Single center study on clinical distribution and drug resistance analysis of Staphylococcus aureus
-
摘要:目的
分析中国人民解放军海军军医大学第一附属医院(下称本院)2016—2020年金黄色葡萄球菌(SA)的临床分布特点及其对抗菌药物的耐药情况,为临床合理应用抗菌药物提供依据。
方法回顾性分析从本院2016年1月—2020年12月1 575例患者送检样本中分离到的SA菌株,采用WHONET 5.6软件和SPSS软件对菌株的科室分布、样本来源和耐药情况等进行统计学分析。
结果送检样本中共分离出1 784株SA, 其中耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(MRSA)926株(占51.9%)。检出SA菌株最多的科室是烧伤科(15.5%), 其后依次是呼吸科(7.3%)和整形外科(5.9%); SA菌株主要来源于呼吸道样本(44.6%), 其后依次是分泌物(30.4%)和血液(5.6%)。2016—2020年, SA菌株对青霉素的耐药率>90%, 对红霉素和克林霉素的耐药率为44.1%~62.4%, 对四环素、环丙沙星、左氧氟沙星和莫西沙星的耐药率为29.2%~44.1%; MRSA菌株对常见抗菌药物的总体耐药率普遍高于SA菌株; 未发现对替加环素、利奈唑胺和万古霉素耐药的SA菌株。
结论本院SA和MRSA的检出率均较高,医务人员应定期监测SA的临床分布和耐药情况,加强抗菌药物的临床应用管理,做好医院感染防控措施。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the clinical distribution characteristics and drug-resistant condition of Staphylococcus aureus (SA) in the First Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University of the Chinese People′s Liberation Army (called our hospital in the following text) from 2016 to 2020, so as to provide a basis for rational clinical application of antibacterial agents.
MethodsSA strains isolated from samples of 1 575 patients in our hospital from January 2016 to December 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. WHONET 5.6 software and SPSS software were used to statistically analyze the department distribution, sample source and drug resistance of the strains.
ResultsA total of 1 784 strains were isolated from the samples, including 926 strains (51.9%) of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The highest detection rate of SA occurred in burn department (15.5%), followed by respiratory department (7.3%) and department of plastic surgery (5.9%). SA strains were mainly derived from respiratory tract samples (44.6%), followed by secretion (30.4%) and blood (5.6%). From year of 2016 to 2020, the resistance rate of SA to penicillin was more than 90%, resistance rates were more than 44.1% to 62.4%to erythromycin and clindamycin, and were more than 29.2% to 44.1%to tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin and moxifloxacin. The overall drug resistance rate of MRSA strains was generally higher than that of SA strains. No SA strains were found to be resistant to tigecycline, linezolid and vancomycin.
ConclusionThe detection rate of SA and MRSA in our hospital is high. Regular monitoring of their clinical distribution and drug resistance has high clinical value for the rational use of antibiotics and the prevention and control of nosocomial infection.
-
金黄色葡萄球菌(SA)在自然界中分布十分广泛,是医院感染和社区感染的重要病原菌之一[1-2]。SA感染常见于皮肤黏膜受损和免疫力低下的人群,能够引起皮肤软组织感染、血流感染、局部化脓性感染及全身多脏器感染等[3]。根据对苯唑西林敏感性的不同, SA可分为耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(MRSA)和甲氧西林敏感金黄色葡萄球菌(MSSA)。近年来,随着临床抗菌药物的广泛应用, SA耐药菌株不断增加,给临床抗感染治疗带来了巨大挑战。因此,定期监测病原菌的流行情况及药物敏感试验结果,有助于临床合理选用抗菌药物,提高患者的治愈率。本研究分析中国人民解放军海军军医大学第一附属医院(下称本院)2016—2020年SA的临床分布特点及其对抗菌药物的耐药情况,现报告如下。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 菌株来源
SA菌株来源于2016年1月—2020年12月本院1 575例患者送检的各类临床样本,包括痰液、支气管肺泡灌洗液、血液、分泌物、中段尿、组织和脓液等。
1.2 仪器与试剂
菌株鉴定使用VITEK 2 Compact全自动微生物分析仪(法国梅里埃公司)或microflex基质辅助激光解析飞行时间质谱仪(德国布鲁克公司)。细菌药物敏感试验使用VITEK 2 Compact全自动微生物分析仪及其配套的GP67药敏卡。
1.3 病原菌培养与鉴定
菌株的接种、培养、分离和鉴定严格按照《全国临床检验操作规程》[4]中不同样本的技术规范要求进行操作。
1.4 体外药物敏感试验
对培养出的所有病原菌进行体外药物敏感试验,结果分为敏感、中介和耐药。药物敏感试验结果按照美国临床实验室标准化协会(CLSI)M100文件[5]标准进行判读,质控菌株为SA菌株ATCC25923、ATCC29213。
1.5 统计学分析
采用WHONET 5.6软件和SPSS软件对SA菌株的科室分布、样本来源和耐药情况进行统计学分析。
2. 结果
2.1 患者一般资料
1 575例患者中,男1 066例(67.7%), 女509例(32.3%); 年龄0~92岁,平均(55.2±22.1)岁; 61~80岁患者占比最高(612例,占38.9%),其后依次为41~60岁患者(426例, 27.0%)、20~40岁患者(245例,占15.6%)、>80岁患者(162例,占10.3%)和 < 20岁患者(130例,占8.2%)。
2.2 菌株来源样本分析
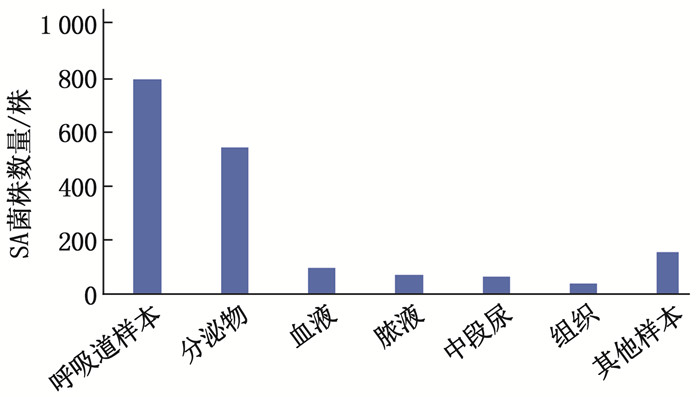
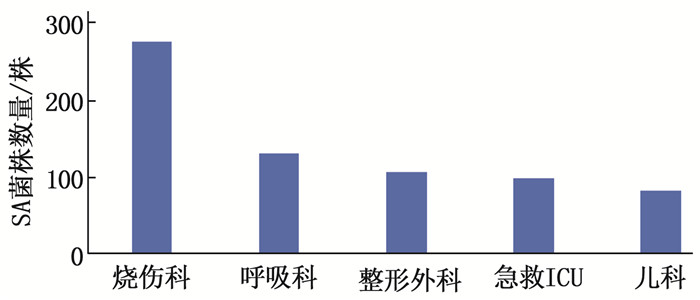
送检样本中共分离出1 784株SA菌株,来源样本分析结果显示,痰液、支气管肺泡灌洗液等呼吸道样本中检出796株SA菌株(44.6%), 分泌物检出543株(30.4%), 血液检出100株(5.6%), 脓液检出78株(4.4%), 中段尿检出66株(3.7%)、组织检出41株(2.3%), 其他样本检出160株(9.0%), 见图 1。SA菌株主要来源于烧伤科(277株,占15.5%)、呼吸科(130株,占7.3%)、整形外科(106株,占5.9%)、急救ICU(99株,占5.5%)和儿科(84株,占4.7%), 见图 2。
2.3 不同年度菌株分布情况
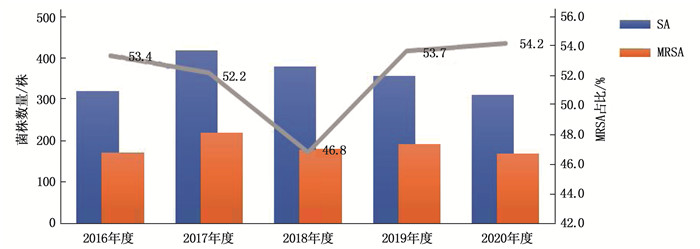
1 575例患者送检样本中共分离出1 784株SA, 其中MRSA 926株,占51.9%。2016—2020年,随着年度的推移, MRSA占比呈缓慢下降又上升的趋势(2018年度占比最低),各年度SA和MRSA的分布情况见图 3。
2.4 SA耐药情况分析
SA对青霉素的总体耐药率最高,达93.3%, 对利福平的总体耐药率仅4.1%, 对庆大霉素的总体耐药率为19.1%。2016—2020年, SA对苯唑西林的耐药率维持在50%左右,对四环素、环丙沙星、左氧氟沙星和莫西沙星的耐药率为29.2%~44.1%,对红霉素和克林霉素的耐药率为44.1%~62.4%, 未检出对替加环素、利奈唑胺和万古霉素耐药的菌株。SA对常见抗菌药物的总体耐药率及不同年度耐药率见表 1。
表 1 2016—2020年SA对常见抗菌药物的耐药率% 抗菌药物 总体 2016年 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 青霉素 93.3 94.4 94.5 92.4 94.4 90.6 苯唑西林 51.9 53.4 52.2 46.8 53.7 54.2 红霉素 58.7 58.4 61.7 53.4 62.4 57.4 克林霉素 53.0 44.1 56.9 49.2 59.0 54.8 庆大霉素 19.1 20.6 17.2 15.0 21.3 22.3 四环素 37.1 38.8 35.4 31.3 44.1 36.8 环丙沙星 38.5 40.9 39.5 31.6 41.9 39.4 左氧氟沙星 38.3 40.6 39.5 31.3 41.6 39.4 莫西沙星 35.5 36.9 35.2 29.2 39.0 38.4 利福平 4.1 7.2 4.5 3.9 4.5 0.3 替加环素 0 0 0 0 0 0 利奈唑胺 0 0 0 0 0 0 万古霉素 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.5 MRSA耐药情况分析
MRSA对常见抗菌药物的总体耐药率均高于SA。2016—2020年, MRSA对青霉素和苯唑西林的耐药率均为100.0%, 对庆大霉素的耐药率维持在30%左右,对四环素、环丙沙星、左氧氟沙星和莫西沙星的耐药率为50.6%~67.5%, 对红霉素和克林霉素的耐药率较高(>60%), 未发现对替加环素、利奈唑胺和万古霉素耐药的菌株。MRSA对抗菌药物的总体耐药率及不同年度耐药率见表 2。
表 2 2016—2020年MRSA对常见抗菌药物的耐药率% 抗菌药物 总体 2016年 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 青霉素 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 苯唑西林 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 红霉素 78.6 77.2 77.1 77.0 84.3 77.4 克林霉素 73.5 61.4 72.9 74.7 83.2 74.4 庆大霉素 33.0 33.9 27.1 29.8 38.7 36.9 四环素 56.8 57.9 55.5 52.2 67.0 50.6 环丙沙星 61.8 64.9 60.6 55.6 67.5 60.1 左氧氟沙星 61.6 64.3 60.6 55.6 67.0 60.1 莫西沙星 59.6 62.6 57.3 53.4 65.4 59.5 利福平 7.5 12.9 8.3 7.3 8.4 0 替加环素 0 0 0 0 0 0 利奈唑胺 0 0 0 0 0 0 万古霉素 0 0 0 0 0 0 3. 讨论
SA是一种致病力较强的革兰阳性菌,具有共生菌和致病菌的双重特性,在人鼻前庭、腋窝、腹股沟和胃肠道等部位均有定植[6-7], 可经皮肤伤口、汗腺、毛囊等多种途径进入体内,引起化脓性感染、食物中毒、烫伤样皮肤综合征等,严重者还可随血液循环至全身,导致血流感染[8]。MRSA是导致医院感染的一种重要病原菌,患者常因外置导管、应用广谱抗生素、透析、免疫抑制性疾病等而发生感染[9],此外医务人员也能在一定程度上导致该菌的院内感染。
本研究结果显示, SA菌株检出率排名前3位的科室为烧伤科(15.5%)、呼吸科(7.3%)和整形外科(5.9%)。烧伤患者皮肤黏膜屏障受损,机体免疫功能受抑制,且创面大量渗液,为SA的侵入和生长繁殖提供了有利条件[10]。SA菌株分离率排名前3位的样本分别是痰液和支气管肺泡灌洗液等呼吸道样本(44.6%)、分泌物(30.4%)和血液(5.6%)。由此提示,SA主要引起呼吸道感染、皮肤软组织或伤口感染、血流感染等,其中呼吸道感染占总感染量近一半,提示临床应加强对呼吸道感染的控制。
自从1961年MRSA被首次分离以来, MRSA分离率(MRSA在SA中的占比)呈现不断上升趋势[11-12]。全国细菌耐药监测网(CARSS)2016—2020年数据均显示MRSA分离率呈逐步下降趋势,其中上海市的MRSA分离率每年均高于全国平均水平[13-14]。本研究结果显示, 2016—2020年,本院总体MRSA分离率高达51.9%, 随着年度的推移,本院MRSA分离率呈缓慢下降又上升的趋势,且本院各年度的MRSA分离率均高于全国MRSA分离率以及上海市MRSA分离率。分析原因,这可能与本院烧伤科收治的重症患者人数较多、抗菌药物使用种类及强度不同有关。此外,本院2018年度MRSA分离率降至最低,这可能与烧伤科2018年正逢成立60周年加强了创面管理、手卫生、消毒隔离等感染控制措施有关[15]。
本研究发现, 2016—2020年, SA菌株对青霉素的耐药率均持续高于90%, 对红霉素和克林霉素的耐药率持续高于40%, 对利福平的耐药率总体呈下降趋势,对庆大霉素、四环素、环丙沙星、左氧氟沙星和莫西沙星的耐药率呈现为先下降又上升的趋势,这可能与2018年MRSA分离率较低有关。本研究结果显示, MRSA菌株对各类抗菌药物的耐药率普遍高于SA, 但尚未发现对替加环素、利奈唑胺和万古霉素耐药的菌株。万古霉素是治疗MRSA感染的首选药物,但目前已有少量耐万古霉素金黄色葡萄球菌的报道[16], 因此临床医生应重视万古霉素的合理使用,根据药物敏感试验结果优先选用敏感药物,避免诱导耐万古霉素菌株的产生。
综上所述,本院SA菌株和MRSA菌株的检出率较高,医院管理者及医务工作者需引起充分重视。防治SA感染,不仅需要合理选用抗菌药物,还需要加强病房管理、手消毒和环境消毒等。
-
表 1 2016—2020年SA对常见抗菌药物的耐药率
% 抗菌药物 总体 2016年 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 青霉素 93.3 94.4 94.5 92.4 94.4 90.6 苯唑西林 51.9 53.4 52.2 46.8 53.7 54.2 红霉素 58.7 58.4 61.7 53.4 62.4 57.4 克林霉素 53.0 44.1 56.9 49.2 59.0 54.8 庆大霉素 19.1 20.6 17.2 15.0 21.3 22.3 四环素 37.1 38.8 35.4 31.3 44.1 36.8 环丙沙星 38.5 40.9 39.5 31.6 41.9 39.4 左氧氟沙星 38.3 40.6 39.5 31.3 41.6 39.4 莫西沙星 35.5 36.9 35.2 29.2 39.0 38.4 利福平 4.1 7.2 4.5 3.9 4.5 0.3 替加环素 0 0 0 0 0 0 利奈唑胺 0 0 0 0 0 0 万古霉素 0 0 0 0 0 0 表 2 2016—2020年MRSA对常见抗菌药物的耐药率
% 抗菌药物 总体 2016年 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 青霉素 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 苯唑西林 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 红霉素 78.6 77.2 77.1 77.0 84.3 77.4 克林霉素 73.5 61.4 72.9 74.7 83.2 74.4 庆大霉素 33.0 33.9 27.1 29.8 38.7 36.9 四环素 56.8 57.9 55.5 52.2 67.0 50.6 环丙沙星 61.8 64.9 60.6 55.6 67.5 60.1 左氧氟沙星 61.6 64.3 60.6 55.6 67.0 60.1 莫西沙星 59.6 62.6 57.3 53.4 65.4 59.5 利福平 7.5 12.9 8.3 7.3 8.4 0 替加环素 0 0 0 0 0 0 利奈唑胺 0 0 0 0 0 0 万古霉素 0 0 0 0 0 0 -
[1] 王大胜, 王大新, 耿平. 成人血流感染金黄色葡萄球菌的临床分布及耐药性分析[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2018, 22(1): 1-3. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201801001 [2] 李敏燕, 王继红, 王吉刚, 等. 血液病住院患者血流感染病原菌分布及耐药性分析[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2021, 49(11): 1261-1263. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGZ202111027.htm [3] CHEUNG G Y C, BAE J S, OTTO M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Virulence, 2021, 12(1): 547-569. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1878688
[4] 尚红, 王毓三, 申子瑜. 全国临床检验操作规程[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2015: 120-123. [5] Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing[M]. 29th ed. Wayne, Pennsylvania: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 2019: 58-66.
[6] SAKR A, BRÉGEON F, MÈGE J L, et al. Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization: an update on mechanisms, epidemiology, risk factors, and subsequent infections[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9: 2419. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02419
[7] 王红, 郁洁, 王博, 等. 住院新生儿鼻腔和体表定植金黄色葡萄球菌的分子特征及耐药性[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2021, 16(5): 379-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2021.05.010 [8] 武杰, 薛丽伟, 赵建平. 金黄色葡萄球菌血流感染111例的临床特征和预后[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志, 2021, 21(3): 264-270. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KGHL202103004.htm [9] HSU Y Y, WU D, HUNG C C, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization among HIV-infected patients in Taiwan: prevalence, molecular characteristics and associated factors with nasal carriage[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2020, 20(1): 254. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-04979-8
[10] 刘云, 黄晓春, 马炜, 等. 烧伤患者院内感染病原菌分布及耐药性分析[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2019, 40(7): 710-715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DEJD201907003.htm [11] LEE A S, DE LENCASTRE H, GARAU J, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4: 18033. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.33
[12] HIRAMATSU K, KATAYAMA Y, MATSUO M, et al. Multi-drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and future chemotherapy[J]. J Infect Chemother, 2014, 20(10): 593-601. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2014.08.001
[13] 全国细菌耐药监测网. MRSA甲氧西林耐药金黄色葡萄球菌检出率[EB/OL]. (2021-11-18)[2022-05-03]. http://www.carss.cn/sys/Htmls/dist/index.html#/resistance.. [14] 全国细菌耐药监测网. 全国细菌耐药监测网2014—2019年胆汁细菌耐药监测报告[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2021, 20(1): 76-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GRKZ202101008.htm [15] 夏照帆, 肖仕初, 葛绳德. 海军军医大学第一附属医院烧伤外科60年发展历程回顾[J]. 中华烧伤杂志, 2018, 34(11): 741-743. [16] MCGUINNESS W A, MALACHOWA N, DELEO F R. Vancomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Yale J Biol Med, 2017, 90(2): 269-281.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 莫亚玲,赵德运. 不同治疗方案对合并反复呼吸道感染史儿童重症社区获得性肺炎的效果观察. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(06): 51-55+64 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 赵欣如,周润龙,明文卓,王璐,张宏飞,张稳稳,李诚博. 黄芪中杀菌抑菌单体分子的筛选及差异表达基因检测. 滨州医学院学报. 2024(04): 248-252 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号