Value of two score systems for unplanned transfer of patients from emergency observation room to emergency room
-
摘要:目的
比较改良早期预警评分(MEWS)与国家早期预警评分(NEWS)对急诊观察室患者非计划性转抢救室的预测效果。
方法回顾性分析急诊观察室333例患者的临床资料,其中非计划性转抢救室患者47例。47例转抢救室患者中, 将37例NEWS≥3分患者设为NEWS异常组, 24例MEWS≥2分的患者设为MEWS异常组。记录患者一般资料、MEWS、NEWS以及转抢救室时重要器官恶化情况。留观72 h后,根据患者转归情况绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,比较2种评分对非计划转抢救室的预测价值,并进一步分析2种评分对重要器官恶化预测价值的差异。
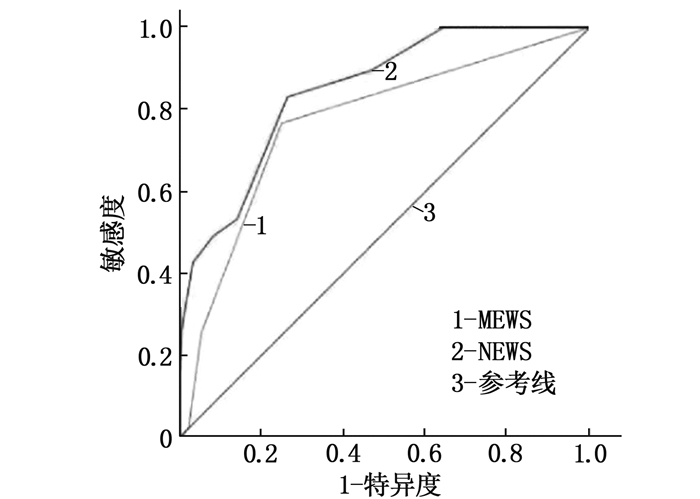
结果2组患者年龄、白蛋白水平、MEWS和NEWS比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。ROC曲线结果显示, NEWS的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.86, 最佳截断值为3分,敏感度为0.83, 特异度为0.77。MEWS的AUC为0.78, 最佳截断值为2分,敏感度为0.77, 特异度为0.75。2种评分预测患者非计划性转入抢救室的AUC比较,差异有统计学意义(Z=2.03, P=0.04)。2组呼吸衰竭患者占比比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论与MEWS相比, NEWS预测急诊观察室患者非计划性转抢救室具有较高的价值,优势可能来自对呼吸衰竭的预测。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo compare the predictive effect of the Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS) and the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) on the unplanned transfer of patients from emergency observation room to emergency room.
MethodsA retrospective analysis was performed for 333 patients in the emergency observation room, including 47 cases who were unplanned transferred to the emergency room. Among 47 patients transferred to the emergency room, 37 patients with NEWS≥3 were included in abnormal NEWS group, and 24 patients with MEWS≥2 were included in abnormal MEWS group. General data, MEWS, NEWS and deterioration condition of vital organs during transfer to the emergency room were recorded. After 72 h of observation, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was drawn according to the outcome of patients, and the predictive value of the two scoring systems for unplanned transfer from emergency observation room to emergency room was compared, and the difference of the predictive value of the two scoring systems for the deterioration of vital organs was further analyzed.
ResultsThere were statistically significant differences in age, albumin level, MEWS and NEWS between two groups (P < 0.05). ROC curve results showed that the area under the curve (AUC) of NEWS was 0.86, the optimum cut-off value scored 3, the sensitivity was 0.83, and the specificity was 0.77. AUC of MEWS was 0.78, the optimum cut-off value scored 2, the sensitivity was 0.77, and the specificity was 0.75. AUC of two scoring systems in predicting unplanned transfer to the emergency room was compared, and the difference was statistically significant (Z=2.03, P=0.04). There was statistical significance in the proportion of respiratory failure patients between the two groups (P < 0.05).
ConclusionCompared with MEWS, NEWS has a higher value in predicting unplanned transfer from emergency observation room to emergency room, and its advantage may be based on the prediction of respiratory failure.
-
急诊观察室患者周转快,病情不稳定,具有一定潜在风险,因此应早期识别患者病情危重信号[1]。如何快速且全面地识别患者病情,做出准确判断是临床面临的问题。目前,临床使用的能够对患者病情进行预警的评分有2001年英国SUBBE C P等[2]提出的改良早期预警评分(MEWS)和2012年英国皇家医学院推出的国家早期预警评分(NEWS)[3], 2种评分均能在一定程度上对患者病情进行预警。研究[4-8]指出, 2种评分可应用于急诊预检分诊、收治重症监护病房(ICU)、预测脓毒败血症患者死亡等,但未将其应用于预警病情相对稳定的患者再次转入抢救室的研究。本研究比较NEWS与MEWS评分对急诊观察室患者非计划性转抢救室的预测价值,并以相关结果为依据选择最佳风险预警评分以指导临床工作,确保医疗安全。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
采用病例对照方法选取2021年1—12月急诊观察室收治的333例患者为研究对象。纳入标准: ①年龄≥18岁者; ②转入急诊观察室时,患者生命体征基本平稳; ③给予Ⅰ级护理者。排除标准: ①资料不全者; ②病情变化时家属放弃转抢救室抢救者。非计划性转入抢救室患者指由抢救室转入观察室后72 h内再次转入抢救室者[9]。所有入组患者均严格执行转入抢救室的标准,病情危重需要进入抢救室救治患者的具体标准如下。①循环系统:收缩压≥180 mmHg或≤90 mmHg, 心率≥120次/min或≤60次/min; ②呼吸系统: 呼吸频率≥35次/min或≤12次/min, 脉氧≤90%; ③神经系统: 格拉斯昏迷评分(GCS)≤12分; ④肝、肾、凝血等器官或系统出现严重损伤或衰竭,并危及生命。最后,转抢救室患者47例,占比14.11%。将转抢救室患者纳入转抢救室组(n=47), 其余患者纳入未转抢救室组(n=286)。本研究已通过医院伦理委员会批准(2021-SR-389)。
1.2 方法
本研究为回顾性研究,收集患者一般资料,包括性别、年龄以及患者收治观察室2 h内呼吸、血压、脉搏、MEWS和NEWS等,查阅患者72 h后的转归情况以及非计划性转入抢救室的原因,包括神经系统、循环系统、呼吸系统或其他指标原因等。转入抢救室患者可能会出现1种或多种器官恶化,比较2种评分对转抢救室患者重要器官恶化的预测价值。
1.3 观察指标
研究工具中, MEWS包括呼吸频率、心率、收缩压、体温、意识状态5个参数,每项参数进行赋值,各项参数得分之和为MEWS分值,总分0~14分,分数越高表示患者病情越严重。NEWS包括7项参数,分别为呼吸频率、血氧饱和度、吸氧、心率、收缩压、体温、意识。计算方法与MEWS相同,为各参数得分之和,总分0~20分,分数越高表示患者病情越严重。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS 25.0统计学软件对数据进行分析,计量资料采用均数±标准差表示,行独立样本t检验,计数资料采用[n(%)]表示,行χ2检验,绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,比较曲线下面积(AUC), 并行Z检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组患者一般资料比较
2组患者年龄、白蛋白水平、MEWS和NEWS比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2组患者一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]一般资料 转抢救室(n=47) 未转抢救室(n=286) 性别 男 29(61.70) 167(58.39) 女 18(38.30) 119(41.61) 年龄/岁 67.51±17.56 61.18±17.59* 吸氧 是 17(36.17) 146(51.05) 否 30(63.83) 140(48.95) 监护 是 5(10.64) 12(4.20) 否 42(89.36) 274(95.80) 查尔森合并症指数 2.57±1.19 2.37±1.75 白细胞计数/(×109/L) 8.83±3.87 8.84±5.49 血红蛋白/(g/L) 115.32±34.91 122.32±27.31 白蛋白/(g/L) 32.50±5.62 35.51±5.60* MEWS/分 2.04±0.75 1.33±0.67* NEWS/分 4.68±2.51 1.63±1.67* MEWS: 改良早期预警评分; NEWS: 国家早期预警评分。
与转抢救室患者比较, *P < 0.05。2.2 2种评分对患者非计划性转抢救室的预测价值
ROC曲线结果显示, NEWS评分的AUC为0.86, 最佳截断值为3分,敏感度为0.83, 特异度为0.77。MEWS评分的AUC为0.78, 最佳截断值为2分,敏感度为0.77, 特异度为0.75。2种评分的AUC比较,差异有统计学意义(Z=2.03, P=0.04)。见表 2、图 1。
表 2 2种评分对急诊观察室患者非计划性转抢救室的预测价值评分 AUC 最佳截断值 约登指数 灵敏度 特异度 NEWS 0.86 3 0.57 0.83 0.74 MEWS 0.78 2 0.52 0.77 0.75 2.3 2种评分对重要器官系统发生恶化的预测价值
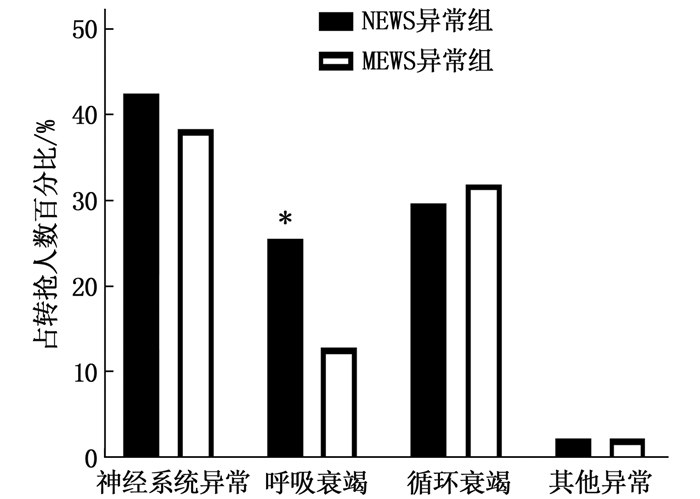
47例转抢救室患者中,将37例NEWS≥3分患者设为NEWS异常组,同时合并有神经系统异常、呼吸衰竭、循坏衰竭3项的患者2例,合并其中2项的患者31例,合并其中1项的患者3例,其他异常的患者1例。将24例MEWS≥2分的患者设为MEWS异常组,同时合并有神经系统异常、呼吸衰竭、循坏衰竭3项的患者2例,合并其中2项的患者18例,其中1项的患者3例,存在其他异常的患者1例。2组患者呼吸衰竭患者占比比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见图 2。
3. 讨论
本研究结果显示, 333例急诊观察室患者中发生非计划性转抢救室的患者47例,占14.11%。2组NEWS、MEWS、白蛋白水平比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), NEWS评分、MEWS是评估病情最直接和最方便的可测量化工具[10], 能在一定程度上反映病情严重程度,且NEWS优于MEWS, 在临床实际工作中可选择性使用。白蛋白可反映机体营养状况,与患者预后息息相关,是影响患者病情转归的重要因素。梁虹艺等[11-12]研究均表明,白蛋白对慢性失代偿性心力衰竭、术后感染率、患者转归以及住院费用等有重要影响。
本研究显示, NEWS、MEWS预测非计划性转抢救室的AUC分别是0.86和0.78, 差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 表明2种评分对急诊观察室患者非计划性转抢救室有中等预测价值,但NEWS对非计划性转抢救室的预测价值优于MEWS, 分析原因可能是NEWS在MEWS基础上融入了血氧饱和度和氧疗指标,提高了判断病情严重程度的敏感度,因此NEWS预测价值优于MEWS。王春源等[13-14]指出, NEWS对收治ICU或死亡患者有中等预测价值。SMITH G B等[15]对35 585例患者进行回顾性分析,结果显示, NEWS对患者心脏事件、收治ICU和死亡事件等都有重要预测价值,在一定程度上支持本研究结果。
本研究结果显示, NEWS的最佳截断值是3分,低于文献中的截断值(≥5分)[16], 分析原因可能为: ①患者的NEWS为转入急诊观察室2 h内的分值,患者生命体征尚处于平稳状态; ②转入急诊观察室的患者普遍存在高龄、低蛋白、查尔森合并症指数高的特点,容易发生病情变化。因此,需要关注NEWS≥3分患者的病情变化。另外,本研究结果显示, NEWS异常组和MEWS异常组患者呼吸衰竭患者占比比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。这可能是因为NEWS在MEWS基础上增加了血氧饱和度指标,收集患者呼吸衰竭体征更加全面,因此血氧饱和度结合预警评分能够更好地预测患者病情[17-18]。本研究进一步验证了NEWS较MEWS对预测急诊观察室患者非计划性转抢救室具有更高的价值。
综上所述, 2种预警评分均可预测急诊观察室患者非计划性转抢救室情况,但NEWS有利于急诊护理人员早期识别危重患者,及时给予相应护理措施。
-
表 1 2组患者一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
一般资料 转抢救室(n=47) 未转抢救室(n=286) 性别 男 29(61.70) 167(58.39) 女 18(38.30) 119(41.61) 年龄/岁 67.51±17.56 61.18±17.59* 吸氧 是 17(36.17) 146(51.05) 否 30(63.83) 140(48.95) 监护 是 5(10.64) 12(4.20) 否 42(89.36) 274(95.80) 查尔森合并症指数 2.57±1.19 2.37±1.75 白细胞计数/(×109/L) 8.83±3.87 8.84±5.49 血红蛋白/(g/L) 115.32±34.91 122.32±27.31 白蛋白/(g/L) 32.50±5.62 35.51±5.60* MEWS/分 2.04±0.75 1.33±0.67* NEWS/分 4.68±2.51 1.63±1.67* MEWS: 改良早期预警评分; NEWS: 国家早期预警评分。
与转抢救室患者比较, *P < 0.05。表 2 2种评分对急诊观察室患者非计划性转抢救室的预测价值
评分 AUC 最佳截断值 约登指数 灵敏度 特异度 NEWS 0.86 3 0.57 0.83 0.74 MEWS 0.78 2 0.52 0.77 0.75 -
[1] 朱莹, 蒋婕, 陶然君, 等. 急诊科患者滞留现象的研究及对策[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2013, 22(12): 1435-1438. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2013.12.034 [2] SUBBE C P, KRUGER M, RUTHERFORD P, et al. Validation of a modified Early Warning Score in medical admissions[J]. QJM, 2001, 94(10): 521-526. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/94.10.521
[3] MENON U, KALSI J, JACOBS I, et al. International Conference on Ovarian Cancer Screening[J]. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer, 2012, 22: S1. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0b013e3182557e41
[4] HWANG J I, CHIN H J. Relationships between the National Early Warning Score 2, clinical worry and patient outcome at discharge: retrospective observational study[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2020, 29(19/20): 3774-3789.
[5] GREEN M, LANDER H, SNYDER A, et al. Comparison of the Between the Flags calling criteria to the MEWS, NEWS and the electronic Cardiac Arrest Risk Triage (eCART) score for the identification of deteriorating ward patients[J]. Resuscitation, 2018, 123: 86-91. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2017.10.028
[6] GOULDEN R, HOYLE M C, MONIS J, et al. qSOFA, SIRS and NEWS for predicting inhospital mortality and ICU admission in emergency admissions treated as Sepsis[J]. Emerg Med J, 2018, 35(6): 345-349. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2017-207120
[7] BRINK A, ALSMA J, VERDONSCHOT R J C G, et al. Predicting mortality in patients with suspected Sepsis at the Emergency Department; A retrospective cohort study comparing qSOFA, SIRS and National Early Warning Score[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(1): e0211133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211133
[8] BRANGAN E, BANKS J, BRANT H, et al. Using the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) outside acute hospital settings: a qualitative study of staff experiences in the West of England[J]. BMJ Open, 2018, 8(10): e022528. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022528
[9] DEWAR Z E, KIRCHNER H L, RITTENBERGER J C. Risk factors for unplanned ICU admission after emergency department holding orders[J]. J Am Coll Emerg Physicians Open, 2020, 1(6): 1623-1629. doi: 10.1002/emp2.12203
[10] KUO S C H, KUO P J, CHEN Y C, et al. Comparison of the new Exponential Injury Severity Score with the Injury Severity Score and the New Injury Severity Score in trauma patients: a cross-sectional study[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(11): e0187871. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187871
[11] 梁虹艺, 黄雪峰, 莫泽珣, 等. 食管癌患者术后发生低蛋白血症的影响因素及其对临床结局的影响[J]. 广东药科大学学报, 2021, 37(3): 117-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDYX202103027.htm [12] 操斌全, 汪芸, 胡星星, 等. 静脉应用白蛋白对慢性失代偿性心力衰竭合并低蛋白血症患者再住院及预后的影响[J]. 中国实用医药, 2021, 16(18): 12-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSSA202118003.htm [13] 王春源, 曹涛, 勤俭, 等. 英国国家早期预警评分对急诊老年严重脓毒症及脓毒症休克患者预后的评估价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2017, 21(15): 1-4. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201715001 [14] 刘芳艳, 李春盛, 何庆, 等. 英国国家早期预警评分对我国急诊老年患者死亡预测的多中心研究[J]. 中国急救医学, 2015, 35(4): 313-316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2015.04.006 [15] SMITH G B, PRYTHERCH D R, MEREDITH P, et al. The ability of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) to discriminate patients at risk of early cardiac arrest, unanticipated intensive care unit admission, and death[J]. Resuscitation, 2013, 84(4): 465-470. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2012.12.016
[16] SMITH G B, REDFERN O C, PIMENTEL M A, et al. The national early warning score 2 (NEWS2)[J]. Clin Med: Lond, 2019, 19(3): 260. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.19-3-260
[17] 林玲, 顾秀萍. 儿童早期预警评分结合指脉氧评分在呼吸科病情评估中的应用[J]. 中国现代医药杂志, 2020, 22(10): 80-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9463.2020.10.025 [18] 张佳佳, 梁世景, 罗诗婷. ICU病人院内转运检查的风险与影响因素[J]. 护理研究, 2019, 33(24): 4343-4346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHZ201924036.htm




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
