Optimization of suspension support structure of cardiac pump and analysis of anti-hemolysis function
-
摘要:目的
优化心脏泵的支承结构,以期增加悬浮力和减少溶血。
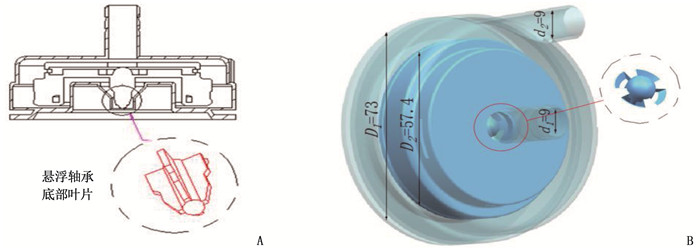
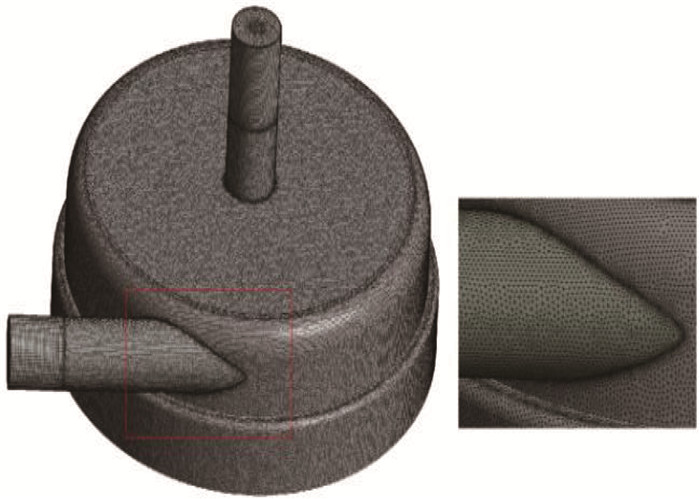
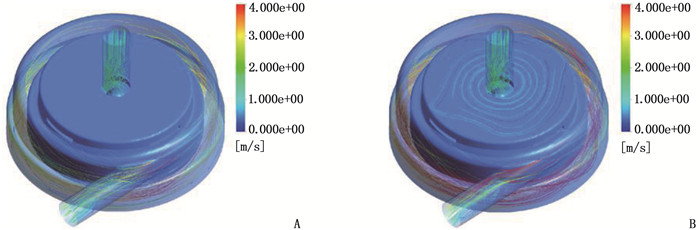
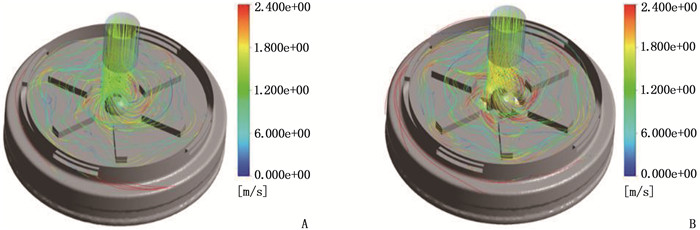
方法设计新型离心式心脏泵的悬浮支承结构,在导流锥附近设计扇形开孔,在悬浮轴承底部设计辅助叶片,并通过计算流体动力学方法比较改进结构前后心脏泵的悬浮力和抗溶血性能。
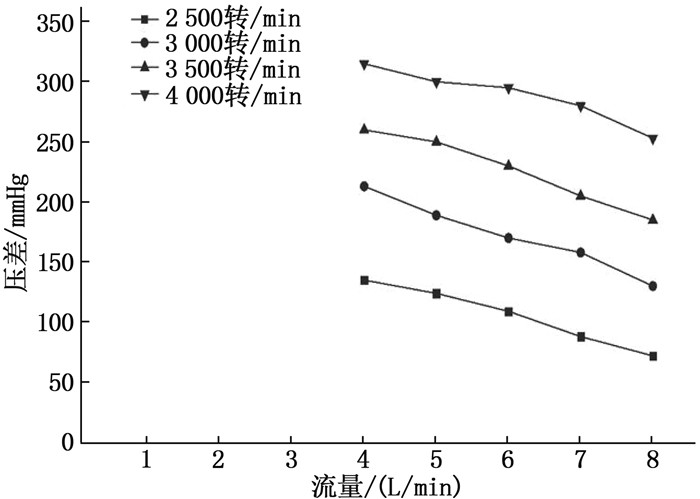
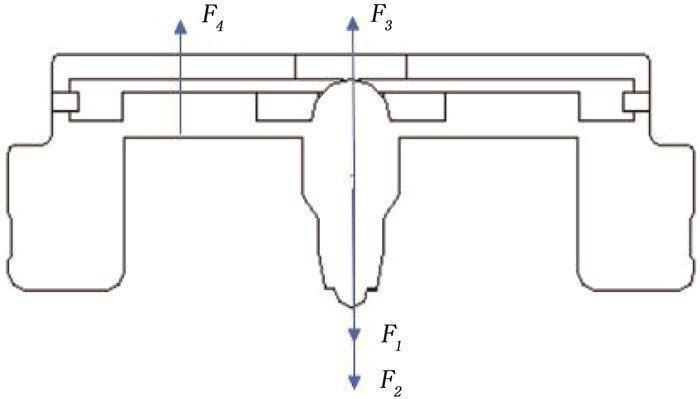
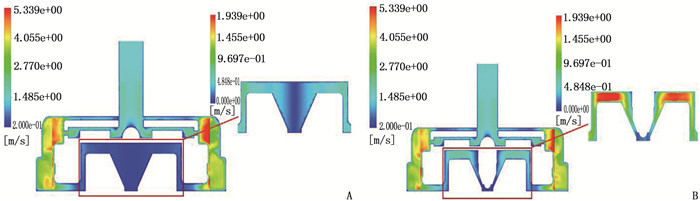
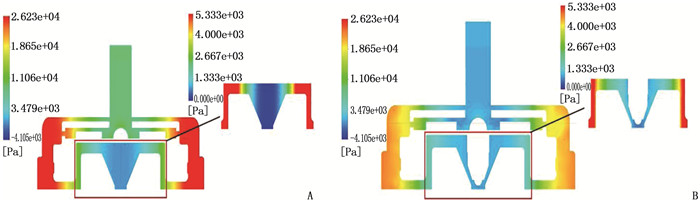
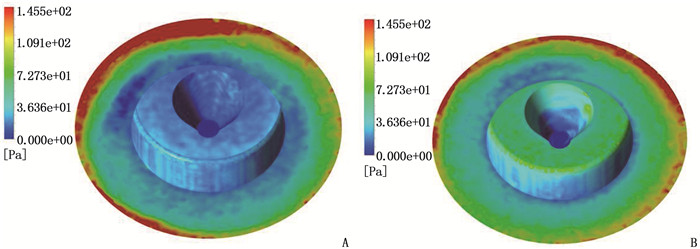
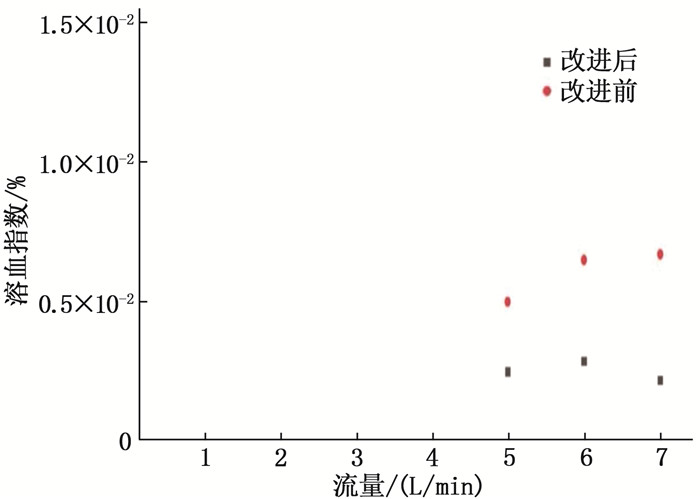
结果改进后心脏泵出入口压差值随流量增大而减小,且随叶轮转速提高而增大,与心脏泵在流体中流量压差情况相同,心脏泵的压差值在允许范围内。叶轮内血液最大速度低于溶血易发生速度(6 m/s),结构改进具有可行性。改进后,叶轮上下表面的压差随着流量的增大而减小,轴向方向向上的悬浮力增大,叶轮受到的悬浮力增加,悬浮性能得到改善;在液力轴承悬浮间隙处,流体平均流速提升,心脏泵底部区域的剪切应力最大值与高剪切应力区域占比均相对降低;液力轴承悬浮间隙处和底部区域溶血减少,改进结构后的心脏泵溶血指数相较于改进前降低了12%。
结论优化后的心脏泵悬浮性能得到改善,且溶血指数降低。改进的悬浮结构也可应用于其他离心式心脏泵,其在增加心脏泵悬浮力与减少悬浮轴承间隙处溶血方面具有实际价值。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo optimize the supporting structure of the heart to increase the suspension force and reduce hemolysis.
MethodsThe suspension support structure of a new centrifugal heart pump was designed, the fan-shaped opening was designed near the diversion cone and the auxiliary blade was designed at the bottom of the suspension bearing. The suspension force and hemolysis performance of the heartpump before and after optimization were compared by using the computational fluid dynamics method.
ResultsAfter improvement, the inlet and outlet pressure difference of the heart pump decreased with the increase of the flow rate, and increased with the increase of the impeller speed. It was the same as the flow pressure difference of the heart pump in the fluid, and the pressure difference of the heart pump was within the allowable range. The maximum blood velocity in the impeller was less than the rate of hemolysis (6 m/s). Structural improvement was feasible. The pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the impeller decreased with the increase of flow rate, and the axial upward suspension force increased, the suspension force of the impeller increased, and the suspension performance was improved. At the suspension gap of the hydraulic bearing, the average fluid velocity increased, the maximum shear stress and the proportion of high shear stress in the bottom region of the heart pump were relatively reduced, and the hemolysis indexes at the suspension gap and the bottom region of the hydraulic bearing was decreased, and the hemolysis indexes of the heart pump was reduced by 12% after the improved structure compared with that before the improvement.
ConclusionThe suspension performance of the optimized heart pump is improved and the hemolysis indexes are reduced. The improved suspension structure can also be applied to other centrifugal heart pumps, which has practical value in increasing the suspension force of the heart pump and reducing hemolysis in the suspension bearing clearance.
-
Keywords:
- centrifugal heart pump /
- suspension bearing /
- suspend gap /
- hemolysis indexes /
- suspension force
-
-
表 1 改进结构前后叶轮上下表面压差值
mmHg 时点 流量 5 L/min 6 L/min 7 L/min 改进结构前 8.3 5.5 3.5 改进结构后 21.2 18.5 16.3 -
[1] 叶桂萍. 整体护理干预对老年冠心病心脏介入治疗的影响[J]. 中国医药导报, 2008, 5(34): 145-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7210.2008.34.099 [2] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组, 胡盛寿. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2021, 36(6): 521-545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.06.001 [3] BENJAMIN E J, MUNTNER P, ALONSO A, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2019, 139(10): e56-e528.
[4] 刘英明, 杨晔. 慢性心力衰竭器械治疗进展[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2017, 33(10): 1018-1022. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1439.2017.10.024 [5] GIERSIEPEN M, WURZINGER L J, OPITZ R, et al. Estimation of shear stress-related blood damage in heart valve prostheses: in vitro comparison of 25 aortic valves[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 1990, 13(5): 300-306. doi: 10.1177/039139889001300507
[6] HEUSER G, OPITZ R. A Couette viscometer for short time shearing of blood[J]. Biorheology, 1980, 17(1/2): 17-24.
[7] SONG X, THROCKMORTON A L, WOOD H G, et al. Quantitative evaluation of blood damage in a centrifugal VAD by computational fluid dynamics[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2004, 126(3): 410-418. doi: 10.1115/1.1758259
[8] BLUDSZUWEIT C. Model for a general mechanical blood damage prediction[J]. Artif Organs, 1995, 19(7): 583-589. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.1995.tb02385.x
[9] BEHBAHANI M, BEHR M, HORMES M, et al. A review of computational fluid dynamics analysis of blood pumps[J]. Eur J Appl Math, 2009, 20: 363-397. doi: 10.1017/S0956792509007839
[10] KOSAKA R, YADA T, NISHIDA M, et al. Geometric optimization of a step bearing for a hydrodynamically levitated centrifugal blood pump for the reduction of hemolysis[J]. Artif Organs, 2013, 37(9): 778-785.
[11] WIEGMANN L, BOËS S, DE ZÉLICOURT D, et al. Blood pump design variations and their influence on hydraulic performance and indicators of hemocompatibility[J]. Ann Biomed Eng, 2018, 46(3): 417-428. doi: 10.1007/s10439-017-1951-0
[12] REZAIENIA M A, PAUL G, AVITAL E, et al. Computational parametric study of the axial and radial clearances in a centrifugal rotary blood pump[J]. Asaio J, 2018, 64(5): 643-650. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000000700
[13] GAWLIKOWSKI M, KURTYKA P, ZALEWSKI J, et al. Methodology for measuring the gap size using a fiber-optic displacement sensor exemplified by a centrifugal blood pump[J]. Photonics Letters of Poland, 2020, 12(2): 46-48. doi: 10.4302/plp.v12i2.1017
[14] 刘泽辉, 张松, 屈一飞. 基于计算流体动力学仿真的离心式人工心脏泵叶片参数优化[J]. 工具技术, 2021, 55(10): 51-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2021.10.010 [15] 王静月. 人工心脏磁液悬浮支承结构设计及性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2020. [16] 武悦, 朱良凡, 罗云. 计算流体力学方法分析一例喷射悬浮血泵的液力、悬浮及溶血特性[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(20): 52-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201820006.htm [17] FERZIGER J H. Computational methods for fluid dynamics[M]. Switzerland: Springer, 2020: 239-256.
[18] SONG G, CHUA L P, LIM T M. Numerical study of a bio-centrifugal blood pump with straight impeller blade profiles[J]. Artif Organs, 2010, 34(2): 98-104. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2009.00756.x
[19] 云忠, 谭建平. 基于血液撞击损伤机理的高速螺旋血泵仿真分析[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(1): 135-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD200801026.htm -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 马利,马政权,马晓瑞,周娜,马楼艳. 维生素D受体BsmI位点与老年原发性高血压的相关性研究. 心肺血管病杂志. 2024(09): 991-997 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱金玉,李燕,牛桂林. 南阳市儿童青少年血压升高现状及影响因素. 中国卫生工程学. 2021(02): 248-249+251 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号

