Roles and molecular mechanism of microRNA-491 on proliferation, invasion and migration of cervical cancer cells
-
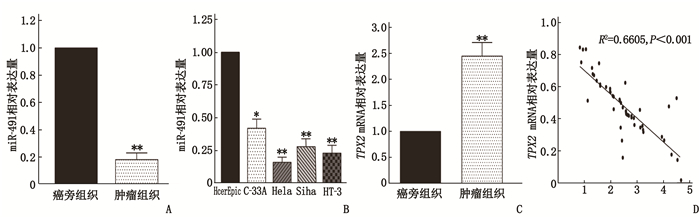
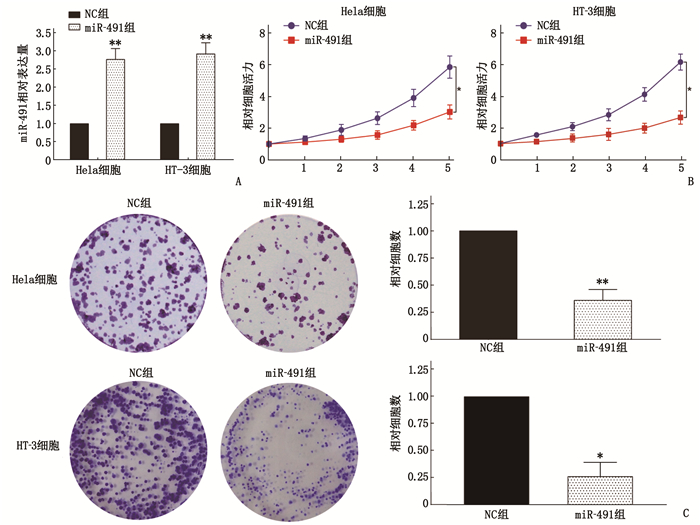
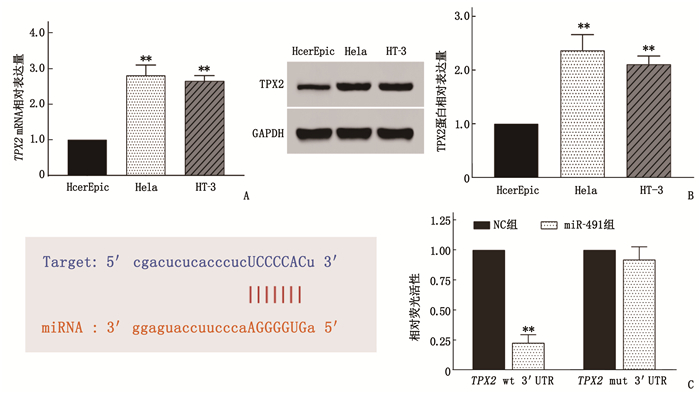
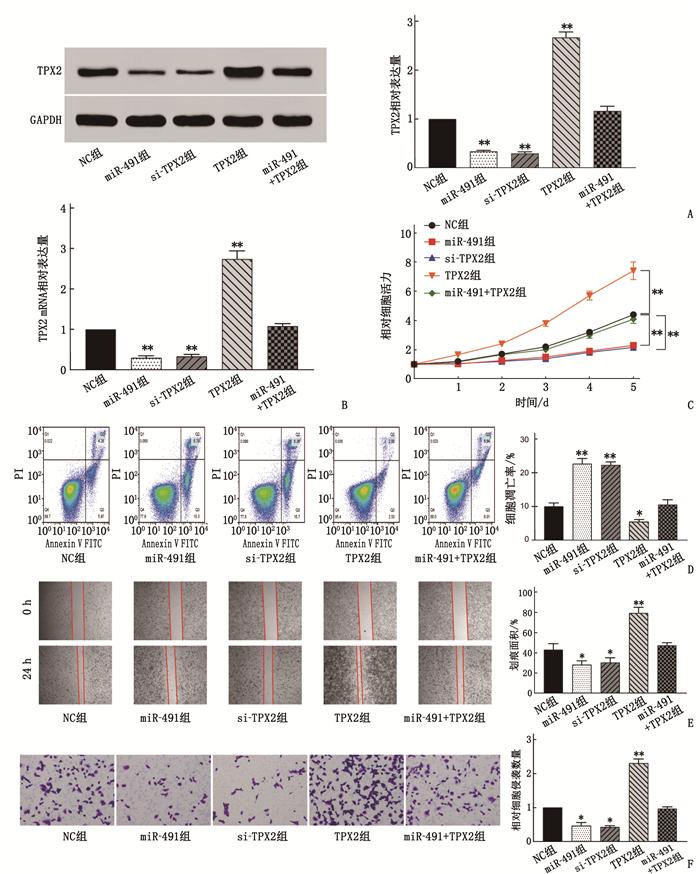
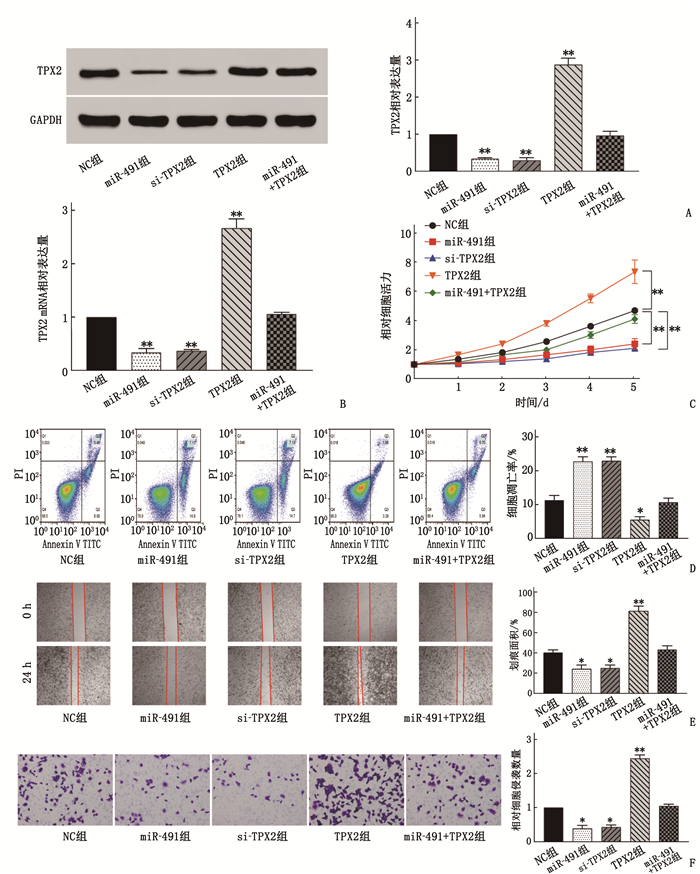
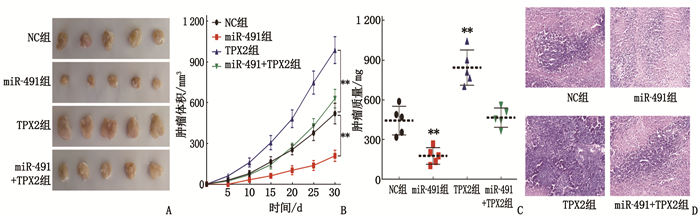
摘要:目的 探讨微小RNA-491(miR-491)在宫颈癌(CC)细胞增殖、侵袭及迁移中的作用及分子机制。方法 收集CC患者的58对癌组织及癌旁组织标本;采用实时荧光定量反转录聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)检测CC组织和癌旁组织(对照组)中miR-491和爪蟾驱动蛋白样蛋白2的靶向蛋白(TPX2)的表达水平。将CC细胞系中的Hela和HT-3细胞随机分为NC组[磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)处理]、miR-491组(过表达miR-491处理)、si-TPX2组(抑制TPX2)、TPX2组(过表达TPX2)及miR-491+TPX2组(同时过表达miR-491和TPX2)。采用细胞活力和克隆形成实验测定miR-491对CC细胞增殖能力的影响;采用双荧光素酶报告实验验证miR-491和 TPX2 的靶向关系;采用划痕和侵袭实验检测miR-491对CC细胞侵袭和迁移能力的影响;构建裸鼠成瘤模型验证miR-491和TPX2对肿瘤生长的影响。结果 miR-491在CC组织和细胞中的表达降低,而TPX2的表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。过表达miR-491能够抑制CC细胞的细胞增殖。双荧光素酶报告结果表明,与NC组比较, miR-491模拟物可以降低PmirGLO-TPX2-3′UTR WT的荧光素酶活性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。细胞活力和凋亡检测结果发现, miR-491能够通过调控TPX2抑制细胞增殖来增高细胞凋亡率。进一步的划痕和transwell检测结果发现, miR-491过表达能够抑制细胞的迁移和侵袭,而TPX2过表达能够促进细胞迁移和侵袭。肿瘤体积和质量检测结果发现, miR-491能够抑制肿瘤生长,而TPX2过表达能够促进肿瘤生长且这种促进作用能够被miR-491逆转。苏木精-伊红染色(HE)检测发现, miR-491组的肿瘤组织出现部分坏死,而TPX2组肿瘤细胞增殖明显。结论 miR-491能够通过调控TPX2的表达影响CC进程,为未来CC生物标志物的选择及治疗靶点提供理论依据。Abstract:Objective To investigate the roles and molecular mechanism of microRNA-491 (miR-491) in the proliferation, invasion and migration of cervical cancer (CC) cells and its molecular mechanism.Methods A total of 58 pairs of cancer tissue and paracancerous tissue samples from CC patients were collected. The expression levels of miR-491 and Xenopus kinesin-like protein 2 target protein (TPX2) in CC tissues and paracancerous tissues were detected by real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Hela and HT-3 cells of CC cell line were randomly divided into NC group[phosphate buffer (PBS) treatment], miR-491 group (overexpression of miR-491 treatment), si-TPX2 group (inhibition of TPX2), TPX2 group (overexpression of TPX2) and miR-491+TPX2 group (simultaneous overexpression of miR-491 and TPX2). Cell viability and clone formation assays were used to determine the effect of miR-491 on the proliferation ability of CC cells. The targeting relationship between miR-491 and TPX2 was verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Scratch and invasion assays were used to detect the effect of miR-491 on the invasion and migration of CC cells. A nude mouse tumorigenic model was constructed to verify the effects of miR-491 and TPX2 on tumor growth.Results The results of the study showed that the expressions of miR-491 in CC tissues and cells were significantly reduced, while the expressions of TPX2 were significantly increased, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Overexpression of miR-491 could inhibit the cell proliferation of CC cells. The results of the dual luciferase report showed that miR-491 could significantly reduce the luciferase activity of PmirGLO-TPX2-3′UTR WT compared with the NC group (P<0.05). The test results of cell viability and apoptosis found that miR-491 mimics can significantly inhibit cell proliferation and increase the rate of apoptosis by regulating TPX2. Further scratches and transwell detection revealed that the miR-491 overexpression inhibited cell migration and invasion, while overexpression of TPX2 could promote cell migration and invasion. In addition, this effect was reversed by the overexpression of miR-491. From the results of tumor volume and weight detection, it is found that miR-491 could inhibit tumor growth, while overexpression of TPX2 can promote tumor growth, and its promotion effect was reversed by miR-491. Further detection of hematoxylin and eosin staining(HE) showed that the tumor tissues in the miR-491 group showed partial ring necrosis, while the tumor cell proliferation effect in the TPX2 group was obvious.Conclusion This study confirms that miR-491 can affect the progress of CC by regulating the expression of TPX2, which provides a theoretical basis for the selection of cervical cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets in the future.
-
Keywords:
- cervical cancer /
- microRNA-491 /
- cell proliferation /
- cell migration /
- tissue necrosis /
- cell vitality
-
-
表 1 临床样本信息
特征 miR-491表达情况 P 低表达(n=41) 高表达(n=17) 性别 男 23 9 0.825 9 女 18 8 年龄/岁 < 60 22 9 0.960 2 ≥60 19 8 TNM分期 Ⅰ~Ⅱ期 21 11 0.347 2 Ⅲ~Ⅳ期 20 6 T分期 T1~T2期 9 10 0.006 5 T3~T4期 32 7 淋巴结转移 无 33 9 0.032 6 有 8 8 表 2 各基因引物序列情况
基因名称 引物 序列 miR-491 上游 5′- ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGTGGGGAACCCTT-3′ 下游 5′-TGGTGTCGTGGAGTCG-3′ TPX2 上游 5′- ACCTTGCCCTACTAAGATT-3′ 下游 5′- AATGTGGCACAGGTTGAGC-3′ U6 上游 CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA 下游 AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT GADPH 上游 5′- GGGTGTGAACCACGAGAAAT-3′ 下游 5′-ACTGTGGTCATGAGCCCTTC -3′ -
[1] 何丽杰, 陈会佳, 王静, 等. miRNA-200b通过靶向RhoA抑制宫颈癌细胞增殖、促进细胞凋亡[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2021, 37(13): 1576-1581. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2021.13.008 [2] 匡婷, 康佳文, 郭思慧, 等. 外泌体miR-217通过下调E-cadherin对宫颈癌Siha细胞淋巴管新生的影响[J]. 湖南师范大学学报: 医学版, 2021, 18(3): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-016X.2021.03.001 [3] 方金华, 原二芳, 张亚芳. microRNA-136-5p通过靶向调控MCM5抑制宫颈癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2021, 37(11): 1385-1388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ202111020.htm [4] AFTAB M, POOJARY S S, SESHAN V, et al. Urine miRNA signature as a potential non-invasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in cervical cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 10323. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89388-w
[5] CHO O, KIM D, CHEONG J. Plasma exosomal miRNA levels after radiotherapy are associated with early progression and metastasis of cervical cancer: a pilot study[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(10): 2110. doi: 10.3390/jcm10102110
[6] 陈春妃, 胡天琼, 韩一栩, 等. miR-146a和miR-196a2基因多态性对高危型HPV感染者宫颈癌易感性的影响[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2021, 31(10): 1566-1570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202110028.htm [7] 黄美园, 杨珍玉, 邓爽, 等. 宫颈癌患者血清miR-574-5p和miR-497-5p表达的临床意义[J]. 现代医学, 2021, 49(4): 377-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7562.2021.04.002 [8] 王庆玮, 倪观太. miRNA与宫颈癌的关系[J]. 沈阳医学院学报, 2019, 21(5): 461-463, 468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYX201905026.htm [9] 雒海瑕, 王伟, 郝敏. 血液循环RNA在宫颈癌液体活检中的研究进展[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2021, 44(4): 352-357. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114452-20200722-00626 [10] XIA W C, LI T H, CHEN E, et al. MiRNA-873-5p acts as a potential novel biomarker and promotes cervical cancer progression by regulating ZEB1 via Notch signaling pathway[J]. Dose-Response, 2021, 19(1): 15593258211001255. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35185415/
[11] WANG T, ZHANG X D, HUA K Q. A CeRNA network of BBOX1-AS1-hsa-miR-125b-5p/hsa-miR-125a-5p-CDKN2A shows prognostic value in cervical cancer[J]. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol, 2021, 60(2): 253-261. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2020.12.006
[12] IVANOV M K, TITOV S E, DZYUBENKO V V, et al. Detection of cervical lesions and cancer in air-dried cytologic smears by combined analysis of mRNA and miRNA expression levels[J]. J Mol Diagn, 2021, 23(5): 541-554. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2021.01.016
[13] YU D S, SONG X L, YAN C. Oncogenic miRNA-1908 targets HDAC10 and promotes the aggressive phenotype of cervical cancer cell[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2021, 37(5): 402-410. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12348
[14] 王庆亮, 赵艳峰, 蒋燕, 等. 基于生物信息学分析的TPX2在肺腺癌中的表达及意义[J]. 同济大学学报: 医学版, 2021, 42(1): 11-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJIY202101004.htm [15] 马玉花, 姜敏, 卡米拉·库来西江, 等. TPX2蛋白在宫颈鳞癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J]. 新疆医学, 2021, 51(1): 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJYI202101004.htm [16] XU Y J, YU H, LIU G X. Hsa_circ_0031288/hsa-miR-139-3p/Bcl-6 regulatory feedback circuit influences the invasion and migration of cervical cancer HeLa cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2020, 121(10): 4251-4260. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29650
[17] YU A J, ZHANG J J, MEI Y X, et al. Correlation between single nucleotide polymorphisms of an miRNA binding site in the 3'UTR of PTEN and risk of cervical cancer among the Han Chinese[J]. Genet Test Mol Biomark, 2020, 24(7): 381-389. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2019.0269
[18] WANG B B, XU Y. Research Progress of Mirna in Screening and Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer[J]. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine Research, 2020, 4(3): 132-136.
[19] YUAN Y Y, SHI X Q, LI B J, et al. Integrated analysis of key microRNAs/TFs/mRNAs/in HPV-positive cervical cancer based on microRNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2020, 216(6): 152952. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.152952
[20] CHEN S L, GAO C, WU Y Y, et al. Identification of prognostic miRNA signature and lymph node metastasis-related key genes in cervical cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 544. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00544
[21] 刘聃, 蔡明慧, 魏力. 子宫颈癌患者血清miRNA-21水平与临床病理因素及预后的关系[J]. 肿瘤研究与临床, 2020, 32(5): 313-317. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115355-20190830-00391 [22] SONG T F, XU A L, ZHANG Z F, et al. CircRNA hsa_circRNA_101996 increases cervical cancer proliferation and invasion through activating TPX2 expression by restraining miR-8075[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(8): 14296-14305. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28128




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
