Application of optical coherence tomography angiography in fundus screening in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes
-
摘要:目的
探讨光学相干断层扫描血管造影技术(OCTA)在初诊为2型糖尿病的患者中进行眼底筛查的诊断价值。
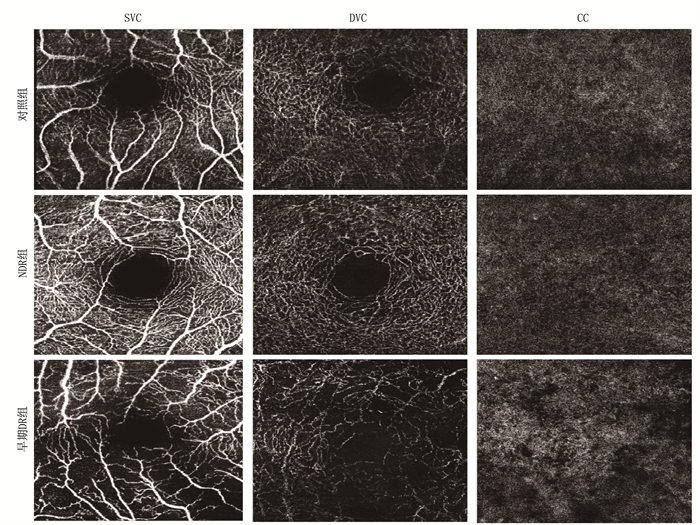
方法将2019年11月-2021年3月初诊确诊的40例2型糖尿病患者纳入本研究,由临床经验丰富的医师对其进行眼底检查,根据患者糖尿病性视网膜病变(DR)情况进行分组,将非DR(NDR)患者纳入NDR组(n=20),将已出现轻度非增殖期糖尿病性视网膜病变(NPDR)的患者纳入早期DR组(n=20)。同时,将与其年龄匹配的20例健康者纳入对照组。采用OCTA对研究对象的黄斑区进行扫描并作定量分析,获得视网膜浅层视网膜血管丛(SVC)、深层视网膜血管丛(DVC)和脉络膜毛细血管层(CC)的黄斑区血流密度(MVD)和黄斑中心凹无血管区(FAZ)面积; 比较各组不同指标的差异以及对早期DR的筛查和诊断价值。
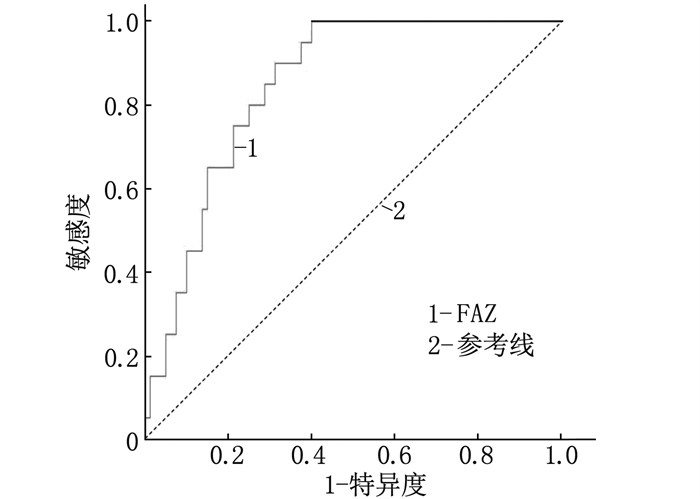
结果NDR组SVC的血流密度为(0.52±0.09), DVC为(0.54±0.13), CC为(0.51±0.07); 早期DR组SVC的血流密度为(0.45±0.09), DVC为(0.43±0.09), CC为(0.45±0.06), 对照组SVC的血流密度为(0.54±0.01), DVC为(0.57±0.01), CC为(0.52±0.02)。与对照组比较, NDR组、早期DR组SVC、DVC、CC血流密度均减小。NDR组的FAZ面积为(0.39±0.06) mm2, 早期DR组为(0.43±0.05) mm2, 对照组为(0.29±0.01) mm2。NDR组和早期DR组的FAZ面积大于对照组, 且早期DR组的FAZ面积扩大最明显。多因素回归Logistic分析发现, DVC血流密度和FAZ面积均会对诊断产生影响。
结论初诊糖尿病患者采用OCTA检查,可以筛查出视网膜黄斑区的早期血运改变。早期糖尿病性视网膜病变患者的MVD减少,且FAZ面积扩大。DVC的血流密度和FAZ面积均能对早期DR的诊断产生影响,而FAZ面积对早期DR有更高的诊断价值。
-
关键词:
- 糖尿病性视网膜病变 /
- 光学相干断层扫描血管造影技术 /
- 筛查 /
- 黄斑区血流密度 /
- 黄斑中心凹无血管区
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the diagnostic value of optical coherence tomography angiography(OCTA) in fundus screening in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients.
MethodsForty patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes from November 2019 to March 2021 were included in this study. Experienced physicians performed fundus examination for them. According to diabetic retinopathy (DR) conditions, non-DR patients were included in NDR group (n=20), those with mild non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) were included in early DR group (n=20). At the same time, 20 healthy subjects matched with age were included in control group. OCTA was used to scan and quantitatively analyze the macular region of the study subjects, and macular blood flow density(MVD) of superficial vascular capillary(SVC), deep vascular capillary (DVC) and choroidal capillaries layer (CC) and the area of the macular fovea without blood vessels (FAZ) were obtained. The difference of different indicators in each group and the value of screening and diagnosis for early DR were compared.
ResultsThe blood flow density of SVC, DVC and CC were (0.52±0.09), (0.54±0.13) and (0.51±0.07), respectively in the NDR group, were (0.45±0.09), (0.43±0.09) and (0.45±0.06), respectively in the early DR group, and were (0.54±0.01), (0.57±0.01) and (0.52±0.02), respectively in the control group. Compared with the control group, blood flow density of SVC, DVC and CC decreased in the NDR group and early DR group. The FAZ area was (0.39±0.06) mm2 in the NDR group, (0.43±0.05) mm2 in the early DR group, and (0.29±0.01) mm2 in the control group. The FAZ area of the NDR group and the early DR group was larger than that of the control group, and the early DR group had the most obvious expansion of FAZ area. Multivariate Logistic analysis showed that DVC blood flow density and FAZ area both affected the diagnosis.
ConclusionEarly changes of macular vascular density and enlargement of FAZ can be observed in early diabetic retinopathy by OCTA. Patients with early diabetic retinopathy have reduced MVD and enlarged FAZ area. Both blood flow density and FAZ area of DVC can affect the diagnosis of early DR, and FAZ area has higher diagnostic value for early DR.
-
研究[1-4]表明,恶性肿瘤的发生、发展与免疫检查点受体有非常紧密的联系,肿瘤细胞可通过激活免疫检查点途径来逃避免疫监视,这些途径由受体-配体成对组成,在受体-配体相互作用后,抑制T细胞和自然杀伤(NK)细胞的功能,从而损害抗肿瘤免疫,关于免疫检查点受体的阻断治疗已经成为肿瘤免疫治疗的研究热点。T细胞免疫球蛋白和免疫受体酪氨酸抑制基序(ITIM)结构域(TIGIT)是一种在免疫细胞上表达的抑制性受体,是肿瘤免疫治疗的主要新兴靶点之一[5]。TIGIT可以通过多种机制抑制T细胞和NK细胞等免疫细胞的功能,使肿瘤细胞逃避免疫系统的监视[6]。本研究将对TIGIT的免疫抑制机制的研究进展进行系统综述。
1. TIGIT的分子结构
TIGIT于2009年首次被确定为免疫细胞上的共抑制受体,属于免疫球蛋白超家族[7]。TIGIT基因位于人类的第16号染色体上,是一种由244个氨基酸组成的跨膜糖蛋白,其结构包括一个细胞外免疫球蛋白可变结构域(IgV), 一个Ⅰ型跨膜结构域和一个细胞质尾,尾部含有ITIM和免疫球蛋白酪氨酸尾(ITT)样基序[8-9]。细胞外区长141个氨基酸,跨膜区长23个氨基酸,胞质区有80个氨基酸[10]。TIGIT在活化的T细胞、NK细胞、记忆T细胞、滤泡性T辅助细胞和调节性T(Treg)细胞上广泛表达[11]。
2. TIGIT的配体
TIGIT具有4种配体,分别是白细胞分化抗原(CD)155、CD112、CD113和连接蛋白4(Nectin-4), 其配体有相似的结构特征: 细胞外包含3个连续的免疫球蛋白样环状结构域、1个跨膜结构域和1个细胞内结构域[12]。TIGIT与其他共刺激受体和共抑制受体竞争或共享前2种配体,而Nectin-4仅与TIGIT相互作用[6, 13], 见图 1。
CD155又名脊髓灰质炎病毒受体(PVR)和Necl-5, CD155可以与共抑制受体TIGIT、CD96结合,也可以与共刺激受体CD226结合,其中, CD155与TIGIT的亲和力最高, TIGIT通过与CD266、CD96竞争来发挥其免疫抑制作用。TIGIT与CD155结合时,每个TIGIT分子结合1个CD155分子, 2个TIGIT/CD155二聚体组装成具有核心TIGIT/TIGIT顺式同源二聚体的异四聚体[14], 随后介导细胞之间的细胞黏附和抑制信号的传导[15-16]。
CD112又称脊髓灰质炎病毒相关蛋白2(PVRL2)或Nectin-2, CD112除了可以与TIGIT结合,还可以与CD226、CD112R结合[17]。CD113在肺腺癌、胆囊癌、乳腺癌、卵巢癌[18]及结直肠癌中呈高表达,与肿瘤的发生、发展及侵袭转移密切相关[19]。Nectin-4在胎儿发育过程中含量丰富,成年后表达下降,且在乳腺癌、肺癌、膀胱癌和胰腺癌等肿瘤中过表达[20]。TIGIT的免疫学功能十分复杂,与其配体相互作用后,可以通过多种作用机制抑制免疫细胞的功能,使肿瘤细胞逃避免疫系统的监视。
3. TIGIT的免疫抑制机制
3.1 ITIM和ITT样基序磷酸化
TIGIT与其配体结合后,可以通过其细胞内的ITIM和ITT样基序磷酸化产生的信号直接抑制NK细胞功能, ITIM被Src家族激酶磷酸化,磷酸化的ITIM负责招募和激活含有SH2结构域的酪氨酸磷酸酶(SHP)-1、SHP-2,这些酪氨酸磷酸酶能够通过去磷酸化作用抑制NK细胞激活受体产生的激活信号,最终引起NK细胞分泌细胞因子的减少[21]。此外, TIGIT与CD155的相互作用可以导致ITT样基序在Tyr225处磷酸化,并与胞质中的生长因子受体结合蛋白2结合,招募肌醇磷酸酶(SHIP-1)抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)信号通路[22], 阻断核因子-κB的活化,进而抑制NK细胞的颗粒极化和细胞毒性[23-25]。
3.2 直接作用于T细胞受体(TCR)
TIGIT可以通过直接作用于TCR来抑制T细胞的增殖和活化。一方面, TIGIT可以下调构成TCR复合物的分子,如TCRα链、CD3ε链; 另一方面,还可以下调T细胞活化过程中的信号转导分子,如磷脂酶C-γ链,从而减弱TCR的激活信号,抑制T细胞的增殖和活化[26]。
3.3 调节其他免疫细胞
TIGIT还可以通过诱导耐受性树突状细胞进而间接抑制T细胞, T细胞表面的TIGIT与DC表面的CD155结合,诱导CD155和Erk磷酸化,抑制促炎细胞因子白细胞介素(IL)-12的分泌并增加抗炎细胞因子IL-10的分泌,从而减弱DC介导的免疫反应。DC是主要的抗原呈递细胞,其活性减弱反过来又会损害T细胞增殖并抑制反应性T细胞产生干扰素(IFN)-γ[27]。记忆B细胞上表达的TIGIT也可以通过结合DC上表达的CD155有效抑制DC成熟,抑制IL-12和IL-6的分泌,从而抑制DC介导的促炎反应来控制T细胞免疫反应[28]。TIGIT还能通过增强和调节Treg细胞的免疫负调节作用来间接抑制免疫反应。TIGIT在Treg细胞上的表达可以诱导纤维蛋白原样蛋白2(Fgl2)的分泌增加,抑制效应T细胞的增殖,并抑制辅助T细胞(Th)1、Th17引导的促炎反应[29]。
3.4 破坏CD226的同源二聚化
TIGIT不仅可以通过与CD266竞争性结合CD155来发挥其免疫抑制作用,还可以通过破坏CD226的同源二聚化间接抑制T细胞功能。研究[30-31]发现,与程序性细胞死亡蛋白1(PD-1)不同,TIGIT并不是通过其细胞内结构域ITIM介导CD226去磷酸化从而抑制CD226的信号传导,而是通过细胞外结构域介导的CD226二聚化和突触定位损伤来抑制CD226的信号传导,从而影响CD226与CD155间的相互作用,间接抑制T细胞功能。JOHNSTON R J等[32]为了确定TIGIT损害CD226活性的分子机制,利用时间分辨荧光共振能量转移(TR-FRET)来定量生物分子之间的相互作用,发现TIGIT和CD226之间产生了显著FRET信号,且TIGIT的表达以剂量依赖性方式衰减CD226/CD226的FRET信号,说明TIGIT和CD226可以直接在细胞表面相互作用,并且这种相互作用损害了CD226的同源二聚化,间接抑制了T细胞功能。
3.5 其他机制
研究[33]发现,具核梭杆菌是一种与结直肠癌相关的厌氧菌,其Fap2蛋白可直接与TIGIT结合,从而抑制NK细胞和T细胞的活性。TIGTI的免疫学功能十分复杂,目前,仍需更多的基础研究来进一步阐明。
4. 小结与展望
综上所述,抑制性免疫检查点TIGIT可以通过多种作用机制抑制T细胞和NK细胞的功能,使免疫细胞耗竭并减少细胞因子的分泌,促进恶性肿瘤的免疫逃逸。在血液系统肿瘤和多种实体瘤的免疫微环境中发现, TIGIT及其配体的表达升高,阻断TIGIT可以获得一定抗肿瘤疗效,且针对多种免疫检查点的联合治疗比单一疗法更有效[34], TIGIT已经作为免疫治疗靶点进入临床试验,从而为抗PD-1耐药肿瘤患者的治疗提供了新的希望[35-36]。尽管目前没有相关的药物获批上市,但可以相信,国内外多家企业对该靶点的积极研发,对恶性肿瘤患者的治疗终将迎来新的曙光。
-
表 1 各组临床资料比较(x±s)
临床资料 NDR组(n=20) 早期DR组(n=20) 对照组(n=20) 年龄/岁 65.70±5.42 65.60±7.10 64.55±8.46 眼压/mmHg 15.25±2.34 16.12±2.03 15.32±1.97 肌酐/(μmol/L) 69.02±22.36 74.29±24.42 60.31±21.44 尿酸/(μmol/L) 384.25±122.14 397.07±83.61 364.22±65.13 表 2 各组SVC、DVC、CC血流密度、FAZ面积的Kruskal-Wallis检验结果
指标 组别 n 中位数 标准差 P Cohen′s f SVC血流密度 对照组 20 0.54 0.01 < 0.001 0.06 NDR组 20 0.52 0.09 早期DR组 20 0.45 0.09 DVC血流密度 对照组 20 0.57 0.01 < 0.001 0.07 NDR组 20 0.54 0.13 早期DR组 20 0.43 0.09 CC血流密度 对照组 20 0.52 0.02 0.012 0.04 NDR组 20 0.51 0.07 早期DR组 20 0.45 0.06 FAZ面积/mm2 对照组 20 0.29 0.01 < 0.001 0.13 NDR组 20 0.39 0.06 早期DR组 20 0.43 0.05 Cohen′s f值表示效应量的大小,其小、中、大区分临界点分别为0.10、0.25、0.40。 表 3 不同指标对早期DR诊断的多因素Logistic回归分析
指标 回归系数 标准误 Z Wald P OR 95%CI SVC血流密度 -4.65 2.56 -1.82 3.30 0.07 0.010 0.001~1.440 DVC血流密度 -9.05 3.29 -2.75 7.54 0.01 < 0.001 0.001~0.075 CC血流密度 1.49 4.30 0.35 0.12 0.723 4.47 0.001~2.057 FAZ面积 19.23 4.78 4.02 16.16 < 0.001 22.52 19.060~266.100 -
[1] MAO W, YIP C W, CHEN W. Complications of diabetes in China: health system and economic implications[J]. BMC Public Health, 2019, 19(1): 269. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6569-8
[2] SONG P, YU J, CHAN K Y, et al. Prevalence, risk factors and burden of diabetic retinopathy in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Glob Health, 2018, 8(1): 010803. doi: 10.7189/jogh.08.010803
[3] DENG Y X, YE W Q, SUN Y T, et al. A meta-analysis of prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in China[J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2020, 100(48): 3846-3852.
[4] KASHIM R M, NEWTON P, OJO O. Diabetic retinopathy screening: a systematic review on patients' non-attendance[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2018, 15(1): E157. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15010157
[5] CARNEVALI A, SACCONI R, CORBELLI E, et al. Optical coherence tomography angiography analysis of retinal vascular plexuses and choriocapillaris in patients with type 1 diabetes without diabetic retinopathy[J]. Acta Diabetol, 2017, 54(7): 695-702. doi: 10.1007/s00592-017-0996-8
[6] LUPIDI M, COSCAS G, COSCAS F, et al. Retinal microvasculature in nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: automated quantitative optical coherence tomography angiography assessment[J]. Ophthalmic Res, 2017, 58(3): 131-141. doi: 10.1159/000471885
[7] TSAI A S H, GAN A T L, TING D S W, et al. DIABETIC MACULAR ISCHEMIA: correlation of retinal vasculature changes by optical coherence tomography angiography and functional deficit[J]. Retina, 2020, 40(11): 2184-2190. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000002721
[8] LI L, ALMANSOOB S, ZHANG P, et al. Quantitative analysis of retinal and choroid capillary ischaemia using optical coherence tomography angiography in type 2 diabetes[J]. Acta Ophthalmol, 2019, 97(3): 240-246. doi: 10.1111/aos.14076
[9] 张占荣, 臧冬晓, 刘华, 等. 采用OCTA分析非增殖期糖尿病视网膜病变患者黄斑区血流密度[J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2020, 20(10): 1780-1785. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJYK202010029.htm [10] UM T, SEO E J, KIM Y J, et al. Optical coherence tomography angiography findings of type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic retinopathy, in comparison with type 2 patients[J]. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, 258(2): 281-288. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04517-6
[11] GUO Y, LIU S, XU H. Uric acid and diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10: 906760.





 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
