Influencing factors of recurrence after cytoreductive surgery in patients with ovarian cancer
-
摘要:目的
分析卵巢癌(OC)患者肿瘤细胞减灭术(CRS)后复发的影响因素。
方法回顾性收集107例OC患者的资料, 所有患者均完成CRS治疗,并随访2年。根据术后2年内肿瘤复发情况将患者分为复发组和未复发组。采用Logistic回归分析探讨导致OC患者CRS术后复发的影响因素。
结果107例OC患者中, CRS术后68例复发,复发率为63.55%;复发组患者乳腺癌易感基因-1(BRCA-1)、聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶-1(PARP-1)表达、残瘤直径、术中淋巴结清扫、糖类抗原125(CA125)水平、人附睾分泌蛋白4(HE4)水平与未复发组比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);复发组和未复发组OC患者的年龄、肿瘤直径、国际妇产科联合会(FIGO)分期、组织分型、产次、术前绝经、淋巴结转移、不同分化程度肿瘤细胞占比、血清糖类抗原199(CA199)、癌胚抗原(CEA)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。Logistic回归分析结果显示, BRCA-1阳性表达、PARP-1阳性表达、残瘤直径>1 cm、术中未清扫淋巴结、CA125水平升高、HE4水平升高可能是OC患者CRS术后复发的危险因素(OR>1, P < 0.05)。
结论BRCA-1阳性表达、PARP-1阳性表达、残瘤直径>1 cm、术中未清扫淋巴结、CA125水平升高、HE4水平升高可能是OC患者CRS术后复发的危险因素。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the influencing factors of recurrence after cytoreductive surgery (CRS) in patients with ovarian cancer (OC).
MethodsData of 107 OC patients were retrospectively collected, and all patients completed CRS treatment and were followed up for 2 years. These patients were divided into recurrence group and non-recurrence group according to tumor recurrence within 2 years after surgery. Logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the influencing factors of postoperative recurrence of CRS in OC patients.
ResultsAmong 107 OC patients, 68 patients relapsed after CRS, with a recurrence rate of 63.55%. The expression of breast cancer susceptibility gene-1 (BRCA-1), poly adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1), residual tumor diameter, intraoperative lymph node dissection, carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA125) level and human epididymal protein 4 (HE4) level showed significant differences between the recurrence group and the non-recurrence group (P < 0.05). Compared age, tumor diameter, International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics(FIGO) stage, disease type, histological type, delivery times, preoperative menopause, lymph node metastasis, proportion of tumor cells with different degrees of differentiation, serum CA199 and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) between recurrent and non-recurrent OC patients, there was no statistical significant difference (P>0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that BRCA-1 positive expression, PARP-1 positive expression, residual tumor diameter >1 cm, unperformed intraoperative lymph node dissection, increased CA125 and HE4 levels might be the influencing factors of postoperative recurrence after CRS in OC patients (OR>1, P < 0.05).
ConclusionBRCA-1 positive expression, PARP-1 positive expression, residual tumor diameter >1 cm, intraoperative uncleaned lymph nodes, increased CA125 and HE4 levels may be the risk factors of postoperative recurrence after CRS in OC patients.
-
GDM(GDM)发病率逐年升高且呈年轻化趋势, 相关研究[1-2]显示孕妇机体血糖过高易出现生殖道和宫内感染,而葡萄糖能促进体内胎儿蛋白质和脂肪合成,出现巨大儿、先天畸形等风险升高,还会导致新生儿红细胞增多、低血糖等并发症的风险升高,导致子代心血管疾病、2型糖尿病风险升高,威胁母婴健康。目前GDM的发病机制尚不明确,有学者[3-4]认为可能与遗传、糖脂代谢、胰岛素抵抗以及炎症反应等有关,胰岛素抵抗被认为是GDM发病的关键因素,其不仅会导致患者血糖升高,还会使胎儿生长环境血糖升高,从而导致不良妊娠结局的发生。
分泌性卷曲相关蛋白-5(sFRP5)是脂肪因子的一种,具有抗炎作用,在糖脂代谢的过程中具有重要作用[5]。研究[6]发现在动物实验中,提高sFRP5水平会导致胰岛素的敏感性增加,刺激脂肪的合成和葡萄糖的摄入。热休克蛋白60(HSP60)是急性时相期蛋白的一种,其在2型糖尿病患者中水平明显升高,且高血糖刺激发生氧化应激、线粒体功能异常,刺激分泌HSP60, 导致HSP60水平增高[7]。HSP60还会刺激免疫细胞释放炎症因子,从而影响机体的代谢[8]。溶质载体家族16成员11( SLC16A11 )是一种新型的糖尿病风险基因, SLC16A11 表达升高可能会导致脂质代谢指标发生变化,特别是甘油三酯升高最为明显,而甘油三酯在糖尿病发生发展中发挥重要作用,因此推测 SLC16A11 可以通过对脂质代谢的调控刺激糖尿病、肥胖等发生发展[9]。本研究探讨GDM患者血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 水平与胰岛素抵抗的关系,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2022年1月—2023年12月在本院就诊的120例GDM患者为研究组。纳入标准: ①符合GDM诊断标准[10] [24~28周行75 g糖耐量试验,空腹血糖(FBG)≥5.1 mmol/L, 餐后1 h血糖(1 h BG)≥10.0 mmol/L, 餐后2 h血糖(2 h BG)≥8.5 mmol/L, 符合其中1项即可确诊]者; ②自然受孕且为单胎妊娠者; ③孕前无糖尿病者; ④患者临床资料完整; ⑤签署知情承诺书者。排除标准: ①孕前合并高血压、高血脂等患者; ②有精神疾病史者; ③有先天性疾病者(心脏病等); ④合并其他恶性肿瘤者。另选取同期健康孕妇(单胎妊娠)120例为对照组。本研究获得本院伦理委员会批准(批号: 2024-168-01)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 血清sFRP5、HSP60检测
入院时采集外周静脉血, 4 000 r/min离心15 min后保存血清备用,采用酶联免疫吸附法检测sFRP5、HSP60水平,试剂盒分别购自美国R&D、上海江莱公司。
1.2.2 SLC16A11 检测
所有患者采集血清后,使用Trizol试剂(北京凯诗源)提取总RNA, 使用NanoDrop ND-12000分光光度计评估总RNA浓度和纯度,使用M-MLV反转录试剂盒反转录成cDNA, 以cDNA为模板,采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)仪检测样本中 SLC16A11 表达水平,内参为GAPDH, 引物序列见表 1。qRT-PCR反应体系共20 μL, 采用2-△△Ct方法计算血清 SLC16A11 表达。
表 1 qRT-PCR引物序列基因 正向引物5′-3′ 反向引物5′-3′ SLC16A11 AACCAGCGCATGGACAGTTA GACTTGACCACCGAACCCAT GAPDH CAGCCGCATCTTCTTGTGC GGTAACCAGGCGTCCGATA 1.2.3 胰岛素抵抗相关指标
采用血糖仪检测空腹血糖(FBG); 采用全自动电化学发光分析仪检测空腹胰岛素(FINS); 采用稳态模型评估胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR), HOMA-IR =FPG×FINS/22.5。
1.2.4 临床资料的收集
收集所有入选孕妇的一般资料,包括年龄、孕次、产次、体质量指数(BMI)、孕周、舒张压、收缩压等。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 25.0软件分析数据。计量资料以(x ±s)表示,比较行t检验; 计数资料以[n(%)]表示,比较行χ2检验。采用Pearson法分析血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 与胰岛素抵抗的相关性。采用Logistic回归分析法分析GDM的影响因素。绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 对妊娠期患者发生GDM的预测价值。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组一般资料比较
2组年龄、孕次、产次、BMI、孕周、舒张压、收缩压等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 2组一般资料比较(x ±s)一般资料 研究组(n=120) 对照组(n=120) 年龄/岁 28.18±5.67 28.84±5.34 孕次/次 1.63±0.51 1.67±0.52 产次/次 0.89±0.19 0.86±0.22 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 24.52±5.06 24.37±5.14 孕周/周 26.43±1.52 26.19±1.67 舒张压/mmHg 83.27±5.92 82.65±6.07 收缩压/mmHg 119.04±11.47 117.46±10.68 1 mmHg=0.133 kPa 2.2 2组患者血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 比较
研究组血清sFRP5表达低于对照组,血清HSP60、 SLC16A11 表达高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 3。
表 3 2组患者血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 比较(x ±s)组别 n sFRP5/(ng/mL) HSP60/(ng/mL) SLC16A11 研究组 120 9.54±1.62* 49.63±6.29* 1.38±0.27* 对照组 120 13.98±3.27 38.71±5.02 1.01±0.21 sFRP5: 分泌性卷曲相关蛋白-5; HSP60: 热休克蛋白60;
SLC16A11 : 溶质载体家族16成员11。与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。2.3 2组患者胰岛素抵抗相关指标比较
研究组FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 4。
表 4 2组患者胰岛素抵抗相关指标比较(x ±s)组别 n FBG/(mmol/L) FINS/(mmol/L) HOMA-IR 研究组 120 5.83±1.02* 5.36±0.71* 1.39±0.23* 对照组 120 4.18±0.61 3.95±0.64 0.74±0.15 FBG: 空腹血糖; FINS: 空腹胰岛素; HOMA-IR: 胰岛素抵抗指数。
与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。2.4 血清sFRP5、HSP60、SLC16A11与胰岛素抵抗相关指标的相关性
Pearson相关性分析显示,血清sFRP5与HSP60、 SLC16A11 、FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR呈负相关(P < 0.05); 血清HSP60与 SLC16A11 、FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR呈正相关(P < 0.05); 血清 SLC16A11 与FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR呈正相关(P < 0.05)。见表 5。
表 5 血清sFRP5、HSP60、SLC16A11与胰岛素抵抗相关指标的相关性指标 sFRP5 HSP60 SLC16A11 r P r P r P FBG -0.559 < 0.01 0.574 < 0.01 0.586 < 0.01 FINS -0.511 < 0.01 0.552 < 0.01 0.524 < 0.01 HOMA-IR -0.573 < 0.01 0.547 < 0.01 0.558 < 0.01 sFRP5 — — -0.538 < 0.01 -0.562 < 0.01 HSP60 -0.538 < 0.01 — — 0.573 < 0.01 SLC16A11 -0.562 < 0.01 0.573 < 0.01 — — 2.5 妊娠期发生GDM的影响因素分析
以妊娠期是否发生GDM作为因变量(是=1, 否=0), 以sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 和FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR相关指标作为自变量(均为实测值),多因素Logistic回归分析显示, HSP60、 SLC16A11 、FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR是妊娠期患者发生GDM的影响因素(P < 0.05), sFRP5是保护因素(P < 0.05)。见表 6。
表 6 妊娠期发生GDM的影响因素分析指标 β SE Wald P OR 95%CI sFRP5 -0.851 0.359 5.619 0.018 0.427 0.211~0.863 HSP60 0.671 0.218 9.471 0.002 1.956 1.276~2.999 SLC16A11 0.796 0.271 8.621 0.003 2.216 1.302~3.769 FBG 0.390 0.427 10.590 0.001 4.013 1.738~9.267 FINS 1.490 0.502 8.807 0.003 4.436 1.658~11.866 HOMA-IR 0.878 0.312 7.926 0.005 2.407 1.306~4.437 2.6 血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 对妊娠期患者发生GDM的诊断价值
ROC曲线显示,血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 诊断妊娠期患者发生GDM的曲线下面积(AUC)依次为0.757、0.800、0.804, 3项指标联合诊断的AUC为0.924; 3项指标联合诊断的价值优于各指标单独诊断(Z联合vs sFRP5=2.708、Z联合vs HSP60=2.645、Z联合vs SLC16A11=2.517, P均 < 0.05), 见表 7、图 1。
表 7 血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 对妊娠期患者发生GDM的诊断价值变量 AUC 95%CI 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 截断值 sFRP5 0.757 0.693~0.821 71.03 82.31 11.08 ng/mL HSP60 0.800 0.742~0.858 75.37 79.49 45.87 ng/mL SLC16A11 0.804 0.749~0.859 76.25 78.87 1.26 联合预测 0.924 0.892~0.956 92.01 76.34 — 3. 讨论
GDM是妊娠期常见的并发症,不同地区、不同人群的发病率差异较大[11]。GDM会导致母婴出现代谢性疾病或者心脑血管疾病等各种并发症及不良妊娠结局,从而威胁母婴的生命安全,还会增加孕妇自身以及后代在后期发生糖尿病和高血压等多种疾病的风险[12]。GDM的发生机制暂不明确,但有研究[13]表明其与胰岛素抵抗和分泌缺陷有关,孕期的女性生理变化明显,在孕中晚期能够分泌出较多的胰岛素拮抗因子,降低胰岛素生物利用度,若机体不能分泌更多胰岛素来调节,则会引发GDM,糖脂代谢也会出现紊乱,从而影响母婴健康。
sFRP5是糖蛋白激素的一种由脂肪细胞分泌,参与多种代谢性疾病(肥胖症、糖尿病等)的调控,具有抗炎作用,可以抑制Wnt信号通路激活。研究[14]表明sFRP5水平降低会导致脂肪组织发生炎症反应,已明确其在动脉粥样硬化、2型糖尿病等疾病中发挥重要作用。sFRP5不仅可以抑制炎症因子释放,还对炎症细胞浸润有抑制作用,可以通过Wnt/JNK通路抑制脂肪的氧化应激,当脂肪功能异常时,Wnt活化从而抑制sFRP5水平,促进炎症因子水平升高,导致氧化应激的发生[15]。刘敏等[16]研究表明,GDM患者sFRP5降低可能是因Wnt通路中的LRP5发生突变,会导致肥胖和糖尿病的发生,而sFRP5对Wnt通路具有抑制作用,有利于胰岛素抵抗的改善和敏感性的增加。有研究[17]表明老年2型糖尿病患者血清sFRP5水平更低,且与视网膜病变呈负相关。本研究结果显示,研究组血清sFRP5较低,血清sFRP5是影响患者发生GDM的保护因素,提示其在GDM发生发展中发挥作用。ROC曲线显示,血清sFRP5诊断妊娠期患者发生GDM的AUC为0.757, 提示其对妊娠期患者发生GDM有一定的预测价值。
HSP是应激蛋白的一种,外界刺激生物体后会产生HSP, 免疫系统将其视为外源分子,会刺激免疫反应的发生,其根据分子质量、功能、结构可分为HSP40、HSP60、HSP90、sHSP等,其中HSP60主要存在于线粒体中[18]。有研究[19-20]表明HSP60可由脂肪组织分泌,并与脂肪细胞特异性结合,进一步刺激HSP60的释放,参与心血管、免疫、排泄和神经系统的各种病理过程,并与肥胖和伴随疾病有关。2型糖尿病患者常会伴随脂代谢紊乱、肥胖等,均是慢性炎症的一种,脂肪组织刺激影响内分泌功能,促进白细胞介素-6、抵抗素等多种因子的释放,从而引起氧化应激的发生,导致血清HSP60水平升高[21]。HSP60作为2型糖尿病的潜在靶点,可用于推进新药物的开发[22]。本研究结果显示,研究组血清HSP60升高,且血清HSP60是影响患者发生GDM的危险因素,提示其在GDM发生发展中发挥作用。ROC曲线显示,血清HSP60诊断妊娠期患者发生GDM的AUC为0.800, 提示其对GDM有一定的预测价值。
SLC16A11 基因位于细胞膜和内质网上,丙酮酸为运输底物,动物实验[23]表明干扰 SLC16A11 的表达可以降低高脂饮食小鼠骨骼肌中甘油三酯的水平,这可能降低 SLC16A11 的表达,促进胰岛素通路的传导,促进骨骼肌转运摄取葡萄糖,从而改善血糖水平,提示 SLC16A11 在糖尿病的发生中具有重要作用。本研究结果显示, GDM患者 SLC16A11 高表达是患者发生GDM的影响危险因素,提示其在GDM的发生中发挥重要作用, SLC16A11 预测GDM发生风险的AUC为0.804, 提示其对GDM有一定的预测价值。
胰岛素抵抗是妊娠期女性发生GDM的重要病理基础,可以抑制机体器官组织对胰岛素的敏感性,从而导致糖脂代谢以及内环境异常[24]。FBG为人体糖代谢的指标, FINS可以反映空腹状态下人体胰岛素水平,通过计算可获得HOMA-IR, 从而评估机体对胰岛素的敏感程度[25]。本研究结果显示, GDM患者FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR较高,提示GDM患者胰岛素的分泌功能出现异常,胰岛素的敏感性降低,从而导致胰岛素抵抗的发生。相关性分析显示, sFRP5与FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR呈负相关, HSP60、 SLC16A11 与FBG、FINS、HOMA-IR呈正相关,表明血清sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 与胰岛素抵抗密切相关。进一步分析发现, 3项指标联合诊断妊娠期患者发生GDM的AUC为0.924, 优于各指标单独预测。本研究的局限性: 未探讨sFRP5、HSP60、 SLC16A11 对GDM患者胰岛素抵抗的具体调控机制、样本量不足等,后续将会扩大样本量、增加动物实验以对本研究结果进行验证。
综上所述, GDM患者血清sFRP5水平降低, HSP60、 SLC16A11 升高, 3项指标均为妊娠期患者发生GDM的影响因素,且与胰岛素抵抗相关。3项指标联用对GDM具有较高的诊断效能。
-
表 1 复发组和未复发组OC患者相关基线资料比较(x±s)[n(%)][M(P25, P75)]
基线资料 分类 复发(n=68) 未复发(n=39) t/Z/χ2/U P 年龄/岁 56.35±2.25 56.00±2.28 0.777 0.439 肿瘤直径/cm 6.85±0.79 6.69±0.75 1.075 0.285 国际妇产科联合会分期 Ⅲ期 35(51.47) 27(69.23) 1.783 0.075 Ⅳ期 33(48.53) 12(30.77) 组织分型 浆液性 33(48.53) 19(48.72) 0.106 0.948 黏液性 23(33.82) 14(35.90) 其他 12(17.65) 6(15.38) 乳腺癌易感基因-1 阳性 63(92.65) 30(76.92) 5.389 0.020 阴性 5(7.35) 9(23.08) 聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶-1 阳性 56(82.35) 25(64.10) 4.488 0.034 阴性 12(17.65) 14(35.90) 残瘤直径 >1 cm 32(47.06) 9(23.08) 6.031 0.014 ≤1 cm 36(52.94) 30(76.92) 产次/次 3.00(2.00, 3.00) 3.00(1.00, 3.00) 0.236 0.813 术前绝经 是 42(61.76) 21(53.85) 0.641 0.423 否 26(38.24) 18(46.15) 淋巴结转移 有 49(72.06) 29(74.36) 0.066 0.796 无 19(27.94) 10(25.64) 术中淋巴结清扫 有 42(61.76) 33(84.62) 6.174 0.013 无 26(38.24) 6(15.38) 肿瘤细胞分化程度 中高分化 34(50.00) 26(66.67) 2.795 0.095 低分化 34(50.00) 13(33.33) 糖类抗原125/(U/mL) 45.41(44.69, 49.92) 41.70(39.12, 44.02) 7.389 < 0.001 糖类抗原199/(U/mL) 44.69±5.26 43.45±4.84 1.215 0.227 人附睾分泌蛋白4/(pmol/L) 185.90(177.40, 193.17) 169.22(161.39, 175.61) 7.156 < 0.001 癌胚抗原/(ng/mL) 12.01±2.53 11.28±2.29 1.485 0.141 表 2 影响因素赋值情况
影响因素 变量类型 赋值 国际妇产科联合会分期 分类变量 0=Ⅲ期, 1=Ⅳ期 乳腺癌易感基因-1 分类变量 0=阴性, 1=阳性 聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶-1 分类变量 0=阴性, 1=阳性 残瘤直径 分类变量 0=≤1 cm, 1=>1 cm 术中淋巴结清扫 分类变量 0=有, 1=无 肿瘤细胞分化程度 分类变量 0=中高分化, 1=低分化 糖类抗原125 连续变量 — 人附睾分泌蛋白4 连续变量 — 表 3 OC患者CRS术后复发的危险因素分析
因素 B S. E. Wald P OR 95%CI 常量 29.823 7.294 16.718 < 0.001 — — 乳腺癌易感基因-1 1.990 0.956 4.330 0.037 7.313 1.123~47.641 聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶-1 0.906 0.640 2.005 0.157 2.474 0.706~8.665 国际妇产科联合会分期 1.113 1.197 0.864 0.352 3.044 0.291~31.800 残瘤直径 1.343 0.621 4.678 0.031 3.831 1.134~12.938 术中淋巴结清扫 1.542 0.671 5.275 0.022 4.674 1.254~17.429 肿瘤细胞分化程度 1.076 1.090 0.975 0.323 2.933 0.347~24.812 糖类抗原125 0.332 0.090 13.680 < 0.001 1.394 1.169~1.663 人附睾分泌蛋白4 0.070 0.032 4.793 0.029 1.073 1.007~1.142 表 4 BCRS术后各因素对OC患者CRS术后复发的预测价值
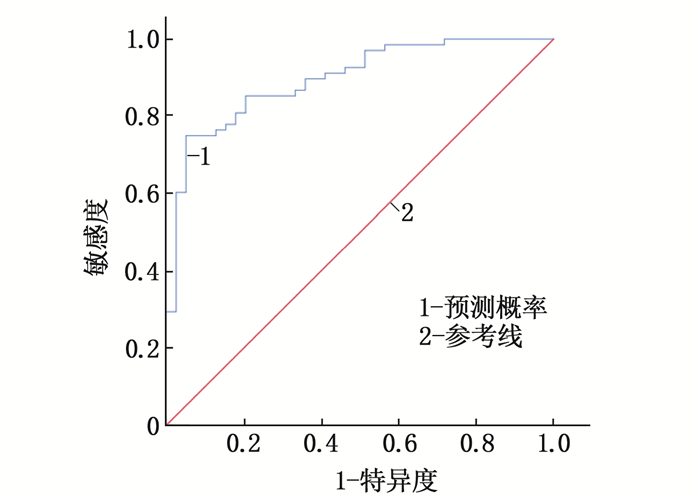
项目 AUC cut-off值 AUC的95%CI P 特异度 敏感度 约登指数 预测概率 0.896 0.550 0.837~0.956 < 0.001 0.821 0.809 0.630 -
[1] ENG O S, RAOOF M, BLAKELY A M, et al. A collaborative surgical approach to upper and lower abdominal cytoreductive surgery in ovarian cancer[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2018, 118(1): 121-126. doi: 10.1002/jso.25120
[2] 谢彦, 王保庆. 肿瘤细胞减灭术后腹腔热灌注化疗对卵巢癌患者生存期及血清Smac表达的影响分析[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2020, 19(23): 2551-2555. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2020.23.025 [3] 毛咪咪, 冯峰. 基于肿瘤全域表观扩散系数纹理分析预测上皮性卵巢癌复发的研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2020, 31(1): 52-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX202001017.htm [4] 陈天敏. 影响上皮性卵巢癌复发的高危因素分析[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2018, 15(21): 3221-3223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2018.21.018 [5] 刘继红. 妇科肿瘤诊疗指南[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2010: 82-84. [6] 王贞. Karnofsky活动状态评分在肿瘤患者护理中的应用[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2012, 27(9): 827-828. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6975.2012.09.028 [7] BARBERA L, SEOW H, HOWELL D, et al. Symptom burden and performance status in a population-based cohort of ambulatory cancer patients[J]. Cancer, 2010, 116(24): 5767-5776. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25681
[8] KEYVER-PAIK M D, ZIVANOVIC O, RUDLOWSKI C, et al. Interval debulking surgery in patients with Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage IIIC and IV ovarian cancer[J]. Onkologie, 2013, 36(6): 324-332.
[9] RADZISZEWSKA A U, KARCZMAREK-BOROWSKA B, WÓJCIK S, et al. Survival rates among women with ovarian cancers diagnosed in the area of Podkarpacie Province in the years 1990-2015[J]. Contemp Oncol (Pozn), 2018, 22(3): 151-157.
[10] ZANG R Y, ZHU J Q. Which patients benefit from secondary cytoreductive surgery in recurrent ovarian cancer[J]. J Gynecol Oncol, 2019, 30(6): e116. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2019.30.e116
[11] CIANCI S, RONSINI C, VIZZIELLI G, et al. Cytoreductive surgery followed by HIPEC repetition for secondary ovarian cancer recurrence[J]. Updates Surg, 2019, 71(2): 389-394. doi: 10.1007/s13304-018-0600-y
[12] BONACHE S, ESTEBAN I, MOLES-FERNÁNDEZ A, et al. Multigene panel testing beyond BRCA1/2 in breast/ovarian cancer Spanish families and clinical actionability of findings[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2018, 144(12): 2495-2513. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2763-9
[13] MITAMURA T, SEKINE M, ARAI M, et al. The disease sites of female genital cancers of BRCA1/2-associated hereditary breast and ovarian cancer: a retrospective study[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2021, 19(1): 36. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02151-3
[14] ZHU M Z, YANG L, WANG X. NEAT1 knockdown suppresses the cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by regulating miR-770-5p/PARP1 axis[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 7277-7289. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S257311
[15] HODGSON D R, DOUGHERTY B A, LAI Z W, et al. Candidate biomarkers of PARP inhibitor sensitivity in ovarian cancer beyond the BRCA genes[J]. Br J Cancer, 2018, 119(11): 1401-1409. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0274-8
[16] 初桂伟, 赵月, 田春燕, 等. 上皮性卵巢癌术后复发影响因素分析[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2019, 31(1): 30-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2019.01.008 [17] 张维维, 张正伟, 何朗. 342例卵巢癌手术患者预后影响因素分析[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2019, 26(17): 1288-1295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL201917014.htm [18] 王遥, 俞梅, 杨佳欣, 等. 子宫内膜和卵巢同期原发性双癌的临床病理特点及预后影响因素分析[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2018, 53(12): 816-822. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2018.12.004 [19] 王秋宇, 李晓翔, 朱军义. 上皮性卵巢癌初次肿瘤细胞减灭术后复发情况及影响因素分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2019, 27(2): 307-310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2019.02.032 [20] 赵晓婷, 马玲. 预测卵巢癌复发的相关因素研究进展[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2017, 42(9): 1290-1293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BANG201709046.htm [21] 王喆, 张颐. 卵巢癌内分泌治疗研究进展[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(13): 115-118, 128. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20211462 [22] 何丽雅, 陈雅卿. 铂敏感复发性卵巢癌手术治疗的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(9): 903-906. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.20.1538 [23] BAERT T, VAN CAMP J, VANBRABANT L, et al. Influence of CA125, platelet count and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio on the immune system of ovarian cancer patients[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2018, 150(1): 31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.05.004
[24] REN T, SUN T T, WANG S, et al. Clinical analysis of chemo-resistance risk factors in endometriosis associated ovarian cancer[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2018, 11(1): 40. doi: 10.1186/s13048-018-0418-8
[25] ZHENG X, CHEN S L, LI L F, et al. Evaluation of HE4 and TTR for diagnosis of ovarian cancer: comparison with CA-125[J]. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod, 2018, 47(6): 227-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2018.03.010
[26] ROWSWELL-TURNER R B, SINGH R K, URH A, et al. HE4 overexpression by ovarian cancer promotes a suppressive tumor immune microenvironment and enhanced tumor and macrophage PD-L1 expression[J]. J Immunol, 2021, 206(10): 2478-2488. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000281
[27] LIU D Y, KONG D, LI J, et al. HE4 level in ascites may assess the ovarian cancer chemotherapeutic effect[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2018, 11(1): 47. doi: 10.1186/s13048-018-0402-3




 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
