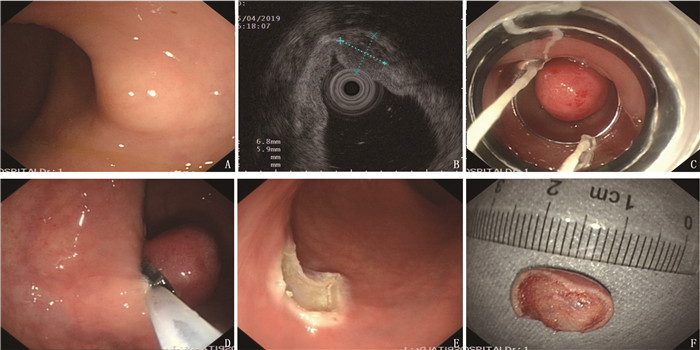
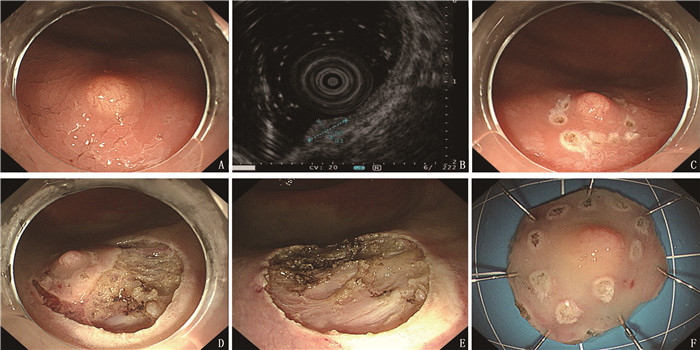
Application of endoscopic mucosal ligation resection in rectal neuroendocrine tumors
-
摘要:目的
比较套扎法内镜下黏膜切除术(EMR-b)和内镜下黏膜剥离术(ESD)对直肠神经内分泌肿瘤(NENs)的治疗效果。
方法回顾性分析56例接受ESD或EMR-b治疗的直肠NENs患者的资料,患者肿瘤直径均 < 10 mm且无淋巴系统转移。根据接受治疗的不同,将患者分为EMR-b组26例和ESD组30例。记录2组患者组织学完整切除率、并发症发生率和操作时间。
结果56例患者的平均年龄为(51.05±11.31)岁。EMR-b组肿瘤直径为(7.12±2.76) mm, ESD组为(7.47±2.32) mm, 2组肿瘤直径差异无统计学意义(P=0.599)。EMR-b组切除时间为(9.08±3.45) min, 短于ESD组的(18.50±3.25) min, 差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。EMR-b组完整切除率为92.31%(24/26), ESD组为93.33%(28/30), 2组完整切除率差异无统计学意义(P=1.000)。非完整切除患者随访期间无局部复发和远处转移。
结论与ESD相比, EMR-b有相似的组织学完整切除率,但切除时间更短,操作更简单, EMR-b对于直径 < 10 mm、不超过黏膜下层的直肠NENs是一种良好的内镜下治疗方法。
-
关键词:
- 套扎法内镜下黏膜切除术 /
- 内镜下黏膜剥离术 /
- 直肠 /
- 神经内分泌肿瘤
Abstract:ObjectiveTo compare the efficacy of endoscopic mucosal resection using band ligation(EMR-b) and endoscopic mucosal dissection(ESD) in the treatment of rectal neuroendocrine tumors(NENs).
MethodsThe data of 56 rectal NENs patients with rectal NENs < 10 mm in diameters, without lymphatic metastasis treated by ESD or EMR-b were retrospectively analyzed. According to different treatments, the patients were divided into EMR-B group (26 cases) and ESD group (30 cases). The complete resection rate, incidence of complications, and length of procedures were compared between the two groups.
ResultsThe mean age was (51.05±11.31) years old of 56 cases. The tumor size of EMR-B group was (7.12±2.76) mm, and was (7.47±2.32) mm in the ESD group, and the between-group difference in tumor size showed no significant difference (P=0.599). The resection time in EMR-B group was (9.08±3.45) min, which was shorter than (18.50±3.25) min in the ESD group, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.001). The complete resection rate of the EMR-B group was 92.31% (24/26), and was 93.33% (28/30) in the ESD group, and the difference was not statistically significant (P=1.000). In the cases of incomplete resection, there was neither local recurrence nor distant metastasis during the follow-up.
ConclusionCompared with ESD, EMR-b has similar histological complete resection rate, but has shorter resection time and simpler operation. EMR-b may be a better choice for rectal NENs with diameter < 10 mm and without invasion of submucosa.
-
妊娠期糖尿病(GDM)是妊娠期常见的内分泌并发症,近年来其患病率在全球范围内逐步升高[1-2]。GDM与不良母婴结局相关,包括母体先兆子痫风险、剖宫产率及会阴外伤数量增加等,同时后代出现新生儿黄疸、新生儿低血糖、大于胎龄儿(LGA)和巨大儿的概率显著升高[3]。从长期风险来看,GDM患者产后发生2型糖尿病的风险是正常孕妇的20倍,其后代出现肥胖及代谢综合征的风险增加2倍[4]。因此关注GDM的治疗显得尤为重要。目前医学营养治疗(MNT)是GDM的一线治疗[5], 营养师通过制定个性化饮食方案,调整GDM患者饮食结构,改善糖代谢及妊娠结局。科学的MNT不是对单一食物或营养素的简单搭配,而是强调多种食物及营养素间的相互作用,因此关注整体的饮食模式更能反映不同食物及营养素对GDM糖代谢及妊娠结局的影响。本文探讨常见GDM饮食模式及其在GDM中的应用效果,为GDM患者饮食模式选择提供依据。
1. 低碳水化合物饮食模式
碳水化合物是机体内葡萄糖的主要来源,限制碳水化合物摄入量可降低血糖水平。低碳水化合物饮食模式要求每日摄入碳水化合物的量低于总能量的45%。MAJOR C A等[6]提出在GDM中限制碳水化合物的量可降低餐后血糖,减少怀孕期间胰岛素用量,并降低LGA、巨大儿和剖宫产风险。而后续对GDM开展的随机对照试验中却显示低碳水化合物饮食模式并未改善GDM的血糖控制及妊娠结局[7]。研究结果的不同可能与低碳水化合物饮食模式中蛋白质及脂肪的占比不同有关。为了探究低碳水化合物高脂肪饮食模式对GDM的影响,HERNANDEZ T L等[8]将12例超重/肥胖GDM患者随机分配至低碳水高脂饮食组(40%碳水化合物/45%脂肪/15%蛋白质)或复合高碳水低脂饮食组(60%碳水化合物/25%脂肪/15%蛋白质),结果发现后者的胰岛素抵抗减轻、空腹血糖降低、促炎基因表达减少,且血清游离脂肪酸有降低趋势。这提示当蛋白质含量相对固定时(15%~20%),通过增加脂肪含量的低碳水化合物饮食模式会增强脂肪分解,促进游离脂肪酸升高,并加重母体胰岛素抵抗[9]。之后为观察低碳水化合物高蛋白质饮食模式(蛋白质>30%)与GDM的关系,同济大学开展的一项前瞻性队列研究发现该饮食模式与GDM风险升高相关[10]。这是由于高蛋白饮食(尤其是动物蛋白)可在短期内增加血浆氨基酸的浓度,引起骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗和内源性葡萄糖的产生[11]。可见含有高脂肪或高蛋白质的传统低碳水化合物饮食模式均可加重胰岛素抵抗和葡萄糖耐量受损,产生一系列的母婴并发症。此外,严格限制碳水化合物摄入量可能会引起GDM患者对进食的焦虑,导致坚持困难、依从性低[12]。目前传统的低碳水化合物饮食模式已不推荐,近期有研究提出适度低碳水化合物饮食模式不仅能够平稳降低2型糖尿病患者血糖水平,还可预防心血管疾病的发生[13]。适度低碳水化合物饮食模式是指在限制碳水化合物含量基础上,将脂肪和蛋白质比例均匀增加。但该饮食模式在GDM中尚无研究,其对GDM血糖控制及妊娠结局的影响有待考证。当前,全球不同指南推荐GDM患者碳水化合物摄入量的范围为每日总能量的35%~60%, 比例跨度较大,因此仍需开展更多研究以探索最佳碳水化合物比例。
2. 低血糖指数饮食模式
血糖指数(GI)是指含50 g可利用碳水化合物的食物与50 g葡萄糖所引起的餐后2 h血糖反应(浓度变化)的百分比值,可反映食物“升糖”效应。GI按0~100的范围对食物进行分级,食物的GI值越高,表明摄入后血糖上升越急剧、血糖水平越高。通常GI < 55的食物为低GI食物。这些食物可降低体内血糖应答水平、减少餐后血糖波动,使血糖曲线变平。
低GI饮食模式在GDM中的作用已经被广泛研究。最初为了探究低GI饮食模式对GDM患者血糖控制的影响,MOSES R G等[14]开展的一项随机对照试验显示低GI饮食组胰岛素治疗人数较对照组减少50%, 且较高GI饮食组的GDM患者转换为低GI饮食组后可避免胰岛素应用。为了进一步研究低GI饮食模式对GDM母婴结局的影响,WEI J H等[15]对5项随机对照试验(n=302)进行了荟萃分析,发现该模式可降低巨大儿的风险。近期国内开展的一项代谢组学研究[16]提出低GI饮食模式还可改善GDM患者的代谢产物,发现在营养干预12周后低GI饮食组GDM患者的代谢产物接近健康孕妇水平,且低GI饮食组的剖宫产率及新生儿出生体质量均显著低于对照组。而最新的荟萃分析(n=532)发现,低GI饮食模式可显著降低GDM患者餐后2 h血糖,但在不良母婴结局方面却没有改善[17]。据目前的研究结果表明,低GI饮食模式有利于GDM患者的血糖控制,但在改善GDM不良母婴结局方面的结论不一,仍需进一步验证。不过明确的是该模式在GDM中是安全的,因为在临床试验中未发现其与不良母婴结局相关[18], 且国内外多个GDM指南均推荐使用低GI食物替代高GI食物的饮食模式。因此在临床护理中,在开始胰岛素治疗之前应考虑对GDM患者给予低GI饮食建议。
3. 低血糖负荷饮食模式
血糖负荷(GL)是指给定食物的GI与其碳水化合物含量的乘积[GL=某食物的GI×食物中可利用的碳水化合物量(g/100)]。通常认为GL≥20为高负荷饮食, GL < 10为低负荷饮食,食物的GL越高对餐后血糖的影响越大。GL兼顾碳水化合物的“质”和“量”,是评定食物血糖效应的有效指标。
研究[19]表明高GL饮食模式与2型糖尿病风险相关,低GL饮食模式有利于2型糖尿病患者的血糖控制。为了探究GL与GDM风险的关系,有学者通过食物频率问卷对294位健康孕妇的饮食进行评估,计算出参与者的GI和GL, 并于孕24~28周对孕妇进行GDM的筛查,结果发现孕妇摄入膳食的GI、GL与GDM发生风险无显著相关性[20]。但在一项对中国孕妇进行的大型前瞻性研究中(n=9 317), 研究者分别调查了参与者妊娠前1年与妊娠T1、T2期摄入的膳食GI、GL, 探讨其对GDM发病风险的影响,并且观察妊娠期(T1~T3)膳食GI、GL对血糖稳态的影响,结果表明在怀孕前或怀孕期间应用较高GI、GL饮食模式可增加中国妇女患GDM的风险,且高GI、GL饮食模式导致孕妇空腹血糖升高、胰岛素抵抗加重[2]。但低GL饮食模式在GDM糖代谢及妊娠结局方面的研究有限。MA W J等[21]开展的一项随机对照试验显示,与对照组相比低GL饮食模式在改善GDM患者血糖及血脂方面存在显著优势。而后LV S F等[22]研究发现,低GL饮食模式还可降低GDM患者妊娠期高血压、子痫、早产的风险。上述研究表明高GL饮食模式可增加孕妇患GDM的风险,低GL饮食模式有益于GDM患者的血糖控制及妊娠结局。但由于相关研究较少,要明确低GL饮食模式改善GDM糖代谢及不良母婴结局的效应,仍需进一步开展长时间、大样本的临床研究验证。
4. 地中海饮食模式
地中海饮食模式多流行于以法国、希腊、西班牙为代表的南欧地区。其主要强调大量食用植物性食物,适量食用鱼类、禽类制品,少量食用动物性、高脂肪的加工食品。地中海饮食模式以低GI为特点,富含丰富的单不饱和脂肪酸、膳食纤维、抗氧化剂(如维生素E和多酚类)和抗炎成分,这些关键成分已被证明有助于预防2型糖尿病[23]。
近年来,一系列研究发现地中海饮食模式可降低孕妇患GDM的风险。St Carlos GDM预防研究是在西班牙进行的一项前瞻性试验,将874例孕早期(孕8~12周)血糖正常的孕妇随机分配至地中海饮食组/常规饮食组,观察孕妇的GDM发病率及妊娠结局,结果表明地中海饮食不仅将GDM发病率从23.4%降至17.1%, 而且还降低了不良母婴结局的发生风险[24]。之后为了观察真实世界中地中海饮食模式对GDM发病率的影响,此小组开展了另一项前瞻性单臂研究,在孕早期(12周前)对932名血糖正常孕妇应用了地中海饮食,并定期随访直至产后12~14周,发现GDM发病率进一步降低至13.9%[25]。因此,该研究者建议孕妇可在妊娠早期采取地中海饮食模式以减少GDM和不良母婴结局的发生。但地中海饮食模式在已确诊GDM患者中的应用证据有限,一项对St Carlos GDM预防研究的二次分析试验显示,患GDM与未患GDM的孕妇应用地中海饮食后,在分娩方式、早产和LGA等妊娠结局方面无显著差异[26], 这表明地中海饮食对GDM患者的营养治疗有效。由于这不是一项随机对照试验,仍需进一步的前瞻性随机对照研究来明确地中海饮食模式对GDM糖代谢及妊娠结局的影响。此外,由于饮食文化的差异,该模式是否适用于中国GDM患者亦需进一步探讨。
5. 其他饮食模式
其他饮食模式还包括热量限制饮食模式、植物性饮食模式等。国内外指南对GDM患者的总热量摄入提出不同建议,其中国际妇产科学联盟[27]和中华医学会妇产科学分会产科学组[28]建议超重/肥胖的GDM患者限制热量的摄入。通常中度热量限制是指摄入热量1 600~1 800 kcal/d或摄入热量较孕前减少30%, 重度热量限制指摄入热量 < 1 500 kcal/d或摄入热量较孕前减少50%[29]。研究[30]显示,超重/肥胖的GDM患者应用中度热量限制饮食模式可改善血糖水平且不会诱导母体酮症或限制胎儿生长,但重度热量限制饮食模式可导致酮尿。因此必须密切监测GDM患者妊娠期间的热量摄入,避免母体酮症的发生[29]。植物性饮食模式强调摄入食物主要来源于植物,这些食物富含大量的纤维素和抗氧化剂,可增加胰岛素敏感性,降低肌细胞内脂质浓度,减少氧化应激[31]。最新研究[32]表明,植物性饮食模式可降低GDM的风险、避免孕妇体质量过度增加,但与小于胎龄儿和新生儿出生体质量百分位数较低有关。对于大多数GDM患者而言,长期植物性饮食难以满足患者对食物选择的偏好与需求,且由于动物制品摄入较少,会导致营养成分的缺失,因此该饮食模式在GDM患者中难以大规模推行。
6. 小结
作为GDM饮食干预方案,以上几种饮食模式对GDM的血糖控制及妊娠结局的改善均有不同程度作用。首先,低GI饮食模式可有效改善GDM患者血糖水平,尽管其对GDM不良母婴结局的改善作用结论不一,但该模式在GDM中的安全性已得到证实,且被多个指南纳入为推荐方案[33]; 其次,低GL饮食模式兼顾食物的GI和碳水化合物的摄入量,目前的证据表明该模式更有利于GDM患者的血糖控制及妊娠结局,但由于相关研究较少,仍需更多的临床研究验证。再次,地中海饮食作为欧洲地区特有的饮食模式,已被证实可预防GDM的发生,但其对GDM血糖控制及妊娠结局的影响有待开展相关的随机对照研究,且地中海饮食与中国传统饮食有一定差异,是否适用于中国GDM患者仍未可知[34]; 最后,目前含有高脂肪或高蛋白质的传统低碳水化合物饮食模式在GDM中已不推荐,相反以低GI为特点、具有较高碳水化合物、较低脂肪和适当蛋白质比例的复合碳水化合物饮食模式更值得推荐,但三大营养物质的具体占比仍需进一步探索。
-
表 1 2组患者基本情况及肿瘤基本特征(x±s)[n(%)]
指标 EMR-b组(n=26) ESD组(n=30) 全组(n=56) P 年龄/岁 49.04±11.71 52.80±10.85 51.05±11.31 0.210 男 12(46.15) 18(60.00) 30(53.57) 0.421 肿瘤直径/mm 7.12±2.76 7.47±2.32 7.30±2.52 0.599 距肛门距离/cm 5.81±1.92 6.73±2.78 6.30±2.44 0.153 住院时间/d 3.27±0.60 4.83±0.79 4.11±1.06 < 0.001 手术费用/元人民币 2 752.69±686.88 8 481.57±1 218.38 5 821.73±3 051.02 < 0.001 表 2 2组内镜治疗效果比较(x±s)[n(%)]
指标 EMR-b组(n=26) ESD组(n=30) 全组(n=56) P 完整切除 24(92.31) 28(93.33) 52(92.86) 1.000 水平切缘阳性 0 1(3.33) 1(1.80) 1.000 垂直切缘阳性 1(3.85) 1(3.33) 2(3.57) 1.000 切缘均阳性 1(3.85) 0 1(1.79) 0.464 切除时间/min 9.08±3.45 18.50±3.25 14.13±6.30 < 0.001 迟发出血 0 1(3.33) 1(1.79) 1.000 -
[1] WANG X Y, CHAI N L, LINGHU E Q, et al. Efficacy and safety of hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with endoscopic submucosal dissection for rectal neuroendocrine tumors and risk factors associated with incomplete endoscopic resection[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(6): 368. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.25
[2] OSAGIEDE O, HABERMANN E, DAY C, et al. Factors associated with worse outcomes for colorectal neuroendocrine tumors in radical versus local resections[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2020, 11(5): 836-846. doi: 10.21037/jgo-20-193
[3] AVENEL P, MCKENDRICK A, SILAPASWAN S, et al. Gastrointestinal carcinoids: an increasing incidence of rectal distribution[J]. Am Surg, 2010, 76(7): 759-763. doi: 10.1177/000313481007600736
[4] SHIM K N, YANG S K, MYUNG S J, et al. Atypical endoscopic features of rectal carcinoids[J]. Endoscopy, 2004, 36(4): 313-316. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-814202
[5] CAPLIN M, SUNDIN A, NILLSON O, et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the management of patients with digestive neuroendocrine neoplasms: colorectal neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. Neuroendocrinology, 2012, 95(2): 88-97. doi: 10.1159/000335594
[6] BASUROY R, HAJI A, RAMAGE J K, et al. Review article: the investigation and management of rectal neuroendocrine tumours[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 44(4): 332-345. doi: 10.1111/apt.13697
[7] ONO A, FUJⅡ T, SAITO Y, et al. Endoscopic submucosal resection of rectal carcinoid tumors with a ligation device[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2003, 57(4): 583-587. doi: 10.1067/mge.2003.142
[8] NAGAI T, TORISHIMA R, NAKASHIMA H, et al. Saline-assisted endoscopic resection of rectal carcinoids: cap aspiration method versus simple snare resection[J]. Endoscopy, 2004, 36(3): 202-205. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-814248
[9] FUJISHIRO M, YAHAGI N, KAKUSHIMA N, et al. Outcomes of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Colorectal Epithelial Neoplasms in 200 Consecutive Cases[J]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2007, 5(6): 678-683. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.01.006
[10] TANAKA S, OKA S, KANEKO I, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: possibility of standardization[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2007, 66(1): 100-107. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2007.02.032
[11] CHOI C W, KANG D H, KIM H W, et al. Comparison of endoscopic resection therapies for rectal carcinoid tumor: endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection using band ligation[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2013, 47(5): 432-436. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31826faf2b
[12] SOLCIA E, KLÖPPEL G, SOBIN L H. Histological Typing of Endocrine Tumours[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2000: 115-119.
[13] HE L, DENG T, LUO H. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection therapies for rectal carcinoid tumors: a meta-analysis[J]. Yonsei Med J, 2015, 56(1): 72-81. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.72
[14] SOGA J. Carcinoids of the rectum: an evaluation of 1271 reported cases[J]. Surg Today, 1997, 27(2): 112-119. doi: 10.1007/BF02385898
[15] KWAAN M R, GOLDBERG J E, BLEDAY R. Rectal carcinoid tumors: review of results after endoscopic and surgical therapy[J]. Arch Surg, 2008, 143(5): 471-475. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.143.5.471
[16] LEE J, PARK Y E, CHOI J H, et al. Comparison between cap-assisted and ligation-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection for rectal neuroendocrine tumors[J]. Ann Gastroenterol, 2020, 33(4): 385-390.
[17] MASHIMO Y, MATSUDA T, URAOKA T, et al. Endoscopic submucosal resection with a ligation device is an effective and safe treatment for carcinoid tumors in the lower rectum[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2008, 23(2): 218-221. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05313.x
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李英,郭玲利,王燕梅. 营养干预联合规范化治疗在妊娠期糖尿病孕妇中的应用. 中国医学创新. 2025(02): 130-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 康雪莲,黄清秀,王小娇. 基于营养管理的饮食干预结合生活护理对糖尿病患者的效果. 西藏医药. 2024(01): 133-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 燕青. 精细化定量饮食联合运动制订在妊娠糖尿病患者中的应用价值. 中国社区医师. 2024(08): 91-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张茜,余洁,肖新华. 中国妊娠期糖尿病母儿共同管理指南(2024版). 中国研究型医院. 2024(06): 11-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 中国研究型医院学会糖尿病学专业委员会. 中国妊娠期糖尿病母儿共同管理指南(2024版). 中华糖尿病杂志. 2024(12): 1324-1345 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 宗海燕. 妊娠期糖尿病及时诊断与治疗对妊娠结局的影响. 实用妇科内分泌电子杂志. 2023(13): 37-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号