Correlation between atherogenic index of plasma and diabetic retinopathy
-
摘要:目的
探讨血浆致动脉硬化指数(AIP)与糖尿病视网膜病变(DR)的相关性。
方法选取在徐州医科大学附属医院内分泌科住院的2型糖尿病患者445例为研究对象,根据DR诊断及分期标准将患者分为无DR(NDR)组188例、非增生型DR(NPDR)组134例、增生型DR(PDR)组123例。比较各组患者一般资料和主要生化指标,计算AIP。采用Logistic回归分析探讨发生DR的危险因素,采用Spearman相关性分析探讨AIP与各危险因素的相关性,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析AIP筛查DR的价值。
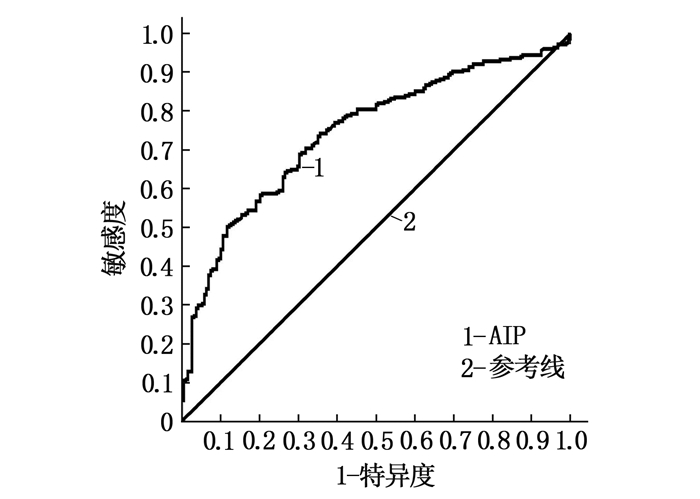
结果PDR组的年龄大于NDR组和NPDR组,病程长于NDR组和NPDR组,空腹血糖(FBG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、甘油三酯(TG)及AIP高于NDR组和NPDR组,估算肾小球滤过率(eGFR)水平低于NDR组和NPDR组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。Logistic回归分析结果显示,年龄、病程、HbA1c、LDL-C、eGFR及AIP是T2DM患者发生DR的独立影响因素。T2DM患者AIP预测发生DR时的曲线下面积为0.745(95%CI为0.700~0.791)。应用AIP筛查DR的阈值为0.186, 灵敏度为74.3%, 特异度为64.4%。
结论AIP可能是T2DM患者DR筛查可靠的新指标。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the correlation between atherogenic index of plasma(AIP) and diabetic retinopathy(DR).
MethodsA total of 445 patients with type 2 diabetes hospitalized in the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University were selected as study objects. According to DR diagnosis and staging criteria, the patients were divided into non-DR group (NDR group, n=188), nonproliferative group (NPDR group, n=134) and proliferative group (PDR group, n=123). The general information of patients and main biochemical indicators were collected. The general data and main biochemical indicators of patients in each group were compared, and AIP was calculated. The risk factors of DR were analyzed by Logistic regression, the correlations of AIP with risk factors were analyzed by Spearman correlation, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyze the value of AIP in screening DR.
ResultsAge in the PDR group was older, duration of diabetes in the PDR group was longer, the level of fasting blood glucose(FBG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride (TG) and AIP in the PDR group were significantly higher, and the level of estimated glomerular filtration (eGFR) were lower than those in the NDR group and NPDR group(P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that age, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, LDL-C, eGFR and AIP were independent influencing factors for DR in T2DM patients. The area under the curve of AIP in predicting DR in T2DM patients was 0.745 (95%CI, 0.700 to 0.791). The threshold of AIP for DR screening was 0.186, the sensitivity was 74.3%, and the specificity was 64.4%.
ConclusionAIP may be a reliable new indicator for DR screening in T2DM patients.
-
临床常采用经外周静脉置入中心静脉导管(PICC)为危重患者和化疗患者提供静脉营养支持及给药[1]。PICC使用方便,可有效降低穿刺频率,更好地保护血管,减轻化疗药物对机体损伤,提高患者生活质量[2-3]。但长期PICC置管可存在一些严重不良反应,而导管相关性皮肤损伤(CASI)是PICC置管患者不良反应之一, CASI不仅给患者带来痛苦,影响患者治疗效果,也为后续的临床治疗带来了一定困难,严重者可能引起感染,对患者预后不利[4-5]。血液系统肿瘤患者由于长期使用化疗药物易诱发多种并发症,造成身体抵御能力急速下降; 一旦发生CASI, 不仅给患者带来疼痛、瘙痒等不适感,还会引起非计划性拔管,影响化疗疗程,进而降低患者生活质量,严重时甚至危及生命。近年来,有关血液系统肿瘤PICC患者CASI护理的报道较多,但目前尚缺乏系统的循证策略作为预防管理方案的依据。本研究总结血液系统肿瘤PICC患者CASI预防及管理的最佳证据,并将其有效应用于血液系统肿瘤病房临床护理工作中,旨在为护士在临床实践中提供理论依据,有效降低血液系统肿瘤PICC患者CASI发生率,保证护理质量,减轻患者经济负担。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
以2020年5月—2021年5月火箭军特色医学中心证据应用前纳入的57例血液系统肿瘤PICC置管患者为证据应用前组,以2021年6月—2022年6月证据应用后纳入的63例血液系统肿瘤PICC置管患者为证据应用后组。纳入标准: ①临床上符合血液系统肿瘤化疗指征者; ②均于本院首次接受PICC导管留置及维护且均持续留置3个月及以上者。排除标准: ①存在免疫系统性疾病患者; ②存在先天性皮肤疾病者; ③置管前存在皮肤水肿、皮炎等情况者; ④存在其他可能导致皮肤损伤等原因者; ⑤临床资料不完整者。本研究患者及其家属对研究内容及目的已知晓,且已签署知情同意书。本研究经本院医学伦理委员会同意。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 置管方法:
所有患者穿刺均采用巴德公司的4F三向瓣膜式、前端开口式耐高压4F或5F的PICC导管穿刺,并在超声系统引导下进行。整个穿刺过程严格进行无菌操作,建立最大化无菌屏障。
1.2.2 CASI判断标准:
(1) 机械性损伤,包括皮肤剥离、撕裂、张力性水泡。①皮肤剥离。胶带或敷贴去除后,有多层角质细胞被一起去除,表现为浅表性损伤且不规则,在神经末梢区皮肤可出现深红色或红色的光泽或潮湿样,无明显不适感,严重者可见红斑和水疱; ②皮肤撕裂伤。由剪切刀、摩擦力所造成的皮肤之间的分离,能造成部分或全皮层的损伤; ③张力性水泡。使用的胶带或者敷料质地比较坚硬,黏贴不当,皮肤出现肿胀或关节活动而形成剪切力,导致表皮和真皮之间分离,水疱常出现在皮缘处。(2) 接触性皮炎,医用黏胶会导致刺激性接触性皮炎,局部发红、肿胀,甚至有水疱,持续时间短。(3) 过敏性皮炎,有明显的红斑、水泡出现,且皮肤损伤区有明显瘙痒感,持续时间较长,可持续1周左右。(4) 皮肤浸润,密闭条件下的胶带会引起皮肤浸润和刺激,皮肤长时间处于过度潮湿环境会导致皮肤变软、起皱,呈白色/灰色,易因摩擦力及刺激导致皮损,且渗透性增强。(5) 毛囊炎,由于剃毛发后使用黏胶产品,导致细菌滞留在胶带或敷贴引起毛囊炎性反应。
1.2.3 基线审查:
成立审查小组,小组由护士长1名、静疗组长1名、静疗专科护士2名、伤口造口失禁专科护士1名、医生1名组成。根据2014版乔安娜布里格斯研究所(JBI)循证卫生保健中心证据预分级及证据推荐级别系统,本研究最终形成15条最佳证据。纳入血液病科护士及PICC门诊护士共20名,均在本科室工作年限≥6个月。(1) 证据和审查指标,对15条最佳证据进行整体分析,最终制订出9条证据审查指标,具体如下。①最佳证据,识别患者年龄、CASI既往史、基础疾病等危险因素,更换黏胶产品前评估患者皮肤,皮肤破损时,评估其破损程度; 审查指标,责任护士对使用黏胶产品的患者进行风险评估并登记详细信息,更换黏胶产品前对皮肤状况进行评估并登记。②最佳证据,选择合适皮肤消毒剂,待消毒剂完全干燥后才可使用敷贴; 审查指标,责任护士每次使用低刺激皮肤消毒剂消毒皮肤组织,干燥后粘贴敷料。③最佳证据,根据需求选择合适的黏胶产品。审查指标,对于水肿及活动大区域,选择伸展度强的敷料; 对于敏感皮肤,选择抗过敏敷料; 对于皮脆弱肤患者,选择硅类敷料。敷料时应顺着皮肤纹理粘贴。④最佳证据,运用正确的粘贴技术,审查指标,无张力粘贴,避免物理性摩擦或牵拉,粘贴后从胶带中央往两边适当按压,手术切口部位粘贴敷料时应与伤口平行。⑤最佳证据,运用正确的移除技术,审查指标,揭除时一只手按压皮肤,另一只手缓慢以0°或180°向伤口移除,避免物理性损伤。同时,应顺着毛发生长方向撕开; 当胶带粘着皮肤揭不掉时不要强行揭除,可将酒精或乳液涂抹在胶布背衬以降低黏性。⑥最佳证据,确保患者舒适度,重视患者出现的疼痛、瘙痒等不适; 审查指标,准确评估患者出现的疼痛、瘙痒情况,并给予相应措施。⑦最佳证据,医疗机构应制订预防CASI的护理标准及医用黏胶使用规则; 审查指标,制订预防CASI的护理标准及规范医用黏胶产品使用流程,并完善查检制度。⑧最佳证据,健全CASI教育培训体系,医护人员、家属、患者均应接受相应CASI教育,共同参与CASI管理; 审查指标,定期开展CASI预防及管理相关知识培训。⑨最佳证据,将“预防CASI的护理标准”纳入护士培训及考核项目中; 审查指标,将“预防CASI的护理标准”纳入护士培训及考核项目。(2) 证据基线审查方法,对2020年5月—2021年5月在本院治疗行PICC置管的57例血液系统肿瘤患者以及审查小组进行证据审查,包括血液系统肿瘤患者CASI发生率、审查小组CASI预防认知水平及审查指标依从情况。
1.2.4 证据应用:
2021年6月—2022年6月实施证据循证,总结障碍因素后制订方案。(1) 障碍因素。①血液科目前尚缺乏针对血液系统肿瘤患者CASI预防及处理的风险评估工具; ②血液科尚无系统性血液系统肿瘤患者CASI预防及处理操作规范化流程、管理制度及标准制定的循证依据; ③患者及患者家属欠缺使用医用黏胶产品期间的皮肤保护相关认知; ④护士对CASI风险评估、预防及管理的证据缺乏认知。(2) 实施方案。①制订“血液系统肿瘤患者CASI风险评估量表”,内容包括高危患者评估,针对风险因素制定干预措施及CASI每日评估记录单,关注血液系统肿瘤PICC置管患者皮肤情况,并如实记录皮肤损伤类型及严重程度。②制订《CASI预防及护理手册》,便于护士识别并采取相应措施。制订正确的敷料粘贴、揭除流程标准及不同部位敷料剪裁及粘贴图谱手册,便于护士查阅。科室根据患者皮肤情况,配备足量的皮肤保护剂、不同类型敷料,便于护士拿取。③加强患者营养供给,保持良好的饮食习惯。采用多种形式进行日常皮肤护理宣教,并指导患者及其家属每日选择温和的皮肤清洁剂进行皮肤清洁,并在清洁后及时涂抹皮肤润肤剂,避免皮肤过于干燥。普及使用医用黏胶产品后皮肤护理相关知识。④定期开展CASI风险识别及预防策略等相关知识培训,并共同制订CASI培训资源包。建立CASI知识危险群,不定期以文字或视频形式发送CASI预防相关知识及粘贴敷料的操作视频。采用情境模拟的方式指导护士正确选择并裁剪预防性敷料。
1.2.5 证据应用后再审查:
对本院行PICC置管的63例血液系统肿瘤患者以及审查小组进行审查,方法同基线审查,计算每条审查标准的执行率。
1.3 观察指标
① 比较2组患者皮肤瘙痒、揭除敷料后疼痛及CASI发生情况。自制血液系统肿瘤患者资料收集表,包括一般资料、入院期间CASI发生部位、性质、症状,记录患者皮肤瘙痒、揭除敷料后疼痛。对使用贴辅料患者周围皮肤进行干燥程度评分, 0分为皮肤光滑、不干燥; 1分为皮肤有轻微干燥,偶有脱屑,分布不均; 2分为中度脱屑,脱屑分布略均匀,鳞屑细小,不易揭起; 3分为重度干燥,鳞屑广泛,周边翘起,皮肤表面发白; 4分为极重度干燥,有大量鳞屑,鳞屑周边广泛分离,有皲裂。患者入组时采用Braden量表评估PICC相关性皮肤损伤风险,该量表包括感觉、潮湿、营养、活动、移动、摩擦和剪切力7项指标。每个条目1~4分,满分23分,最低得分6分,评分越高表示皮肤损伤风险越小。②比较审查小组循证实践后审查指标的执行情况。根据10条审查指标设计CASI预防核查方案,核查护士对10条审查指标执行情况。③比较审查小组循证实践前后CASI预防知识的知晓情况: 自行设计调查问卷对护士CASI预防知识的知晓情况进行调查,问卷包括皮肤评估、皮肤护理、预防性敷料的选择、操作手法、观察及维护等5个方面,每个方面4题,每题5分,总分为100分。
1.4 统计学分析
使用SPSS 23.0软件对获得的研究数据进行统计学分析。计量资料(年龄、血清白蛋白、皮肤干燥度评分、Braden评分、皮肤评估评分、皮肤保护评分、预防性敷料选择评分、操作手法评分和观察及维护评分)采用(x±s)表示,血液系统肿瘤患者证据应用前后数据差异行两样本独立t检验; 审查小组证据应用前后数据差异行配对t检验。计数资料(性别、血液系统肿瘤类型)采用[n(%)]表示,证据应用前后数据差异行χ2检验。检验水准为α=0.05, 双侧P < 0.05说明差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组血液系统肿瘤患者一般资料比较
2组血液系统肿瘤患者性别、年龄、血液系统肿瘤类型、血清白蛋白、皮肤干燥度评分和Braden评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2组血液系统肿瘤患者一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]一般资料 分类 证据应用前组(n=57) 证据应用组后(n=63) 性别 男 26(45.61) 24(38.10) 女 31(54.39) 39(61.90) 年龄/岁 48.65±4.73 49.02±4.54 血液系统肿瘤类型急性 白血病 16(28.07) 17(26.98) 恶性淋巴瘤 21(36.84) 25(39.68) 多发性骨髓瘤 20(35.09) 21(33.33) 血清白蛋白/(g/L) 33.12±3.65 32.97±3.71 皮肤干燥度评分/分 1.81±0.23 1.87±0.26 Braden评分/分 19.46±2.75 19.11±2.36 2.2 2组血液系统肿瘤患者皮肤瘙痒、揭除敷料后疼痛及CASI发生率比较
证据应用前,发生皮肤瘙痒11例(19.30%), 揭除敷料后疼痛24例(45.61%), CASI 12例(21.05%); 证据应用后,皮肤瘙痒4例(6.35%), 揭除敷料后疼痛7例(11.11%), CASI 12例(6.35%)。证据应用后,皮肤瘙痒和揭除敷料后疼痛患者占比及CASI发生率低于证据应用前,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。证据应用前组CASI种类包括机械性损伤3例,接触性皮炎2例,过敏性皮炎3例,皮肤浸润2例,毛囊炎2例。证据应用后组CASI种类包括机械性损伤2例,接触性皮炎1例,皮肤浸润1例。
2.3 证据应用后审查指标的执行情况
指标1执行达标率为93.33%, 指标2~7的达标率分别提升至81.67%、83.33%、86.67%、88.33%、78.33%、91.67%, 指标8~10的达标率均达到100.00%。
2.4 审查小组循证实践前后CASI预防知识知晓情况比较
证据应用后组护士的皮肤评估、皮肤保护、预防性敷料选择、操作手法、观察及维护评分以及总分高于证据应用前组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 审查小组循证实践前后CASI预防知识知晓情况比较(x±s)分 指标 证据应用前组(n=20) 证据应用后组(n=20) 皮肤评估 10.36±2.43 17.47±3.17* 皮肤保护 11.08±2.66 16.76±3.63* 预防性敷料选择 14.52±2.82 18.19±3.58* 操作手法 12.32±2.88 17.01±3.42* 观察及维护 11.78±2.73 16.27±3.28* 总分 60.43±7.14 87.67±9.03* 与证据应用前组比较, *P < 0.05。 3. 讨论
PICC对于长期需要静脉输液的血液系统肿瘤患者是首要选择[7],该方法具有操作简单、维护方便、保留时间长的优势,但因患者长期PICC置管,导管固定部位反复使用黏胶拉扯导致CASI[8]。目前,中国临床并未十分重视CASI的预防及管理,同时也无规范化护理流程及标准管理体系,造成CASI发生率常年居高不下。同时,临床医护人员对CASI缺乏清晰认知,尚不能有效识别CASI的高危因素及高风险患者,影响临床护理工作的开展。本研究通过总结血液系统肿瘤患者CASI预防及管理最佳证据进行循证实践,为制订科学、有效的护理流程及管理制度提供支持,有利于临床实践。定时对护士开展CASI知识培训,帮助护士有效识别风险因素,能够降低血液系统肿瘤患者CASI发生率。由于血液系统肿瘤患者在化疗后可能出现皮肤不良反应,若患者受到过多物理摩擦或牵拉,容易损伤皮肤组织。因此,护士需要选择合适黏胶产品、使用规范粘贴及揭除手法,避免因操作不当对患者造成皮肤损伤。审查小组不定期在微信群中发送CASI相关操作视频和规范操作手法,同时采用情境模拟的方式有利护士选择正确预防性敷料并规范剪裁,减轻患者皮肤瘙痒、疼痛等不适感,进而提高患者生活质量。本研究将CASI发生率作为血液科护理质量检测的结果指标,将循证护理应用于护理质量控制中,有效降低CASI发生的可能性。
护士是患者治疗期间除家属外接触最频繁的人群, CASI的发生在一定程度上有赖护士对CASI的认知水平、CASI发生风险的识别以及预防能力[9]。本研究通过对护士开展CASI知识培训,并通过碎片化的学习提高护士对CASI预防知识认知水平。本研究中,基线审查时护士CASI总分为(60.43±7.14)分,而证据应用后护士CASI总分提升至(87.67±9.03)分,说明循证证据应用有助于提高护士CASI预防知识水平,进而降低CASI发生风险。
应用循证护理理论进行临床决策过程的核心是将临床证据、个人经验与患者实际状况和意愿相结合[10-11]。最佳研究证据是指对临床相关研究的文献应用临床流行病学原则、方法及有关质量评价标准,经过认真分析与评价获得真实可靠且具有临床主要价值的科研成果或证据[12-13]。审查指标是评价护理人员实践活动是否符合最佳证据的重要依据,也是衡量质量改进和照护质量的标准[14]。本研究显示,最佳证据与临床实践结果存在差距。同时本研究总结出4个主要障碍因素,并及时制订方案,确保循证实践完成。证据应用前,指标1~10执行率均 < 50%,根本原因是血液科护士对CASI认知不足,缺乏CASI护理的规范化流程,导致护理效果不佳,增大CASI发生风险。证据应用过程中,循证护理培训内容以及执行循证实践纳入绩效考核,结果显示,各审查指标基本达到80.00%以上,其达标率明显提高,说明循证护理实践能够提高护士CASI认知水平及风险识别能力,并提高护理质量。
综上所述,本研究分析了CASI预防及管理的最佳证据并制订审查指标,并与血液科情境相结合,总结出障碍因素并制订相应实施计划,促进证据向临床转化,进而预防血液系统肿瘤患者CASI的发生,加强CASI预防的规范化管理,提高护士循证执行能力。但受制于时间、人员等因素,数据可能存在偏倚。今后需扩大样本量,联合多中心进行CASI预防和管理的循证实践,进一步推广运用循证方法。
-
表 1 各组患者临床指标水平比较(x±s)[n(%)]
临床指标 NDR组(n=188) NPDR组(n=134) PDR组(n=123) F/χ2 P 男 118(62.77) 84(62.69) 70(56.91) 1.27 0.530 女 70(23.23) 50(37.31) 53(43.09) 年龄/岁 46.56±10.86 54.52±9.83* 63.85±10.75*# 100.75 <0.001 病程/年 2(1, 50) 8(3, 12)* 15(10, 20)*# 162.83 <0.001 BMI/(kg/m2) 25.10±3.12 25.46±3.56 25.66±3.70 1.11 0.330 高血压 56(29.80) 35(26.10) 44(35.80) 2.87 0.240 吸烟 48(25.50) 22(16.40) 33(26.80) 4.95 0.090 饮酒 31(16.50) 29(21.60) 17(13.80) 2.89 0.240 SBP/mmHg 128.93±12.81 130.08±17.03 133.02±19.92 2.38 0.090 DBP/mmHg 81.85±9.33 81.45±10.36 81.98±11.65 0.10 0.910 HbA1c/% 7.98±2.20 8.65±2.11* 9.38±2.09*# 15.98 <0.001 FBG/(mmol/L) 8.35±2.62 9.21±3.23* 10.10±3.19*# 12.95 <0.001 ALT/(U/L) 19.00(14.00, 28.00) 18.50(14.00, 26.00) 18.00(13.00, 26.00) 1.65 0.450 TBIL/(μmol/L) 11.80(9.00, 15.10) 10.30(7.95, 14.03)* 9.70(7.00, 12.90)* 17.48 <0.001 DBIL/(μmol/L) 3.84±1.40 3.91±1.68 3.67±1.36 0.86 0.420 TBA/(μmol/L) 3.40(2.03, 5) 3.90(2.40, 5.10) 3.50(2.20, 5.90) 2.64 0.270 UREA/(mmol/L) 5.61±1.49 5.66±1.86 6.03±2.52 1.96 0.140 Scr/(μmol/L) 56(48, 65) 58(50, 69) 65(56, 90) *# 35.77 <0.001 UA/(μmol/L) 288.32±75.81 296.31±88.92 296.13±88.61 0.49 0.615 CysC/(mg/L) 0.73±0.14 0.89±0.43* 0.96±0.38* 20.58 <0.001 TC/(mmol/lL) 5.09±1.09 5.11±1.29 5.24±1.52 0.55 0.580 TG(mmol/L) 1.47(1.13, 1.89) 1.96(1.40, 2.81) * 2.36(1.88, 3.00) *# 77.93 <0.001 HDL-C/(mmol/L) 1.20±0.33 1.07±0.27* 1.01±0.33* 14.50 <0.001 LDL-C/(mmol/L) 2.67±0.83 3.02±1.10* 3.34±1.47*# 13.25 <0.001 eGFR 120.88±22.60 106.49±28.74* 83.63±33.61*# 66.42 <0.001 AIP 0.11(-0.05, 0.27) 0.26(0.14, 0.49)* 0.39(0.25, 0.56)*# 89.06 <0.001 BMI: 体质量指数; SBP: 收缩压; DBP: 舒张压; HbA1c: 糖化血红蛋白; FBG: 空腹血糖; ALT: 谷丙转氨酶; TBIL: 总胆红素;
DBIL: 直接胆红素; TBA: 总胆汁酸; UREA: 尿素; Scr: 肌酐; UA: 尿酸; CysC: 胱抑素C; TC: 总胆固醇; TG: 甘油三酯;
HDL-C: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; eGFR: 估算肾小球滤过率; AIP: 血浆致动脉硬化指数。
与NDR组比较, * P<0.05; 与NPDR组比较, #P<0.05。表 2 T2DM患者发生DR的影响因素多元Logistic回归分析
因素 B SE Wald χ2 P OR(95%CI) 年龄 0.043 0.016 7.674 0.006 1.044(1.013~1.076) 病程 0.212 0.034 39.870 <0.001 1.236(1.157~1.32) HbA1c 0.149 0.064 5.347 0.021 1.161(1.023~1.317) LDL-C 0.326 0.151 4.633 0.031 1.385(1.030~1.862) eGFR -0.022 0.006 12.389 <0.001 0.978(0.966~0.990) AIP 0.341 0.054 40.152 <0.001 1.406(1.266~1.563) 常量 -3.737 1.301 8.252 0.004 — HbA1c: 糖化血红蛋白; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; eGFR: 估算的肾小球滤过率; AIP: 血浆致动脉硬化指数。 -
[1] LI Y Z, TENG D, SHI X G, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: national cross sectional study[J]. BMJ, 2020, 369: m997.
[2] TEO Z L, THAM Y C, YU M, et al. Global prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and projection of burden through 2045: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ophthalmology, 2021, 128(11): 1580-1591. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2021.04.027
[3] DOBIÁSOVÁ M, RASLOVÁK, RAUCHOVÁH, et al. Atherogenic lipoprotein profile in families with and without history of early myocardial infarction[J]. Physiol Res, 2001, 50(1): 1-8.
[4] ZHOU Y P, SHANG X L. Usefulness of atherogenic index of plasma for estimating reduced eGFR risk: insights from the national health and nutrition examination survey[J]. Postgrad Med, 2021, 133(3): 278-285. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2020.1838138
[5] HERNÁNDEZ J L, OLMOS J M, PARIENTE E, et al. The atherogenic index of plasma is related to a degraded bone microarchitecture assessed by the trabecular bone score in postmenopausal women: the Camargo Cohort Study[J]. Maturitas, 2021, 148: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2021.03.008
[6] FLAXEL C J, ADELMAN R A, BAILEY S T, et al. Diabetic retinopathy preferred practice pattern[J]. Ophthalmology, 2020, 127(1): P66-P145. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.09.025
[7] ISMAIL-BEIGI F, CRAVEN T, BANERJI M A, et al. Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial[J]. Lancet, 2010, 376(9739): 419-430. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60576-4
[8] ONAT A, CAN G, KAYA H S, et al. "Atherogenic index of plasma" (log10 triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol) predicts high blood pressure, diabetes, and vascular events[J]. J Clin Lipidol, 2010, 4(2): 89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2010.02.005
[9] NATIONAL CHOLESTEROL EDUCATION PROGRAM (NCEP) EXPERT PANEL ON DETECTION E. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel Ⅲ) final report[J]. Circulation, 2002, 106(25): 3143-3421. doi: 10.1161/circ.106.25.3143
[10] FU L Y, ZHOU Y, SUN J X, et al. Atherogenic index of plasma is associated with major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2021, 20(1): 201. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01393-5
[11] 张倩倩, 时涵远, 李馨航, 等. 甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数和血浆致动脉硬化指数评价冠心病的临床价值[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2022, 28(1): 73-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYK202201016.htm [12] QIN Z, ZHOU K, LI Y P, et al. The atherogenic index of plasma plays an important role in predicting the prognosis of type 2 diabetic subjects undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: results from an observational cohort study in China[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2020, 19(1): 23. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-0989-8
[13] 赵洁, 李淑英, 张英, 等. 中青年和老年冠心病患者LDL不同亚型与AIP的相关性分析[J]. 天津医药, 2021, 49(1): 54-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ202101013.htm [14] AKBAS E M, TIMUROGLU A, OZCICEK A, et al. Association of uric acid, atherogenic index of plasma and albuminuria in diabetes mellitus[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2014, 7(12): 5737-5743.
[15] WONG T Y, CHEUNG N, TAY W T, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy: the Singapore Malay Eye Study[J]. Ophthalmology, 2008, 115(11): 1869-1875. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.05.014
[16] RELHAN N, FLYNN H W Jr. The Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study historical review and relevance to today's management of diabetic macular edema[J]. Curr Opin Ophthalmol, 2017, 28(3): 205-212. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000362
[17] SRINIVASAN S, RAMAN R, KULOTHUNGAN V, et al. Influence of serum lipids on the incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy and macular oedema: Sankara Nethralaya Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology And Molecular genetics Study-Ⅱ[J]. Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2017, 45(9): 894-900. doi: 10.1111/ceo.12990
[18] EBELING P, KOIVISTO V A. Occurrence and interrelationships of complications in insulin-dependent diabetes in Finland[J]. Acta Diabetol, 1997, 34(1): 33-38. doi: 10.1007/s005920050062
[19] KANTER J E, HSU C C, BORNFELDT K E. Monocytes and macrophages as protagonists in vascular complications of diabetes[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2020, 7: 10. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00010
[20] CANPOLAT A G, EMRAL R, KESKIN Ç, et al. Association of monocyte-to-high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio with peripheral neuropathy in patients with Type Ⅱdiabetes mellitus[J]. Biomark Med, 2019, 13(11): 907-915. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2018-0451
[21] ROLIN J, MAGHAZACHI A A. Implications of chemokines, chemokine receptors, and inflammatory lipids in atherosclerosis[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2014, 95(4): 575-585. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1113571
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 陈慧,班锦青,梁静林. 不同送鞘方式在改良赛丁格PICC技术中的应用研究进展. 微创医学. 2024(02): 187-190 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈静,丁菊香. 莫匹罗星软膏联合新癀片贴敷应用于化疗药物皮下注射所致皮肤损害的临床研究. 生命科学仪器. 2024(03): 50-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 阳艳晖,肖少文,梁桂兴. 专科护理门诊实施责任制整体护理对留置PICC导管相关性皮肤损伤患者的影响. 中外医疗. 2024(27): 156-159+176 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈金莲,蔡燕萍. 改良型中等长度导管在晚期恶性肿瘤患者中的应用效果. 中国医药指南. 2023(34): 81-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
