Effect of Yiqi Huoxue Lishui Recipe on calcium transport and endoplasmic reticulum stress in cardiomyocytes f rats with heart failure
-
摘要:目的
探讨益气活血利水方对心力衰竭(HF)大鼠心肌细胞钙转运、内质网应激凋亡及血管紧张素Ⅱ(AngⅡ)、转化生长因子β1(TGF-β1)表达的影响。
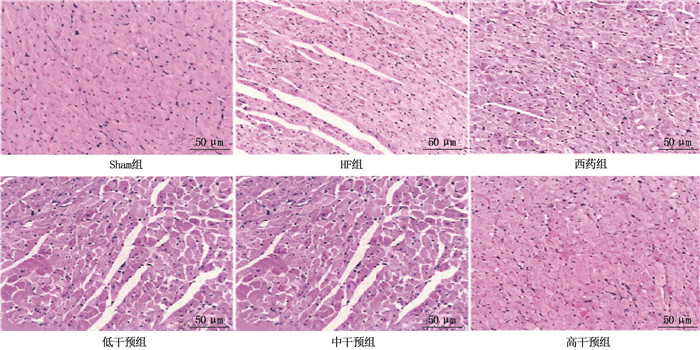
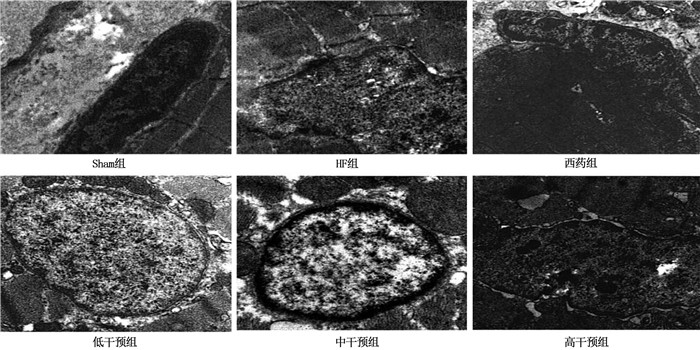
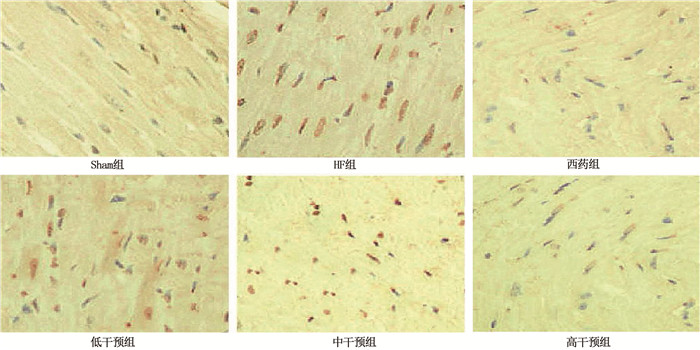
方法将10只健康大鼠设为Sham组,另将45只建模成功大鼠分为HF组、低干预组、中干预组、高干预组和西药组,每组9只。低干预组、中干预组、高干预组分别灌胃2.6、5.2、10.4 g/(kg·d)益气活血利水溶液,西药组灌胃10.0 mg/(kg·d)曲美他嗪, Sham组和HF组分别灌胃等体积0.9%NaCl溶液。采用苏木精-伊红(HE)染色法及电镜分别观察各组大鼠心肌组织病理形态; 采用Bradford染料结合法分析心肌肌质网中钙摄取量; 采用脱氧核糖核苷酸末端转移酶介导的缺口末端标记(TUNEL)法检测各组大鼠心肌细胞凋亡情况; 采用免疫印迹法检测心肌组织中内质网应激相关蛋白[B细胞淋巴瘤/白血病-2(Bcl-2)、Bcl-2关联X蛋白(Bax)、半胱天冬酶-3(Caspase3)蛋白]和钙运转相关蛋白[钙/钙调蛋白依赖性蛋白激酶Ⅱ(CaMKⅡ)、兰尼碱受体2(RyR2)、肌浆网钙离子ATP酶2a(SERCA2a)]表达水平; 采用免疫组织化学法检测心肌组织中TGF-β1、AngⅡ阳性表达率。
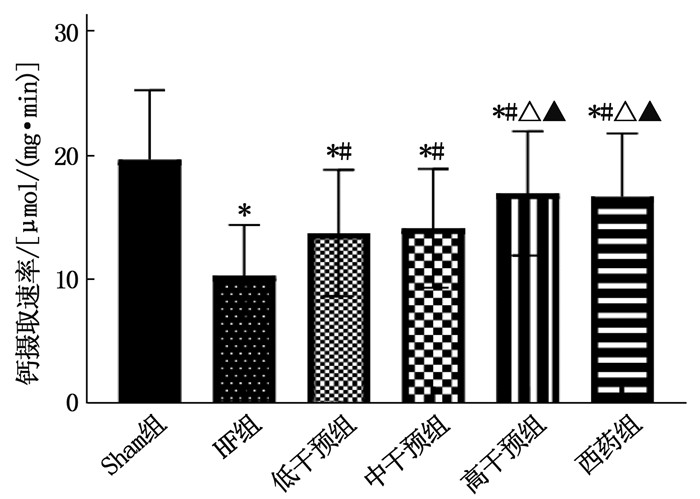
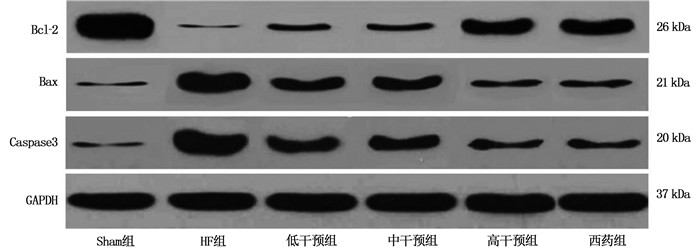
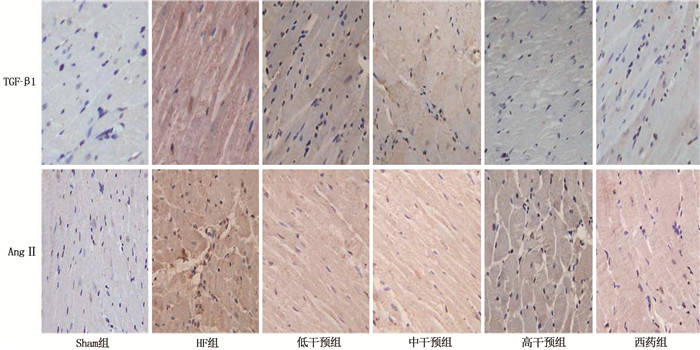
结果Sham组、HF组、低干预组、中干预组、高干预组、西药组大鼠心肌肌质网钙摄取速率分别为(19.63±5.63)、(10.25±4.11)、(13.70±5.12)、(14.08±4.80)、(16.91±5.03)、(16.65±5.10) μmol/(mg·min), 多组间比较差异有统计学意义(F=3.946, P=0.004); Sham组、HF组、低干预组、中干预组、高干预组、西药组大鼠心肌细胞凋亡率分别为(7.52±2.01)%、(30.63±6.58)%、(19.14±5.03)%、(18.41±5.21)%、(13.61±3.65)%、(13.17±4.11)%, 多组间比较差异有统计学意义(F=28.900,P < 0.001)。与Sham组比较, HF组大鼠心肌组织Bcl-2、SERCA2a表达均降低, Bax、Caspase3、CaMKⅡ、RyR2、TGF-β1、AngⅡ表达均升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 与HF组比较,低干预组、中干预组、高干预组、西药组Bcl-2、SERCA2a表达均升高, Bax、Caspase3、CaMKⅡ、RyR2、TGF-β1、AngⅡ表达均降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 低干预组与中干预组上述8项指标比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 高干预组上述8项指标与中干预组比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 但与西药组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
结论益气活血利水方可改善HF大鼠心肌细胞钙转运,通过抑制内质网应激减少心肌细胞凋亡,并呈现浓度依赖性,其机制可能与抑制TGF-β1、AngⅡ表达有关。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of Yiqi Huoxue Lishui Recipe on calcium transport, endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis and the expressions of angiotensin Ⅱ (Ang Ⅱ) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in cardiomyocytes of heart failure (HF) rats.
MethodsTen healthy rats were set as Sham group, and another 45 successfully modeled rats were divided into HF group, low intervention group, medium intervention group, high intervention group and western medicine group, with 9 rats in each group. The low intervention group, middle intervention group and high intervention group were gavaged with 2.6, 5.2 and 10.4 g/(kg·d) of Yiqi Huoxue Lishui Recipe, the western medicine group was gavaged with 10 mg/(kg·d) trimetazidine, and the Sham and HF groups were gavaged with the same volume of 0.9% NaCl solution, respectively. HE staining and electron microscopy were used to observe the pathological morphology of myocardial tissue. Bradford dye binding method was used to analyze the calcium intake in the myocardial sarcoplasmic reticulum. The apoptosis of cardiomyocytes in each group was detected by Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL). Western blotting was used to detect the expressions of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins[B cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 (Bcl-2), Bcl-2 associated X protein (Bax), caspase-3 protein (Caspase3)]and calcium transport-related proteins[calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Ⅱ (CAMK Ⅱ), ryanodine receptor (RyR2) and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA2a); the positive expression rates of TGF-β1 and Ang Ⅱ in myocardial tissue were detected by immunohistochemistry.
ResultsThe calcium uptake rates of rats in the Sham group, HF group, low intervention group, middle intervention group, high intervention group and western medicine group were (19.63±5.63) μmol/(min·mg), (10.25±4.11) μmol/(min·mg), (13.70±5.12) μmol/(min·mg), (14.08±4.80) μmol/(min·mg), (16.91±5.03) μmol/(min·mg), (16.65±5.10) μmol/(min·mg), respectively, there were differences among different groups (F=3.946, P=0.004). The apoptosis rates of cardiomyocytes in the Sham group, HF group, low intervention group, medium intervention group, high intervention group and western medicine group were (7.52±2.01)%, (30.63±6.58)%, (19.14±5.03)%, (18.41±5.21)%, (13.61±3.65)% and (13.17±4.11)%, respectively, there were differences among different groups (F=28.900, P < 0.001); compared with the Sham group, Bcl-2 and SERCA2a levels in the HF group in myocardial tissue of rats were decreased, and Bax, Caspase3, CaMK Ⅱ, RyR2, TGF-β1 and Ang Ⅱ expression were increased (P < 0.05). Compared with the HF group, expressions of Bcl-2 and SERCA2a were increased in the low, medium and high intervention groups and western medicine group, Bax, Caspase3, CaMK Ⅱ, RyR2, TGF-β1 and Ang Ⅱ were all decreased (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the low intervention group in above eight indicators compared with the medium intervention group (P>0.05). Compared with the medium intervention group, the high intervention group showed significant differences in above indexes (P < 0.05), but there was no significant differences compared with the western medicine group in above indexes (P>0.05).
ConclusionYiqi Huoxue Lishui Formula can improve calcium transport in heart failure rats, and reduce myocardial apoptosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in a concentration-dependent manner. The mechanism may be related to the inhibition of TGF-β1 and Ang Ⅱ expression.
-
-
表 1 各组大鼠内质网应激相关蛋白Bcl-2、Bax、Caspase3表达量比较(x±s)
组别 n Bcl-2 Bax Caspase3 Sham组 10 1.25±0.11 0.52±0.04 0.25±0.05 HF组 9 0.65±0.08* 1.54±0.17* 0.96±0.07* 低干预组 9 0.87±0.10*# 1.14±0.11*# 0.72±0.10*# 中干预组 9 0.90±0.06*# 1.12±0.08*# 0.68±0.14*# 高干预组 9 1.10±0.09*#△▲ 0.90±0.06*#△▲ 0.44±0.06*#△▲ 西药组 9 1.07±0.11*#△▲ 0.92±0.08*#△▲ 0.42±0.05*#△▲ F — 47.300 111.100 86.310 P — < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 Bcl-2: B细胞淋巴瘤/白血病-2; Bax: Bcl-2关联X蛋白; Caspase3: 半胱天冬酶-3。与Sham组比较, *P < 0.05;
与HF组比较, #P < 0.05; 与低干预组比较, △P < 0.05; 与中干预组比较, ▲P < 0.05。表 2 各组大鼠钙转运蛋白CaMKⅡ、RyR2、SERCA2a表达量比较(x±s)
组别 n CaMKⅡ RyR2 SERCA2a Sham组 10 0.16±0.05 0.34±0.07 1.08±0.07 HF组 9 0.97±0.15* 1.12±0.12* 0.47±0.04* 低干预组 9 0.60±0.07*# 0.84±0.05*# 0.62±0.07*# 中干预组 9 0.58±0.08*# 0.80±0.06*# 0.65±0.04*# 高干预组 9 0.30±0.04*#△▲ 0.51±0.10*#△▲ 0.89±0.11*#△▲ 西药组 9 0.29±0.03*#△▲ 0.49±0.13*#△▲ 0.90±0.08*#△▲ F — 125.900 88.970 90.940 P — < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 CaMKⅡ: 钙/钙调蛋白依赖性蛋白激酶Ⅱ; RyR2: 兰尼碱受体2; SERCA2a: 肌浆网钙离子ATP酶2a。
与Sham组比较, *P < 0.05; 与HF组比较, #P < 0.05; 与低干预组比较, △P < 0.05; 与中干预组比较, ▲P < 0.05。表 3 各组大鼠心肌组织TGF-β1、AngⅡ阳性表达率比较(x±s)
% 组别 n TGF-β1 AngⅡ Sham组 10 6.12±1.25 4.20±0.54 HF组 9 25.47±4.17* 15.56±3.41* 低干预组 9 17.33±2.54*# 12.25±2.14*# 中干预组 9 16.95±3.02*# 11.47±2.05*# 高干预组 9 11.24±2.20*#△▲ 8.55±1.28*#△▲ 西药组 9 10.55±2.31*#△▲ 9.02±1.17*#△▲ F — 58.590 36.470 P — < 0.001 < 0.001 AngⅡ: 血管紧张素Ⅱ; TGF-β1: 转化生长因子β1。
与Sham组比较, *P < 0.05; 与HF组比较, #P < 0.05;
与低干预组比较, △P < 0.05; 与中干预组比较, ▲P < 0.05。 -
[1] MONZO L, GAUDIO C, CICOGNA F, et al. Impact of sacubitril/valsartan on implantable defibrillator eligibility in heart failure: a real-world experience[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 25(18): 5690-5700.
[2] KONIARI I, ARTOPOULOU E, VELISSARIS D, et al. Biomarkers in the clinical management of patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure[J]. J Geriatr Cardiol, 2021, 18(11): 908-951.
[3] LEE Y, CHAKRABORTY S, MUTHUCHAMY M. Roles of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase pump in the impairments of lymphatic contractile activity in a metabolic syndrome rat model[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 12320. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69196-4
[4] HUANG A N, LI H H, ZENG C, et al. Endogenous CCN5 participates in angiotensin Ⅱ/TGF-β1 networking of cardiac fibrosis in high angiotensin Ⅱ-induced hypertensive heart failure[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 1235. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01235
[5] 贺小芳, 唐蓓蕾, 王显, 等. 益气活血利水方治疗冠心病心力衰竭气虚血瘀水饮证患者疗效分析[J]. 现代中医临床, 2020, 27(3): 9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6606.2020.03.003 [6] 刘俊杰, 赵慧辉, 张建, 等. 基于"虚、毒、瘀"浅述芪参颗粒治疗慢性心力衰竭气虚血瘀证中医理论依据[J]. 世界中医药, 2019, 14(6): 1447-1449. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2019.06.019 [7] 徐香玲, 杨继, 赵英强. 附子温阳功效在治疗心力衰竭病中的临床应用进展[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2021, 30(31): 3520-3525. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2021.31.022 [8] LI A, STROIK D, SCHAAF T, et al. Biophysics of the SERCA2A/DWORF complex, implications for treatment of heart failure[J]. Biophys J, 2020, 118(3): 593a.
[9] ONAL B, GRATZ D, HUND T J. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase Ⅱ-dependent regulation of atrial myocyte late Na+ current, Ca2+ cycling, and excitability: a mathematical modeling study[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2017, 313(6): H1227-H1239. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00185.2017
[10] 王柳, 郑颖, 林德洪, 等. 美托洛尔片联合曲美他嗪片治疗老年冠心病心力衰竭患者的临床研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2020, 36(15): 2175-2177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ202015004.htm [11] 彭朗, 鲁晓斌, 梅应兵, 等. 益气活血利水方联合螺内酯治疗老年射血分数保留心力衰竭的效果[J]. 中国医药导报, 2020, 17(17): 57-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202017015.htm [12] 于春泉, 王怡, 李芳, 等. 益气活血方对慢性心力衰竭大鼠心肌NCX与SERCA2a mRNA及蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 中草药, 2011, 42(3): 555-558. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO201103036.htm [13] 吴佳妮. 基于网络药理学技术探讨益气活血方治疗心肌缺血的分子机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2016. [14] XU L Y, GAO X, YANG P, et al. EHMT2 inhibitor BIX-01294 induces endoplasmic Reticulum stress mediated apoptosis and autophagy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(4): 1011-1022. doi: 10.7150/jca.48310
[15] CHIKKA M R, MCCABE D D, TYRA H M, et al. C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) contributes to suppression of metabolic genes during endoplasmic Reticulum stress in the liver[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(6): 4405-4415. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.432344
[16] 刘璐, 李思耐, 高群, 等. 党参对压力负荷致心衰小鼠电生理重构的影响[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2018, 16(3): 287-290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY201803009.htm [17] 张颖, 肖骏, 徐艺, 等. 羟基红花黄色素A对缺氧/复氧心肌细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2020, 36(24): 3995-3998. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ202024008.htm [18] 徐京育, 李宗瑛, 叶婷, 等. 强心胶囊对心力衰竭模型大鼠AngⅡAT1R的影响[J]. 中国急救医学, 2020, 40(4): 348-351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2020.04.017 [19] SUI X Z, WEI H C, WANG D C. Novel mechanism of cardiac protection by valsartan: synergetic roles of TGF-β1 and HIF-1α in Ang Ⅱ-mediated fibrosis after myocardial infarction[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2015, 19(8): 1773-1782. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12551
[20] 狄宁宁, 崔振川, 孙云静, 等. 丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠联合卡维地洛对心力衰竭患者心功能及内分泌激素水平的影响[J]. 中国药业, 2021, 30(5): 51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2021.05.014 -
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 岳佳丽,海光,雷卓颖,王丽君. 环硅酸锆钠联合肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统抑制剂治疗慢性肾脏病的机制和效果的研究进展. 中国医药导报. 2024(16): 188-190 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 竹琳,郑浩天,万正红,何莉,周莉. 血液透析患者高钾血症相关领域研究热点及发展动态的可视化分析. 华西医学. 2024(08): 1259-1264 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄湘干,赵艳,关毅标,翁春亮,谢双燕. 维持性血液透析患者高钾血症发生的相关因素分析. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志. 2024(21): 116-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 董生荣,景舒梦,苟伟康,房浩亮,刘彬彬,刘永峰. 环硅酸锆钠治疗围透析期患者慢性高钾血症的有效性研究. 中国卫生标准管理. 2023(02): 140-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陈丽,常文秀. 环硅酸锆钠散治疗慢性肾脏病高钾血症的临床研究. 现代诊断与治疗. 2023(05): 700-703 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 陈文文,方芦炜,丁越越,马红珍. 马红珍教授治疗慢性肾病伴高钾血症的中药应用策略. 浙江中医药大学学报. 2023(08): 874-879 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 蔡享兰. 不同剂量肾康注射液辅助治疗慢性肾脏病3~5期的效果及对肾功能的影响. 中国医学创新. 2023(30): 49-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 宋欣芫,常文秀. 慢性肾脏病5期合并高钾血症饮食干预1例报告. 中国实用内科杂志. 2022(05): 438-440 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张灿,王静. 慢性肾脏疾病患者血钾异常的影响因素及对预后的影响研究. 医药论坛杂志. 2022(13): 20-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘环,罗琰琨,王晨丹. 环硅酸锆钠散治疗慢性高钾血症1例. 中国医药. 2022(12): 1877-1879 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 丁苗佳,沈水娟,吴佳盈. 新型口服降钾药物环硅酸锆钠治疗慢性肾脏病高钾血症临床进展. 中国医药科学. 2021(21): 66-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
