Clinical significance of angiogenin protein 4, interleukin-17 and nuclear factor-kappa B ligand in serum and articular fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
-
摘要:目的
探讨类风湿关节炎患者血清及关节液血管生成素样蛋白4(ANGPTL4)、白细胞介素-17(IL-17)、核因子κB受体活化因子配体(RANKL)的表达水平及其临床意义。
方法选取165例类风湿关节炎患者纳入观察组,选取同期165例骨关节炎患者纳入疾病对照组,并选取165名健康体检者纳入正常对照组。采用酶联免疫吸附法检测3组研究对象血清和(或)关节液中ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL表达水平,分析观察组患者血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL水平与疾病活动度的相关性。
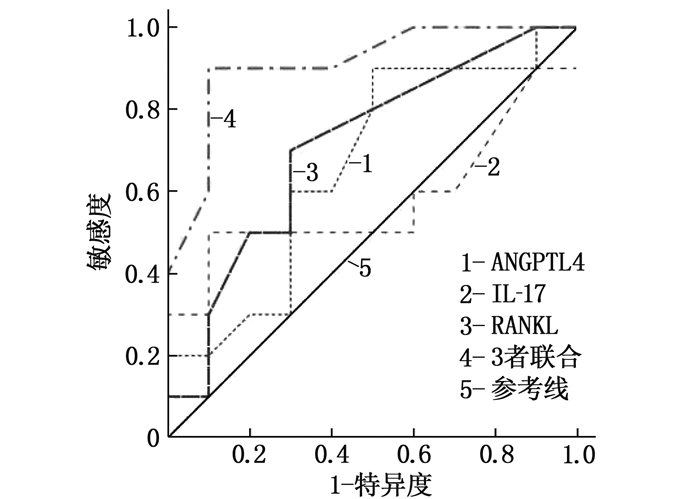
结果观察组血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL水平高于疾病对照组和正常对照组,疾病对照组血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL水平高于正常对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组关节液ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL表达水平与疾病对照组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 观察组和疾病对照组关节液ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL表达水平均低于血清表达水平,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组不同疾病活动度患者中,高度活动者血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL水平高于低度活动者、中度活动者,且中度活动者高于低度活动者,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。Pearson相关分析显示,类风湿关节炎患者血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL水平均与疾病活动度指标28个关节疾病活动度(DAS28)评分、红细胞沉降率(ESR)、C反应蛋白(CRP)水平呈正相关(P<0.001)。受试者工作特征曲线显示,血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL联合预测类风湿关节炎患者1年关节影像学进展的曲线下面积为0.910。
结论类风湿关节炎患者血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL与疾病活动度均呈正相关,三者联合预测1年关节影像学进展的效能较好,为监测类风湿关节炎病情变化提供了新途径。
-
关键词:
- 类风湿关节炎 /
- 血管生成素样蛋白4 /
- 白细胞介素-17 /
- 核因子-κB受体活化因子配体 /
- 疾病活动度
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the clinical significance and expression levels of angiogenin protein 4(ANGPTL4), interleukin-17(IL-17) and receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) in serum and joint fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
MethodsA total of 165 patients with rheumatoid arthritis were selected as observation group, 165 patients with osteoarthritis during the same period were selected as disease control group, and another 165 healthy physical examination subjects as normal control group. The expressions of ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL in serum and(or) joint fluid of the observation group, normal control group and disease control group were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The correlations of the levels of ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL in serum of the observation group with disease activity were analyzed.
ResultsThe serum levels of ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL in the observation group were higher than those of the disease control group and the normal control group, while the ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL in the disease control group were higher than the normal control group (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the expression levels of ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL in the joint fluid between the observation group and the disease control group (P > 0.05). The expression levels of ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL in the joint fluid of the observation group and the disease control group were lower than those in the serum, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). In patients with different disease activity degree in the observation group, the serum levels of ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL in the highly active patients were higher than those in the low and moderate activity degree patients, and were higher in the moderate activity degree patients than those in the low activity degree patients, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that serum ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL levels were positively correlated with Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) score, erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR) and C-reactive protein(CRP) levels(P < 0.001). Receiver operating characteristic curve showed that the area under the curve of ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL in combination in predicting the 1-year joint imaging progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis was 0.910.
ConclusionSerum levels of ANGPTL4, IL-17 and RANKL are significantly positively correlated with disease activity degree in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, their combined prediction of 1-year joint imaging progression has better efficacy, providing a new way to monitor the changes of rheumatoid arthritis.
-
颅脑外伤是指于头颅部发生的常见外部损伤,多由跌坠伤和撞伤导致。颅内高压是导致脑外伤患者发生不良预后的主要原因,有效降压是临床抢救重点[1]。去骨瓣减压术是临床常用治疗脑外伤手术方案,能有效降低颅内压,保护脑组织,但术后颅骨缺损影响大脑神经功能与脑皮质血液灌注,对术后患者行颅骨成形术能有效改善术后不良影响[2]。硬膜下积液是脑外伤行去骨瓣减压术的常见并发症,治疗难度较高,易加重病情,增高不良预后风险[3]。本研究观察脑外伤去骨瓣减压术联合早期颅骨成形术的临床效果,并分析术后硬膜下积液的危险因素,现将结果报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2019年7月—2020年7月脑外伤行去骨瓣减压术的120例患者为研究对象,根据术后行颅骨成形术的时间分为对照组(常规时间行颅骨成形术, n=80)与研究组(早期行颅骨成形术, n=40)。对照组男50例,女30例; 年龄20~55岁,平均(43.42±7.32)岁; 体质量指数(BMI)19~28 kg/m2, 平均(22.51±2.23) kg/m2; 发病至就诊时间3~21 h, 平均(11.43±6.13) h; 致病原因为高处跌伤21例、交通事故32例、打架斗殴27例。研究组男21例,女19例; 年龄19~54岁,平均(42.57±7.12)岁; BMI为18~27 kg/m2, 平均(22.31±2.35) kg/m2; 发病至就诊时间2~20 h, 平均(12.05±5.98) h; 致病原因为高处跌伤11例、交通事故24例、打架斗殴5例。2组患者一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 具有可比性。
纳入标准: ①经诊断确诊,并行去骨瓣减压术治疗的的脑外伤患者; ②患者可正常沟通,听力与理解能力正常; ③入院时格拉斯哥昏迷评分不超过8分者; ④临床资料完整者。排除标准: ①合并严重心、肝、肺、肾疾病患者; ②既往有颅脑手术史患者; ③术后发生感染、颅位病变患者; ④术后随访失联患者。
1.2 方法
颅骨成形术使用三维朔性钛网经颅骨三维重建加工为修补材料,经高压灭菌后备用。根据患者手术部位选择合适体位,经全身麻醉后沿去骨瓣减压术切口做马蹄形切开暴露骨缘,分离骨膜和皮瓣粘连部分,修整骨缘成斜坡状,置入修补材料并固定,使用自体捏肌筋膜进行硬脑膜颞成形。冲洗创面,留置引流管,逐层缝合头皮,使用弹力绷带加压包扎。对照组患者去骨瓣减压术后3~6个月行颅骨成形术,研究组术后5~8周行颅骨成形术。2组均于术后15 d、2个月对神经、运动、日常生活功能进行评分。
1.3 观察指标
采用神经功能缺损(NIHSS)评分评价神经功能[4], 包括11个项目,共计42分,分数越高,表示神经损伤越严重。运动功能[5]采用肢体运动功能量表(Fugl-Meyer)进行评定,总分为100分, 100分为正常, 95~ < 100分为轻度障碍, 85~ < 95分为中度障碍, 50~ < 85分为明显障碍, 50分以下为重度障碍。日常生活功能[6]采用Barthel指数评分进行评定,共包括10个项目,共计100分, 70分以上为轻度障碍, >46~70分为中度障碍, >25~46分为重度障碍, ≤25分为极度障碍。记录2组患者的临床特征,包括年龄、性别、颅内血肿情况、中线移位、术前是否有脑疝、骨瓣情况等。硬膜下积液标准: CT诊断表现为积液量>5 mm, 中线移位以移位>5 mm为有移位[7]。
1.4 统计学处理
所有数据均采用统计软件SPSS 22.0进行处理。计数资料采用[n(%)]表示,行χ2检验; 计量资料采用(x±s)表示,行t检验或重复测量分析,两两比较采用LSD-t检验。组间比较行单因素方差分析,多因素采用二元Logistic回归分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组手术前后神经功能、肢体运动能力、生活能力比较
术前, 2组NIHSS评分、Fugl-Meyer评分、Barthel评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 术后2个月,研究组NIHSS评分低于对照组, Fugl-Meyer评分、Barthel评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2组手术前后神经功能、肢体运动能力、生活能力评分比较(x±s)分 指标 组别 术前 术后15 d 术后2个月 NIHSS评分 研究组(n=40) 31.22±4.11 20.84±4.95* 15.63±3.69*#△ 对照组(n=80) 31.61±3.94 23.06±4.80* 19.62±5.06*# Fugl-Meyer评分 研究组(n=40) 51.34±16.58 69.76±17.81* 82.55±19.41*#△ 对照组(n=80) 52.48±16.25 66.42±19.46* 70.20±20.81*# Barthel评分 研究组(n=40) 30.54±7.22 50.45±15.73* 76.57±22.96*#△ 对照组(n=80) 31.22±8.33 46.67±14.80* 62.53±20.87*# 与术前比较, *P < 0.05; 与术后15 d比较, #P < 0.05; 与对照组比较, △P < 0.05。 2.2 2组术后并发症发生情况比较
2组术后脑积水、癫痫、侧脑室扩大移位发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 研究组硬膜下积液、颅脑缺损综合征发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 2组术后并发症发生情况比较[n(%)]组别 脑积水 癫痫 硬膜下积液 颅脑缺损综合征 侧脑室扩大移位 研究组(n=40) 2(5.00) 4(10.00) 4(10.00)* 6(15.00)* 1(2.50) 对照组(n=80) 12(15.00) 5(6.25) 24(30.00) 26(32.50) 5(6.25) 与对照组比较, *P < 0.05。 2.3 术后硬膜下积液影响因素分析
根据患者是否发生硬膜下积液将其分为硬膜下积液组和非硬膜下积液组。2组患者年龄、性别、脑室内出血、脑池受压、硬膜下血肿、硬膜外血肿、脑疝、哥斯拉昏迷评分、去骨瓣侧边、骨瓣最长径、骨瓣最高径比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 2组患者中线移位、脑内血肿、蛛网膜撕裂、皮层切开、骨瓣边缘距中线距离、骨窗面积比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 3。
表 3 术后硬膜下积液单因素分析(x±s)[n(%)]指标 硬膜下积液组
(n=28)非硬膜下积液组
(n=92)年龄/岁 44.83±7.12 43.33±7.22 性别 男 20(71.43) 69(75.00) 女 8(28.57) 23(25.00) 脑室内出血 2(7.14) 5(5.43) 中线移位 20(71.43)* 30(32.61) 脑池受压 23(82.14) 71(77.17) 硬膜下血肿 25(89.29) 69(75.00) 硬膜外血肿 7(25.00) 33(35.87) 脑内血肿 25(89.29)* 31(33.70) 蛛网膜撕裂 25(89.29)* 56(60.87) 皮层切开 18(64.29)* 33(35.87) 脑疝 15(53.57) 33(35.87) 哥斯拉昏迷评分 3~ < 5分 15(53.57) 62(67.39) 5~ < 8分 13(46.43) 30(32.61) 去骨瓣侧边 单侧 16(57.14) 36(39.13) 双侧 12(42.86) 56(60.87) 骨瓣最长径/cm 11.19±2.14 10.64±2.38 骨瓣最高径/cm 8.17±1.53 7.84±1.46 骨瓣边缘距中线距离 ≤2 cm 19(67.86)* 31(33.70) >2 cm 9(32.14)* 61(66.30) 骨窗面积/cm2 139.70±43.38* 112.94±34.61 与非硬膜下积液组比较, *P < 0.05。 2.4 术后硬膜下积液影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析
以“术后硬膜下积液”为因变量(赋值: 0=是, 1=否),以“中线移位、脑内血肿、蛛网膜撕裂、皮层切开、骨瓣边缘距中线距离、骨窗面积”为自变量纳入Logistic回归分析,赋值情况见表 4。多因素Logistic回归分析显示,中线移位、脑内血肿、蛛网膜撕裂、皮层切开、骨瓣边缘距中线距离、骨窗面积均为术后硬膜下积液的独立影响因素(P < 0.05), 见表 5。
表 4 术后硬膜下积液影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析赋值情况变量 变量名 赋值方法 硬膜下积液 Y 是=0, 否=1 中线移位 X1 是=0, 否=1 脑内血肿 X2 是=0, 否=1 蛛网膜撕裂 X3 是=0, 否=1 皮层切开 X4 是=0, 否=1 骨瓣边缘距中线距离 X5 是=0, 否=1 骨窗面积 X6 变量参数 表 5 术后硬膜下积液影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析变量 B S. E. Wald 自由度 P Exp(B) 95% CI 中线移位 -1.642 0.474 12.015 1 0.001 0.194 0.076~0.490 脑内血肿 -2.797 0.650 18.541 1 <0.001 0.061 0.017~0.218 蛛网膜撕裂 -1.678 0.647 6.724 1 0.010 0.187 0.052~0.664 皮层切开 -1.169 0.450 6.736 1 0.009 0.311 0.129~0.751 骨瓣边缘距中线距离 -1.424 0.461 9.549 1 0.002 0.241 0.098~0.594 骨窗面积 -0.019 0.006 9.601 1 0.002 0.981 0.969~0.993 3. 讨论
去骨瓣减压术是临床抢救脑伤患者的常用方案,能缓解脑内因水肿造成的高压,但易引发多种并发症,因此术后实行颅骨成形术非常重要[8-10]。本研究中,术后2个月研究组NIHSS评分低于对照组, Fugl-Meyer评分、Barthel评分高于术前与对照组,且研究组硬膜下积液、颅脑缺损综合征发生率低于对照组,提示早期行颅骨成形术有利于改善脑伤患者术后神经功能、运动功能与生活功能,且能有效减少并发症的发生,原因可能为[11-12]: ①脑损伤患者去骨瓣减压术后由于脑组织缺少骨瓣支撑,脑脊液循环、脑皮质灌注、血流动力学易发生异常,早期颅骨成形术能够避免长时间颅骨缺损,稳定颅内压,缓解血管压迫,改善血流循环。②去骨瓣减压术后使颅骨生理稳定性破坏,脑搏动使脑脊液进入硬膜下腔,早期颅骨修补能够使颅骨正常生理结构得以修复,消除颅内压力失衡状态。
既往研究[13]表明,去骨瓣减压术后高发硬膜下积液严重时可发展为脑积水、脑水瘤,严重威胁患者生命安全,因此分析其相关因素有利于预防术后硬膜下积液的发生。本研究显示,中线移位、脑内血肿、蛛网膜撕裂、皮层切开、骨瓣边缘距中线距离、骨窗面积均为术后硬膜下积液的独立影响因素,原因为[14-15]: ①蛛网膜与蝶骨脊紧密相连,蛛网膜撕裂发生于大脑裂缝或视交叉区域,缝蛛网膜撕裂易引发半球硬膜下积液,视交叉区域蛛网膜撕裂易致使纵裂积液; ②中线位移超过5 mm颅脑损伤较严重,手术性皮层切开易导致蛛网膜撕裂; ③脑内血肿影响脑脊液吸收途径; ④骨瓣边缘距中线距离小于2 cm的患者,脑桥静脉压力减小,脑静脉回流易发生障碍; ⑤骨窗面越大患者硬膜下、蛛网膜下及颅内存在梯度压力,使脑脊液吸收失衡,且压力越大,梯度压力越明显。
综上所述,脑外伤去骨瓣减压术联合早期颅骨成形术能有效改善患者神经功能、运动功能与日常生活功能,减少术后并发症的发生。中线移位、脑内血肿、蛛网膜撕裂、皮层切开、骨瓣边缘距中线距离、骨窗面积均为术后硬膜下积液的独立影响因素,临床可根据患者具体情况进行有效防治。
-
表 1 3组一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
组别 n 性别 年龄/岁 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 病程/月 男 女 正常对照组 165 44(26.67) 121(73.33) 52.76±5.03 22.76±1.15 — 疾病对照组 165 45(27.27) 120(72.73) 52.06±4.98 22.98±1.31 34.61±9.07 观察组 165 43(26.06) 122(73.94) 52.55±5.01 22.89±1.29 36.42±8.74 表 2 3组血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL表达水平比较(x±s)
组别 n ANGPTL4/(ng/mL) IL-17/(pg/mL) RANKL/(pg/mL) 正常对照组 165 2.65±0.72 4.84±1.13 81.24±4.63 疾病对照组 165 7.89±2.17* 9.56±3.72* 126.93±12.77* 观察组 165 15.64±5.43*# 22.48±6.95*# 212.25±25.78*# ANGPTL4: 血管生成素样蛋白4; IL-17: 白细胞介素-17; RANKL: 核因子κB受体活化因子配体。
与正常对照组比较, *P<0.05; 与疾病对照组比较, #P<0.05。表 3 观察组与疾病对照组血液、关节液中ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL表达水平比较(x±s)
组别 n 样本 ANGPTL4/(ng/mL) IL-17/(pg/mL) RANKL/(pg/mL) 疾病对照组 165 关节液 3.42±1.11* 4.57±1.27* 95.61±8.71* 血清 7.89±2.17 9.56±3.72 126.93±12.77 观察组 165 关节液 3.65±1.37* 4.79±1.54* 97.32±9.56* 血清 15.64±5.43# 22.48±6.95# 212.25±25.78# ANGPTL4: 血管生成素样蛋白4; IL-17: 白细胞介素-17; RANKL: 核因子κB受体活化因子配体。
与血清比较, *P<0.05; 与疾病对照组比较, #P<0.05。表 4 观察组不同疾病活动度患者血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL水平比较(x±s)
组别 n ANGPTL4/(ng/mL) IL-17/(pg/mL) RANKL/(pg/mL) 低度活动组 80 11.37±3.82 7.94±2.56 101.42±9.86 中度活动组 42 15.45±5.64* 20.82±5.53* 200.53±18.57* 高度活动组 43 20.83±8.91*# 27.91±8.72*# 261.86±31.29*# ANGPTL4: 血管生成素样蛋白4; IL-17: 白细胞介素-17; RANKL: 核因子κB受体活化因子配体。
与低度活动组比较, *P<0.05; 与中度活动组比较, #P<0.05。表 5 血清ANGPTL4、IL-17、RANKL与疾病活动度指标的相关性分析
指标 DAS28评分 ESR CRP r P r P r P ANGPTL4 0.562 <0.001 0.748 <0.001 0.718 <0.001 IL-17 0.618 <0.001 0.705 <0.001 0.842 <0.001 RANKL 0.584 <0.001 0.691 <0.001 0.803 <0.001 DAS28: 28个关节疾病活动度; ESR: 红细胞沉降率; CRP: C反应蛋白; ANGPTL4: 血管生成素样蛋白4;
IL-17: 白细胞介素-17; RANKL: 核因子κB受体活化因子配体。 -
[1] 陈光耀, 胡琪, 徐愿, 等. 类风湿关节炎超声下亚临床滑膜炎的特征分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(6): 735-738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX201906030.htm [2] 田新平, 李梦涛, 曾小峰. 我国类风湿关节炎诊治现状与挑战: 来自中国类风湿关节炎2019年年度报告[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2021, 60(7): 593-598. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20210207-00113 [3] ORTEGA-SENOVILLA H, VAN POPPEL M N M, DESOYE G, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) is related to gestational weight gain in pregnant women with obesity[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 12428. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29731-w
[4] 吕英姿, 高薇. 白细胞介素-17通过信号传导与转录激活因子3诱导类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞释放炎症及骨侵蚀因子[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2017, 21(5): 338-341. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-7480.2017.05.010 [5] ZHANG R, WAN J, WANG H. Mechanical strain triggers differentiation of dental mesenchymal stem cells by activating osteogenesis-specific biomarkers expression[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2019, 11(1): 233-244.
[6] 刘璐, 刘传慧, 段智霞. 膝关节炎患者血清RANKL、IL-17水平与疾病严重程度的关系[J]. 中国实用医刊, 2021, 48(19): 16-19. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115689-20210615-02050 [7] ALETAHA D, NEOGI T, SILMAN A J, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62(9): 2569-2581. doi: 10.1002/art.27584
[8] 陈楚涛, 张学培, 杨莉娟, 等. 抗突变型瓜氨酸波形蛋白抗体对类风湿关节炎患者一年关节影像学进展的预测价值[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2021, 60(2): 128-133. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20200318-00261 [9] 王玉梅, 刘秀梅, 郑晓, 等. ANGPTL4、RANKL在类风湿关节炎患者血清及关节液中的表达水平及其相关性研究[J]. 中华临床医师杂志: 电子版, 2017, 11(10): 1691-1695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYD201710009.htm [10] MAKOVEICHUK E, RUGE T, NILSSON S, et al. High concentrations of angiopoietin-like protein 4 detected in serum from patients with rheumatoid arthritis can be explained by non-specific antibody reactivity[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(1): e0168922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168922
[11] LIU T J, GUO J L. Overexpression of microRNA-141 inhibits osteoporosis in the jawbones of ovariectomized rats by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2020, 113: 104713. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104713
[12] CHEN L, WU X, ZHONG J, et al. L161982 alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by increasing Treg cells and down-regulating Interleukin-17 and monocyte-chemoattractant protein-1 levels[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2017, 18(1): 462. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1819-3
[13] 刘洪江, 郭晓锋, 胡凡磊, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血B10细胞高表达核因子κB受体活化因子配体[J]. 北京大学学报: 医学版, 2018, 50(6): 968-974. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BYDB201806005.htm [14] 叶夏, 赵娟, 张卓莉. 类风湿关节炎患者Syndecan-4的表达及其与疾病活动度的关系[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2020, 19(22): 2389-2392. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2020.22.011 [15] 杜凌燕, 张明娇, 刘鹏飞, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者血清趋化因子配体20与疾病严重程度的相关性研究[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2021, 55(2): 226-232. [16] MEEDNU N, ZHANG H, OWEN T, et al. Production of RANKL by memory B cells: a link between B cells and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2016, 68(4): 805-816. doi: 10.1002/art.39489
[17] LI B, QIAN M, CAO H, et al. TGF-β2-induced ANGPTL4 expression promotes tumor progression and osteoclast differentiation in giant cell tumor of bone[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(33): 54966-54977. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18629
[18] 韩玉生, 李东东, 侯志涛, 等. 丹溪痛风胶囊对类风湿性关节炎大鼠血清IL-17和IL-23水平的影响[J]. 中医学报, 2018, 33(9): 1705-1708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZK201809026.htm [19] JOHANSSON L, ÄRLESTIG L, KOKKONEN H, et al. An increased concentration of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand pre-dates the onset of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheumatology: Oxford, 2017, 56(12): 2190-2196. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex339
[20] 李艳琴, 孙强. 来氟米特联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎患者的疗效及对血清生长因子的影响[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2020, 24(21): 108-111. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.202021031 [21] 安新, 冯超, 高利常. 类风湿关节炎患者血清白细胞介素-32、白细胞介素-17和白细胞介素-10表达水平及临床意义[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2021, 50(12): 1585-1588. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7377.2021.12.030 -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 刘一博,齐丹,郑冬,刘梦,傅群峰,刘昕. 类风湿性关节炎患者超声滑膜血流特征、血清ANGPTL4、IL-18水平及临床意义. 临床和实验医学杂志. 2025(04): 430-435 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 丁蓓蓓,陈雷鸣,林永强. 雷公藤多苷联合托法替布治疗类风湿关节炎临床研究. 新中医. 2024(01): 99-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 喻杨,何吉,岑村红,支太发,黄聪,邓颖,罗进芳. 基于网络药理学探讨川续断治疗类风湿关节炎的作用机制. 医学信息. 2024(06): 14-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 付鹏,张敏. 血清抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体、类风湿因子、免疫球蛋白G、补体C3、补体C4检测在类风湿关节炎诊断中的应用价值. 中国社区医师. 2024(07): 80-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 徐任菊,陈雁,陈玉洁,朱昱璇,靳子义,孙玥,朱曼莉. 类风湿关节炎患者衰弱发生率的系统评价. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(11): 45-52 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 兰维娅,马武开,姚血明,蒋总,熊浪,杨淑芬,唐芳. 来氟米特调控HIF-1α信号通路对类风湿关节炎滑膜细胞自噬的影响. 安徽医科大学学报. 2024(10): 1823-1828 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 田塬,冯俊,黄海涛,章美华,孙召金,余世成,丁胜楷,李峰云,张梦达,许盼,马玲玲. 急性心肌梗死患者血清ITLN-1、ANGPTL4水平与冠状动脉病变程度的相关性分析. 疑难病杂志. 2023(03): 236-240 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 阿力泰. 蒙医对类风湿关节炎患者有何效果. 家庭生活指南. 2023(06): 136-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张艳,王明杰,徐风金,薛燕. 瘀血痹胶囊联合托法替布治疗类风湿关节炎的临床研究. 现代药物与临床. 2023(10): 2573-2578 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李晓军,马芹,张同桐. 血清血管紧张素原和淀粉样蛋白4在类风湿关节炎患者中的表达水平及临床意义. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(21): 37-41 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号