Relationships of preoperative serum ferritin, albuminand ratio of ferritin to albumin with prognosis after hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要:目的
探讨术前血清铁蛋白、白蛋白、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值与肝细胞癌患者肝切除术预后的关系。
方法回顾性分析2015年1月—2020年1月行肝切除术治疗的112例肝细胞癌患者的临床资料。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析血清铁蛋白、白蛋白、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值预测不良预后的最佳临界值。根据临界值对患者进行分类,分析不同血清铁蛋白、白蛋白、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值与临床病理特征的关系。采用多因素Cox比例风险回归分析影响预后的相关因素。
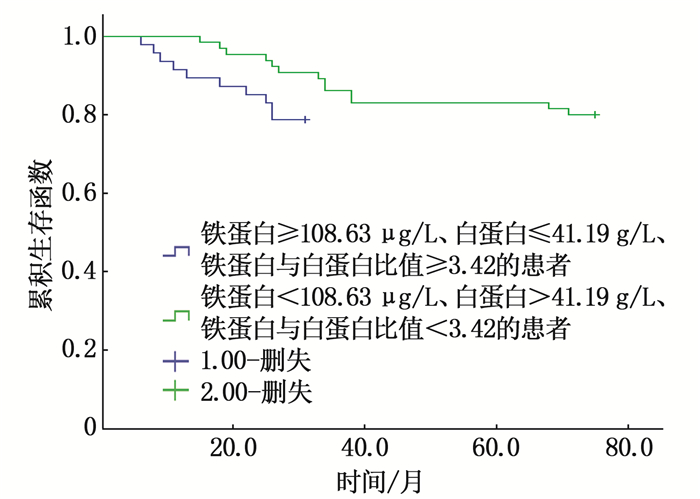
结果112例患者总生存期为5~75个月,平均(53.84±6.51)个月; 对于铁蛋白≥108.63 μg/L、白蛋白≤41.19 g/L、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值≥3.42的患者,其生存期为5~31个月,平均(28.56±3.12)个月; 对于铁蛋白<108.63 μg/L、白蛋白>41.19 g/L、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值<3.42的患者,其生存期为12~75个月,平均(72.11±1.25)个月; 上述差异有统计学意义(t=101.924, P<0.001)。术前血清铁蛋白、白蛋白、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值与肝硬化有相关性(P<0.05)。多因素Cox比例风险回归分析结果显示,血清铁蛋白≥108.63 μg/L、白蛋白≤41.19 g/L、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值≥3.42、有肝硬化是肝细胞癌患者肝切除术后预后不良的影响因素。
结论术前血清铁蛋白≥108.63 μg/L、白蛋白≤41.19 g/L、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值≥3.42是肝细胞癌患者肝切除术预后的独立危险因素,术前血清铁蛋白、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值升高以及白蛋白水平降低提示预后不良。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the relationships of preoperative serum ferritin, albumin and ratio of ferritin to albumin with prognosis after hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
MethodsClinical materials of 112 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by hepatectomy from January 2015 to January 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. The optimal critical value of serum ferritin, albumin and the ratio of ferritin to albumin in predicting poor prognosis was analyzed by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The patients were classified according to the critical value, and the relationships of different serum ferritin, albumin, and ratio of ferritin to albumin ratio with clinicopathological features were analyzed. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression was used to analyze the related factors affecting the prognosis.
ResultsThe overall survival of 112 patients was 5 to 75 months, with an average of (53.84±6.51) months; for patients with ferritin ≥ 108.63 μg/L, albumin ≤ 41.19 g/L and the ratio of ferritin to albumin ≥ 3.42, their survival was 5 to 31 months, with an average of (28.56±3.12) months; for patients with ferritin < 108.63 μg/L, albumin>41.19 g/L and ratio of ferritin to albumin < 3.42, their survival was 12 to 75 months, with an average of (72.11±1.25) months; the differences mentioned above were statistically significant (t=101.924, P < 0.001). Preoperative serum ferritin, albumin and the ratio of ferritin to albumin were correlated with liver cirrhosis (P < 0.05). Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis showed that serum ferritin ≥ 108.63 μg/L, albumin ≤ 41.19 g/L, the ratio of ferritin to albumin ≥ 3.42 and cirrhosis were the influencing factors of poor prognosis after hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
ConclusionPreoperative serum ferritin ≥ 108.63 μg/L, albumin ≤ 41.19 g/L and ratio of ferritin to albumin ≥ 3.42 are the independent risk factors for the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy, and the increase of serum ferritin and ratio of ferritin to albumin as well as the decrease of albumin level before hepatectomy suggest poor prognosis.
-
Keywords:
- hepatocellular carcinoma /
- hepatectomy /
- ferritin /
- albumin /
- ratio of ferritin to albumin /
- cirrhosis /
- prognosis
-
急性有机磷农药中毒(AOPP)是临床常见的急性药物性中毒类型,具有并发症发生率高、病死率高等特点,尤其是AOPP患者因肝肾损伤、呼吸衰竭等严重不良事件而导致的死亡风险较高[1]。AOPP患者往往存在心理状态不稳定,而导泻、灌肠等处理也可能对患者造成一定的痛苦,严重的心理应激将影响患者的治疗依从性及康复,部分患者甚至存在自杀倾向[2]。既往临床救治及干预多注重挽救生命或医学模式的转变,对患者心理状况的重视度不足。在当前生理-心理-社会综合医疗模式下,心理状态及其护理干预也是疾病干预的重要内容。本研究调查分析了71例AOPP患者的心理状况及不良事件发生情况,总结了有效的护理干预策略,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取本院2020年1月—2021年9月住院治疗的71例AOPP患者为研究对象。纳入标准: ①具有明确的有机磷农药接触史者; ②符合AOPP的诊断标准者[3]; ③首次发生农药中毒者; ④患者或其家属对本研究知情同意且签署知情同意书。排除标准: ①合并其他类型中毒者; ②既往已存在心、脑、肝、肺、肾等重要脏器功能障碍者; ③合并免疫系统疾病或长期使用免疫抑制剂、恶性肿瘤者; ④严重糖尿病者; ⑤入院24 h内死亡者。本研究获得本院伦理委员会的批准。
1.2 调查工具
1.2.1 一般资料调查表
由研究小组自行设计一般资料调查表,包括性别、年龄、文化程度、中毒农药种类、入院24 h内的急性生理和慢性健康状况评分量表(APACHE Ⅱ)等。APACHE Ⅱ[4]包含体温、平均动脉压、呼吸频率、心率等12个项目,单项评分0~4分,总分0~71分,得分越高提示病情越严重。
1.2.2 不良事件调查表
由研究小组自行设计,由临床护士记录,由专科医生诊断后报告,统计住院期间不良事件发生率,包括代谢性酸中毒、高钠血症、低血压、肺部感染、肝损伤、肾损伤、呼吸衰竭、休克等。
1.2.3 心理状况评定表量
采用齐艳等[5]设计的非精神科住院患者心理状态评定量表(MSSNS)进行评价,包括焦虑(13项)、抑郁(10项)、孤独(7项)与愤怒(8项)4个维度,共38个项目,单项按0~4分的Likert 5级法评价, 4个维度累积得分为MSSNS总分,得分范围0~152分,得分越高提示负性心理状况越严重。量表内部的一致性系数为0.933, 分半信度系数为0.894, 信效度良好。得分 < 60分为正常, 60~ < 70分为轻度异常, ≥70分为中重度异常。
1.3 研究方法
由经过统一培训的研究人员进行问卷调查,待患者生命体征平稳后24 h内,在征得患者和(或)家属同意的情况下,在住院病房内进行一对一的现场调查,阅读或填写困难者,由研究人员采用通俗易懂的语言询问患者后代为填写。调查人员采用统一指导语指导患者回答问卷,现场回收问卷。累计发放问卷71份,回收有效问卷71份,有效回收率为100%。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 22.0统计学软件进行数据分析。计量资料以均数±标准差表示,符合正态分布、方差齐性的数据比较采用t检验,不符合正态分布的数据采用Mann-Whitney U检验; 计数资料以[n(%)]表示,数据比较采用卡方(χ2)检验,有序分类变量比较采用秩和检验; 采用Logistic多元回归模型分析影响因素。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 患者的一般资料
71例AOPP患者中,男31例,女40例; 年龄15~90岁,平均(41.96±6.01)岁; 文化水平为小学及以下39例,初中18例,高中及以上14例; 就诊时间0.5~5.0 h, 平均(3.01±0.45) h; 服毒量35~210 mL, 平均(85.95±15.21) mL; 中毒农药种类为敌敌畏17例,氧化乐果16例,辛硫磷12例,乐果9例,甲拌磷7例,其他10例; 患者均为口服中毒。
2.2 患者的不良事件发生情况
71例患者中, 14例患者发生不良事件,发生率为19.72%(14/71), 其中7例发生1种并发症, 6例发生2种并发症, 1例发生3种并发症,具体为肺部感染8例次,呼吸衰竭3例次,中间综合征3例次,多器官功能衰竭(MODS)3例次,应激性溃疡出血2例次,其他3例次,共计22例次。
2.3 患者的心理状态MSSNS评分
以齐艳等[5]研究中常模数据为参照,本研究71例AOPP患者的MSSNS各维度评分及总分均高于常模水平,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 1。本研究共检出轻度异常23例(32.39%), 中重度异常9例(12.68%), 总异常率为45.07%(32/71), 见表 2。
表 1 AOPP患者与常模的MSSNS评分比较(x±s)分 组别 n 焦虑 抑郁 孤独 愤怒 总分 AOPP组 71 26.71±5.93* 17.21±4.55* 14.96±4.14* 12.86±3.01* 70.74±15.19* 常模组 1 010 19.20±5.82 13.70±4.20 12.25±3.72 9.19±2.17 54.33±13.36 与常模组比较, *P < 0.05。 表 2 患者的心理状态异常检出率[n(%)]项目 组别 n 正常 轻度异常 中重度异常 总异常 Z P 焦虑 AOPP 71 53(74.65) 10(14.08) 8(11.27) 18(25.35) 8.618 0.013 常模 1 010 877(86.83) 82(8.12) 51(5.05) 133(13.17) 抑郁 AOPP 71 50(70.42) 13(18.31) 8(11.27) 21(29.58) 12.470 0.002 常模 1 010 867(85.84) 94(9.31) 49(4.85) 143(14.16) 孤独 AOPP 71 50(70.42) 14(19.72) 7(9.86) 19(26.76) 6.468 0.039 常模 1 010 814(80.59) 154(15.25) 42(4.16) 196(19.41) 愤怒 AOPP 71 56(78.87) 10(14.08) 5(7.04) 15(21.13) 10.577 0.005 常模 1 010 912(90.29) 54(5.35) 44(4.36) 98(9.71) 总分 AOPP 71 39(54.93) 23(32.39) 9(12.68) 32(45.07) 43.856 < 0.001 常模 1 010 860(85.15) 101(10.00) 49(4.85) 150(14.85) 2.4 不同特征AOPP患者的心理状态
单因素分析显示,不同性别、中毒药物种类及中毒类型患者的心理状态评分比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05); 年龄 < 30岁者的焦虑情绪更重, ≥45岁者的抑郁、孤独、愤怒及总分均高于其他年龄组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 小学及以下文化水平者的焦虑及总分高于其他学历者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分者的焦虑、抑郁及心理状态总评分高于 < 20分者,有不良事件者的心理状态评分高于无不良事件者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。不同年龄、性别、文化程度、中毒类型及中毒原因患者的不良事件发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 但APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分者的不良事件发生率高于 < 20分者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 3。
表 3 不同特征AOPP患者的心理状态评分及不良事件分析(x±s)[n(%)]项目 分类 n MSSNS评分/分 心理状态异常 不良事件 焦虑 抑郁 孤独 愤怒 总分 年龄 < 30岁 17 29.72±6.43*# 16.02±4.31* 13.35±2.26* 11.21±2.85* 70.30±15.04* 7(41.18)* 3(17.65) 30~ < 45岁 30 26.32±6.01 16.83±4.46* 13.14±2.37* 12.14±2.79* 68.43±13.05* 11(36.67)* 4(13.33) ≥45岁 24 25.06±5.44 18.53±5.06 18.37±4.27 14.93±3.15 76.89±16.21 14(58.33) 7(29.17) 性别 男 31 26.44±5.61 17.45±4.49 15.07±4.12 13.01±3.12 71.97±15.63 13(41.94) 6(19.35) 女 40 26.92±5.72 17.02±5.12 14.87±4.26 12.74±3.24 71.55±14.98 19(47.50) 8(20.00) 文化程度 小学及以下 39 28.02±6.14 17.33±4.64 16.01±3.82 12.91±3.14 74.27±14.38 18(46.15) 8(20.51) 初中 18 25.95±5.11△ 17.06±4.12 14.03±3.74 12.87±3.02 69.74±13.32△ 8(44.44) 4(22.22) 高中及以上 14 24.04±5.02△ 17.07±4.32 13.23±3.65 12.71±2.89 67.05±13.15△ 6(42.86) 2(14.29) 中毒类型 敌敌畏 17 26.52±5.74 17.33±4.62 14.97±4.02 13.01±3.11 71.83±15.59 8(47.06) 4(23.53) 氧化乐果 16 26.89±6.01 17.09±4.15 14.91±4.13 12.94±2.85 71.83±14.38 7(43.75) 3(18.75) 辛硫磷 12 26.43±5.58 17.26±4.03 14.68±4.32 12.96±3.06 71.33±13.49 6(50.00) 2(16.67) 乐果 9 26.96±6.01 17.41±4.73 15.01±4.26 12.74±3.11 72.12±13.85 4(44.44) 2(22.22) 甲拌磷 7 26.43±5.58 17.22±4.05 14.96±4.15 12.71±3.05 71.32±14.39 3(42.86) 1(14.29) 其他 10 26.64±5.72 17.13±4.09 15.03±4.22 12.71±3.12 71.51±15.25 4(40.00) 2(20.00) 中毒原因 自杀性 56 26.32±5.64 17.41±4.67 15.21±4.23 12.89±3.11 71.83±15.24 24(42.86) 11(19.64) 误食、误用 15 28.17±5.72 16.46±5.01 14.03±4.01 12.75±3.04 71.41±14.98 8(53.33) 3(20.00) APACHE Ⅱ评分 < 20分 24 25.02±4.69 15.44±4.13 14.01±4.21 12.06±2.74 66.83±6.85 8(33.33) 2(8.33) ≥20分 47 27.87±5.84▲ 18.11±4.26▲ 15.44±4.36 13.27±3.01 74.54±7.14▲ 24(51.06) 12(25.53) 不良事件 无 57 25.59±5.42 16.11±4.09 14.26±4.09 12.41±2.84 68.73±6.94 21(36.84) — 有 14 31.27±6.03◆ 21.69±4.63◆ 17.81±4.33◆ 14.69±3.01◆ 83.99±11.38◆ 11(78.57)◆ — 与≥45岁比较, *P < 0.05; 与30~ < 45岁比较, #P < 0.05; 与小学及以下比较, △P < 0.05;
与APACHE Ⅱ评分 < 20分比较, ▲P < 0.05; 与无不良事件比较, ◆P < 0.05。2.5 AOPP患者不良事件及心理状态异常的影响因素的多因素分析
非条件多因素Logistic回归模型分析结果显示, APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分是影响AOPP患者不良事件的独立危险因素(P < 0.05); 年龄≥45岁、APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分、有不良事件是影响AOPP患者心理状态异常的独立危险因素(P < 0.05)。见表 4。
表 4 影响AOPP患者不良事件及心理状态异常因素的多因素分析项目 变量 回归系数 标准误 Wald P OR(95%CI) 不良事件 APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分 0.696 0.271 10.332 < 0.001 1.979(1.163~3.352) 心理状态异常 ≥45岁 0.536 0.211 7.419 < 0.001 1.632(1.013~2.662) APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分 0.793 0.262 11.163 < 0.001 2.013(1.334~3.695) 有不良事件 0.609 0.223 8.134 < 0.001 1.782(1.163~2.269) 3. 讨论
3.1 AOPP患者不良事件分析
AOPP具有并发症多、致死率高等特点,因极易损伤中枢神经系统、呼吸循环系统等,部分患者可能因呼吸循环衰竭、肝肾损伤等而死亡,或抢救成功后仍存在后遗症[6]。世界卫生组织(WHO)统计显示,全球每年约有20万人因有机磷农药中毒致死,中国因有机磷农药中毒死亡者占全球的半数以上,早期准确评估病情并及时抢救是降低病死率的关键[7]。本组71例经抢救成功的患者中,有14例发生至少1种并发症,并发症种类较多,其中又以肺部感染、呼吸衰竭等居多,严重影响患者的生命安全。
3.2 AOPP患者心理状态分析
目前,临床常规抢救AOPP的主要原则是及早洗胃、导泻和清除体内毒物等,以挽救患者的生命,降低不良事件发生风险,但对患者心理状态的重视度不足。AOPP多为自杀性中毒,本研究中自杀性中毒者占78.87%, 这类患者往往具有复杂的心理变化,中毒后又存在后悔或恐慌等情绪,患者处于高度心理应激状态,再加上洗胃等治疗所致的不适、并发症等,这些均可能导致患者产生抵触情绪,加重焦虑、抑郁等负性心理状态。误服、误用中毒者则往往因担心康复效果而具有明显的焦虑、恐慌等情绪。本研究结果显示, 71例AOPP患者的MSSNS总分达(70.74±15.19)分,心理状态异常率高达45.07%, 显著高于常模水平,提示AOPP患者即便抢救成功后,仍普遍存在不同程度的心理问题。从心理严重程度及类别分布显示,本组患者中轻度异常率为32.39%,中重度异常率为12.68%, 临床多表现为焦虑、抑郁情绪,与郝会莹等[8]报道基本相符。分析其原因为部分AOPP患者往往自身就存在一定的人格缺陷或心理疾病,或因中毒后导致人格改变等,进而引发不同程度的心理应激反应。严重、持续性心理应激反应可能引起精力过度消耗,不利于病情康复,且可能影响患者的治疗配合度,部分患者可能再次萌生轻生念头[9]。因此,在AOPP的临床救治中,强化心理干预非常必要。
3.3 AOPP患者一般人口学特征对心理状态的影响
比较不同一般情况患者的心理状态显示,不同性别、中毒药物种类及中毒类型患者的心理状态MSSNS总评分及各维度评分均无显著差异(P>0.05), 初步推测性别、中毒药物种类及中毒类型对AOPP患者的心理状态影响有限。
在不同年龄亚组中,心理问题分布存在一定差异, < 30岁患者表现出更强的焦虑状态, ≥45岁者则表现出更强的抑郁、孤独、愤怒等情绪,且发生心理状态异常率明显高于其他年龄段。Logistic回归分析显示,年龄≥45岁是发生心理状态异常的独立危险因素。分析其原因为年轻患者往往更容易受环境因素影响,而年龄≥45岁者往往面临更沉重的社会、家庭负担及职场压力,心理状态影响因素较多,心理问题往往也更为复杂,整体而言发生心理状态异常的风险更高。本研究还显示,不同文化水平的AOPP患者的心理状态评分差异显著,其中小学及以下文化者的焦虑情绪更重,整体MSSNS评分高于其他文化水平患者。分析其原因为低文化水平患者可能对中毒后救治知识的认知程度相对薄弱,对护士的健康教育内容理解能力相对较差,更容易产生焦虑等负性情绪。
任何躯体疾病或不适均可引起一定程度的心理反应。本研究中,在APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分的患者中,焦虑、抑郁及MSSNS总分高于 < 20分患者,且APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分患者具有更高的不良事件发生率,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。同时,在具有不良事件患者中, MSSNS总分及各维度评分均显著升高(P < 0.05)。Logistic回归分析显示,APACHE Ⅱ评分≥20分是发生不良事件及心理状况异常的独立危险因素,而合并不良事件也是心理状况异常的独立危险因素。分析其原因为病情较重、不良事件较多者可能因诊疗更为复杂、康复难度更大及生命威胁更严重等而产生更强的负性心理状态。因此,在AOPP的临床救治中更应注重对患者的个体化心理干预。研究[10]显示,对AOPP患者开展心理护理有助于缓解患者的负性心理,甚至对改善临床预后也有积极的意义。
3.4 AOPP患者负性心理状态的护理建议
在当前生理-心理-社会新型医学模式下,在加强对AOPP患者基础护理的同时,开展个体化的心理干预意义重大,具体表现为: ①建立良好的护患关系。通过与患者及其家属建立良好的护患关系,帮助患者及其家属稳定情绪,这也是确保心理护理取得成功的关键。②加强健康教育。充分尊重、关心和爱护患者,主动、全面分析患者中毒原因、中毒后心理状况变化及认知情况,了解患者的真实需求,制订心理卫生及中毒防治相关健康教育标准,在合理评估的情况下针对性地开展住院护理,加强康复护理、心理护理与健康知识宣教,提高患者的认知程度与干预配合度,为患者提供饮食、睡眠休息、康复运动等多方面的健康指导,全面满足患者的生理、心理与社会需求,更有利于病情及负性心理状态的缓解。③提供个性化心理干预。针对患者的具体情况,因人而异地使用心理疏导技巧,例如倾听、赋能、共情等,帮助患者敞开心扉,坦诚地接受帮助。鼓励患者建立正确的人生观,促使其积极地面对生活或挫折。因误服、误用而中毒者,加强日常管理及健康教育较为重要; 对于轻生患者,则更应侧重轻生原因的分析,及时予以安抚、调解等,帮助患者正确面对困难或挫折,调动其对生活的积极认知,最大限度地预防再次轻生。④加强社会家庭支持。强调家属或亲友的在患者康复中的作用,鼓励家属多与患者沟通交流,满足患者的合理需求,尽量控制自身情绪,给予患者更多的鼓励与安慰。⑤转变患者对生活的负面认知,通过一对一疏导、康复案例现身说法等形式帮助患者调整心态,引导通过阅读、听音乐等缓解焦虑、紧张情绪[11-13]。
综上所述, AOPP患者具有病情严重、并发症多等特点,且普遍存在不同程度的异常心理状况,突出表现为焦虑、抑郁情绪较重,尤其是在病情严重、合并不良事件者中表现更为突出。在AOPP的临床救治中,及时介入个体化、支持性的心理干预,对确保治疗及护理效果非常重要。
-
表 1 术前血清铁蛋白、白蛋白、铁蛋白与白蛋白比值与肝癌临床病理特征的关系[n(%)]
临床病理 分类 例数 铁蛋白/(μg/L) 白蛋白/(g/L) 铁蛋白与白蛋白比值 ≥108.63 <108.63 ≤41.19 >41.19 ≥3.42 <3.42 年龄 <50岁 52 25(48.08) 27(51.92) 23(44.23) 29(55.77) 20(38.46) 32(61.54) ≥50岁 60 22(36.67) 38(63.33) 24(40.00) 36(60.00) 27(45.00) 33(55.00) 性别 男 78 30(38.46) 48(61.54) 29(37.18) 49(62.82) 31(39.74) 47(60.26) 女 34 17(50.00) 17(50.00) 18(52.94) 16(47.06) 16(47.06) 18(52.94) 症状 有 67 30(44.78) 37(55.22) 28(41.79) 39(58.21) 26(38.81) 41(61.19) 无 45 17(37.78) 28(62.22) 19(42.22) 26(57.78) 21(46.67) 24(53.33) 乙型肝炎表面抗原 阴性 31 12(38.71) 19(61.29) 14(45.16) 17(54.84) 10(32.26) 21(67.74) 阳性 81 35(43.21) 46(56.79) 33(40.74) 48(59.26) 37(45.68) 44(54.32) 甲胎蛋白/(ng/mL) <20 67 33(49.25) 34(50.75) 30(44.78) 37(55.22) 31(46.27) 36(53.73) ≥20 45 14(31.11) 31(68.89) 17(37.78) 28(62.22) 16(35.56) 29(64.44) 肿瘤直径/cm <5 58 25(43.10) 33(56.90) 23(39.66) 35(60.34) 29(50.00) 29(50.00) ≥5 54 22(40.74) 32(59.26) 24(44.44) 30(55.56) 18(33.33) 36(66.67) 肿瘤多发 是 13 3(23.08) 10(76.92) 4(30.77) 9(69.23) 3(23.08) 10(76.92) 否 99 44(44.44) 55(55.56) 43(43.43) 56(56.57) 44(44.44) 55(55.56) 肝硬化 有 77 40(51.95) 37(48.05) 39(50.65) 38(49.35) 42(54.55) 35(45.45) 无 35 7(20.00)* 28(80.00)* 8(22.86)* 27(77.14)* 5(14.29)* 30(85.71)* 肿瘤家族史 有 21 7(33.33) 14(66.67) 9(42.86) 12(57.14) 6(28.57) 15(71.43) 无 91 40(43.96) 51(56.04) 38(41.76) 53(58.24) 41(45.05) 50(54.95) 与有肝硬化比较, *P<0.05。 表 2 多因素Cox比例风险回归分析肝细胞癌患者肝切除术后预后不良的影响因素
因素 β Waldχ2 HR 95%CI P 铁蛋白≥108.63 μg/L 1.569 11.265 2.523 2.051~9.305 <0.001 白蛋白≤41.19 g/L 1.712 10.348 1.649 1.002~7.561 <0.001 铁蛋白与白蛋白比值≥3.42 1.665 11.141 1.742 1.114~6.598 <0.001 有肝硬化 1.452 9.589 2.119 1.459~10.230 <0.001 -
[1] 麦荣云, 叶甲舟, 王言焱, 等. ALBI联合APRI对HBV相关肝细胞癌肝切除术后肝衰竭发生的预测价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(2): 292-297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.02.015 [2] 牛广林, 程昌盛, 潘卫珍, 等. 血清铁蛋白水平诊断原发性肝癌的价值[J]. 广西医学, 2018, 40(2): 209-210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYYX201802032.htm [3] 赵惠柳, 舒宏, 欧超, 等. 原发性肝癌病人血清高尔基蛋白73、铁蛋白、甲胎蛋白联合检测的早期诊断价值分析[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2020, 45(2): 246-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BANG202002031.htm [4] 杜学峰, 徐永富, 戴启强, 等. C-反应蛋白/血清白蛋白比值与原发性肝癌临床病理特征及预后的关系[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2019, 29(10): 47-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ201910013.htm [5] BOGDANOVIC A, BULAJIC P, MASULOVIC D, et al. Liver resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for huge hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matched analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 4493. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83868-9
[6] 中国抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会, 中华医学会肝病学分会肝癌学组, 中国抗癌协会病理专业委员会, 等. 原发性肝癌规范化病理诊断指南(2015年版)[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2015, 21(3): 145-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFJY201511003.htm [7] 王清睿, 胡赤丁, 吴琳, 等. 原发性肝细胞癌切除术后复发的危险因素分析[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2018, 17(7): 706-709. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2018.07.014 [8] GARRIDO I, MARQUES M, SANTOS A L, et al. S1053 risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C cirrhotic patients after successful direct antiviral agents therapy[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020, 115(1): S534.
[9] 李欢, 陈娟娟, 祝成亮, 等. 血清生长分化因子15和甲胎蛋白联合检测对HBV相关肝细胞癌的诊断价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(3): 569-572. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.03.020 [10] 周晨阳, 周江敏, 胡新昇, 等. 肝细胞癌患者术后早期复发的危险因素分析及风险评估模型构建[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2020, 29(8): 973-978. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPWZ202008011.htm [11] 毛玉环, 谭黎明, 李建英, 等. 血清壳多糖酶3样蛋白1和甲胎蛋白及铁蛋白检测在原发性肝癌诊断中的应用评价[J]. 实用预防医学, 2018, 25(4): 401-404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYY201804005.htm [12] RICH N E, HESTER C, ODEWOLE M, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in presentation and outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 17(3): 551-559, e1.
[13] 汪硕敏, 顾康生. 血清癌胚抗原、铁蛋白和糖基抗原199在非小细胞肺癌诊断中的临床价值[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2018, 53(9): 1444-1447. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YIKE201809026.htm [14] 钱相君, 许强, 姚明解, 等. 白蛋白与球蛋白比值对肝癌患者术后生存预后的影响[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2018, 26(9): 670-675. [15] DENG L, WANG C, HE C, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles promote TRAIL-related apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the delivery of microRNA-20a-3p[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2021, 30(2): 223-235.
[16] 张旺, 梁文全, 蔡爱珍, 等. 术前血清白蛋白水平对评估胃神经内分泌肿瘤患者预后的意义[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2020, 41(2): 143-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYJX202002014.htm -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 宋惠芳,王敏,李俊杰,冯宪梅. 共情共赢心理护理联合愉悦因子输入对有机磷农药中毒患者心理状况的影响. 医学理论与实践. 2024(10): 1760-1762 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 徐香港,汪杏. 重症有机磷农药中毒患者的急诊急救护理效果. 名医. 2024(01): 36-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 饶巧,张志坚,程春梅. 有机磷农药中毒康复期患者自我隐瞒现状及其影响因素. 中国工业医学杂志. 2024(03): 298-300 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周创宇,兰浩云,张增强,李海峰. PSS、APACHE-Ⅱ评分对急性有机磷农药中毒患者近期预后不良预测价值比较. 现代医药卫生. 2024(22): 3849-3854 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张丽平. 急性有机磷农药中毒康复期患者负性情绪现状调查及其影响因素分析. 心理月刊. 2024(23): 214-216 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
