Analysis in antibody levels in blood of patients infected with Coronavirus disease 2019 after inoculation with novel coronavirus inactivated vaccine and disease status
-
摘要:目的 探讨新型冠状病毒灭活疫苗(简称新冠疫苗)对接种后感染Delta变异株新型冠状病毒肺炎(简称新冠肺炎)人群是否具有保护作用。方法 观察2021年7月20日—8月27日在本院隔离病区住院的接种过新冠疫苗(接种1针或2针)的47例新冠肺炎成年患者的病例资料以及血新型冠状病毒免疫球蛋白M(IgM)、免疫球蛋白G(IgG)抗体滴度的动态变化,并与30例未接种新冠疫苗的新冠肺炎成年患者进行组间比较。结果 未接种疫苗成年患者的病情严重程度重于接种2针疫苗患者; 病程4周内,新冠肺炎患者血新型冠状病毒IgM抗体滴度均呈先升高后下降恢复趋势,接种2针组在第2周即快速到达峰值,接种1针组峰值大多出现在第3周,未接种成年组峰值出现在第3周, 3组峰值滴度比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 77例新冠肺炎成年患者血新型冠状病毒IgG抗体滴度于第2、3周到达峰值,病程第4周有降低趋势但仍维持在高水平,未接种成年组峰值滴度低于接种2针组、接种1针组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 新冠疫苗对新冠肺炎患者具有免疫保护作用,可减轻患者病情严重程度。新冠疫苗诱导的机体特异性免疫反应可能随着时间的延长而衰减。Abstract:Objective To explore whether novel coronavirus inactivated vaccine has protective effects or not on Coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19) people infected with Delta variant of the virus after vaccination.Methods During the period from July 20, 2021 to August 27, 2021, the data of 47 patients with COVID-19 who were inoculated with inactivated vaccines(one dose or two doses of vaccine against COVID-19) in the isolation ward of our hospital, and the changes in the dynamic levels of blood immunoglobulin M (IgM) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against COVID-19 were observed, and the results were compared with 30 patients with COVID-19 who were not vaccinated inactivated vaccine for COVID-19.Results The severity of illness of unvaccinated adult patients was significantly heavier than that of patients who received two doses of vaccine; within 4 weeks of course of disease, the blood IgM antibody titer of patients with COVID-19 showed a trend of firstly increasing, then decreasing and finally recovering. The patients receiving two doses of vaccine quickly reached the peak in the second week, while most of patients with one dose of vaccine and those without vaccination reached the peak at the third week of vaccination. The peak titer showed a significant difference among the three groups(P < 0.05). The titer of IgG antibody in 77 adult patients with COVID-19 peaked at 2 or 3 weeks and decreased at week 4 but still remained at a high level. The peak titer of the unvaccinated adult group was significantly lower than that of the two doses of vaccine group and the one dose of vaccine group(P < 0.05).Conclusion The inactivated vaccine has an immune protection effect in patients with new coronary pneumonia, which can reduce the severity of the disease. The body-specific immune responses induced by inactivated vaccines may attenuate over time.
-
2021年7月下旬开始,江苏省南京、扬州等地先后出现本土新冠肺炎病例,病毒经基因测序确定为新型冠状病毒Delta(δ)变异株。目前,中国已将新型冠状病毒灭活疫苗(简称新冠疫苗)大规模应用于临床,国内外多个Ⅱ/Ⅲ期临床试验[1]结果显示,新冠疫苗的保护作用可达60%~80%, 但接种新冠疫苗后的人群仍有部分会感染新冠肺炎。为探讨接种过新冠疫苗的新冠肺炎患者的病情严重程度与未接种新冠疫苗的新冠肺炎患者有无区别,本研究收集47例接种过新冠疫苗的新冠肺炎患者的病例资料,并与30例未接种新冠疫苗的新冠肺炎患者的资料进行组间比较,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
随机选取2021年7月20日—2021年8月27日南京市第二医院(南京市公共卫生医疗中心)隔离病区收治的90例Delta变异株新冠肺炎患者作为研究对象。纳入患者全部为中国籍本地病例,男37例,女53例; 接种2针新冠疫苗者25例,接种时间34~170 d, 年龄23~70岁; 接种1针新冠疫苗者22例,接种时间13~28 d, 年龄21~67岁; 未接种新冠疫苗者43例,年龄2~75岁,其中13例年龄小于18岁,其余30例为成年患者。新冠疫苗为北京生物公司或科兴中维生物公司生产。
1.2 方法
根据疫苗接种情况及年龄将患者分为接种2针组、接种1针组、未接种成年组和未接种未成年组,其中前3组均为成年患者。回顾性分析4组患者发病1周内的肺部病灶范围、血淋巴细胞计数及病变开始吸收时间,并比较3组成年患者病程4周内血新型冠状病毒免疫球蛋白M(IgM)、免疫球蛋白G(IgG)抗体滴度的动态变化。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 19.0软件对数据进行统计学分析,符合正态分布的计量资料以(x±s)表示,组间比较行t检验, P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 新冠肺炎分型结果
接种2针组(n=25)中,轻型3例,普通型22例; 接种1针组(n=22)均为普通型; 未接种成年组(n=30)中,重型5例,普通型25例; 未接种未成年组(n=13)中,轻型5例,普通型8例。
2.2 临床症状情况
接种2针组出现发热4例,其中3例体温低于38 ℃, 1例体温升至38.5 ℃(糖尿病患者,病程中出现低氧血症,加用中和抗体治疗后发热减退,病情好转出院); 接种1针组出现发热3例,体温均低于38 ℃; 未接种成年组出现发热5例,其中3例发热患者体温升高至39 ℃(病情于1周内加重,并发呼吸衰竭,均加用中和抗体治疗, 1例好转, 2例好转不明显转至重症ICU病房治疗); 未接种未成年组出现发热2例,体温38~39 ℃, 发热在3 d内消退。
2.3 发病1周内肺部影像学改变
接种2针组中, 3例肺部无病灶, 22例普通型患者中有1例糖尿病低氧血症患者肺部病灶范围为20%, 1例69岁老年患者肺部病灶范围为10%, 其他患者为1%~5%。接种1针组中, 3例老年患者肺部病灶范围为10%~15%, 1例糖尿病患者为20%, 其他患者为2%~10%。未接种成年组中, 5例患者病灶范围大于20%(其中3例老年患者病灶范围为50%), 其他患者病灶范围5%~20%。未接种未成年组中, 5例病灶范围3%~8%, 其余8例肺部无病灶。未接种成年组的病灶范围大于其他3组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
2.4 肺部病灶吸收时间
接种2针组肺部病灶开始吸收时间为6~15 d, 平均11 d; 接种1针组肺部病灶开始吸收时间8~20 d,平均13 d; 未接种成年组肺部病灶开始吸收时间10~19 d, 平均14 d。3组肺部病灶吸收时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。未接种未成年组肺部病灶开始吸收时间5~10 d, 平均7 d。
2.5 发病1周内血淋巴细胞计数水平
接种2针组血淋巴细胞计数水平为(0.53~2.63)×109/L, 接种1针组为(0.73~1.72)×109/L, 未接种成年组为(0.46~1.99)×109/L, 未接种未成年组为(0.85~7.39)×109/L。
2.6 病程4周内血新型冠状病毒IgM抗体滴度变化
90例新冠肺炎患者血新型冠状病毒IgM抗体滴度均呈先升高后下降趋势,但不同组别的血IgM抗体滴度峰值有差异,且出现峰值的时间不同。接种2针组患者血IgM抗体滴度在病程第1周即开始上升,在第2周即快速到达峰值,第3~4周逐渐下降,但不同患者的峰值不同,其中5例在4周内一直阴性,其余20例患者血IgM抗体滴度最高时超过200,最低仅1.38, 个体之间差异显著,考虑与个体体质不同有关。接种1针组患者血IgM抗体滴度亦在第1周升高,但出现峰值时间晚于接种2针组,多数出现在第3周,不同个体峰值浓度差异显著,其中3例患者在4周内一直阴性,其余患者血IgM抗体滴度3.32~88.69。未接种成年组中, 9例患者一直阴性,其余患者血IgM抗体滴度在病程中仅轻度升高,峰值滴度为1.18~7.43, 出现峰值时间在第3周,第4周开始呈下降趋势。接种1针组的血新型冠状病毒IgM抗体滴度与接种2针组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 未接种成年组的血新型冠状病毒IgM抗体滴度低于接种1针组、接种2针组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见图 1。
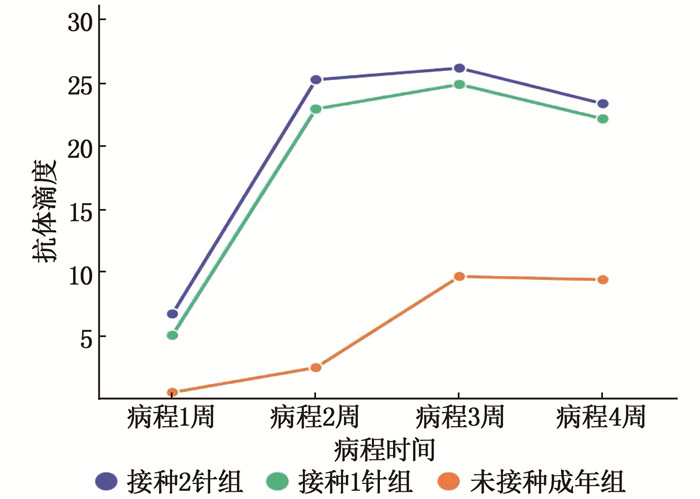
2.7 病程4周内血新型冠状病毒IgG抗体水平变化
77例新冠肺炎成年患者血新型冠状病毒IgG抗体滴度均于第1周开始升高,第2~3周到达峰值,病程第4周有降低趋势但仍维持在高水平。接种2针组血IgG抗体滴度峰值为71.3~177.8, 接种1针组为24.89~144.6。未接种成年组血IgG抗体滴度峰值(30例中有27例峰值滴度均低于10)低于接种2针组、接种1针组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图 2。
3. 讨论
接种疫苗是防止新冠肺炎疫情进一步扩散的根本途径,目前临床已开发的新型冠状病毒疫苗主要有灭活疫苗、基因工程疫苗(亚单位疫苗、纳米颗粒疫苗、病毒载体疫苗)、核酸疫苗(DNA疫苗、RNA疫苗)[2]。现有疫苗中, RNA疫苗安全性高,抗变异能力强,可同时激活体内的细胞和体液免疫[3],而灭活疫苗属于第1代疫苗,是当前世界范围内使用最广泛的疫苗之一。2020年4月武汉生物研究所首先研制出新型冠状病毒灭活疫苗(Vero细胞), 2021年5月8日和6月1日,北京生物和北京科兴中维研发的2款灭活疫苗分别获得世界卫生组织(WHO)紧急认证[4]。
灭活疫苗路线是传统的经典疫苗研发路线,已被广泛应用于多种传染性疾病中。灭活疫苗是利用物理或化学方法将病毒灭活,但仍具有免疫原性,其安全性高,免疫原性全。因其技术水平成熟,稳定性高,使用安全,灭活疫苗目前仍是中国新型冠状病毒疫苗的首选技术路线,且该类疫苗已在中国居民中大规模接种。灭活疫苗主要引起体液免疫,已被临床实验证实能产生很好的中和抗体滴度[5-6], 且未发现严重不良反应[7-8]。
本研究结果显示,未接种疫苗的新冠肺炎成年患者病情严重程度显著重于接种过2针疫苗的患者。未接种患者中, 3例重症患者病情进展迅速,肺部病灶短期内迅速增多,均在病程1周内出现呼吸衰竭。此外,未接种疫苗患者的病灶范围亦显著大于接种过疫苗的患者,接种2针疫苗与接种1针疫苗患者的病灶范围则未见显著差异。由此可得出初步结论,接种新冠疫苗对新冠肺炎患者具有免疫保护作用,可减轻病情严重程度。
本研究中,各组患者血淋巴细胞计数水平无显著差异,但接种过疫苗患者在新冠肺炎病程中的血新型冠状病毒抗体滴度显著高于未接种患者,推测接种灭活疫苗是通过激活机体体液免疫达到免疫保护作用。本研究还发现,接种过疫苗患者的血新型冠状病毒IgG抗体滴度在病程第4周呈缓慢下降趋势,提示灭活疫苗诱导的机体特异性免疫反应可能随着时间延长而衰减。本次江苏新冠肺炎疫情存在家庭成员间传播现象,未成年患者例数也较多,虽然临床发现未成年患者病情轻且好转快,但因其感染率高,故建议未成年人也应尽快接种新冠疫苗。
病毒变异是疫苗有效性的最大威胁,在病毒不断变异的情况下,新冠疫苗的有效性受到影响。全印医学科学研究所公布,新型冠状病毒Delta变异株对接种了印度生产的阿斯利康疫苗及印度国产covaxin疫苗的人群仍具有高度传染性,但这些感染患者中无死亡病例[9]。本研究显示,接种新冠疫苗并不能杜绝新型冠状病毒变异株感染,但接种过疫苗患者的病重率显著低于未接种疫苗患者,表明接种灭活疫苗可建立人群对新型冠状病毒的免疫屏障,可预防重症感染及死亡,具有明确的保护力和有效性。
-
[1] PALACIOS R, PATIÑO E G, DE OLIVEIRA PIORELLI R, et al. Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase Ⅲ Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of treating Healthcare Professionals with the Adsorbed COVID-19(Inactivated) Vaccine Manufactured by Sinovac-PROFISCOV: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial[J]. Trials, 2020, 21(1): 853-855. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04775-4
[2] 石云, 王宁, 邹全明. 新型冠状病毒疫苗研发进展与挑战[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2020, 54(6): 614-619. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200317-00366 [3] 高雪, 成立. mRNA疫苗作用机制的研究进展[J]. 国际生物制品学杂志, 2021, 44(5): 290-295. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311962-20210620-00034 [4] 光明日报. 向病毒发出挑战, 向科学探寻答案——中国生物新冠灭活疫苗研发团队攻关纪实[EB/OL]. (2020-11-28)[2020-12-11]. https://politics.gmw.cn/2020-11/28/content_34410884.htm. [5] XIA S, DUAN K, ZHANG Y, et al. Effect of an inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 on safety and immunogenicity outcomes: interim analysis of 2 randomized clinical trials[J]. JAMA, 2020, 324(10): 951-960. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.15543
[6] XIA S, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2021, 21(1): 39-51. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30831-8
[7] 陈靖, 李晓清, 卢晓晓, 等. 新型冠状病毒灭活疫苗不同接种间隔的免疫原性和安全性研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(12): 2077-2081. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20210807-00617 [8] 杨中楠, 赵韵芽, 李璐, 等. 新型冠状病毒灭活疫苗(Vero细胞)大规模紧急使用安全性评价[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(6): 977-982. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?dbid=WF_QK&id=PeriodicalPaper_zhlxbx202106003 [9] 北京日报. 印度研究机构: 变异毒株Delta对接种过疫苗的人仍具有高度传染性[EB/OL]. (2021-06-11)[2021-06-13]. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/sid=1702207794872326642&wfr=spider&for=pc. -
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 祁潇然,张芮宁,贺俊清,邹涵,孙迪,郑楠,高洋. 新冠病毒疫苗接种的必要性及大学生疫苗接种现状. 预防医学论坛. 2023(01): 75-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邢菲菲,冯欢欢,杜昱,魏丹,杜阳光,童晶. 新冠病毒感染者恢复期血清抗体水平及诊断价值. 中华实验和临床病毒学杂志. 2023(04): 404-409 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 沈隽霏,杨静,邵文琦,王蓓丽,潘柏申,郭玮. 新型冠状病毒灭活疫苗接种后血清抗体水平调查分析. 国际检验医学杂志. 2023(19): 2315-2319 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 董柯,王琳,邵束钰,程春荣,杜浩峰. 新型冠状病毒疫苗不同接种剂次免疫效果研究. 标记免疫分析与临床. 2023(12): 2082-2085+2141 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张雪梅,孙成栋,刘佳,王燕,白鹭,童晶晶,尹海涛. 205例新型冠状病毒疫苗加强针接种者的血清新型冠状病毒抗体IgG检测结果分析. 山东医药. 2022(21): 26-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 曾丽娇,李晓鹤,陈凤,黄华,袁静. 新型冠状病毒Omicron变异株BA.2感染的老年病例临床特征分析. 实用中西医结合临床. 2022(08): 1-6+28 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
