Role and mechanism of developmental endothelial locus-1 in collagen-induced arthritis
-
摘要:目的
探讨内皮细胞发育调节基因-1(Del-1)对胶原诱导性关节炎(CIA)的作用及机制。
方法构建CIA小鼠模型,分为CIA组、Del-1组(Del-1干预CIA), 并另设正常对照组。Del-1组给予每只小鼠尾静脉注射Del-1, 2 μg/次,共2次。采用关节炎指数(AI)评估关节炎病情进展; 采用苏木精-伊红染色(HE染色)观察小鼠关节病变; 采用酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)检测小鼠血清白细胞介素-6(IL-6)、基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)表达。
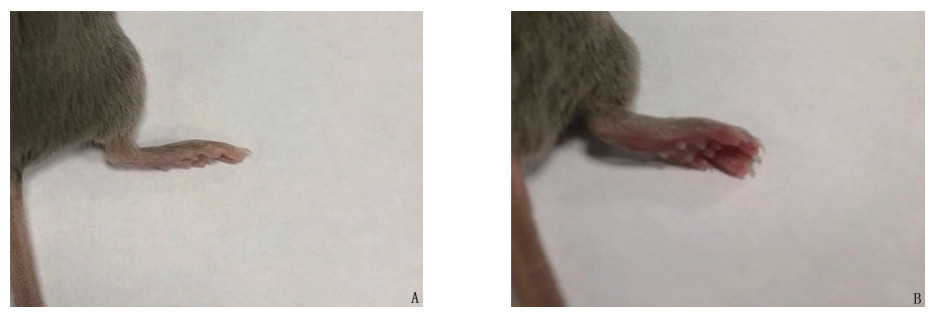
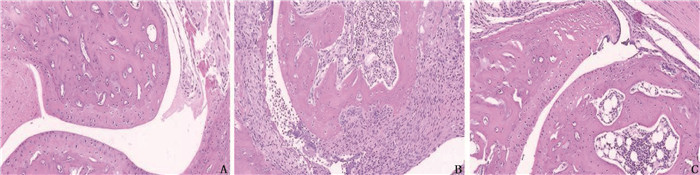
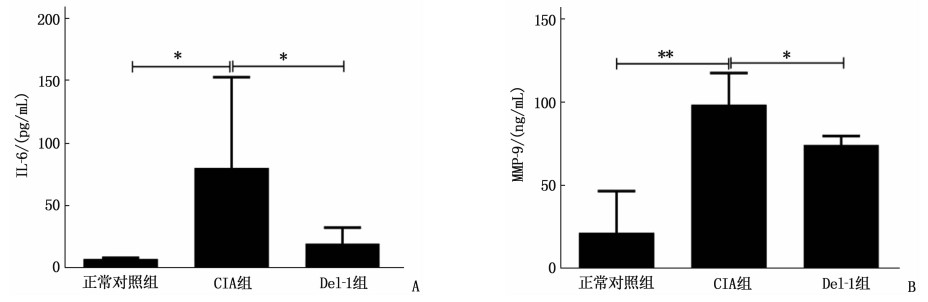
结果初次免疫后第34、36、38、40天, Del-1组AI评分依次为(3.80±1.17)、(3.80±1.17)、(4.20±1.17)、(4.20±1.17)分,低于CIA组的(6.80±1.94)、(8.80±3.19)、(9.60±3.61)、(9.40±3.61)分,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。初次免疫后第42天,HE染色显示Del-1组小鼠较CIA组关节局部炎症浸润和滑膜增生明显减轻,软骨破坏明显减少。初次免疫后第42天, ELISA结果显示CIA组小鼠血清IL-6、MMP-9表达较正常对照组升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01), 而Del-1组小鼠血清IL-6、MMP-9表达较CIA组下降,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论Del-1能改善CIA模型小鼠关节症状,减轻炎症和骨破坏,抑制关键细胞因子IL-6和MMP-9的表达,可能在RA治疗中发挥一定的作用。
-
关键词:
- 内皮细胞发育调节基因-1 /
- 胶原诱导性关节炎 /
- 类风湿关节炎 /
- 白细胞介素-6 /
- 基质金属蛋白酶
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the role and mechanism of developmental endothelial locus-1 (Del-1) in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA).
MethodsCIA mouse model was constructed, and the mice were divided into control group, CIA group, and Del-1 group (Del-1 for intervention of CIA). In the Del-1 group, each mouse was injected with Del-1 for 2 μg each time through caudal vein for 2 times in total. Arthritis index (AI) was used to assess the progression of arthritis; hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was used to observe the arthritic lesions in mice; enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the expression of serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9) in mice.
ResultsOn the 34th, 36th, 38th and 40th days after the primary immunization, the AI scores in the Del-1 group were (3.80±1.17), (3.80±1.17), (4.20±1.17) and (4.20±1.17) respectively, which were significantly lower than (6.80±1.94), (8.80±3.19), (9.60±3.61) and (9.40±3.61) in the CIA group (P < 0.05). On the 42nd day after the primary immunization, when compared to the CIA group, the HE staining showed that the local inflammatory infiltration and synovial hyperplasia of the joints in the Del-1 group were obviously alleviated, and the cartilage destruction was obviously reduced. On the 42nd day after the initial immunization, ELISA result showed that the expression levels of serum IL-6 and MMP-9 in the CIA group were significantly higher than that in the normal control group (P < 0.05), while those in the Del-1 group were significantly lower than the CIA group (P < 0.05).
ConclusionDel-1 can improve the joint symptoms of CIA mouse model, reduce inflammation and bone destruction, inhibit the expression of key cytokines such as IL-6 and MMP-9, and these actions may play certain roles in the treatment of RA.
-
-
表 1 各组小鼠AI评分比较(x±s)[M(P25, P75)]
分 时点 CIA组 Del-1组 第21天 0(0, 1.00) 0(0, 0) 第23天 1.00(0, 4.50) 0(0, 1.00) 第25天 2.00(0, 4.50) 0(0, 1.50) 第27天 2.00(0.50, 4.00) 0(0, 1.50) 第29天 2.00(1.00, 6.50) 4.00(1.50, 5.50) 第32天 5.60±3.07 3.40±1.96 第34天 6.80±1.94 3.80±1.17* 第36天 8.80±3.19 3.80±1.17* 第38天 9.60±3.61 4.20±1.17* 第40天 9.40±3.61 4.20±1.17* CIA: 胶原诱导性关节炎; Del-1: 内皮细胞发育调节基因-1。
与CIA组比较, *P < 0.05。 -
[1] JIANG Q, WANG X, HUANG E Y, et al. Inflammasome and its therapeutic targeting in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 12: 816839. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.816839
[2] HUANG J, FU X K, CHEN X X, et al. Promising therapeutic targets for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 686155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.686155
[3] SHIN J, MAEKAWA T, ABE T, et al. DEL-1 restrains osteoclastogenesis and inhibits inflammatory bone loss in nonhuman Primates[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2015, 7(307): 307ra155. https://www.uab.edu/medicine/rheumatology/images/JJ_-_Shin_et_al_2015.pdf
[4] LIU C, ZHANG H Y, TANG X J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote the osteogenesis in collagen-induced arthritic mice through the inhibition of TNF- Α[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2018, 2018: 4069032. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/sci/2018/4069032/
[5] 赵成, 张璐, 王红, 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠胶原诱导关节炎模型的疗效观察[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2015, 19(9): 1-4, 8. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201509001 [6] HAJISHENGALLIS G, CHAVAKIS T. DEL-1: a potential therapeutic target in inflammatory and autoimmune disease[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2021, 17(6): 549-552. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1915771
[7] LI M, ZHONG D, LI G Z. Regulatory role of local tissue signal Del-1 in cancer and inflammation: a review[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2021, 26(1): 31. doi: 10.1186/s11658-021-00274-9
[8] HAJISHENGALLIS G, CHAVAKIS T. DEL-1-regulated immune plasticity and inflammatory disorders[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2019, 25(5): 444-459. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.02.010
[9] NARAZAKI M, TANAKA T, KISHIMOTO T. The role and therapeutic targeting of IL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2017, 13(6): 535-551. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2017.1295850
[10] NOACK M, MIOSSEC P. Selected cytokine pathways in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2017, 39(4): 365-383. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0619-z
[11] HASHIZUME M, MIHARA M. The roles of interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis, 2011, 2011: 765624. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/arthritis/2011/765624/
[12] FUJIMOTO M, SERADA S, MIHARA M, et al. Interleukin-6 blockade suppresses autoimmune arthritis in mice by the inhibition of inflammatory Th17 responses[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2008, 58(12): 3710-3719. doi: 10.1002/art.24126
[13] PANDOLFI F, FRANZA L, CARUSI V, et al. Interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(15): 5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155238
[14] GRILLET B, YU K R, UGARTE-BERZAL E, et al. Proteoform analysis of matrix metalloproteinase-9/gelatinase B and discovery of its citrullination in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluids[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 763832. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.763832
[15] KRABBEN A, HUIZINGA T W J, MIL A H. Biomarkers for radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2015, 21(2): 147-169.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
