Mechanism of electroacupuncture at Taichong and Quchi points in antagonizing adventitia remodeling of thoracic aorta in stress-induced prehypertension rats
-
摘要:目的
探讨电针太冲穴、曲池穴拮抗应激性高血压前期大鼠(SIPR)胸主动脉外膜重构的机制。
方法应用足底电击结合噪声刺激的方法制备SIPR模型。电针组选取太冲穴、曲池穴进行干预,并在不同时间点测量空白组、模型组和电针组大鼠血压值,观察动物行为学的改变。干预14 d结束后取材,采用苏木素-伊红染色(HE染色)及Masson染色观察胸主动脉病理变化;采用逆转录-聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)检测胸主动脉转化生长因子β1(TGF-β1)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)、Smad3、白细胞介素-10(IL-10)的mRNA表达;采用Western blot法检测胸主动脉Smad7、α-平滑肌激动蛋白(α-SMA)、Ⅰ型及Ⅲ型胶原蛋白表达。
结果模型组大鼠血压升高且血管外膜损伤明显;电针组大鼠血压下降且外膜损伤较轻。与空白组相比,模型组TGF-β1、IL-6、IL-10、Smad3的mRNA表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与模型组相比,电针组TGF-β1、Smad3、IL-6的mRNA表达下降,IL-10 mRNA表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与空白组相比,模型组大鼠Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白及α-SMA蛋白表达升高,Smad7蛋白表达下降,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与模型组相比,电针组Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白及α-SMA蛋白表达下降,Smad7蛋白表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。
结论电针太冲穴、曲池穴可显著降低SIPR血压并能有效预防血管外膜重构,其机制可能与调控TGF-β1/Smads信号通路并减轻炎症反应有关。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the mechanism of electroacupuncture at Taichong and Quchi points in antagonizing adventitia remodeling of thoracic aorta in stress-induced prehypertension rats (SIPR).
MethodsFoot shock combined with noise stimulation was used to prepare SIPR model. In the electroacupuncture group, Taichong point and Quchi point were selected for intervention, and the blood pressure values of rats in the blank group, model group and electroacupuncture group were measured at different time points, and the change of animal behavior was observed. At the end of 14 d intervention, the samples were taken and the thoracic aortic lesions were detected by hematoxylin eosin staining (HE staining) and Masson staining; reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to detect the mRNA expressions of transforming growth factor β1(TGF-β1), interleukin-6(IL-6), Smad3 and interleukin-10(IL-10) in thoracic aorta; western blot was used to detect expressions of Smad7, α-smooth muscle activator protein (α-SMA), and typeⅠ and Ⅲ collagen.
ResultsIn the model group, the blood pressure increased and the vascular adventitia was damaged obviously; in the electroacupuncture group, the blood pressure decreased but the adventitia was slightly damaged. Compared with blank group, the mRNA expressions of TGF-β1, IL-6, IL-10 and Smad3 increased significantly in model group (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the mRNA expressions of TGF-β1, Smad3 and IL-6 decreased significantly in the electroacupuncture group, while the expression of IL-10 mRNA increased significantly (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Compared with the blank group, expressions of type Ⅰand Ⅲ collagen and α-SMA protein increased significantly, and expression of Smad7 protein decreased significantly (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Compared with the model group, expressions of type Ⅰand Ⅲ collagen and α-SMA protein decreased significantly, and expression of Smad7 protein increased significantly (P<0.05 or P<0.01).
ConclusionElectroacupuncture at Taichong and Quchi points can significantly reduce blood pressure in SIPR and effectively prevent vascular adventitia remodeling, and its mechanism may be related to the regulation of TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway and alleviation of inflammatory response.
-
随着现代社会生活节奏的加快,全球应激性高血压发病率逐年攀升,为将高血压防治阵线前移,美国预防、检测、评估与治疗高血压全国联合委员会第七次报告(JNC 7) 提出了“高血压前期(收缩压120~139 mmHg, 舒张压80~89 mmHg)”的概念[1]。研究[2]表明,高血压前期发病呈年轻化的趋势,并且已经出现了心、脑、肾等靶器官的损害,而血管重构(VR)是导致靶器官损伤的病理基础,若能在前期阶段进行有效的干预,则能较大程度上逆转靶器官损伤进程。近年来研究[3]表明,血管外膜是血管病变的始动者,其病变顺序应该是“由外向内”。目前,血管外膜已成为治疗血管病变的新方向,“外膜炎症”是动脉硬化(AS)的始动环节,在AS发生早期即被激活,产生白细胞介素-6(IL-6)等炎性因子,并可促使血管外膜成纤维细胞(AF)被激活,刺激细胞外基质(ECM)合成增多,进而导致AS[4]。
转化生长因子β1(TGF-β1)可参与调节AF增殖、转化、迁移和ECM产生,是公认的影响AF最直接、最重要的细胞因子。Smads是TGF-β1信号通路下游的关键调节因子,可将其信号由膜外转至核内[5]。TGF-β1可通过Smads通路促进AF转化为肌成纤维细胞(MF)与ECM沉积,最终导致AS[6]。高血压前期属于中医治未病的典型,在这一阶段即运用针刺治疗方法具有独特的优势。本研究在针刺治未病理论的指导下,观察电针太冲、曲池穴对应激性高血压前期大鼠(SIPR)血压、血管外膜病理形态的影响,探讨电针降压及保护靶器官的具体机制,现报告如下。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物与分组
将30只由北京维通利华公司提供的无特定病原体(SPF)级雄性Wistar大鼠饲养于北京呼吸疾病研究所动物房,大鼠体质量(220±30)g, 室温(20±1)℃,相对湿度50%,通风良好,定期紫外线消毒,清扫粪便,更换垫料。将30只大鼠随机分为模型组、电针组、空白组,每组10只。
1.2 造模方法
运用足底电击结合噪声刺激造模。采用MG-2型迷宫刺激器(上海继德教学实验器械厂)制备SIPR模型。模型组、电针组大鼠在每天上午、下午同一时间各接受1次持续2 h的电击足底结合噪声应激刺激。应激时将大鼠放入由细铜栅组成的90cm×90cm×50cm的笼子底部,通过铜栅间断给予大鼠足底电脉冲电刺激(脉冲电压为40~80V, 每2~25s随机发生1次,每次持续50ms), 迷宫刺激器上方的蜂鸣器同时发出噪声刺激,强度为80~100 db, 持续50ms, 造模周期为14d。
1.3 干预方式
将各组大鼠固定在特制鼠套中,露出四肢、尾部,固定20min。选穴参照《实验针灸学》: 双侧太冲穴(后肢足背1、2趾骨凹陷处),直刺1mm; 双侧曲池穴(肘关节外侧前方凹陷中),直刺4mm。选用针具为中研太和牌一次性毫针(规格0.16mm×7mm), 电针组进针后连接LH202H型韩式电针仪,阳极接太冲,阴极接曲池穴,电流刺激强度为1mA, 频率2Hz, 留针20min。电针组大鼠从接受造模的第1天起接受针刺干预,直到第14天造模结束,所有操作均由同一人于每天下午固定时间进行。
1.4 血压测定
在复合应激刺激开始的前ld以及复合应激刺激开始的第3、5、7、9、11、13、15天下午刺激结束后2h以及电针治疗14d结束后,分别用智能无创血压仪(BP-98A,德国制造)测量各组大鼠尾动脉的收缩压(连测3次,取均值),数值波动范围不超过±10mmHg为宜。
1.5 动物取材
采用20%氨基甲酸乙酯腹腔注射进行全身麻醉,剂量为每100g 1mL, 将大鼠固定于手术架上,开胸腔,剪取胸主动脉0.5cm, 立即置于冰上操作,剔除结缔组织,采用生理盐水清洗,置于-80℃冰箱中保存备用。
1.6 苏木素-伊红染色(HE染色)观察组织形态改变
取1.5步骤中的大鼠胸主动脉组织约1cm, 置于4%多聚甲醛中固定后脱水,石蜡包埋切片,经二甲苯脱蜡乙醇水化, HE染色,梯度乙醇脱水,二甲苯透化,中性树胶封片固定,光镜下观察。
1.7 Masson染色观察组织胶原纤维改变
取1.6步骤中的切片,将切片脱蜡至水,苏木素染色,丽春红浸染,磷钼酸分化,苯胺蓝染色,1%冰醋酸分化,中性树胶固封,镜下观察。
1.8 逆转录-聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)测定各组大鼠主动脉组织TGF-β1、IL-6、Smad3、白细胞介素-10(IL-10)的mRNA表达
取1.5步骤中的大鼠胸主动脉组织约10 mg, 按照Trizol试剂(美国GBCO公司)说明书提取主动脉组织总RNA, 采用核酸蛋白分析仪检测其浓度和纯度,取总RNA, 参照RT-PCR试剂盒(日本Toyobo)说明书进行逆转录反应,取2μL的逆转录产物,以TaqDAN聚合酶进行PCR扩增反应,以β-action为内参,计算各样本TGF-β1、IL-6、Smad3、IL-10的mRNA条带光密度值与β-action mRNA条带的比值。
1.9 Western blot法检测各组大鼠主动脉中Smad7、α-平滑肌激动蛋白(α-SMA)、Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原的蛋白表达水平
取1.5步骤中的大鼠胸主动脉组织约30mg, 加入300μL蛋白裂解液中研磨,提取胸主动脉组织总蛋白,采用BCA定量法测定总蛋白浓度,按照试剂盒说明书制备分离胶与浓缩胶; 电泳结束后,转印至PVDF膜上,室温封闭60 min, 加入一抗Ⅰ型胶原(1∶1 000)、Ⅲ型胶原(1∶1 000)、Smad7 (1∶800)、α-SMA (1∶1 000) 4 ℃孵育过夜,室温下用TBST清洗膜3次,添加二抗(1∶10000), 室温孵育60min, TBST洗膜,化学发光法进行曝光拍照保存,以β-actin蛋白为内参,采用Image J软件分析Smad7、α-SMA、Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原条带的灰度值。
1.10 统计学方法
采用SPSS 20.0软件统计数据,计量资料以(x±s)表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用LSD-t检验, P<0.05为差异有统计意义。
2. 结果
2.1 各组大鼠收缩压变化
3组大鼠针刺治疗前的收缩压比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。第3天时,与空白组比较,模型组大鼠收缩压升高到120 mmHg, 第14天时收缩压持续升高并始终保持在高血压前期状态(120~139 mmHg), 提示造模成功。与模型组比较,电针组第5、7、9、11、13、15天时收缩压下降,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见表 1。
表 1 各组大鼠收缩压变化(x±s)mmHg 组别 刺激前1d 第3天 第5天 第7天 第9天 第11天 第13天 第15天 空白组(n=10) 112.2±3.39 112.3±3.30 111.0±4.40 109.7±3.97 110.4±3.95 107.3±5.85 108.0±4.90 108.3±4.88 模型组(n=9) 114.2±3.99 124.5±2.92 129.6±7.52** 130.7±2.67** 133.5±6.72** 136.7±4.60** 138.1±2.64** 141.0±2.16** 电针组(n=10) 114.6±2.46 121.3±4.97 121.6±5.66**## 126.6±2.50**## 127.4±3.03**## 130.5±3.24**# 133.9±4.84**# 136.4±3.86**# 与空白组比较, * * P<0.01; 与模型组比较, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01。 2.2 各组大鼠胸主动脉外膜HE染色的病理变化
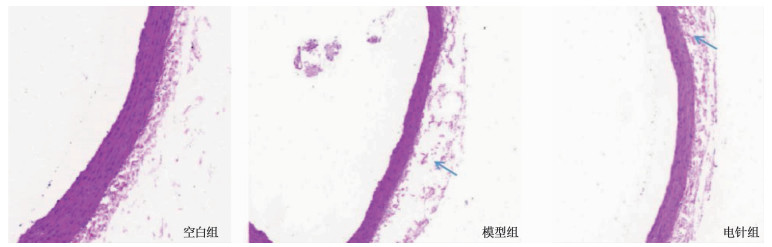
空白组胸主动脉管壁无增厚,血管内膜均匀光滑,外膜厚度均一,外膜与中膜分界明显; 模型组胸主动脉管壁增厚,外膜厚度明显增加,细胞增生活跃,排列紊乱,有较多炎性细胞附着,有的出现剥脱甚至断裂,血管内皮欠光滑,不均匀,内膜上有少量炎症细胞附着,外膜与中膜分界不清晰; 电针组胸主动脉内膜较为光滑均匀,中层平滑肌细胞排列较规整,炎性细胞浸润减少,较空白组虽有外膜厚度增加、细胞轻度增生、排列欠整齐,但外膜与中膜分界较清晰,较模型组有明显改善。见图 1(蓝色箭头处为增厚的血管外膜)。
2.3 各组大鼠胸主动脉Masson染色的病理变化
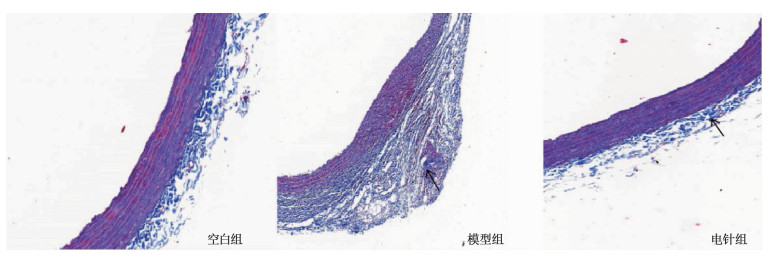
空白组胸主动脉细胞排列整齐,血管内膜、中膜、外膜细胞间质散在有少量蓝色胶原纤维; 模型组胸主动脉细胞排列紊乱,血管内膜、中膜、外膜均可见大量蓝色胶原蛋白沉积,以外膜较为明显; 电针组胶原沉积程度减轻。见图 2(黑色箭头处为胶原蛋白沉积)。
2.4 各组大鼠胸主动脉组织TGF-β1、IL-6、Smad3 、IL-10的mRNA表达
与空白组比较,模型组大鼠TGF-β1、Smad3、IL-6、IL-10的mRNA表达量均增加,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01); 与模型组比较,电针组大鼠TGF-β1、 Smad3 、IL-6的mRNA表达量均降低, IL-10 mRNA增高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见表 2。
表 2 各组大鼠胸主动脉组织TGF-β1、IL-6、Smad3、IL-10的mRNA表达(x±s)组别 TGF-β1 Smad3 IL-6 IL-10 空白组(n=10) 0.99±0.05 0.92±0.28 0.70±0.19 1.16±0.24 模型组(n=10) 1.20±0.09** 1.23±0.24* 1.08±0.38* 1.65±0.31** 电针组(n=10) 0.89±0.13## 0.79±0.14## 0.42±0.07## 1.84±0.26# TGF-β1: 转化生长因子β1; IL-6: 白细胞介素-6;IL-10: 白细胞介素-10。与空白组比较, *P<0.05, **P<0.01;与模型组比较, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01。 2.5 各组大鼠胸主动脉组织Smad7、α-SMA、Ⅰ型及Ⅲ型胶原蛋白表达
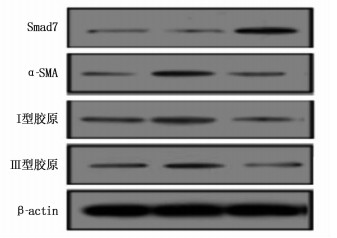
与空白组比较,模型组大鼠Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白以及α-SMA蛋白表达均增加, Smad7蛋白表达下降,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01); 与模型组比较,电针组Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白、α-SMA蛋白表达降低, Smad7蛋白表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见表 3、图 3。
表 3 各组大鼠胸主动脉Smad7、α-SMA、Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原的蛋白表达(x±s)组别 Smad7 α-SMA Ⅰ型胶原 Ⅲ型胶原 空白组(n=10) 0.20±0.03 0.22±0.09 0.31±0.05 0.42±0.04 模型组(n=10) 0.15±0.02* 0.41±0.05** 0.45±0.14* 0.62±0.11* 电针组(n=10) 0.49±0.03**## 0.30±0.06# 0.13±0.003*## 0.27±0.18## α-SMA: α-平滑肌激动蛋白。与空白组比较, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; 与模型组比较, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01。 3. 讨论
高血压前期属于中医学“眩晕” “头痛”“肝风”等范畴[7-8], 属本虚标实之证,基本病机为气血失调、气血上逆,故应采取清泄降逆、调和气血为基础的治疗原则。太冲穴归于少气多血之足厥阴经,为其输穴,又是肝的原穴,故太冲穴具有较好的平冲降逆功效。阳明经气血丰富,曲池穴为手阳明经之合,且大肠又为六腑之一,以通降为顺,五行亦属金,专克肝木,故曲池穴偏于清热调气和血,两穴相配可标本兼顾发挥平肝潜阳、柔肝熄风、调气降逆之效,是临床治疗高血压病常用且较好的穴位配伍[9-11]。本研究发现电针对于SIPR具有明显的降压效果,且短期效果较好,同时电针组主动脉损害较轻,说明电针对于SIPR主动脉具有一定的保护作用[12-14]。本研究应用足底电击结合噪声刺激的复合造模方法[15-16]制备SIPR大鼠模型,发现模型组大鼠均出现易激怒、互相撕咬打架、睛红充血、毛色发黄变涩、食欲下降、粪便干结等外观和行为变化,为近似高血压中医辨证肝阳上亢型模型[17-18]。根据模型组HE染色、Masson染色结果显示,在高血压前期阶段即可出现血管损伤,且外膜损伤出现早于内膜,损伤程度重于内膜[19-20]。
针对AS的发病机制,既往研究[3]多集中在血管内膜方面,近年来发现AS的本质是血管壁炎症反应,而外膜炎症是引起AS的始动因素。作为血管外膜主要细胞成分的AF在生理条件下处于静息状态,当受到缺氧、炎症和细胞因子等因素刺激时,会被激活并表型转化为MF,MF增殖、迁移能力增强,并分泌TGF-β1、TNF-α、IL-6、基质金属蛋白酶等多种细胞因子和Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白等ECM, 推动AS的发生发展[4]。血管外膜的早期活化增殖及炎症反应在AS中发挥了关键作用,血管外膜有可能成为治疗血管重构的新靶点。研究[21]表明SHR大鼠血管外膜AF上炎症介质表达上调,可进一步增强大鼠血管外膜AF的迁移能力和炎症级联反应,加快AS进程。IL-6是由血管外膜AF所产生,可以促进外膜AF的增殖和ECM中胶原的合成,导致AS[22]。IL-10是由单核巨噬细胞分泌的一种抗炎细胞因子,已被证明可以抑制AF的增殖和Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型胶原的表达[23]。本研究表明,电针能降低IL-6 mRNA并升高IL-10 mRNA水平,提示电针太冲、曲池穴可改善SIPR血管外膜重构,其机制可能与通过抑制IL-6 mRNA和升高IL-10 mRNA表达从而减轻血管外膜炎症反应有关。
AF是血管外膜的主要细胞成分,在生理条件下, AF处于静息状态。当受到炎症、缺氧和细胞因子的刺激时,其会被激活并转化为MF, 研究[24]表明AF的增殖与胶原纤维等ECM的增加是AS的重要机制,TGF-β1参与其中,并且是公认的影响AF生物功能最直接、最重要的细胞因子。TGF-β1可使AF表型发生改变而成为MF,其中α-SMA作为AF活化的主要标记物,亦是探讨血管老化的重要检测指标,可以用来衡量AS的程度[25]。目前TGF-β1的信号转导通路已基本阐明。近年来研究[5]表明, TGF-β1及其介导的Smads信号转导通路在血管外膜重构机制中发挥重要作用。TGF-β1可以招募其下游效应转录因子Smad2、Smad3、Smad4, 并将其磷酸化形成Smads复合物,能将信号从膜外转导至核内,上调与ECM合成相关的基因表达,导致胶原等沉积,并能促进AF向MF转化,最终导致血管外膜重构。Smad7是抑制性信号蛋白,是TGF-β信号通路关键负调控因子,能与Smad2、Smad3竞争性地结合TGF-β1受体并阻断其激活,进而抑制AS。本研究模型组大鼠胸主动脉TGF-β1 mRNA和Smad3 mRNA表达量均明显增加,而电针组均明显下降,且电针能有效抑制SIPR胸主动脉α-SMA以及Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白表达,增加Smad7蛋白表达[26], 表明电针改善SIPR血管外膜重构机制可能与参与调控TGF-β1/Smads信号通路有关。
综上所述,电针太冲、曲池穴对SIPR的血管外膜重构有良好的改善作用,电针发挥作用机制可能与参与调控TGF-β1/Smads信号转导通路和抑制血管外膜炎症反应相关。
-
表 1 各组大鼠收缩压变化(x±s)
mmHg 组别 刺激前1d 第3天 第5天 第7天 第9天 第11天 第13天 第15天 空白组(n=10) 112.2±3.39 112.3±3.30 111.0±4.40 109.7±3.97 110.4±3.95 107.3±5.85 108.0±4.90 108.3±4.88 模型组(n=9) 114.2±3.99 124.5±2.92 129.6±7.52** 130.7±2.67** 133.5±6.72** 136.7±4.60** 138.1±2.64** 141.0±2.16** 电针组(n=10) 114.6±2.46 121.3±4.97 121.6±5.66**## 126.6±2.50**## 127.4±3.03**## 130.5±3.24**# 133.9±4.84**# 136.4±3.86**# 与空白组比较, * * P<0.01; 与模型组比较, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01。 表 2 各组大鼠胸主动脉组织TGF-β1、IL-6、Smad3、IL-10的mRNA表达(x±s)
组别 TGF-β1 Smad3 IL-6 IL-10 空白组(n=10) 0.99±0.05 0.92±0.28 0.70±0.19 1.16±0.24 模型组(n=10) 1.20±0.09** 1.23±0.24* 1.08±0.38* 1.65±0.31** 电针组(n=10) 0.89±0.13## 0.79±0.14## 0.42±0.07## 1.84±0.26# TGF-β1: 转化生长因子β1; IL-6: 白细胞介素-6;IL-10: 白细胞介素-10。与空白组比较, *P<0.05, **P<0.01;与模型组比较, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01。 表 3 各组大鼠胸主动脉Smad7、α-SMA、Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原的蛋白表达(x±s)
组别 Smad7 α-SMA Ⅰ型胶原 Ⅲ型胶原 空白组(n=10) 0.20±0.03 0.22±0.09 0.31±0.05 0.42±0.04 模型组(n=10) 0.15±0.02* 0.41±0.05** 0.45±0.14* 0.62±0.11* 电针组(n=10) 0.49±0.03**## 0.30±0.06# 0.13±0.003*## 0.27±0.18## α-SMA: α-平滑肌激动蛋白。与空白组比较, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; 与模型组比较, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01。 -
[1] CHATURVEDI S. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7): is it really practical[J]. Natl Med J India, 2004, 17(4): 227.
[2] 任邦嘉欣, 陈明. 高血压前期的研究进展[J]. 心血管病学进展, 2021, 42(4): 356-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXGB202104018.htm [3] 毛艳燕. 骨桥蛋白在尾加压素Ⅱ诱导大鼠血管外膜成纤维细胞迁移中的作用[D]. 汕头: 汕头大学, 2009. [4] 韩淑娴, 王春淼, 李玉洁, 等. 血管外膜炎症在动脉粥样硬化中的作用及研究进展[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2019, 29(9): 114-119, 126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2019.09.018 [5] 陈纪烨, 周国锋, 王永成, 等. 桂枝汤桂枝-白芍不同比例配伍通过调节TGF-β1/Smads信号通路及慢性炎症改善盐敏感高血压大鼠心肌纤维化[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(1): 50-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX202001009.htm [6] 李欣欣. 电针对高血压前期大鼠肾脏TGF-β1/Smads信号通路影响的研究[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁中医药大学, 2017. [7] 何婧, 王艺霖, 陈丽娜. 观察中医体质辨识及干预在高血压前期"治未病"健康管理中的效果[J]. 中医临床研究, 2020, 12(3): 8-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2020.03.004 [8] 罗婕萌, 陈瑜, 张腾. 高血压前期中医临床研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2017, 19(12): 2063-2067. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJKX201712029.htm [9] 张丽丽, 魏鹏飞, 陈少宗. 针刺治疗原发性高血压病的现状与存在问题[J]. 中国针灸, 2018, 38(3): 338-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZE201803044.htm [10] 孙启胜, 郭骐影, 贾文睿, 等. 针刺捻转泻法对应激性高血压前期大鼠下丘脑基因表达谱的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2017, 42(3): 209-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYJ201703004.htm [11] 杨启帆, 马界. 穴位埋线治疗高血压选穴规律文献研究[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2019, 31(8): 1481-1483. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHLC201908030.htm [12] 莫莉, 卿俊, 刘慧敏, 等. 复方七芍降压片对高血压血管外膜重构的影响[J]. 临床合理用药杂志, 2016, 9(24): 21-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PLHY201624009.htm [13] 马田, 郭妍, 芦娟, 等. 基因芯片研究针刺人迎穴对SHR主动脉弓基因表达的影响[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2018, 34(2): 234-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CZXX201802010.htm [14] 李芳潇, 张立德, 乔铁, 等. 电针"足三里""曲池"穴对高血压前期大鼠黏附分子P-选择素、E-选择素含量影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2017, 19(3): 107-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB201703033.htm [15] HEJAZI M M, BACHA A O, KALEEMUDDIN M, et al. Alteration of serum immunoglobins, C-reactive protein, vitamin D, and electrolyte by atenolol and amlodipine in stress-induced hypertensive rats[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2018, 445(1/2): 99-103.
[16] WU Q, CHEN Y P, ZHANG W Y, et al. Upregulation of chemokines in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in rats with stress-induced hypertension[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2020, 26: e926807.
[17] 姚佳梅, 相玲丽, 陈雨丝, 等. 平肝潜阳法方药对高血压病肝阳上亢证大鼠血管组织中AngⅡ和PDGF-BB表达的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2020, 35(1): 363-367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202001098.htm [18] 杨聪, 郑刚, 齐婧, 等. 原发性高血压中医证候数据挖掘研究进展[J]. 亚太传统医药, 2020, 16(11): 165-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTCT202011060.htm [19] BUNAI Y S, ISHII A, AKAZA K, et al. A case of sudden death after Japanese encephalitis vaccination[J]. Leg Med (Tokyo), 2015, 17(4): 279-282.
[20] SIOW R C M, MALLAWAARACHCHI C M, WEISSBERG P L. Migration of adventitial myofibroblasts following vascular balloon injury: insights from in vivo gene transfer to rat carotid arteries[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2003, 59(1): 212-221.
[21] 张静. 丹参有效成份配伍配比对血管外膜成纤维细胞和自发性高血压大鼠模型的作用及其机制研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2017. [22] ZHAO L, CHENG G M, JIN R M, et al. Deletion of interleukin-6 attenuates pressure overload-induced left ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction[J]. Circ Res, 2016, 118(12): 1918-1929.
[23] 黄志刚, 赵连友, 郑强荪, 等. 白细胞介素10对血管升压素诱导心脏成纤维细胞增殖及胶原合成的影响[J]. 高血压杂志, 2006, 14(2): 135-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ200602017.htm [24] 任敏. 芩丹胶囊对血管外膜成纤维细胞TGF-β1/Smad信号转导通路影响的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2011. [25] 方靖漪, 王雪, 雷燕, 等. 人参-三七-川芎提取物延缓高糖诱导的小鼠血管衰老的机制探讨[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019, 25(4): 81-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX201904013.htm [26] WANG J, SHEN W, ZHANG J Y, et al. Stevioside attenuates isoproterenol-induced mouse myocardial fibrosis through inhibition of the myocardial NF-κB/TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Food Funct, 2019, 10(2): 1179-1190.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 夏恺,林夏,李峰. 祛湿清热针刺疗法治疗急性湿疹患者的疗效及对其AhR、IFN-γ、EOS、IL-17水平的影响. 世界中西医结合杂志. 2024(10): 2056-2060+2066 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 都梦岩,吴威,李威莹,姜晓西,孟岩,杨关林,张会永. 高血压动物模型的造模方法与评价. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化. 2023(10): 3254-3263 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号