Research progress in regulation of microglial polarization by RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway
-
摘要:
小胶质细胞广泛参与中枢神经系统的多种病理生理过程, 其极化特性则与神经元的炎症反应和损伤修复密切相关。Ras同源基因家族蛋白A(RhoA)/Rho相关卷曲螺旋蛋白激酶(ROCK)信号通路对小胶质细胞极化具有重要的调控功能。目前,通过促进小胶质细胞M2型极化治疗神经元受损的相关研究已成为神经科学领域的热点之一,但RhoA/ROCK通路对极化的调控作用仍未明确。本文综述RhoA/ROCK信号通路对小胶质细胞极化的影响,以期为脑保护分子机制研究及临床治疗提供新思路。
Abstract:Microglia are widely involved in various pathophysiological processes of the central nervous system, and their polarization characteristics are closely related to the inflammatory response and injury repair of neurons. Ras homologous gene family protein A (RhoA)/Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase (ROCK) signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating microglia polarization. At present, the related research on the treatment of neuronal damage by promoting microglial M2-type polarization has become one of the hot spots in the field of neuroscience, but the effect of RhoA/ROCK pathway on polarization is still unclear. This article reviewed the effect of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway on microglial polarization in order to provide new ideas for the study of molecular mechanism of brain protection and clinical treatment.
-
Keywords:
- Rho factor /
- Rho-associated kinases /
- microglia /
- polarization /
- inflammation /
- cerebral injury
-
脑卒中、脑创伤、脓毒症脑病和阿尔茨海默病(AD)等疾病会造成神经元水肿、死亡,损害正常的脑功能[1-3]。小胶质细胞是机体主要免疫细胞,可激活为M1与M2表型,分别发挥增强和减弱炎症反应的作用[4]。研究[5]发现,促进小胶质细胞极化为M2型有益于减轻脑损伤和恢复神经元功能,这让调控小胶质细胞极化成为改善认知功能的新兴领域。
Ras同源基因家族蛋白A(RhoA)/Rho相关卷曲螺旋蛋白激酶(ROCK)通路参与细胞的多种生理活动,包括细胞骨架重构、收缩、迁移、吞噬、黏附、应激纤维形成、炎症反应和血管新生等,近年来发现其与小胶质细胞的极化也密切相关[6-7]。ROCK作为Ras同源家族蛋白的下游靶点,具有ROCK1与ROCK2亚型,但两者对小胶质细胞极化可能产生不同作用[8]。阐明ROCK调控小胶质细胞极化的过程并分析相关差异,有助于深入了解小胶质细胞极化的分子机制,可为寻找更加有效的脑损伤治疗新靶点提供方向和理论依据。
1. 小胶质细胞概述
1.1 小胶质细胞与巨噬细胞的关系
巨噬细胞主要来源于卵黄囊和胎肝[9], 小胶质细胞作为定居中枢神经系统的巨噬细胞同样来源于卵黄囊[10], 两者都在免疫应答中发挥重要作用。小胶质细胞不仅具有巨噬细胞介导炎症、免疫监视、极化和吞噬细胞碎片等功能和特征,还共同表达多种表面标志物,包括CD11b、F4/80和钙离子接头蛋白(Iba)-1等[11-13]。脑损伤发生时,血脑屏障破坏,巨噬细胞浸润脑组织,此时会难以准确区分巨噬细胞和小胶质细胞,所以中枢神经系统疾病研究中常将小胶质细胞称为小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞[4]。
1.2 小胶质细胞极化
静息态小胶质细胞受外界刺激后激活,通过经典激活途径和替代激活途径分别极化为M1与M2这2种功能迥异的细胞表型[5]。M1型小胶质细胞表达CD32、CD86和CD16等表面标记物,并分泌肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)-α、诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)、白细胞介素(IL)-1β和IL-6等促炎因子,加剧炎症反应; M2型小胶质细胞则表达CD206和CD163等细胞表面标记物,分泌转化生长因子(TGF)-β、精氨酸酶(Arg)-1、IL-4和IL-10等抑炎因子,吞噬细胞碎片,从而抑制炎症反应并促进组织修复[5, 14-15]。小胶质细胞极化表型主要受机体内环境影响,组织液中脂多糖(LPS)和干扰素(INF)-γ能诱导小胶质细胞向M1型极化,而IL-10和IL-4可刺激M2型极化发生[16]。小胶质细胞极化后的产物能促使细胞继续向初始极化方向改变,该过程是典型的正反馈调节。此外,间充质干细胞也会影响小胶质细胞极化[17]。M2型小胶质细胞存在多种亚型,包括M2a、M2b和M2c, M2a通过释放抑炎因子和神经营养因子修复受损组织; M2b主要由Toll样受体(TLR)/IL-18介导,表达抗炎介质; M2c具有吞噬功能,能清除细胞碎片,但无法杀灭病原菌[18]。
然而, M2型小胶质细胞也存在负面影响。研究[19]发现,在特发性肺纤维化患者中, M2型巨噬细胞表达增加会导致肺纤维化加重。这可能与M2型细胞释放TGF-β、促进组织修复进而导致成纤维细胞增生有关。在眼科疾病研究中亦存在类似发现,脉络膜中M2型小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞会导致血管增生,加重视力受损程度[8, 14]。此外,研究[20]发现M2型巨噬细胞也会促进高侵袭性口腔鳞癌细胞迁移。另有研究[21]表明,巨噬细胞经LPS刺激后虽然为M1型,释放促炎因子,但产生的外泌体却能促进小胶质细胞的M2型极化,这可能与外泌体中所含的微小RNA(miRNA)有关。上述结果表明, M2型小胶质细胞虽然发挥抗炎、促进损伤组织修复等积极作用,但其促进修复的作用如果过强或作用于癌细胞时,就会对机体产生严重后果。
2. RhoA/ROCK信号通路概述
2.1 RhoA 家族
Rho鸟苷三磷酸酶包括3类分子: Rho、Rac、Cdc42。作为其中之一的Rho分子又细分为A、B、C、D、E共5种亚型,均能作用于下游ROCK分子。但RhoE较特殊,对ROCK起着抑制作用[22]。Rho蛋白作为小G蛋白的一种,同样受鸟嘌呤核苷酸交换因子(GEFs)调控,静息状态下, Rho结合GDP, 无生物活性,但经GEFs催化后, Rho转而结合GTP,转化成激活态[23]。空间上, RhoA激活时会从胞质转移到细胞膜,调节肌球蛋白收缩、产生应力纤维、形成黏着斑和伪足[24-25]。
2.2 ROCK1与ROCK2的异同
ROCK是RhoA的下游分子,存在ROCK1亚型与ROCK2亚型,二者结构极为相似,激酶结构域的同源性高达92%[26]。ROCK在全身组织中均有分布, ROCK1主要表达于非神经组织,如肝、肺和血液中, ROCK2则在脑和肌肉组织中占主导地位[27]。ROCK激活后磷酸化下游分子,主要包括肌球蛋白轻链(MLC)、肌球蛋白磷酸酯酶靶点亚单位(MYPT)1和肌球蛋白轻链磷酸酶(MLCP)[8]。磷酸化MYPT1会促进MLC磷酸化,而磷酸化的MLCP会丧失促进MLC脱磷酸基的作用[28]。两者从增加来源和抑制去路2个方面调节磷酸化MLC含量。RhoA/ROCK通路主要通过增加磷酸化的MLC, 进而发挥多种基于细胞骨架改变的生理作用,如细胞间黏附[29]、细胞运动[30]、轴突回缩[31]和平滑肌细胞收缩[32]等,所以磷酸化MLC表达量在研究[27, 33]中常被用于判断RhoA/ROCK信号通路激活程度。
RhoA/ROCK改变细胞骨架的机制主要与肌丝滑行有关。细胞膜受到刺激后,开放阳离子钙通道,内流的钙离子结合并激活肌钙蛋白,带动原肌球蛋白转位,暴露出肌动蛋白。此后肌动蛋白再与肌球蛋白横桥结合,引发肌细胞收缩或微丝滑动,改变细胞骨架。RhoA/ROCK通过作用于MLC参与这一过程,激活的ROCK使肌球蛋白轻链磷酸化,增加对肌动蛋白的敏感性,促进肌细胞收缩或改变细胞骨架[22, 32]。
3. RhoA/ROCK调控小胶质细胞极化
3.1 ROCK促进小胶质细胞M1型极化
细胞实验[34]表明,对小胶质细胞进行氧糖剥夺/再灌注(OGD/R)[35]和LPS诱导,触发了IL-1β和iNOS的释放,以及相应M2型小胶质细胞的标志物下调,如Arg-1和CD206, 而对ROCK进行抑制后,上述导致损伤加重的分子则被有效逆转。多项实验[36-38]同样证实了该结论,在慢性偏头痛、实验性过敏性脑脊髓炎、AD和脑缺血再灌注损伤小鼠模型中,RhoA/ROCK的表达都发生了上调,且iNOS、IL-6和CD86等M1型小胶质细胞的标志物表达增加。ROCK抑制剂则能有效抑制促炎因子释放,增加抑炎因子释放,减轻中枢神经系统损伤,改善认知功能。
虽然诸多研究表明抑制RhoA/ROCK后,能降低神经细胞死亡率,减轻脑损伤,但ROCK抑制剂的脑保护作用是否主要依靠小胶质细胞M2型极化,迄今尚不清楚。究其原因,炎症下ROCK激活还会引发脑血管痉挛,增加血管通透性,破坏血脑屏障,这些均是加重脑损伤的重要因素。2014年的1项研究[31]为解决该问题提供了依据。研究人员用1-甲基-4-苯基-1, 2, 3, 6-四氢吡啶(MPTP)处理大鼠胚胎来源的中脑细胞培养液和不含小胶质细胞的中脑培养液,诱导其多巴胺能神经元变性,再对2种培养液使用ROCK抑制剂Y-27632干预,最后发现ROCK抑制剂可显著减轻含小胶质细胞的中脑培养液中多巴胺能神经元变性死亡,在不含小胶质细胞的中脑培养液中却未观察到该现象。此体外细胞实验表明,M2型小胶质细胞数量增加在ROCK抑制剂减轻神经元损伤的机制中发挥重要作用,但缺乏进一步动物实验提供更有力的证据。
3.2 ROCK调控小胶质细胞极化的相关机制
3.2.1 神经元损伤时RhoA/ROCK引起的病理生理改变
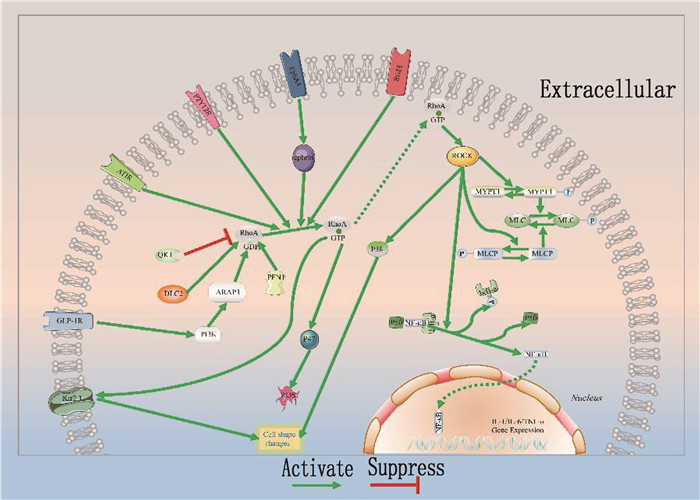
静息态小胶质细胞胞体较小,具有纤细的分支状结构,从而监控大脑微环境[40]。人罹患神经系统疾病或损伤导致内环境剧烈改变时,小胶质细胞随之激活,胞体增大,突起回缩甚至消失,呈阿米巴样,此时细胞代谢、运动和吞噬能力均会增强[8, 40-41], 且M2型小胶质细胞的吞噬能力强于M1型。而小胶质细胞激活时,这一系列形态改变均依赖于细胞骨架的可塑性, RhoA/ROCK通路的重要性不言而喻。RhoA/ROCK作为调控细胞骨架主要的信号通路参与其中。炎症反应发生时,激活的RhoA/ROCK信号通路会减少肺血管内皮细胞间的紧密连接蛋白,增大毛细血管通透性,导致炎症因子和免疫细胞渗出[42]。进入脑组织液中的炎症因子,如IL-1、IL-10和TNF-α, 能直接促进小胶质细胞极化。将内皮剥脱后的大鼠主动脉环浸泡于含有GTP类似物GTPγS的溶液中,发现RhoA/ROCK通路激活,导致血管平滑肌收缩[33]。这提示发生脑损伤时,激活的ROCK可能使脑血管痉挛,加重脑缺血缺氧,引发更多炎症因子聚集,导致定居于中枢神经系统的小胶质细胞和浸润巨噬细胞持续极化。极化过程中RhoA/ROCK不仅是多种上游分子的靶点,还可以通过调控相关信号通路分子表达,进而调节小胶质细胞极化(见图 1)。
3.2.2 极化过程中调节RhoA/ROCK的上游分子
用硝酸甘油建立小鼠慢性偏头痛(CM)模型, JING F等[36]发现模型中GTP-RhoA、ROCK2、降钙素基因相关肽(CGRP)、c-fos和iNOS蛋白水平显著升高; 进一步研究发现,嘌呤能受体P2Y12(P2Y12R)和ROCK2活性降低能抑制硝酸甘油(NTG)诱导的小胶质细胞形态改变并产生iNOS, 最后证明三叉神经尾侧核中小胶质细胞P2Y12R激活后,通过RhoA/ROCK途径调节小胶质细胞活化,且其在CM发病机制中起重要作用。此外,神经退行性疾病领域研究[1, 38, 43]发现, AD小鼠中淀粉样蛋白沉淀会激活RhoA/ROCK通路,从而促进小胶质细胞的迁移、趋化、浸润和吞噬。GUO M F等[1]进一步揭示了具体机制,法舒地尔作为广泛认可并使用的ROCK抑制剂,在AD大鼠中发挥了抑制(TLR4/髓样分化因子88(Myd88)/核因子-κB(NF-κB)通路的作用,促进小胶质细胞向M2型极化,增加M2型小胶质细胞的数量,但研究人员未讨论RhoA/ROCK通路的作用。ROCK能直接促进NF-κB[44], 因此RhoA很可能是TLR4或Mydd88的下游靶点。而法舒地尔抑制TLR4的作用可能是由于分泌促炎因子的M1型小胶质细胞数量减少,而间接抑制TLR4相关通路。
另有研究[34]表明,阻断神经元和小胶质细胞之间EphA4/ephrin信号通路后, RhoA/ROCK2通路被抑制,促进小胶质细胞M2极化,进而减轻OGD/R诱导的神经元凋亡。此外, RNA结合蛋白QUAKING(QKI)和肝癌细胞中缺失的抑癌基因DLC2分别抑制和上调RhoA表达,发挥小胶质细胞调控作用,影响神经细胞修复[45-46]。
除信号分子外,一些膜受体也在小胶质细胞极化过程中参与调控RhoA/ROCK。MPTP诱导的帕金森病模型[47]发现表达上调的血管紧张素(AT)Ⅱ结合AT受体后,激活RhoA/ROCK通路,从而增强小胶质细胞反应性并加重多巴胺能神经元变性。HAN X N等[48]发现凝血酶结合前列腺素E2的EP3受体, EP3受体偶联RhoA/ROCK通路并将其激活,进而增加CD68阳性的M1型小胶质细胞,最终导致神经损伤。创伤性脑损伤(TBI)大鼠的传统中医治疗[49]发现,手针能通过抑制RhoA/ROCK2通路抑制小胶质细胞M1型极化,减轻急性颅脑创伤后的神经炎症。这一结论提示RhoA/ROCK通路可能受到机械门控通道的调节。此外,肠促胰岛素类似物-4(EX-4)能激活胰高血糖素样肽-1受体(GLP-1R), 从而在转录水平抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)/ARAP3/RhoA通路,促进小胶质细胞M2极化,减轻神经损伤[50]。
3.2.3 极化过程中由RhoA/ROCK影响的下游分子
RhoA/ROCK在调节极化过程中还涉及诸多其他中间信号分子,如激发炎症级联反应的NF-κB[44]。NF-κB作为被广泛研究的重要转录因子,通常以p50-NF-κB二聚体形式与NF-κB抑制蛋白-α(IκB-α)结合,在细胞质中处于非活性状态; 当受相关因子刺激时, IκB-α磷酸化降解, NF-κB与p50分离并迅速发生转核,结合调控基因启动子上的κB位点,进而启动IL-1、IL-6和TNF-α等促炎因子基因转录。RhoA/ROCK磷酸化下游靶目标IκB-α, IκB-α随后从与NF-κB组成的复合体中解离,不再抑制NF-κB进入细胞核发挥作用[8]。
小鼠脑缺血再灌注模型中, LU E M等[39]发现,血清前纤维蛋白1(PFN1)下调能减少p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38MAPK)表达并且抑制RhoA/ROCK激活,导致M2型极化。进一步研究发现, p38MAPK在福尔马林引起炎性疼痛小鼠模型[45]和脊髓损伤大鼠模型[51]中受RhoA/ROCK通路激活,促进小胶质细胞聚集。对脊髓损伤大鼠模型其他相关研究[52]还发现, p38MAPK在RhoA/ROCK调节小胶质细胞形态变化中也起关键作用。但目前仍缺乏强有力证据证明p38MAPK与M1型极化直接相关。除了最关键的p65NF-κB和p38MAPK因子, MUESSEL M J等[53]发现Kir2.1钾通道也是RhoA引起小胶质细胞形态变化的重要中间分子。RhoA还能通过磷酸化烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸(NADPH)氧化酶亚基p47, 促进M1型BV2细胞(小鼠小胶质细胞)分泌活性氧(ROS)[54]。
RhoA/ROCK通路对小胶质细胞极化的调控是多方面的,既有改变细胞骨架,促进细胞形态变化的直接调节,又有通过激活其他信号通路,引发炎症因子聚集,对小胶质细胞的间接活化。
3.3 ROCK与小胶质细胞极化关系的探讨
多数观点认为抑制RhoA/ROCK活化能通过促进小胶质细胞M2型极化产生有益作用,但有部分研究得出了不同结论。采用荧光免疫方法分析脉络膜新生血管(CNV)小鼠和猴脉络膜巨噬细胞,发现RhoA/ROCK表达上调导致M2型巨噬细胞增多,进一步研究[8]发现激活ROCK1促进M1型极化,而ROCK2促进M2型细胞增多。基于该结论,有研究[14]发现,对CNV小鼠注射褪黑素能显著抑制眼部炎症导致的RhoA/ROCK通路激活,进而抑制小胶质细胞M2型极化。LPS使BV-2细胞向M1型极化,而蓝莓提取物促进细胞骨架相关Rho蛋白表达,进而逆转小胶质细胞极化方向[55]。
虽然有研究证实RhoA/ROCK既能促进M1型极化,又能促进M2型极化,但是RhoA/ROCK本身就在炎性微环境中激活,且组织损伤导致免疫细胞分泌炎症因子的过程也依赖细胞骨架改变。此外,ROCK还能以增大血管通透性、收缩血管等方式加重炎症反应,所以RhoA/ROCK信号通路激活更可能促进小胶质细胞M1型极化。细胞不管是何种极化,都会导致细胞形态变化与细胞因子分泌,而分泌细胞因子必然借助于囊泡形成。这均涉及细胞骨架改变,因此作为改变细胞骨架的关键通路RhoA/ROCK很可能参与其中。M1型与M2型细胞中上调的RhoA/ROCK分子使MLC蛋白磷酸化从而改变细胞骨架,但M1型中RhoA/ROCL分子的另一核心作用是激活NF-κB和MAPK这2种关键且广泛的促炎分子,在胞核中从基因转录水平影响小胶质细胞极化过程。因此, RhoA/ROCK通路更倾向介导M1型极化,但也参与M2型极化。抑制RhoA/ROCK导致M2型细胞增加,可能是将过度上调的RhoA/ROCK降至主要改变M2型细胞骨架的水平。此时,小胶质细胞极化更倾向于M2型。
4. 结语
综上所述, RhoA/ROCK通路在小胶质细胞作用发挥的调控中具有重要地位,其上下游存在广泛的中间因子,抑制其激活促使小胶质细胞从加重炎症的M1型极化,向具有神经保护作用的M2型转化。虽然ROCK调节小胶质细胞极化的作用被广泛研究,但因缺乏选择性抑制ROCK1或ROCK2的药物,所以临床针对ROCK分子的靶向治疗陷入了瓶颈。此外, ROCK分子在中枢神经系统损伤时作用广泛,其中复杂的关联机制亟待进一步研究阐明。RhoA/ROCK分子分布于全身各组织细胞,而外泌体技术可能在辅助ROCK抑制剂穿过血脑屏障、靶向作用于中枢神经系统的过程中发挥重要作用。ROCK抑制剂法舒地尔因具有改善血管痉挛的作用,成为临床上治疗蛛网膜下腔出血的常用药物,但其介导小胶质细胞极化产生抗炎作用的研究多集中在基础实验。KOCH J C等[56]报道3例肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者经法舒地尔治疗后,病情得到显著改善,且无明显副作用,这可能与其调控极化的作用有关。未来更多的相关临床研究有望推动扩大RhoA/ROCK抑制剂的适用范围。
尽管存在诸多难题,但随着研究手段不断发展,各种分子如miRNA、长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)和外泌体对RhoA/ROCK极化调控机制进一步阐明, RhoA/ROCK通路相关药物及诊疗手段有望在小胶质细胞与脑保护领域中发挥更有意义的作用。
-
[1] GUO M F, ZHANG H Y, LI Y H, et al. Fasudil inhibits the activation of microglia and astrocytes of transgenic Alzheimer′s disease mice via the downregulation of TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB pathway[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2020, 346: 577284. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2020.577284
[2] MEI B, LI J, ZUO Z Y. Dexmedetomidine attenuates Sepsis-associated inflammation and encephalopathy via central α2A adrenoceptor[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2021, 91: 296-314. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.10.008
[3] MARINO LEE S, HUDOBENKO J, MCCULLOUGH L D, et al. Microglia depletion increase brain injury after acute ischemic stroke in aged mice[J]. Exp Neurol, 2021, 336: 113530. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113530
[4] XIONG X Y, LIU L, YANG Q W. Functions and mechanisms of microglia/macrophages in neuroinflammation and neurogenesis after stroke[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2016, 142: 23-44. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.05.001
[5] YE Y Z, JIN T, ZHANG X, et al. Meisoindigo protects against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and regulating microglia/macrophage polarization via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2019, 13: 553. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00553
[6] IRING A, TÓTH A, BARANYI M, et al. The dualistic role of the purinergic P2Y12-receptor in an in vivo model of Parkinson's disease: signalling pathway and novel therapeutic targets[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2022, 176: 106045. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106045
[7] LIU Y L, WU C F, HOU Z J, et al. Pseudoginsenoside-F11 accelerates microglial phagocytosis of myelin debris and attenuates cerebral ischemic injury through complement receptor 3[J]. Neuroscience, 2020, 426: 33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.11.010
[8] ZANDI S, NAKAO S, CHUN K H, et al. ROCK-isoform-specific polarization of macrophages associated with age-related macular degeneration[J]. Cell Rep, 2015, 10(7): 1173-1186. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.01.050
[9] VAROL C, MILDNER A, JUNG S. Macrophages: development and tissue specialization[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2015, 33: 643-675. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112220
[10] SAIJO K, GLASS C K. Microglial cell origin and phenotypes in health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2011, 11(11): 775-787. doi: 10.1038/nri3086
[11] WANG J. Preclinical and clinical research on inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2010, 92(4): 463-477. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.08.001
[12] GINHOUX F, GRETER M, LEBOEUF M, et al. Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages[J]. Science, 2010, 330(6005): 841-845. doi: 10.1126/science.1194637
[13] CHIOT A, ZAÏDI S, ILTIS C, et al. Modifying macrophages at the periphery has the capacity to change microglial reactivity and to extend ALS survival[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2020, 23(11): 1339-1351. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-00718-z
[14] XU Y, CUI K X, LI J, et al. Melatonin attenuates choroidal neovascularization by regulating macrophage/microglia polarization via inhibition of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway[J]. J Pineal Res, 2020, 69(1): e12660.
[15] 庄欣琪, 王玉尊, 王瑶琪, 等. 氢对LPS致BV-2小胶质细胞炎症反应的影响及自噬在其中的作用[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2020, 40(3): 350-354. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn131073.20190726.00324 [16] HU X M, LEAK R K, SHI Y J, et al. Microglial and macrophage polarization—new prospects for brain repair[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2015, 11(1): 56-64. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.207
[17] 刘太聪, 史永强, 张海鸿. 间充质干细胞在神经病理性疼痛中的作用及机制研究[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26(6): 113-117. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20213816 [18] ZHANG L J, ZHANG J Q, YOU Z L. Switching of the microglial activation phenotype is a possible treatment for depression disorder[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2018, 12: 306.
[19] LARSON-CASEY J L, VAID M, GU L L, et al. Increased flux through the mevalonate pathway mediates fibrotic repair without injury[J]. J Clin Invest, 2019, 129(11): 4962-4978. doi: 10.1172/JCI127959
[20] ALVES A, DIEL L, RAMOS G, et al. Tumor microenvironment and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: a crosstalk between the inflammatory state and tumor cell migration[J]. Oral Oncol, 2021, 112: 105038. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.105038
[21] ZHENG Y, HE R Y, WANG P, et al. Exosomes from LPS-stimulated macrophages induce neuroprotection and functional improvement after ischemic stroke by modulating microglial polarization[J]. Biomater Sci, 2019, 7(5): 2037-2049. doi: 10.1039/C8BM01449C
[22] TANG Y Y, HE Y, ZHANG P, et al. LncRNAs regulate the cytoskeleton and related Rho/ROCK signaling in cancer metastasis[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 77. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0825-x
[23] HEMKEMEYER S A, VOLLMER V, SCHWARZ V, et al. Local Myo9b RhoGAP activity regulates cell motility[J]. J Biol Chem, 2021, 296: 100136. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013623
[24] GARCÍA-MARISCAL A, LI H, PEDERSEN E, et al. Loss of RhoA promotes skin tumor formation and invasion by upregulation of RhoB[J]. Oncogene, 2018, 37(7): 847-860. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.333
[25] ALKASALIAS T, ALEXEYENKO A, HENNIG K, et al. RhoA knockout fibroblasts lose tumor-inhibitory capacity in vitro and promote tumor growth in vivo[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114(8): E1413-E1421.
[26] LAI A Y, MCLAURIN J. Rho-associated protein kinases as therapeutic targets for both vascular and parenchymal pathologies in Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Neurochem, 2018, 144(5): 659-668. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14130
[27] LU W Z, WEN J Y, CHEN Z W. Distinct roles of ROCK1 and ROCK2 on the cerebral ischemia injury and subsequently neurodegenerative changes[J]. Pharmacology, 2020, 105(1/2): 3-8.
[28] SZASZ T, WEBB R C. Rho-mancing to sensitize calcium signaling for contraction in the vasculature: role of rho kinase[J]. Adv Pharmacol, 2017, 78: 303-322.
[29] KANG H, YANG B G, ZHANG K Y, et al. Immunoregulation of macrophages by dynamic ligand presentation via ligand-cation coordination[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 1696. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09733-6
[30] KANG H, WONG S H D, PAN Q, et al. Anisotropic ligand nanogeometry modulates the adhesion and polarization state of macrophages[J]. Nano Lett, 2019, 19(3): 1963-1975. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b05150
[31] BORRAJO A, RODRIGUEZ-PEREZ A I, VILLAR-CHEDA B, et al. Inhibition of the microglial response is essential for the neuroprotective effects of Rho-kinase inhibitors on MPTP-induced dopaminergic cell death[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2014, 85: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.05.021
[32] XUE H, ZHANG Y H, GAO Q S, et al. Sevoflurane post-conditioning ameliorates neuronal deficits and axon demyelination after neonatal hypoxic ischemic brain injury: role of microglia/macrophage[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2021, 41(8): 1801-1816. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00949-5
[33] YU J G, OGAWA K, TOKINAGA Y, et al. Sevoflurane inhibits guanosine 5′-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-stimulated, Rho/Rho-kinase-mediated contraction of isolated rat aortic smooth muscle[J]. Anesthesiology, 2003, 99(3): 646-651. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200309000-00020
[34] ZHANG H F, LI Y H, YU J Z, et al. Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil regulates microglia polarization and function[J]. Neuroimmunomodulation, 2013, 20(6): 313-322. doi: 10.1159/000351221
[35] WEI H X, YAO P S, CHEN P P, et al. Neuronal EphA4 regulates OGD/R-induced apoptosis by promoting alternative activation of microglia[J]. Inflammation, 2019, 42(2): 572-585. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0914-4
[36] JING F, ZHANG Y X, LONG T, et al. P2Y12 receptor mediates microglial activation via RhoA/ROCK pathway in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis in a mouse model of chronic migraine[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 217. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1603-4
[37] CHEN C, LI Y H, ZHANG Q, et al. Fasudil regulates T cell responses through polarization of BV-2 cells in mice experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2014, 35(11): 1428-1438. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.68
[38] ZHANG X X, YE P, WANG D D, et al. Involvement of RhoA/ROCK signaling in aβ-induced chemotaxis, cytotoxicity and inflammatory response of microglial BV2 cells[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2019, 39(5): 637-650. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00668-6
[39] LU E M, WANG Q, LI S C, et al. Profilin 1 knockdown prevents ischemic brain damage by promoting M2 microglial polarization associated with the RhoA/ROCK pathway[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2020, 98(6): 1198-1212. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24607
[40] REFOLO V, STEFANOVA N. Neuroinflammation and glial phenotypic changes in alpha-synucleinopathies[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2019, 13: 263.
[41] SACKMANN V, ANSELL A, SACKMANN C, et al. Anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophage media reduce transmission of oligomeric amyloid beta in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2017, 60: 173-182. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.08.022
[42] 张琳, 张伟, 张加强, 等. 利多卡因对大鼠内毒素性肺损伤时Rho/ROCK信号通路的影响[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2019, 39(1): 109-112. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1416.2019.01.028 [43] SCHEIBLICH H, BICKER G. Regulation of microglial phagocytosis by RhoA/ROCK-inhibiting drugs[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2017, 37(3): 461-473. doi: 10.1007/s10571-016-0379-7
[44] PENG F, LU L Y, WEI F, et al. The onjisaponin B metabolite tenuifolin ameliorates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson′s disease[J]. Neuroreport, 2020, 31(6): 456-465. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001428
[45] WONG S S C, LEE U M, WANG X M, et al. Role of DLC2 and RhoA/ROCK pathway in formalin induced inflammatory pain in mice[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2019, 709: 134379. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134379
[46] LEE J, VILLARREAL O D, CHEN X R, et al. QUAKING regulates microexon alternative splicing of the rho GTPase pathway and controls microglia homeostasis[J]. Cell Rep, 2020, 33(13): 108560. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108560
[47] VILLAR-CHEDA B, DOMINGUEZ-MEIJIDE A, JOGLAR B, et al. Involvement of microglial RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway activation in the dopaminergic neuron death. Role of angiotensin via angiotensin type 1 receptors[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2012, 47(2): 268-279. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.04.010
[48] HAN X N, LAN X, LI Q, et al. Inhibition of prostaglandin E2 receptor EP3 mitigates thrombin-induced brain injury[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2016, 36(6): 1059-1074. doi: 10.1177/0271678X15606462
[49] ZHU M M, LIN J H, QING P, et al. Manual acupuncture relieves microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in a rat model of traumatic brain injury by inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK2 pathway[J]. Acupunct Med, 2020, 38(6): 426-434. doi: 10.1177/0964528420912248
[50] QIAN Z Y, CHEN H T, XIA M J, et al. Activation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor in microglia attenuates neuroinflammation-induced glial scarring via rescuing Arf and Rho GAP adapter protein 3 expressions after nerve injury[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(4): 1328-1346. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.68974
[51] KISHIMA K, TACHIBANA T, YAMANAKA H, et al. Role of Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase in the spinal cord injury induced neuropathic pain[J]. Spine J, 2021, 21(2): 343-351. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2020.08.011
[52] TATSUMI E, YAMANAKA H, KOBAYASHI K, et al. RhoA/ROCK pathway mediates p38 MAPK activation and morphological changes downstream of P2Y12/13 receptors in spinal microglia in neuropathic pain[J]. Glia, 2015, 63(2): 216-228. doi: 10.1002/glia.22745
[53] MUESSEL M J, HARRY G J, ARMSTRONG D L, et al. SDF-1α and LPA modulate microglia potassium channels through rho gtpases to regulate cell morphology[J]. Glia, 2013, 61(10): 1620-1628. doi: 10.1002/glia.22543
[54] MOON M Y, KIM H J, LI Y, et al. Involvement of small GTPase RhoA in the regulation of superoxide production in BV2 cells in response to fibrillar Aβ peptides[J]. Cell Signal, 2013, 25(9): 1861-1869. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.05.023
[55] DE CARIS M G, GRIECO M, MAGGI E, et al. Blueberry counteracts BV-2 microglia morphological and functional switch after LPS challenge[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(6): 1830. doi: 10.3390/nu12061830
[56] KOCH J C, KUTTLER J, MAASS F, et al. Compassionate use of the ROCK inhibitor fasudil in three patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Front Neurol, 2020, 11: 173. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00173
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 展立芬,曾学究,梁柔筠,丁强盛,胡晓妹,艾坤,刘琼,张泓. 基于转录组学探讨电针对脊髓横断损伤后脊髓修复的调节作用及相关的分子机制. 时珍国医国药. 2024(09): 2273-2278 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张慧敏,廖丽婷,胡春苗,胡翔宇,龚卫娟,贾筱琴. 糖基化磷脂酰肌醇锚定高密度脂蛋白结合蛋白1对胶质瘤生长及巨噬细胞浸润的影响. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(19): 1-9 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 杨鹏,王梦梦,宋梅梅,张晓宇,王淑燕. 隐丹参酮对脂多糖诱导的小胶质细胞功能的作用机制研究. 长春中医药大学学报. 2023(08): 875-880 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
