Influencing factors of recurrence after cytoreductive surgery in patients with ovarian cancer
-
摘要:目的
分析卵巢癌(OC)患者肿瘤细胞减灭术(CRS)后复发的影响因素。
方法回顾性收集107例OC患者的资料, 所有患者均完成CRS治疗,并随访2年。根据术后2年内肿瘤复发情况将患者分为复发组和未复发组。采用Logistic回归分析探讨导致OC患者CRS术后复发的影响因素。
结果107例OC患者中, CRS术后68例复发,复发率为63.55%;复发组患者乳腺癌易感基因-1(BRCA-1)、聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶-1(PARP-1)表达、残瘤直径、术中淋巴结清扫、糖类抗原125(CA125)水平、人附睾分泌蛋白4(HE4)水平与未复发组比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);复发组和未复发组OC患者的年龄、肿瘤直径、国际妇产科联合会(FIGO)分期、组织分型、产次、术前绝经、淋巴结转移、不同分化程度肿瘤细胞占比、血清糖类抗原199(CA199)、癌胚抗原(CEA)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。Logistic回归分析结果显示, BRCA-1阳性表达、PARP-1阳性表达、残瘤直径>1 cm、术中未清扫淋巴结、CA125水平升高、HE4水平升高可能是OC患者CRS术后复发的危险因素(OR>1, P < 0.05)。
结论BRCA-1阳性表达、PARP-1阳性表达、残瘤直径>1 cm、术中未清扫淋巴结、CA125水平升高、HE4水平升高可能是OC患者CRS术后复发的危险因素。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the influencing factors of recurrence after cytoreductive surgery (CRS) in patients with ovarian cancer (OC).
MethodsData of 107 OC patients were retrospectively collected, and all patients completed CRS treatment and were followed up for 2 years. These patients were divided into recurrence group and non-recurrence group according to tumor recurrence within 2 years after surgery. Logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the influencing factors of postoperative recurrence of CRS in OC patients.
ResultsAmong 107 OC patients, 68 patients relapsed after CRS, with a recurrence rate of 63.55%. The expression of breast cancer susceptibility gene-1 (BRCA-1), poly adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1), residual tumor diameter, intraoperative lymph node dissection, carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA125) level and human epididymal protein 4 (HE4) level showed significant differences between the recurrence group and the non-recurrence group (P < 0.05). Compared age, tumor diameter, International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics(FIGO) stage, disease type, histological type, delivery times, preoperative menopause, lymph node metastasis, proportion of tumor cells with different degrees of differentiation, serum CA199 and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) between recurrent and non-recurrent OC patients, there was no statistical significant difference (P>0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that BRCA-1 positive expression, PARP-1 positive expression, residual tumor diameter >1 cm, unperformed intraoperative lymph node dissection, increased CA125 and HE4 levels might be the influencing factors of postoperative recurrence after CRS in OC patients (OR>1, P < 0.05).
ConclusionBRCA-1 positive expression, PARP-1 positive expression, residual tumor diameter >1 cm, intraoperative uncleaned lymph nodes, increased CA125 and HE4 levels may be the risk factors of postoperative recurrence after CRS in OC patients.
-
-
表 1 复发组和未复发组OC患者相关基线资料比较(x±s)[n(%)][M(P25, P75)]
基线资料 分类 复发(n=68) 未复发(n=39) t/Z/χ2/U P 年龄/岁 56.35±2.25 56.00±2.28 0.777 0.439 肿瘤直径/cm 6.85±0.79 6.69±0.75 1.075 0.285 国际妇产科联合会分期 Ⅲ期 35(51.47) 27(69.23) 1.783 0.075 Ⅳ期 33(48.53) 12(30.77) 组织分型 浆液性 33(48.53) 19(48.72) 0.106 0.948 黏液性 23(33.82) 14(35.90) 其他 12(17.65) 6(15.38) 乳腺癌易感基因-1 阳性 63(92.65) 30(76.92) 5.389 0.020 阴性 5(7.35) 9(23.08) 聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶-1 阳性 56(82.35) 25(64.10) 4.488 0.034 阴性 12(17.65) 14(35.90) 残瘤直径 >1 cm 32(47.06) 9(23.08) 6.031 0.014 ≤1 cm 36(52.94) 30(76.92) 产次/次 3.00(2.00, 3.00) 3.00(1.00, 3.00) 0.236 0.813 术前绝经 是 42(61.76) 21(53.85) 0.641 0.423 否 26(38.24) 18(46.15) 淋巴结转移 有 49(72.06) 29(74.36) 0.066 0.796 无 19(27.94) 10(25.64) 术中淋巴结清扫 有 42(61.76) 33(84.62) 6.174 0.013 无 26(38.24) 6(15.38) 肿瘤细胞分化程度 中高分化 34(50.00) 26(66.67) 2.795 0.095 低分化 34(50.00) 13(33.33) 糖类抗原125/(U/mL) 45.41(44.69, 49.92) 41.70(39.12, 44.02) 7.389 < 0.001 糖类抗原199/(U/mL) 44.69±5.26 43.45±4.84 1.215 0.227 人附睾分泌蛋白4/(pmol/L) 185.90(177.40, 193.17) 169.22(161.39, 175.61) 7.156 < 0.001 癌胚抗原/(ng/mL) 12.01±2.53 11.28±2.29 1.485 0.141 表 2 影响因素赋值情况
影响因素 变量类型 赋值 国际妇产科联合会分期 分类变量 0=Ⅲ期, 1=Ⅳ期 乳腺癌易感基因-1 分类变量 0=阴性, 1=阳性 聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶-1 分类变量 0=阴性, 1=阳性 残瘤直径 分类变量 0=≤1 cm, 1=>1 cm 术中淋巴结清扫 分类变量 0=有, 1=无 肿瘤细胞分化程度 分类变量 0=中高分化, 1=低分化 糖类抗原125 连续变量 — 人附睾分泌蛋白4 连续变量 — 表 3 OC患者CRS术后复发的危险因素分析
因素 B S. E. Wald P OR 95%CI 常量 29.823 7.294 16.718 < 0.001 — — 乳腺癌易感基因-1 1.990 0.956 4.330 0.037 7.313 1.123~47.641 聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶-1 0.906 0.640 2.005 0.157 2.474 0.706~8.665 国际妇产科联合会分期 1.113 1.197 0.864 0.352 3.044 0.291~31.800 残瘤直径 1.343 0.621 4.678 0.031 3.831 1.134~12.938 术中淋巴结清扫 1.542 0.671 5.275 0.022 4.674 1.254~17.429 肿瘤细胞分化程度 1.076 1.090 0.975 0.323 2.933 0.347~24.812 糖类抗原125 0.332 0.090 13.680 < 0.001 1.394 1.169~1.663 人附睾分泌蛋白4 0.070 0.032 4.793 0.029 1.073 1.007~1.142 表 4 BCRS术后各因素对OC患者CRS术后复发的预测价值
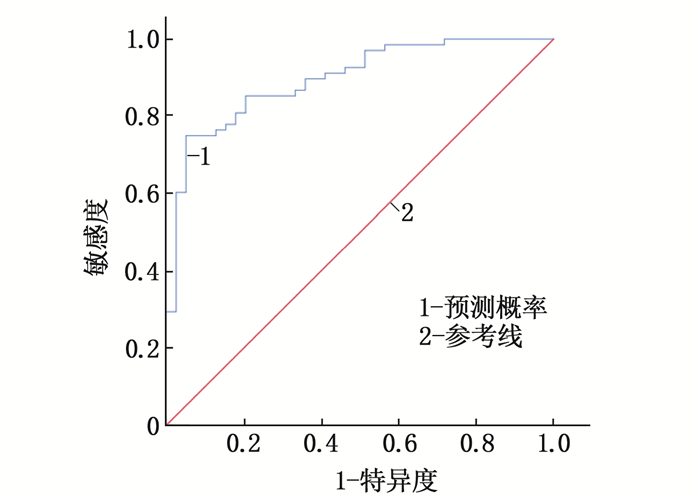
项目 AUC cut-off值 AUC的95%CI P 特异度 敏感度 约登指数 预测概率 0.896 0.550 0.837~0.956 < 0.001 0.821 0.809 0.630 -
[1] ENG O S, RAOOF M, BLAKELY A M, et al. A collaborative surgical approach to upper and lower abdominal cytoreductive surgery in ovarian cancer[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2018, 118(1): 121-126. doi: 10.1002/jso.25120
[2] 谢彦, 王保庆. 肿瘤细胞减灭术后腹腔热灌注化疗对卵巢癌患者生存期及血清Smac表达的影响分析[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2020, 19(23): 2551-2555. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2020.23.025 [3] 毛咪咪, 冯峰. 基于肿瘤全域表观扩散系数纹理分析预测上皮性卵巢癌复发的研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2020, 31(1): 52-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX202001017.htm [4] 陈天敏. 影响上皮性卵巢癌复发的高危因素分析[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2018, 15(21): 3221-3223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2018.21.018 [5] 刘继红. 妇科肿瘤诊疗指南[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2010: 82-84. [6] 王贞. Karnofsky活动状态评分在肿瘤患者护理中的应用[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2012, 27(9): 827-828. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6975.2012.09.028 [7] BARBERA L, SEOW H, HOWELL D, et al. Symptom burden and performance status in a population-based cohort of ambulatory cancer patients[J]. Cancer, 2010, 116(24): 5767-5776. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25681
[8] KEYVER-PAIK M D, ZIVANOVIC O, RUDLOWSKI C, et al. Interval debulking surgery in patients with Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage IIIC and IV ovarian cancer[J]. Onkologie, 2013, 36(6): 324-332.
[9] RADZISZEWSKA A U, KARCZMAREK-BOROWSKA B, WÓJCIK S, et al. Survival rates among women with ovarian cancers diagnosed in the area of Podkarpacie Province in the years 1990-2015[J]. Contemp Oncol (Pozn), 2018, 22(3): 151-157.
[10] ZANG R Y, ZHU J Q. Which patients benefit from secondary cytoreductive surgery in recurrent ovarian cancer[J]. J Gynecol Oncol, 2019, 30(6): e116. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2019.30.e116
[11] CIANCI S, RONSINI C, VIZZIELLI G, et al. Cytoreductive surgery followed by HIPEC repetition for secondary ovarian cancer recurrence[J]. Updates Surg, 2019, 71(2): 389-394. doi: 10.1007/s13304-018-0600-y
[12] BONACHE S, ESTEBAN I, MOLES-FERNÁNDEZ A, et al. Multigene panel testing beyond BRCA1/2 in breast/ovarian cancer Spanish families and clinical actionability of findings[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2018, 144(12): 2495-2513. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2763-9
[13] MITAMURA T, SEKINE M, ARAI M, et al. The disease sites of female genital cancers of BRCA1/2-associated hereditary breast and ovarian cancer: a retrospective study[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2021, 19(1): 36. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02151-3
[14] ZHU M Z, YANG L, WANG X. NEAT1 knockdown suppresses the cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by regulating miR-770-5p/PARP1 axis[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 7277-7289. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S257311
[15] HODGSON D R, DOUGHERTY B A, LAI Z W, et al. Candidate biomarkers of PARP inhibitor sensitivity in ovarian cancer beyond the BRCA genes[J]. Br J Cancer, 2018, 119(11): 1401-1409. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0274-8
[16] 初桂伟, 赵月, 田春燕, 等. 上皮性卵巢癌术后复发影响因素分析[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2019, 31(1): 30-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2019.01.008 [17] 张维维, 张正伟, 何朗. 342例卵巢癌手术患者预后影响因素分析[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2019, 26(17): 1288-1295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL201917014.htm [18] 王遥, 俞梅, 杨佳欣, 等. 子宫内膜和卵巢同期原发性双癌的临床病理特点及预后影响因素分析[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2018, 53(12): 816-822. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2018.12.004 [19] 王秋宇, 李晓翔, 朱军义. 上皮性卵巢癌初次肿瘤细胞减灭术后复发情况及影响因素分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2019, 27(2): 307-310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2019.02.032 [20] 赵晓婷, 马玲. 预测卵巢癌复发的相关因素研究进展[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2017, 42(9): 1290-1293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BANG201709046.htm [21] 王喆, 张颐. 卵巢癌内分泌治疗研究进展[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(13): 115-118, 128. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20211462 [22] 何丽雅, 陈雅卿. 铂敏感复发性卵巢癌手术治疗的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(9): 903-906. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.20.1538 [23] BAERT T, VAN CAMP J, VANBRABANT L, et al. Influence of CA125, platelet count and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio on the immune system of ovarian cancer patients[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2018, 150(1): 31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.05.004
[24] REN T, SUN T T, WANG S, et al. Clinical analysis of chemo-resistance risk factors in endometriosis associated ovarian cancer[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2018, 11(1): 40. doi: 10.1186/s13048-018-0418-8
[25] ZHENG X, CHEN S L, LI L F, et al. Evaluation of HE4 and TTR for diagnosis of ovarian cancer: comparison with CA-125[J]. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod, 2018, 47(6): 227-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2018.03.010
[26] ROWSWELL-TURNER R B, SINGH R K, URH A, et al. HE4 overexpression by ovarian cancer promotes a suppressive tumor immune microenvironment and enhanced tumor and macrophage PD-L1 expression[J]. J Immunol, 2021, 206(10): 2478-2488. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000281
[27] LIU D Y, KONG D, LI J, et al. HE4 level in ascites may assess the ovarian cancer chemotherapeutic effect[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2018, 11(1): 47. doi: 10.1186/s13048-018-0402-3
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 王惠霞. 无创正压通气联合保金化痰利肺汤对慢阻肺急性加重期效果观察. 临床研究. 2024(01): 119-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 岑坚兴,梁守敬,郑普光. 无创通气治疗老年COPD伴睡眠障碍的效果及对患者睡眠质量的影响. 世界睡眠医学杂志. 2022(05): 836-838 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨雍,吕汝琦,刘丹. 早期无创正压通气对重症急性胰腺炎合并肺损伤的保护作用机制. 医学信息. 2019(03): 55-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李菡,周志刚. 无创正压通气联合呼吸兴奋剂治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并肺性脑病的效果观察. 实用临床医药杂志. 2019(07): 68-71 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号