2 252 1 133 18.71 合计 56 434 6 563 15 567 22 130 12 900 22.86 多重感染者的各HPV亚型项次均分别计数。 3. 讨论
本研究对江苏省扬州市妇幼保健院56 434例就诊女性进行HPV筛查的结果显示, 2018—2020年就诊女性HPV阳性率为22.86%(12 900/56 434), 低于安徽省铜陵市的25.36%[4], 略高于江苏省苏州市的22.55%[5]。中国地域辽阔、人口众多,不同地区居民经济条件、生活方式差异较大,可能是导致女性HPV阳性率表现出地域差异的原因[6]。
本研究中2018—2020年各HPV亚型检出情况显示,每年高危型HPV亚型的检出项次均远高于低危型HPV亚型,提示本地区女性HPV感染以高危型HPV亚型为主,其中检出率居前3位的高危型HPV亚型分别为HPV52、HPV16、HPV58。该高危型HPV亚型分布特征与北京市通州区[7]一致,但与某些地区的分布特征略有不同,如广州市香禺区的主要高危型HPV亚型为HPV16、HPV18、HPV31、HPV33等[8], 而河北省邯郸市的主要高危型HPV亚型为HPV16、HPV 52、HPV18、HPV53、HPV39[9]。由此表明,高危型HPV亚型分布呈现地区差异,但整体以HPV52、HPV16、HPV58为主。
本研究结果显示,受检女性中, HPV单一感染率最高,为17.68%(9 978/56 434), 与其他地区[10]结果一致。由此说明,虽然不同地区存在着经济、文化等多方面差异, HPV感染状况也存在着地域性差异,但HPV感染者还是以单一HPV亚型感染为主。此外,本研究发现大多数(80%以上)单一HPV亚型阳性者为高危型HPV亚型感染,与此前多项研究[11-12]结论一致。因此,高危型HPV亚型的筛查和控制仍是今后全世界范围内的宫颈癌防治工作的重点内容。相关研究[13]报道,多重HPV感染会使HPV阳性持续时间延长,并使患者发生宫颈病变的风险增大。本研究中,受检女性的多重HPV亚型感染率为5.18%(2 922/56 434), 关于多种HPV亚型阳性感染会否促使宫颈瘤变的发生、发展,有待后期继续开展临床跟踪随访研究加以证实。
本研究结果表明,本地区共检出36种HPV基因亚型,其中HPV52、HPV16、HPV58是本地区常见的高危型HPV亚型, HPV54、HPV81(CP8304)则是本地区常见的低危型HPV亚型。接种HPV疫苗是预防宫颈癌的有效手段,目前中国临床应用的预防性疫苗主要为二价疫苗(针对HPV16、HPV18)、四价疫苗(针对HPV16、HPV18、HPV6、HPV11)和九价疫苗(针对HPV6、HPV11、HPV16、HPV18、HPV31、HPV33、HPV45、HPV52和HPV58)。二价疫苗、四价疫苗均未涵盖本地区高危型HPV亚型HPV52、HPV58, 而九价疫苗虽涵盖了本地区感染率较高的HPV基因亚型及高危亚型,但存在着年龄使用限制,重要的是最适宜接种疫苗的年龄为16~26岁,且以无性生活者最佳。本研究结果显示,本地区26~35岁、36~45岁女性的HPV阳性率高于其他年龄段女性(这可能与26~45岁女性处于青壮年期、身体机能好、性生活史多有关),故预防性HPV九价疫苗并不完全适用于本地区女性。
综上所述,2018—2020年江苏省扬州市妇幼保健院就诊女性的HPV感染以单一型感染、高危型感染为主,其中以HPV52、HPV16、HPV58、HPV53和HPV51基因亚型多见,这为扬州地区女性宫颈癌预防方案的制订和HPV疫苗的选用(本地区女性预防接种宜选用针对亚型中包含这5种亚型的HPV疫苗)提供了一定参考依据。随着“后疫苗时代”的到来,对于HPV疫苗预防HPV感染和宫颈癌的效果,临床还需建立多学科、多中心数据共享机制,加强合作研究,以期降低HPV感染发生率,使女性同胞更多获益。
-
表 1 2018年—2020年HPV基因亚型分布
项次 类型 HPV亚型 2018年 2019年 2020年 合计 占比/% 高危型 HPV16 769 653 514 1 936 12.44 HPV18 495 268 241 1 004 6.45 HPV31 180 191 137 508 3.26 HPV33 316 212 189 717 4.61 HPV35 95 89 50 234 1.50 HPV39 170 339 310 819 5.26 HPV45 58 91 72 221 1.42 HPV51 417 430 310 1 157 7.43 HPV52 1 068 912 847 2 827 18.16 HPV53 549 691 466 1 706 10.96 HPV56 233 184 184 601 3.86 HPV58 745 662 526 1 933 12.42 HPV59 99 104 88 291 1.87 HPV66 208 170 165 543 3.49 HPV68 354 263 174 791 5.08 HPV26 0 0 41 41 0.26 HPV73 40 24 8 72 0.46 HPV82 69 56 41 166 1.07 合计 5 865 5 339 4 363 15 567 100.00 低危型 HPV6 150 127 116 393 5.99 HPV11 106 69 88 263 4.01 HPV42 105 43 48 196 2.99 HPV43 91 35 14 140 2.13 HPV44 167 120 98 385 5.87 HPV81(CP8304) 457 302 301 1 060 16.15 HPV34 84 82 62 228 3.47 HPV40 159 17 14 190 2.90 HPV54 349 417 362 1 128 17.19 HPV55 38 87 83 208 3.17 HPV61 356 339 187 882 13.44 HPV67 17 11 9 37 0.56 HPV69 8 25 4 37 0.56 HPV70 187 139 183 509 7.76 HPV71 82 89 100 271 4.13 HPV72 4 10 2 16 0.24 HPV83 34 34 7 75 1.14 HPV84 220 159 166 545 8.30 合计 2 614 2 105 1 844 6 563 100.00 多重感染者的各HPV亚型均分别计数。 表 2 不同年龄段女性的HPV感染检出情况
组别 n HPV亚型/项次 HPV感染/例 感染检出率/% 低危型 高危型 合计 ≤25岁组 2 400 156 697 853 429 17.88 26~35岁组 17 917 2 168 5 300 7 468 4 492 25.07 36~45岁组 15 623 2 037 4 123 6 160 3 820 24.45 46~55岁组 14 439 1 717 3 680 5 397 3 026 20.96 >55岁组 6 055 485 1 767 2 252 1 133 18.71 合计 56 434 6 563 15 567 22 130 12 900 22.86 多重感染者的各HPV亚型项次均分别计数。 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA: Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] WALBOOMERS J M, JACOBS M V, MANOS M M, et al. Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide[J]. J Pathol, 1999, 189(1): 12-19. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199909)189:1<12::AID-PATH431>3.0.CO;2-F
[3] TOMMASINO M. The human papillomavirus family and its role in carcinogenesis[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2014, 26: 13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.11.002
[4] 胡志军, 朱娟娟, 潘晓龙, 等. 铜陵市2815例女性高危型HPV感染状况及基因型分布特征[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2020, 32(3): 322-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWS202003018.htm [5] 李伟, 王燕华, 杨如, 等. 苏州地区不同年龄女性HPV感染的流行病学调查[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2020, 28(10): 1753-1756. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2020.10.032 [6] 韦梦娜, 余艳琴, 徐慧芳, 等. 中国大陆地区不同宫颈病变人群中人乳头瘤病毒感染率及型别分布的系统研究[J]. 中国肿瘤临床与康复, 2020, 27(2): 133-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZK202002002.htm [7] 张爱凤, 贾丽华, 裴俊丽. 北京通州地区女性生殖道高危型HPV感染现状与宫颈病变关系的研究[J]. 中国妇产科临床杂志, 2020, 21(1): 58-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKLC202001020.htm [8] 高惠芳, 叶耀群, 冼海燕, 等. 番禺区8000例宫颈HPV检查结果分析[J]. 国际医药卫生导报, 2013, 19(8): 1083-1085. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-1245.2013.08.010 [9] 李静霞, 刘文利, 刘悦君, 等. 邯郸地区女性人乳头瘤病毒感染基因型分布特点临床分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2017, 32(20): 4926-4928. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFYB201720011.htm [10] NAMUDURI R P, LEE L Y, AAN KOH M J. Combination of oral acitretin, antiretroviral therapy, human papillomavirus vaccine, and carbon dioxide laser ablation for the treatment of giant condyloma acuminatum of the vulva in a patient with AIDS[J]. Dermatol Ther, 2020, 33(6): el4253. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32862466/
[11] JIN R, QIAN H, ZHANG Y, et al. The prevalence and genotype distribution of human papillomaviruses among women in Taizhou, China[J]. Medicine: Baltimore, 2019, 98(39): e17293. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017293
[12] ZHANG C, CHENG W, LIU Q, et al. Distribution of human papillomavirus infection: a population-based study of cervical samples from Jiangsu Province[J]. Virol J, 2019, 16(1): 67. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1175-z
[13] CAMARGO M, DEL RÍO-OSPINA L, SOTO-DE LEÓN S C, et al. Association of HIV status with infection by multiple HPV types[J]. Trop Med Int Heal, 2018, 23(11): 1259-1268. doi: 10.1111/tmi.13142
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 蒲茜,文曰,卢春燕. 腹腔镜结直肠癌术后吻合口瘘的防治与护理进展. 实用临床医药杂志. 2025(02): 143-148 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 赵云,崔健. 食管癌术后吻合口瘘的危险因素研究. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(01): 37-40 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 黄晓媚,郭明,骆俊龙,包传恩,胡蒙. 血清血管内皮生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子-1水平与胸腔镜食管癌根治术后食管胃吻合口漏的相关性研究. 临床外科杂志. 2024(03): 276-280 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 黄淑珍,刘杰,刘翠. 早期营养护理干预对食管癌根治术后患者免疫功能及营养指标的影响. 中外医疗. 2024(08): 179-182 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郭丽娟,陈燕青. 早期营养支持和睡眠干预对食管癌患者术后睡眠质量的效果观察. 世界睡眠医学杂志. 2024(06): 1414-1416+1420 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 林金娇,林春燕,许妙灵. 针对性护理方案对食管癌患者术后睡眠质量的影响. 中国卫生标准管理. 2023(04): 169-173 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 苗露,刘智慧,李荣. 国内成人癌症患者鼻肠管肠内营养不良反应发生率的Meta分析. 河南外科学杂志. 2023(02): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李宁宁,李翠,龚兰娟,周林荣,李金霞,谢静. 基于ERAS理念的营养管理模式对食管癌患者术后恢复的影响. 中华养生保健. 2023(04): 130-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
