Value of prediction model established based on ultrasound features combined with clinical data in evaluating axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with early breast cancer
-
摘要:目的
探讨基于超声特征联合临床资料建立的预测模型对早期乳腺癌患者腋窝淋巴结(ALN)转移的评估价值。
方法回顾性分析203例单侧早期乳腺癌女性患者的超声特征和临床资料,根据患者病理结果判定是否发生ALN转移并将患者分为转移组和非转移组。先对2组患者各项指标进行单因素分析,再行多因素Logistic回归分析,建立预测模型。应用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线检测模型的区分度,应用拟合优度检验评价模型的校准度,另选取78例单侧早期乳腺癌患者对该模型进行临床验证。
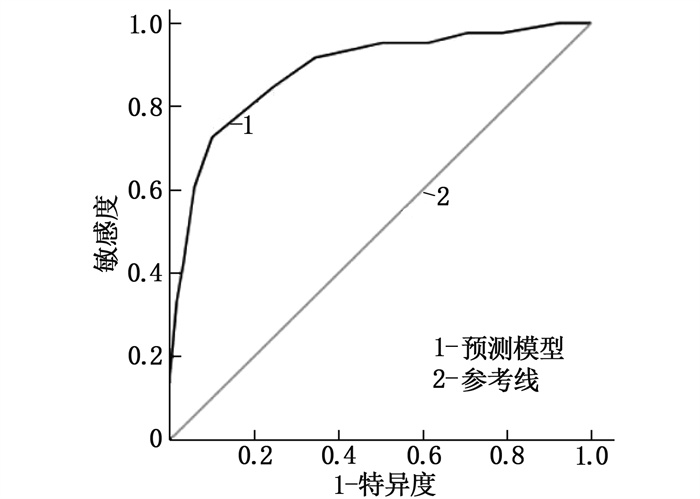
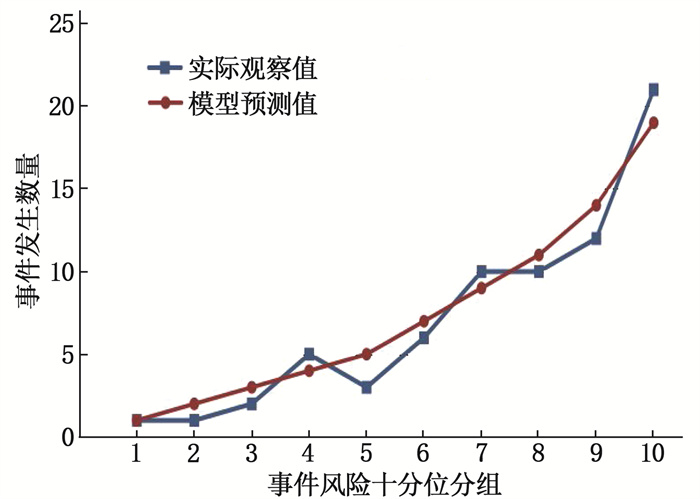
结果203例乳腺癌患者的病理结果显示, 71例患者出现ALN转移(转移组),占34.98%。肿瘤直径≥3 cm、肿瘤边缘模糊、ALN短径较长、ALN短径与长径比值(短径/长径)较高、ALN皮质厚度较厚、分化程度低、血清微小RNA-21(miRNA-21)表达量高均为早期乳腺癌患者ALN转移的危险因素(P<0.05)。根据危险因素建立预测模型,方程为Logit(P)=1.912×肿瘤直径≥3 cm(是=1, 否=0)+2.040×肿瘤边缘模糊(是=1, 否=0)+1.582×ALN短径(实测值)+3.374×ALN短径/长径(实测值)+2.264×ALN皮质厚度(实测值)+2.497×分化程度(高分化=0, 中分化=1, 低分化=2)+2.921×miRNA-21表达量(实测值)-33.615。ROC曲线分析结果显示,该模型的曲线下面积为0.886(95%CI: 0.838~0.933), 最大约登指数(0.736)对应的灵敏度、特异度分别为88.50%、83.60%。拟合优度检验显示,该模型不存在过拟合现象(χ2=2.067, P=0.394)。临床验证结果显示,该模型的灵敏度为87.10%, 特异度为82.98%, 准确度为84.62%。
结论基于肿瘤分化程度、血清miRNA-21表达量、肿瘤直径、肿瘤边缘以及ALN的短径、短径/长径、皮质厚度指标建立的预测模型对早期乳腺癌患者ALN转移风险具有较好的评估价值。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore value of prediction model established based on ultrasound features combined with clinical data in evaluating axillary lymph node (ALN) metastasis in patients with early breast cancer.
MethodsThe ultrasonic characteristics and clinical data of 203 women with unilateral early breast cancer were retrospectively analyzed. The patients were divided into metastatic group and non-metastatic group, and were determined whether they had ALN metastasis or not according to the pathological results. Single factor screening was performed for each index of the two groups. Logistic multivariate regression analysis was performed again and a prediction model was established. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to detect its discrimination, and goodness-of-fit test was used to evaluate the degree of calibration. Another 78 unilateral early breast cancer patients in our hospital were selected for clinical validation of the model.
ResultsThe pathological results of 203 breast cancer patients showed that ALN metastasis occurred in 71 cases(metastasis group), accounting for 34.98%. Tumor diameter ≥3 cm, blurred tumor margin, longer ALN short diameter, higher ALN short diameter to long diameter ratio, higher value of ALN cortical thickness, lower degree of differentiation, and higher level of serum microRNA-21(miRNA-21) expression were all risk factors for ALN metastasis in breast cancer patients (P<0.05). According to the risk factors, the prediction model expression equation was as follows. Logit(P)=1.912×tumor diameter ≥3 cm(yes=1, no=0)+2.040×tumor margin blur(yes=1, no=0)+1.582×ALN short diameter(measured value)+3.374×ALN short/long diameter(measured value)+2.264×ALN cortical thickness(measured value)+2.497×differentiation degree(yes=1, no=0)+2.921×miRNA-21 expression amount(measured value)-33.615. The area of the ROC curve of this model was 0.886 (95%CI, 0.838 to 0.933), the sensitivity and specificity corresponding to the maximum Youden index (0.736) were 88.50% and 83.60% respectively. Goodness of fit test showed that the model did not overfit (χ2=2.067, P=0.394). Clinical validation results showed that the sensitivity of the model was 87.10%, the specificity was 82.98%, and the accuracy was 84.62%.
ConclusionIt is valuable in predicting the risk of ALN metastasis by constructing a predictive model based on degree of tumor differentiation, serum miRNA-21 expression, tumor diameter, tumor margin, and ALN short-diameter, short-diameter/long-diameter ratio, and cortical thickness in early breast cancer patients.
-
-
表 1 2组超声特征及临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
指标 转移组(n=71) 非转移组(n=132) t/χ2 P 年龄≥60岁 26(36.62) 39(29.55) 1.061 0.303 绝经 32(45.07) 47(35.61) 1.740 0.187 肿瘤直径≥3 cm 24(33.80) 19(14.39) 8.568 0.003 肿瘤边缘模糊 35(49.30) 41(31.06) 6.554 0.010 肿瘤形态不规则 49(69.01) 77(58.33) 2.235 0.135 腋窝淋巴结长径/mm 14.06±3.54 13.58±3.31 0.962 0.337 腋窝淋巴结短径/mm 8.65±1.83 5.13±1.28 16.001 <0.001 腋窝淋巴结短径/长径 0.62±0.14 0.41±0.11 11.201 <0.001 腋窝淋巴结皮质厚度/mm 3.69±0.87 1.74±0.38 22.150 <0.001 临床分期 Ⅰ期 46(64.79) 93(70.45) 0.890 0.345 Ⅱ期 25(35.21) 39(29.55) 分化程度 低分化 28(39.44) 31(23.48) 6.440 0.040 中分化 31(43.66) 65(49.24) 高分化 12(16.90) 36(27.27) 雌激素受体阳性 25(35.21) 32(24.24) 2.751 0.097 孕激素受体阳性 29(40.85) 41(31.06) 1.956 0.162 人表皮生长因子受体2阳性 27(38.03) 36(27.27) 2.495 0.114 肿瘤增殖抗原Ki-67阳性 31(43.66) 47(35.61) 1.266 0.260 糖链抗原153/(U/mL) 29.05±4.93 27.98±4.25 1.616 0.108 D-二聚体/(μg/L) 184.56±46.73 179.75±41.87 0.749 0.455 白蛋白/(g/L) 29.48±6.84 30.86±7.32 1.310 0.192 微小RNA-21表达量 4.53±0.87 4.07±0.56 4.569 <0.001 表 2 早期乳腺癌患者ALN转移的多因素Logistic回归分析
变量 β S.E Waldχ2 P OR(95%CI) 肿瘤直径≥3 cm 0.648 0.317 4.179 0.031 1.912(1.375~3.981) 肿瘤边缘模糊 0.713 0.294 5.881 0.019 2.040(1.569~3.792) 腋窝淋巴结短径 0.459 0.238 3.719 0.036 1.582(1.184~2.787) 腋窝淋巴结短径/长径 1.216 0.548 4.924 0.027 3.374(2.447~5.895) 腋窝淋巴结皮质厚度 0.817 0.295 7.670 0.008 2.264(1.348~3.896) 分化程度 0.915 0.379 5.829 0.020 2.497(1.611~3.584) 微小RNA-21表达量 1.072 0.415 6.673 0.014 2.921(2.014~5.787) 常数项 -33.615 9.518 12.473 <0.001 — 表 3 预测模型的临床验证结果
模型预测结果 实际结果 合计 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 准确度/% 腋窝淋巴结转移 腋窝淋巴结未转移 腋窝淋巴结转移 27 8 35 — — — 腋窝淋巴结未转移 4 39 43 — — — 合计 31 47 78 87.10 82.98 84.62 -
[1] BUNDRED N J, BARNES N L P, RUTGERS E, et al. Is axillary lymph node clearance required in node-positive breast cancer[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2015, 12(1): 55-61. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.188
[2] JOO J H, KIM S S, SON B H, et al. Evaluation of the prognostic stage in the 8th edition of the American joint committee on cancer in patients with breast cancer and internal mammary lymph node metastasis[J]. Anticancer Res, 2018, 38(9): 5357-5361. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12864
[3] 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会. 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2011版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2011, 21(5): 367-417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3639.2011.05.010 [4] 牛昀. 2012年版《WHO乳腺肿瘤分类》新变化与临床治疗的关系[J]. 中华乳腺病杂志: 电子版, 2014, 8(3): 156-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHRD201403002.htm [5] 周子君, 古林, 张乃千, 等. T1a~1b期老年乳腺癌腋窝淋巴结转移的相关影响因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(19): 4209-4211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.19.016 [6] 王宋, 权毅. Luminal A型乳腺癌发生腋窝淋巴结转移的风险因素分析[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2021, 28(6): 789-793. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPWL202106019.htm [7] BLVTHNER E, BEDNARSCH J, MALINOWSKI M, et al. Dynamic liver function is an independent predictor of recurrence-free survival after curative liver resection for HCC-A retrospective cohort study[J]. Int J Surg, 2019, 71: 56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.08.033
[8] 刘信礼, 王雯, 牛学才, 等. 早期浸润性乳腺癌患者腋窝淋巴结转移的影响因素分析[J]. 山东医药, 2021, 61(28): 62-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYY202128015.htm [9] TSENG H S, CHEN L S, KUO S J, et al. Tumor characteristics of breast cancer in predicting axillary lymph node metastasis[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2014, 20: 1155-1161. doi: 10.12659/MSM.890491
[10] ANDERSSON Y, BERGKVIST L, FRISELL J, et al. Long-term breast cancer survival in relation to the metastatic tumor burden in axillary lymph nodes[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2018, 171(2): 359-369. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4820-0
[11] SUSINI T, NORI J, OLIVIERI S, et al. Predicting the status of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer: a multiparameter approach including axillary ultrasound scanning[J]. Breast, 2009, 18(2): 103-108. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2009.02.001
[12] YILMAZ M H, ESEN G, AYARCAN Y, et al. The role of US and MR imaging in detecting local chest wall tumor recurrence after mastectomy[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2007, 13(1): 13-18.
[13] WU J L, TSENG H S, YANG L H, et al. Prediction of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients based on pathologic information of the primary tumor[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2014, 20: 577-581. doi: 10.12659/MSM.890345
[14] 许睿, 钱军, 张明亮, 等. 长链非编码RNA MEG3对乳腺癌细胞侵袭及迁移的影响[J]. 赣南医学院学报, 2021, 41(3): 256-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GNYX202103008.htm [15] ZHANG C F, LIU K, LI T, et al. miR-21: a gene of dual regulation in breast cancer[J]. Int J Oncol, 2016, 48(1): 161-172. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3232
[16] 张瑞瑞, 赵桓玉, 周武碧, 等. 乳腺癌组织中Bmi-1和CARD9表达及其与淋巴结转移和预后的关联[J]. 西部医学, 2021, 33(11): 1642-1646, 1659. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIBU202111019.htm [17] LAMPIS A, CAROTENUTO P, VLACHOGIANNIS G, et al. MIR21 drives resistance to heat shock protein 90 inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154(4): 1066-1079. e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.043
[18] 唐诗聪, 陈东, 郭瑢, 等. miRNA-21调控HER-2阳性乳腺癌的血管生成[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2020, 41(8): 39-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KMYX202008007.htm -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 李孝辉,张晓彬,刘浩,徐继鹏,姜其学,刘磊. 苄星青霉素联合多西环素在早期梅毒治疗中的应用. 医药论坛杂志. 2025(05): 535-538 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 付家富,张红萍. 苄星青霉素联合头孢曲松钠治疗梅毒患者的效果. 中国当代医药. 2024(19): 34-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 许纯,李锦成,杨文彬,姜艳,杨科佼,周天祺,刘甲野. 2013—2023年扬州市梅毒流行病学特征分析. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(21): 22-27 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 崖顺波,陆桂甫. 头孢曲松联合苄星青霉素对梅毒患者免疫功能的影响及安全性分析. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志. 2023(07): 92-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王润龙,张海璐. 苄星青霉素联合复方甘草酸苷片治疗梅毒的临床疗效观察. 医学理论与实践. 2023(15): 2592-2594 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 吴晓燕. 复方黄柏液辅助治疗早期梅毒的效果及对RPR滴度、Wnt信号通路的影响. 中国性科学. 2023(08): 132-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陈筱铮. 孕产妇妊娠期梅毒治疗对新生儿预后的影响. 中国妇幼卫生杂志. 2021(05): 44-47+52 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 乔国安,张晓忠,杨晶雪. 早期梅毒患者应用头孢曲松治疗的效果研究. 黑龙江中医药. 2021(06): 476-477 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
