Effects of electroacupuncture on hippocampal neuron autophagy and IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage
-
摘要:目的
探讨电针对缺氧缺血性脑损伤(HIBD)新生大鼠海马神经元自噬及胰岛素样生长因子1(IGF-1)/磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(Akt)通路的影响。
方法将108只新生大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、IGF-1组(0.2 mg/kg)、电针组、电针联合LY294002组(电针+PI3K抑制剂0.3 mg/kg),每组18只。采用左颈总动脉结扎和低氧处理2 h的方法构建新生大鼠HIBD模型(造模成功率为80%)。各组大鼠在手术清醒后和电针治疗结束后进行神经功能缺陷评分;酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)检测脑组织IGF-1的含量;苏木精-伊红(HE)染色观察脑组织病理学变化;透射电镜观察细胞自噬情况;免疫荧光双标法检测自噬标志物与神经元特异性核蛋白(NeuN)的共定位表达;Western blot法检测海马组织PI3K/Akt通路、自噬相关蛋白的表达[PI3K、磷酸化PI3K(p-PI3K)、Akt、磷酸化p-Akt(p-Akt)、Beclin-1、微管相关蛋白轻链3Ⅱ(LC3-Ⅱ)、微管相关蛋白轻链3Ⅰ(LC3-Ⅰ)]。
结果与假手术组相比,HIBD模型组大鼠海马中神经元损伤加重,神经功能缺损评分、海马组织Beclin-1和LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ表达增加,脑组织IGF-1的含量以及海马组织p-PI3K/PI3K、p-Akt/Akt的表达降低;与模型组相比,IGF-1组、电针组神经元损伤减轻,神经功能缺损评分、Beclin-1和LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ、自噬小体数量、LC3/NeuN共表达的神经元减少或降低,脑组织IGF-1的含量、p-PI3K/PI3K、p-Akt/Akt的表达升高;上述差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。LY294002能显著降低IGF-1的水平,减弱电针对海马组织IGF-1/PI3K/Akt通路的激活和海马神经元自噬的抑制作用。
结论电针可能通过激活IGF-1/PI3K/Akt通路,抑制海马神经元过度自噬,减轻新生大鼠HIBD。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the effects of electroacupuncture on hippocampal neuron autophagy and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway in neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD).
MethodsA total of 108 neonatal rats were randomly divided into sham operation group, model group, IGF-1 group (0.2 mg/kg), electroacupuncture group, electroacupuncture combined with LY294002 group (electroacupuncture combined with 0.3 mg/kg PI3K inhibitor), with 18 rats in each group. HIBD model of neonatal rats was established by ligation of left common carotid artery and hypoxia treatment for 2 hours (the success rate of modeling was 80%). The rats in each group were scored for neurological deficits at being awake after the operation and after electroacupuncture treatment; ELISA was used to detect the content of IGF-1 in brain tissues; hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was used to observe the pathological change of brain tissues; transmission electron microscope was used to observe the cell autophagy; immunofluorescence double-labeling method was used to detect the colocalization expression of autophagy markers and neuron-specific nuclear protein (NeuN); western blot method was used to detect the expression of PI3K/Akt pathway and autophagy-related proteins in hippocampus[PI3K, phosphorylated PI3K (p-PI3K), Akt, phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), Beclin-1, microtubule-related protein light chain 3Ⅱ (LC3-Ⅱ), and microtubule-related protein light chain 3Ⅰ (LC3-Ⅰ)].
ResultsCompared with the sham operation group, the neuron damage in the hippocampus of the HIBD model group was aggravated, the neurological deficit score, the Beclin-1 and LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-I expression in the hippocampus were increased, while the IGF-1 content in brain tissues, p-PI3K/PI3K and p-Akt/Akt expression in hippocampus were reduced; compared with the model group, the neuron damage in the IGF-1 group and the electroacupuncture group was alleviated, the neurological deficit score, Beclin-1 and LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ, the number of autophagosomes and the LC3/NeuN co-expressed neurons were decreased or reduced, while the IGF-1 content in brain tissues, p-PI3K/PI3K and p-Akt/Akt expression were increased; the differences mentioned above were statistically significant (P<0.05). LY294002 was able to significantly reduce the level of IGF-1, weaken the activation of the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway of hippocampus and the inhibition of hippocampal neuron autophagy by electroacupuncture.
ConclusionElectroacupuncture may inhibit excessive autophagy of hippocampal neurons by activating the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway, thereby alleviating HIBD in neonatal rats.
-
缺氧缺血性脑损伤(HIBD)是一种因氧气和流向大脑的脑血流减少导致神经功能缺损而引发的疾病,是新生儿中常见且严重的神经系统疾病,也是导致新生儿死亡的主要原因之一[1]。幸存的婴儿通常伴有脑瘫、智力低下和其他后遗症,严重影响生存质量[2]。目前,临床尚缺乏用于治疗HIBD的标准和具体措施,因此迫切需要寻找新的神经保护疗法来减轻HIBD导致的神经损伤。近年来研究[3]发现胰岛素样生长因子1(IGF-1)与HIBD关系密切,具有促进神经元及胶质细胞增生分化和营养支持的功能,在脑缺血、缺氧后保护神经元、修复受损神经元及恢复认知功能损害等过程中发挥重要作用,有望作为脑保护剂用于临床缺血缺氧的治疗。
自噬参与HIBD的发生,研究[4-5]发现当缺氧缺血刺激诱导自噬过度激活时会加剧脑损伤,在HIBD后通过抑制自噬激活可发挥神经保护作用。研究[6]显示针刺可通过上调IGF-1的表达来改善脑卒中后血管性认知障碍,促进神经发育,治疗小儿脑性瘫痪[7]。电针是在针灸针上接通微量不连续或连续的电流,以进一步将针刺刺激产生的效应传导至大脑,从而促进神经功能的恢复与重塑[8]。电针能提高IGF-1表达水平,改善脑梗死患者神经功能及脑血流动力学[9]。IGF-1主要通过调控磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(Akt) 发挥神经保护作用[10-11]。本研究通过建立新生大鼠HIBD模型,探讨电针对新生大鼠IGF-1的影响及其可能的作用机制,现将结果报告如下。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物
Sprague Dawley孕鼠15只,产仔10~12只,购自上海SLAC实验动物有限公司,生产许可证号为SCXK(沪)2019-0006, 动物质量合格证号为202021 563.65。将孕鼠在单独的无菌塑料笼中饲养,在22~23 ℃、55%~60%湿度以及12 h光照与12 h黑暗的周期交替下进行,孕鼠可自由进食和饮水。使用108只7 d日龄的Sprague Dawley(SD)大鼠幼崽进行实验,体质量15~20 g。本研究获得机构动物护理和使用委员会批准{2020[伦理]第(3)号)},并遵循《实验动物的护理和使用指南》。
1.2 主要试剂及仪器
IGF-1(瑞士Roche公司,货号250-19); LY294002(PI3K抑制剂,北京百奥莱博科技有限公司,货号YT333); HE染色试剂(C0105)、RIPA裂解液(P0013B)、BCA试剂盒(P0010)均购自碧云天生物科技公司; 大鼠胰岛素样生长因子1(IGF-1) 检测试剂盒(北京百奥莱博科技有限公司,货号ZN2874-HXK); 兔抗大鼠PI3K(ab191606)、p-PI3K(ab182651)、AKT(ab18785)、p-AKT(ab38449)、LC3A/B(ab128025)、Beclin-1(ab210498)、β-actin(ab8227)、山羊抗兔IgG H & L(HRP)(ab205718)、山羊抗兔IgG H & L(Alexa Fluor®488)(ab150077)(绿色)、小鼠抗NeuN (ab279296)、山羊抗小鼠IgG H & L(Alexa Fluor®594)(ab150116)(红色)均购自英国abcam公司。
电针仪(G6805-2A)购自上海华谊医疗仪器有限公司; 透射电子显微镜(H-7500)购自日本日立公司; iMark680多功能酶标仪、蛋白转膜装置(美国Bio-Rad公司); 倒置荧光显微镜(IX73)购自日本Olympus公司。
1.3 分组、模型制备及处理
从108只新生大鼠中随机选取18只为假手术组,均用3%的异氟烷麻醉,并在整个手术过程中以2%的麻醉剂量进行维持。除假手术组外,其他大鼠采用左颈总动脉结扎和低氧处理2 h的方法构建新生大鼠HIBD模型[12]。在颈部中线做小切口,分离并结扎左颈总动脉; 缝合切口,将幼崽置于加热的毯子上恢复1 h, 而后将其放入部分浸没在37 ℃水浴中的500 mL密封广口瓶中; 将含8%氧气和92%氮气的混合气体送入广口瓶中2 h; 将大鼠移出并暴露于空气中,观察大鼠的自由运动,然后将其放回各自的母鼠笼中。假手术组仅分离左颈总动脉,不进行结扎和缺氧处理。若大鼠出现乏力、站立不稳、左侧肢体瘫痪与提尾时左侧前爪紧抱等表现,提示HIBD模型构建成功。造模成功后存活72只大鼠,死亡18只,考虑到新生大鼠各器官发育不完善,造模比较艰难,故造模成功率80%属正常可接受的范围。
将模型制备成功的大鼠随机分为4组,即模型组、IGF-1组(0.2 mg/kg)[13]、电针组、电针联合LY294002组(电针+PI3K抑制剂0.3 mg/kg)[14], IGF-1组在缺氧缺血后即刻腹腔注射IGF-1(0.2 mg/kg), 电针组在造模后2 h按照实验动物学所公认的针灸取穴位置,选取神庭(大鼠头前正中线,额顶骨缝交线前方)、百会穴(大鼠头部前正中线,两耳尖连线中点)开始电针治疗,应用G6805-2A电针仪进行电针刺激,电压峰值4 V, 疏密波,以针体轻轻抖动为标准,频率维持在5~10 Hz, 10 min/次, 1次/d; 电针联合LY294002组在缺氧缺血后即刻腹腔注射LY294002(0.3 mg/kg), 造模后2 h开始电针治疗,操作方法同电针组。电针治疗14 d后进行取材和相关指标的检测。
1.4 取材及指标检测
1.4.1 神经功能缺陷评分
各组大鼠在手术清醒后和电针治疗结束后进行神经行为评分。评分标准: 0分为无明显神经功能缺损; 1分为提尾时不能伸展对侧前肢; 2分为行走时向对侧旋转; 3为行走时向对侧倾斜; 4分为不能自主活动或伴意识障碍。分数越高表示神经功能缺陷越严重。
1.4.2 酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)检测脑组织IGF-1的含量
行为学检测结束后,每组随机选取6只大鼠,断头取脑,分离海马组织,称重后按1∶9的比例加入预冷的生理盐水,研磨后离心,取上清为10%的脑组织匀浆, ELISA试剂盒检测大鼠脑组织匀浆中IGF-1的含量。
1.4.3 脑组织病理学变化
每组随机选取6只大鼠进行麻醉,用4.0%多聚甲醛与2.5%戊二醛的混合溶液灌注,然后断头取脑,沿冠状位切分为2个部分,一部分经2.5%戊二醛溶液固定,用于透射电镜; 另一部分经4.0%多聚甲醛固定,石蜡包埋、切片后行HE染色,观察脑组织病理学变化。
1.4.4 透射电镜观察细胞自噬情况
取戊二醛溶液固定的脑组织,采用0.1 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液冲洗3次后, 1%锇酸固定液, 4 ℃固定2 h。梯度酒精脱水,浸透包埋,行超薄切片(60~70 nm厚),染色,显微镜下观察海马CA1区自噬小体的形成情况并拍照。
1.4.5 免疫荧光双标法检测LC3与神经元特异性核蛋白(NeuN)的共定位表达
取1.4.3步骤中的脑组织石蜡切片,二甲苯脱蜡, 磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)清洗后微波修复15 min, 正常山羊血清封闭20 min, 加入一抗(兔抗LC3和小鼠抗NeuN, 1∶100), 4 ℃孵育过夜,洗去一抗,分别加入荧光二抗(Alexa Fluor 488标记的山羊抗兔和Alexa Fluor 594标记的山羊抗小鼠IgG, 1∶300), 37 ℃避光孵育1 h, PBS冲洗3次,抗荧光淬灭剂封片,显微镜下对切片进行观察和拍照。
1.4.6 Western blot法检测海马组织PI3K/Akt通路、自噬相关蛋白的表达
每组剩余6只大鼠,取脑,分离海马组织。按照试剂盒说明书的操作提取海马组织中的总蛋白, BCA法测定蛋白浓度后取等量蛋白质样品上样, SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳,湿转法转膜, 5%脱脂奶粉封闭,加入一抗(PI3K、p-PI3K、Akt、p-Akt、自噬基因Beclin-1、LC3A/B, 按1∶1 000的比例稀释; β-actin按1∶2 000的比例稀释), 4 ℃下孵育过夜, HRP标记的羊抗兔IgG二抗(1∶5 000)室温孵育1 h, ECL显色,以β-actin为内参,通过与内参的灰度比得出目的条带的相对表达水平。
1.5 统计学分析
采用SPSS 21.0和Image pro plus 6.0软件进行统计分析。数据采用均值±标准差(x±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA), 组间有差异进一步采用SNK-q检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 各组大鼠神经功能缺损评分比较
在模型制备前,所有大鼠的神经功能均正常; 模型制备成功后,与假手术组相比,HIBD模型组大鼠出现行动迟缓、活动减少、左侧肢体瘫痪、提尾时左侧前爪紧抱等表现,神经功能缺损评分升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 治疗结束后,与模型组相比, IGF-1组、电针组、电针联合LY294002组神经功能改善,神经功能缺损评分降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 与电针组相比,电针联合LY294002组神经功能缺损评分升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 各组大鼠神经功能缺损评分比较(x±s)分 组别 n 治疗前 治疗后 假手术组 18 0±0 0±0 模型组 18 2.45±0.20* 2.34±0.22* IGF-1组 18 2.38±0.19* 1.45±0.17*# 电针组 18 2.37±0.23* 1.53±0.16*# 电针联合LY294002组 18 2.42±0.21* 1.98±0.21*#△ 与假手术组比较, * P<0.05; 与模型组相比, #P<0.05;与电针组相比, △P<0.05。 2.2 各组大鼠脑组织IGF-1的含量
与假手术组相比,模型组大鼠脑组织IGF-1的含量降低; 与模型组相比, IGF-1组、电针组、电针联合LY294002组大鼠脑组织IGF-1的含量增加; 与电针组相比,电针联合LY294002组脑组织IGF-1的含量降低; 上述组间差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 各组大鼠脑组织IGF-1的含量(x±s)组别 n IGF-1/(pg/mL) 假手术组 6 226.78±11.30 模型组 6 131.34±12.16* IGF-1组 6 195.66±15.47*# 电针组 6 182.75±13.23*# 电针联合LY294002组 6 154.06±12.75*#△ IGF-1: 胰岛素样生长因子1。
与假手术组相比, * P<0.05;与模型组相比, #P<0.05; 与电针组相比, △P<0.05。2.3 各组大鼠脑组织病理学变化
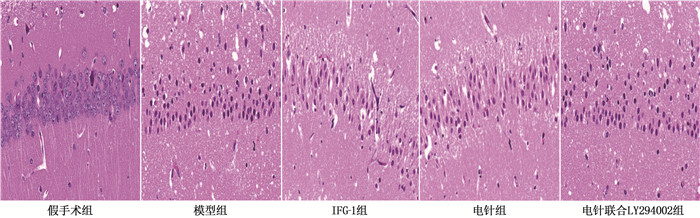
假手术组大鼠脑组织海马CA1区细胞形态规则、排列紧密,未出现明显的损伤; 模型组大鼠海马中存在严重的病理损伤, CA1区可见神经元肿胀、细胞核固缩、排列疏松、神经元密度降低; IGF-1组、电针组大鼠上述病理改变明显减轻,神经元密度增加; 与电针组相比,电针联合LY294002组大鼠海马神经细胞数量明显减少。见图 1。
2.4 各组大鼠海马CA1区自噬情况
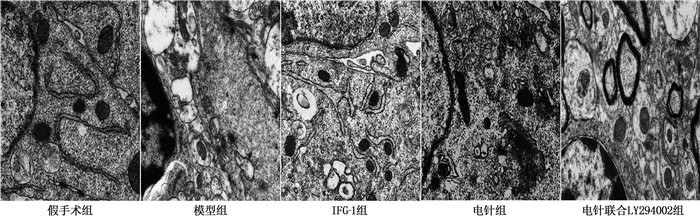
假手术组大鼠海马CA1区神经元结构基本正常,胞质内细胞器形态及数量正常,未见自噬小体/溶酶体的形成; 模型组大鼠海马CA1区细胞结构破坏,呈空泡样变的神经元较多,可见大量溶酶体和自噬小体形成; IGF-1组、电针组大鼠海马CA1区可见自噬小体/溶酶体数量减少,且细胞形态相对正常,可见相对完整的线粒体和内质网; 与电针组相比,电针联合LY294002组自噬小体/溶酶体数量增加。见图 2。
2.5 各组大鼠海马CA1区LC3与NeuN的共定位表达
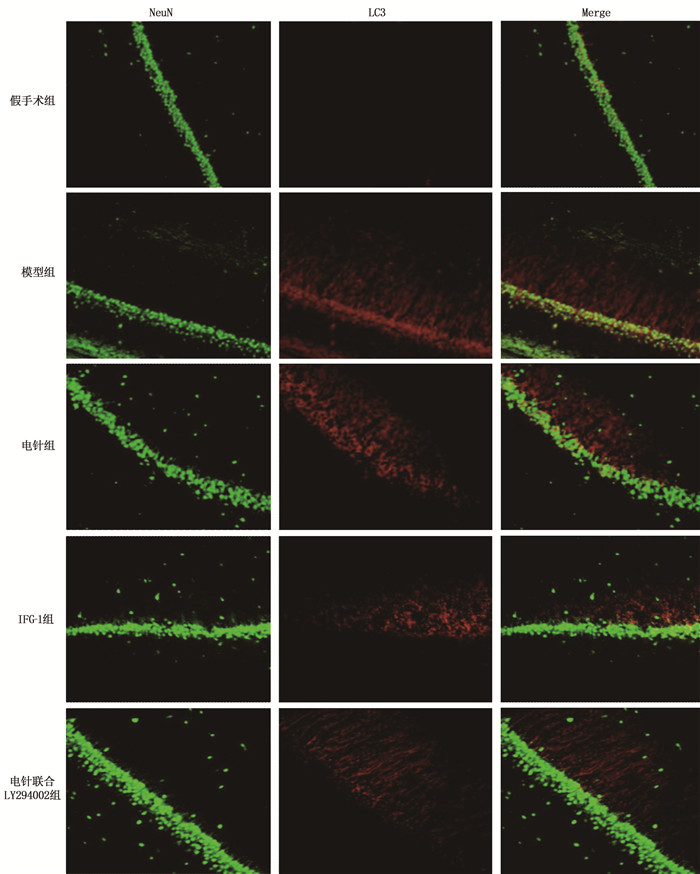
假手术组大鼠海马CA1区未见LC3与NeuN共表达的神经元; 模型组海马中可见大量LC3/NeuN强阳性的LC3神经元; IGF-1组、电针组大鼠海马CA1区LC3/NeuN共表达的神经元明显减少; 与电针组相比,电针联合LY294002组LC3/NeuN共表达的神经元数量增加。见图 3。
2.6 各组大鼠海马组织PI3K/Akt通路、自噬相关蛋白的表达
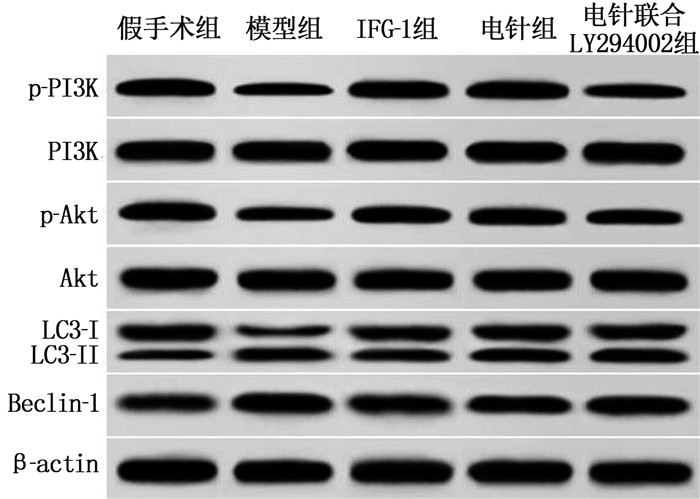
Western blot法检测结果显示,与假手术组相比,模型组大鼠海马组织中p-PI3K/PI3K、p-Akt/Akt的表达降低, Beclin-1和LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ表达升高; 与模型组相比, IGF-1组、电针组p-PI3K/PI3K、p-Akt/Akt的表达升高, Beclin-1和LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ表达降低; 与电针组相比,电针联合LY294002组海马组织p-Akt/Akt的表达降低, Beclin-1和LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ表达升高; 上述组间差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图 4、表 3。
表 3 各组大鼠脑组织PI3K/Akt通路、自噬相关蛋白的表达(x±s)组别 n p-PI3K/PI3K p-Akt/Akt LC3-II/LC3-Ⅰ Beclin-1 假手术组 6 0.86±0.05 0.72±0.07 0.51±0.05 0.35±0.04 模型组 6 0.43±0.04* 0.36±0.04* 1.28±0.09* 0.84±0.07* IGF-1组 6 0.75±0.07* 0.61±0.06* 0.74±0.07*# 0.53±0.05*# 电针组 6 0.72±0.05*# 0.58±0.05*# 0.80±0.06*# 0.61±0.07*# 电针联合LY294002组 6 0.54±0.06*#△ 0.43±0.06*#△ 0.96±0.09*#△ 0.73±0.06*#△ 与假手术组比较, * P<0.05; 与模型组比较, #P<0.05; 与电针组比较, △P<0.05。 3. 讨论
HIBD可能引起永久性的脑损伤,导致神经系统残疾甚至死亡。在缺血的早期阶段,海马神经元很容易受损,而坏死、凋亡和自噬是神经元死亡的主要途径。自噬参与了HIBD的发病机制,有研究[15]认为促进自噬或可部分缓解HIBD病情,但当缺氧、缺血刺激诱导自噬过度激活时,则会加剧脑损伤[16]。本研究结果显示, HIBD模型大鼠具有明显的神经功能缺损表现,通过观察海马神经细胞的超微结构变化,发现HIBD大鼠缺血侧CA1区细胞结构破坏,溶酶体和自噬小体数量显著增多,免疫荧光共定位结果进一步显示海马LC3/NeuN共表达的神经元显著增多,说明HIBD大鼠海马神经元自噬被激活。研究[17-18]表明自噬的抑制在体内和体外的新生儿脑缺氧、缺血模型中可以提供神经保护作用。
针刺对HIBD的疗效肯定[7-8]。研究[19-20]发现,针刺可通过改善脑血流量、调节自噬、抑制细胞凋亡、促进神经营养因子及其受体表达、刺激神经干细胞的增殖和分化等发挥对损伤脑组织的保护作用。电针是在针灸针上接通微量电流,可加强针刺刺激产生的效应,在镇痛、缓解肢体痉挛、改善运动障碍等方面疗效显著,具有不良反应少、可重复性好、疗效佳等优点。黄金等[21]发现,电针可上调大鼠皮质及海马区PI3K、AKT、Beclin-1的表达,改善脑卒中后认知障碍; 孙晓伟等[22]发现电针在再灌注中晚期可降低LC3A/B蛋白表达,抑制脑缺血再灌注大鼠神经细胞自噬的过度激活,从而拮抗神经元的进一步损伤; 黄倩茹等[23]发现电针可促进缺氧缺血性脑损伤大鼠的发育; 上述研究均说明电针可能通过调节自噬来减轻脑缺血缺氧后的神经元损伤。本研究结果显示,电针干预后大鼠神经功能缺损情况明显减轻; HE染色和免疫荧光共定位结果显示电针可减少海马神经元丢失,减少自噬小体和LC3阳性表达的神经元的数量,减轻海马组织损伤; 上述结果说明电针可能通过抑制自噬减轻新生大鼠HIBD。
IGF-1是一种活性单链多肽分子,广泛存在于哺乳动物中枢神经系统中,可以透过血脑屏障,是维持神经元存活的神经因子之一,能对各种神经损伤产生反应,激活多种细胞内信号传导通路。UMRAN R M等[24]研究表明,新生儿在子宫内或出生时发生缺血缺氧时, IGF-1水平较低,与HIBD的预后相关; 增加神经细胞对IGF-1的分泌作用可能减轻HIBD[3-4]。实验和临床研究均表明早期补充IGF-1可以减少缺氧/缺血事件后的脑损伤[25-26]。本研究结果也显示,与正常新生大鼠相比, HIBD大鼠脑组织中IGF-1水平显著降低,而给予IGF-1和电针干预后, IGF-1的水平明显增加,海马神经元损伤减轻,说明电针可能是通过上调IGF-1的表达而减轻新生大鼠HIBD。PI3K/Akt信号通路是其发挥作用的主要通路, Akt是PI3K途径的中心介质, IGF-1与其受体结合后,可通过PI3K激活Akt的磷酸化,进一步磷酸化下游的mTOR及其他靶蛋白,从而介导炎症、自噬和凋亡等多种生物学效应,并对新生大鼠脑缺氧缺血损伤发挥神经保护作用[14]。WANG X W等[5]发现IGF-1通过IGF-1R/PI3K-Akt-mTOR途径抑制帕金森病动物和细胞模型中的过度自噬;ZHAO B等[27]发现在缺氧缺血性脑病中, IGF-1可改善缺氧引起的磷酸化Akt的下调,保护神经干细胞免受缺氧诱导的凋亡。本研究结果显示,给予IGF-1和电针干预后, HIBD大鼠海马组织p-PI3K/PI3K、p-Akt/Akt的表达显著升高, Beclin-1和LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ表达显著降低;使用PI3K的抑制剂LY294002能显著降低IGF-1的水平,减弱电针对海马组织IGF-1/PI3K/Akt通路的激活和海马神经元自噬的抑制作用; 上述结果提示电针可能通过激活IGF-1/PI3K/Akt通路来抑制HIBD大鼠海马神经元过度自噬。
综上所述,电针可能通过激活IGF-1/PI3K/Akt通路而抑制海马神经元过度自噬,减轻新生大鼠HIBD。由于自噬的双重作用,在脑缺氧缺血的不同时期,电针可能发挥不同的作用,其在脑缺氧、缺血的早期对自噬的影响有待进一步的研究。
-
表 1 各组大鼠神经功能缺损评分比较(x±s)
分 组别 n 治疗前 治疗后 假手术组 18 0±0 0±0 模型组 18 2.45±0.20* 2.34±0.22* IGF-1组 18 2.38±0.19* 1.45±0.17*# 电针组 18 2.37±0.23* 1.53±0.16*# 电针联合LY294002组 18 2.42±0.21* 1.98±0.21*#△ 与假手术组比较, * P<0.05; 与模型组相比, #P<0.05;与电针组相比, △P<0.05。 表 2 各组大鼠脑组织IGF-1的含量(x±s)
组别 n IGF-1/(pg/mL) 假手术组 6 226.78±11.30 模型组 6 131.34±12.16* IGF-1组 6 195.66±15.47*# 电针组 6 182.75±13.23*# 电针联合LY294002组 6 154.06±12.75*#△ IGF-1: 胰岛素样生长因子1。
与假手术组相比, * P<0.05;与模型组相比, #P<0.05; 与电针组相比, △P<0.05。表 3 各组大鼠脑组织PI3K/Akt通路、自噬相关蛋白的表达(x±s)
组别 n p-PI3K/PI3K p-Akt/Akt LC3-II/LC3-Ⅰ Beclin-1 假手术组 6 0.86±0.05 0.72±0.07 0.51±0.05 0.35±0.04 模型组 6 0.43±0.04* 0.36±0.04* 1.28±0.09* 0.84±0.07* IGF-1组 6 0.75±0.07* 0.61±0.06* 0.74±0.07*# 0.53±0.05*# 电针组 6 0.72±0.05*# 0.58±0.05*# 0.80±0.06*# 0.61±0.07*# 电针联合LY294002组 6 0.54±0.06*#△ 0.43±0.06*#△ 0.96±0.09*#△ 0.73±0.06*#△ 与假手术组比较, * P<0.05; 与模型组比较, #P<0.05; 与电针组比较, △P<0.05。 -
[1] GRECO P, NENCINI G, PIVA I, et al. Pathophysiology of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review of the past and a view on the future[J]. Acta Neurol Belg, 2020, 120(2): 277-288. doi: 10.1007/s13760-020-01308-3
[2] YANG L J, ZHAO H H, CUI H. Treatment and new progress of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2020, 35(9): 929-936.
[3] JANOWSKA J, GARGAS J, ZIEMKA-NALECZ M, et al. Oligodendrocyte response to pathophysiological conditions triggered by episode of perinatal hypoxia-ischemia: role of IGF-1 secretion by glial cells[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2020, 57(10): 4250-4268. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02015-z
[4] JIANG L J, XU Z X, WU M F, et al. Resatorvid protects against hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2020, 15(7): 1316-1325. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.272615
[5] WANG X W, YUAN L J, YANG Y, et al. IGF-1 inhibits MPTP/MPP+-induced autophagy on dopaminergic neurons through the IGF-1R/PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway and GPER[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 319(4): E734-E743. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00071.2020
[6] 王琼芬, 王科, 王风波, 等. 智三针联合头针治疗卒中后血管性认知障碍的疗效及对VILIP-1、IGF-1水平影响[J]. 针灸临床杂志, 2020, 36(9): 5-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJLC202009003.htm [7] 鲍劲松, 童光磊, 周陶成, 等. 五神针联合Bobath运动疗法治疗小儿脑性瘫痪临床疗效及对血清白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、胰岛素样生长因子1水平的影响[J]. 河北中医, 2020, 42(1): 106-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBZY202001022.htm [8] 梁勤. 针刺治疗在新生儿缺血缺氧性脑损伤中的应用研究[J]. 中医临床研究, 2018, 10(22): 30-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYLY201822013.htm [9] 徐文文, 廖庆红, 王丽芳. 电针对急性脑梗死患者脑血流动力学及血清bFGF、IGF-1的影响[J]. 上海针灸杂志, 2019, 38(9): 969-972. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHZJ201909005.htm [10] ZAMBERLETTI E, GABAGLIO M, PISCITELLI F, et al. Cannabidivarin completely rescues cognitive deficits and delays neurological and motor defects in male Mecp2 mutant mice[J]. J Psychopharmacol, 2019, 33(7): 894-907. doi: 10.1177/0269881119844184
[11] LIN J Y, KUO W W, BASKARAN R, et al. Swimming exercise stimulates IGF1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α survival signaling to suppress apoptosis and inflammation in aging Hippocampus[J]. Aging, 2020, 12(8): 6852-6864. doi: 10.18632/aging.103046
[12] XUE H, XU Y, WANG S, et al. Sevoflurane post-conditioning alleviates neonatal rat hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury via Ezh2-regulated autophagy[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2019, 13: 1691-1706. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S197325
[13] LI J, AN Y, WANG J N, et al. Curcumin targets vascular endothelial growth factor via activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and improves brain hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rats[J]. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol, 2020, 24(5): 423-431. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.5.423
[14] 胥虹贝, 母松, 朱艳含, 等. 电针通过PI3K/AKT信号通路动员脑缺血/再灌注大鼠骨髓内皮祖细胞至外周血[J]. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2018, 27(6): 527-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGZZ201806005.htm [15] 陈彰强, 余丹, 彭晓红, 等. 依托咪酯调控Sirt1/FOXO1通路对心肌缺血再灌注大鼠模型的保护作用[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 医学版, 2021, 50(3): 308-314. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1672-0741.2021.03.007 [16] CORTI O, BLOMGREN K, POLETTI A, et al. Autophagy in neurodegeneration: new insights underpinning therapy for neurological diseases[J]. J Neurochem, 2020, 154(4): 354-371. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15002
[17] WANG S, XUE H, XU Y, et al. Sevoflurane postconditioning inhibits autophagy through activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade, alleviating hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats[J]. Neurochem Res, 2019, 44(2): 347-356. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2682-9
[18] WU J J, YANG Y L, GAO Y F, et al. Melatonin attenuates Anoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting excessive mitophagy through the MT2/SIRT3/FoxO3a signaling pathway in H9c2 cells[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2020, 14: 2047-2060. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S248628
[19] 曲乐, 吴君燕, 袁青. 针刺对宫内窘迫导致的缺氧缺血脑损伤大鼠海马炎性反应的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2021, 46(1): 14-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYJ202101003.htm [20] 高静, 赖名殷, 秦玮珣, 等. 针刺对宫内窘迫缺血缺氧脑损伤新生大鼠行为学及海马神经元自噬的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2020, 45(4): 275-280, 324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYJ202004005.htm [21] 黄金, 李瑞青, 吴明莉, 等. 电针神庭、百会穴对脑缺血再灌注大鼠学习记忆能力及自噬相关蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2019, 37(4): 838-841, 1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS201904015.htm [22] 孙晓伟, 刘婷婷, 孙忠人, 等. 电针对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠神经细胞自噬影响的实验研究[J]. 针灸临床杂志, 2019, 35(1): 58-63, 89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJLC201901016.htm [23] 黄倩茹, 萨喆燕, 潘晓华, 等. 电针长强穴对缺血缺氧脑损伤大鼠发育的影响[J]. 云南中医学院学报, 2018, 41(1): 25-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZY201801006.htm [24] UMRAN R M, AL-TAHIR M, JAGDISH D, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in term newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Am J Perinatol, 2016, 33(7): 640-645.
[25] VAES J E G, KOSMEIJER C M, KAAL M, et al. Regenerative therapies to restore interneuron disturbances in experimental models of encephalopathy of prematurity[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 22(1): E211.
[26] HELLSTRÖM A, LEY D, HANSEN-PUPP I, et al. Role of insulinlike growth factor 1 in fetal development and in the early postnatal life of premature infants[J]. Am J Perinatol, 2016, 33(11): 1067-1071.
[27] ZHAO B, ZHENG Z B. Insulin growth factor 1 protects neural stem cells against apoptosis induced by hypoxia through Akt/mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Akt/MAPK/ERK) pathway in hypoxia-ishchemic encephalopathy[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2017, 23: 1872-1879.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 苑功名,苏枫雅,李佩云,郭永明,张健,徐媛,吕中茜,赵季宇,公一囡. 基于针刺调节程序性细胞死亡探讨其脑保护作用. 针刺研究. 2025(02): 210-216 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 田秀文,梁启恒. 瑞马唑仑通过调控miR-155/JAK2/STAT3信号通路对缺氧缺血性脑损伤大鼠神经功能的保护作用. 中国老年学杂志. 2025(05): 1209-1213 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 蔡昭莲,陈薏帆,喻仁宇,钟晓勇,洪燕飞,周慧坪,张兵. 早期电针长强穴对缺血缺氧性脑损伤大鼠海马CA1区神经元损伤及细胞自噬的影响. 福建中医药. 2024(09): 12-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 潘廷辉,陈成贤,郭系文,杨德慧,丁俊东,陈丹,罗红相. 骨髓间充质干细胞(MSCs)对氧糖剥夺(OGD)损伤后海马神经元自噬的作用. 中国典型病例大全. 2024(04): 23-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 孙婧妍,吴臣,于国强,于晓红,杨添淞. 血管性痴呆相关生物标志物的应用价值及针刺干预方案研究进展. 中华全科医学. 2023(08): 1379-1382+1387 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号