Application of artificial intelligence-assisted pulmonary nodule screening and qualitative diagnosis
-
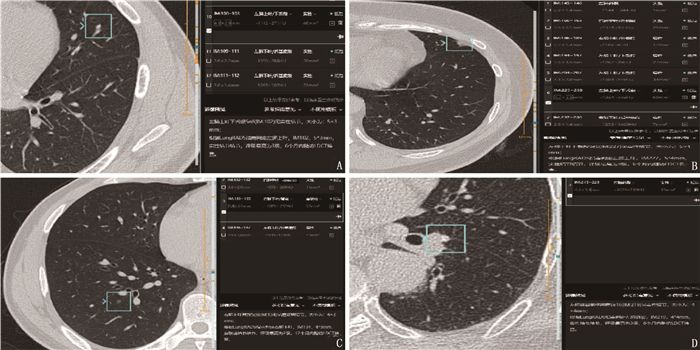
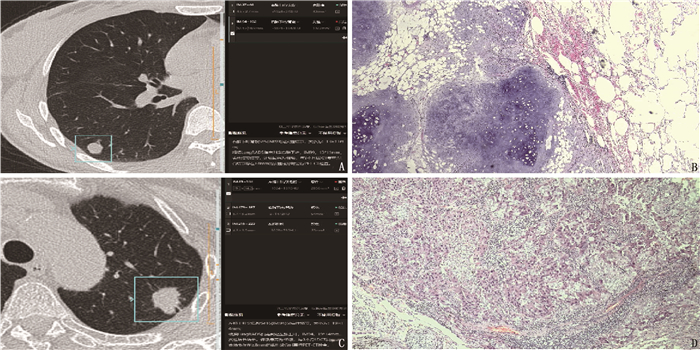
摘要:目的 探讨人工智能(AI)辅助诊断软件在胸部低剂量CT肺结节筛查及定性诊断的临床研究与应用价值。方法 回顾性分析病理确诊的103例肺结节患者的临床资料,将103例肺结节患者术前的胸部低剂量CT图像导入杏脉锐影肺结节AI分析软件中,采用AI及放射医师阅片的方法筛查肺结节并进行良恶性诊断,将AI辅助诊断软件与放射医师对肺结节的筛查情况进行比较,并以病理诊断为金标准,分析AI辅助诊断软件与放射医师诊断的准确性。结果 103例患者胸部低剂量CT共筛查出258个结节, AI辅助软件与放射医师检出肺结节的敏感度分别为96.12%、89.53%, 阳性预测值分别为95.00%、100.00%; AI辅助诊断软件筛查检出肺结节的假阳性率为5.00%, 放射医师未检查出假阳性肺结节。AI辅助诊断软件与放射医师对肺结节的筛查能力比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。103例肺结节患者病理检查共诊断出108个肺结节, AI辅助诊断软件及放射医师诊断肺结节的敏感度分别为95.35%、91.86%,特异度分别为72.73%、81.82%。结论 AI辅助诊断软件在肺结节筛查检出及恶性结节诊断方面具有较高的准确性,但肺结节良恶性鉴别准确率低于放射医师。因此, AI辅助诊断软件可作为一种辅助手段与放射医师诊断相结合来提高肺结节的总体诊疗效能。
-
关键词:
- 人工智能辅助诊断软件 /
- 低剂量计算机断层扫描 /
- 肺结节 /
- 良恶性 /
- 筛查 /
- 定性诊断
Abstract:Objective To explore the clinical research and application value of artificial intelligence (AI) aided diagnosis software in lung nodule screening and qualitative diagnosis of CT screening of chest low-dose CT.Methods The clinical data of 103 patients with pulmonary nodules diagnosed by pathology were analyzed retrospectively. The preoperative chest low-dose CT images of 103 patients with pulmonary nodules were imported into the AI analysis software of apricot pulse sharp shadow pulmonary nodules. The methods of AI and radiologists′film reading were used to screen pulmonary nodules and make benign and malignant diagnosis. The AI aided diagnosis software was compared with the screening of pulmonary nodules by radiologists, and the pathological diagnosis was taken as the gold standard, the accuracy of AI aided diagnosis software and radiologist diagnosis was analyzed.Results A total of 258 nodules were detected by chest low-dose CT in 103 patients. The sensitivity of pulmonary nodules detected by AI assistant software and radiologist were 96.12% and 89.53%, respectively, the positive predictive values were 95.00% and 100.00%, respectively, the false positive rate of pulmonary nodules detected by AI assisted diagnostic software was 5.00%, and radiologists did not detect false positive pulmonary nodules. There was significant difference between AI aided diagnosis software and radiologists in screening ability of pulmonary nodules (P < 0.05). A total of 108 nodules were diagnosed by pathological examination in 103 patients with pulmonary nodules, the sensitivity of AI aided diagnosis software and radiologists in diagnosing pulmonary nodules were 95.35% and 91.86%, respectively, and the specificities were 72.73% and 81.82%, respectively.Conclusion AI aided diagnosis software has high accuracy in the screening and detection of pulmonary nodules and the diagnosis of malignant nodules, but the accuracy of differentiating benign from malignant pulmonary nodules is lower than that of radiologists. Therefore, AI aided diagnosis software as an auxiliary approach can be combined with diagnosis of radiologists to improve the overall diagnosis and treatment efficiency of pulmonary nodules. -
-
表 1 AI与放射医师对真性肺结节筛查能力的比较[n(%)]
阅片方式 阳性 阴性 AI辅助诊断软件阅片 248(96.12) 10(3.88) 放射医师阅片 231(89.53)* 27(10.47)* 与AI阅片比较, *P < 0.05。 表 2 AI与放射医师对肺结节诊断效能比较
% 阅片方式 敏感度 特异度 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 χ2 P AI辅助诊断软件阅片 95.35 72.73 93.18 80.00 0.100 0.752 放射医师阅片 91.86 81.82 95.18 72.00 0.364 0.547 -
[1] CHRISTIE J R, LANG P, ZELKO L M, et al. Artificial intelligence in lung cancer: bridging the gap between computational power and clinical decision-making[J]. Can Assoc Radiol J, 2021, 72(1): 86-97. doi: 10.1177/0846537120941434
[2] TANDON Y K, BARTHOLMAI B J, KOO C W. Putting artificial intelligence (AI) on the spot: machine learning evaluation of pulmonary nodules[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2020, 12(11): 6954-6965. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2019-cptn-03
[3] JOY MATHEW C, DAVID A M, JOY MATHEW C M. Artificial Intelligence and its future potential in lung cancer screening[J]. Excli J, 2020, 19: 1552-1562.
[4] MOLDOVANU D, DE KONING H J, VAN DER AALST C M. Lung cancer screening and smoking cessation efforts[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2021, 10(2): 1099-1109. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-899
[5] MESA- GUZMÁN M, GONZÁLEZ J, ALCAIDE A B, et al. Surgical outcomes in a lung cancer-screening program using low dose computed tomography[J]. Arch Bronconeumol, 2021, 57(2): 101-106. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2020.03.026
[6] SATHYAKUMAR K, MUNOZ M, SINGH J, et al. Automated lung cancer detection using artificial intelligence (AI) deep convolutional neural networks: a narrative literature review[J]. Cureus, 2020, 12(8): e10017.
[7] OUDKERK M, LIU S Y, HEUVELMANS M A, et al. Lung cancer LDCT screening and mortality reduction-evidence, pitfalls and future perspectives[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18(3): 135-151. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-00432-6
[8] PINSKY P. Artificial intelligence and data mining to assess lung cancer risk: challenges and opportunities[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2020, 173(9): 760-761. doi: 10.7326/M20-5673
[9] ATHER S, KADIR T, GLEESON F. Artificial intelligence and radiomics in pulmonary nodule management: current status and future applications[J]. Clin Radiol, 2020, 75(1): 13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2019.04.017
[10] 戴正行, 胡春洪, 王希明, 等. 基于DenseNet网络深度学习法CT图像人工智能分析技术判断肺结节良恶性[J]. 放射学实践, 2020, 35(4): 484-488. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202004020.htm [11] BINCZYK F, PRAZUCH W, BOZEK P, et al. Radiomics and artificial intelligence in lung cancer screening[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2021, 10(2): 1186-1199. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-708
[12] 王亮, 许迪, 孙丹丹, 等. 人工智能辅助软件可提升疲劳状态下放射科规培医师对肺结节的检测效能[J]. 放射学实践, 2021, 36(4): 475-479. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202104017.htm [13] 彭志强, 郭静波, 邓晓, 等. 人工智能在肺小结节诊断中的临床研究与应用[J]. 中国医学装备, 2021, 18(9): 42-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZB202109011.htm [14] 李欣菱, 郭芳芳, 周振, 等. 基于深度学习的人工智能胸部CT肺结节检测效能评估[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2019, 22(6): 336-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ201906002.htm [15] PRAYER F, RÖHRICH S, PAN J, et al. Künstliche Intelligenz in der Bildgebung der Lunge[Artificial intelligence in lung imaging][J]. Radiologe, 2020, 60(1): 42-47. doi: 10.1007/s00117-019-00611-2
[16] 蔡雅倩, 张正华, 韩丹, 等. AI对肺磨玻璃结节筛查及定性的临床应用研究[J]. 放射学实践, 2019, 34(9): 958-962. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS201909008.htm [17] 赵呈华. 人工智能辅助诊断系统联合CT检查肺结节的诊断价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2020, 24(19): 9-11. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.202019003 -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 张伟. NT-proBNP、D-D、CRP检测在中老年急性脑梗死患者中的临床诊断价值分析. 中国实用医药. 2024(10): 81-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨光,毛婷婷,陈红蕾,张海燕. 间质性肺疾病急性加重期患者外周血D-二聚体、B型钠尿肽的检测应用. 锦州医科大学学报. 2024(03): 61-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘爱平. 动态检测D-二聚体浓度在急性脑梗死患者溶栓治疗中的意义. 中国实用医药. 2023(05): 89-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孙培丽,孙贵祥,许秀兰. 急性脑梗死静脉溶栓短期预后的影响因素分析. 北京医学. 2022(03): 209-212 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张洁菁,余小萍,沈捷玉. cTnⅠ、Mb、D-D、Hcy水平变化与急性脑梗死患者预后的相关性研究. 黑龙江医药. 2021(02): 447-449 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李海燕,肖瑾,刘兵荣,吴婷. 凝血酶原时间、活化部分凝血酶原时间、纤维蛋白原、C反应蛋白、脑钠肽检测对急性脑梗死诊断价值研究. 临床军医杂志. 2020(02): 219-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘芳卉. 急性大面积脑梗死患者的临床急救护理措施探讨. 心理月刊. 2020(07): 123 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 林梓波. 血清指标因子在急性脑梗死治疗前后的评估意义. 黑龙江医药. 2020(04): 933-934 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 俞峰,郑毅敏,张帅,吴峰. 血清可溶性肿瘤坏死因子样弱凋亡诱导因子、B型利钠肽、基质金属蛋白酶1水平与扩张型心肌病患者左心室重构的关系. 中国基层医药. 2020(12): 1472-1476 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 王珏,孙杰,徐乾治. 急性脑梗死患者的血浆D-二聚体和N末端B型钠尿肽前体水平及其意义分析. 内科. 2020(05): 592-593+610 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号