Relationships of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 1 in serum and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 levels with in-stent restenosis
-
摘要:目的
探讨血清含凝血酶敏感素1型基序的解聚素样金属蛋白酶(ADAMTS-1)、组织金属蛋白酶抑制因子3(TIMP3)水平与冠心病患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)后支架内再狭窄(ISR)的关系。
方法选取455例行PCI的冠心病患者作为研究对象,根据随访1年后冠状动脉造影的影像学观察结果分为ISR组43例和非ISR组412例。采用Gensini评分及狭窄支数评价狭窄程度,采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测ADAMTS-1、TIMP3水平。采用Spearman相关分析法分析ADAMTS-1、TIMP3水平与造影后Gensini评分的相关性;采用Pearson相关系数法分析ADAMTS-1与TIMP3的相关性;采用Logistic回归分析法分析ISR发生的影响因素;采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评估ADAMTS-1、TIMP3对ISR发生的预测价值。
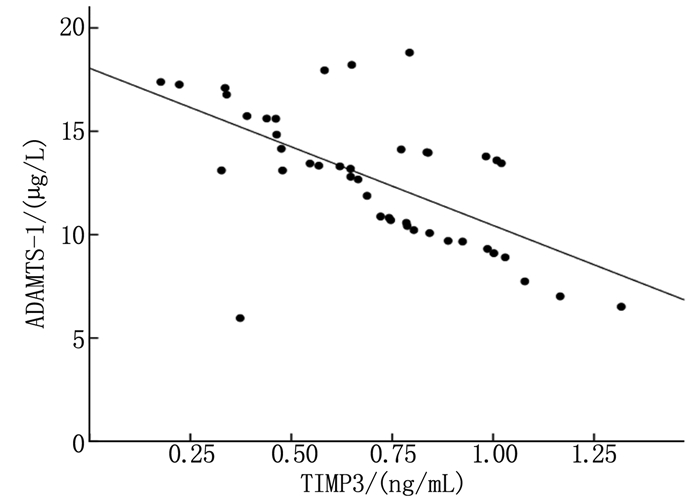
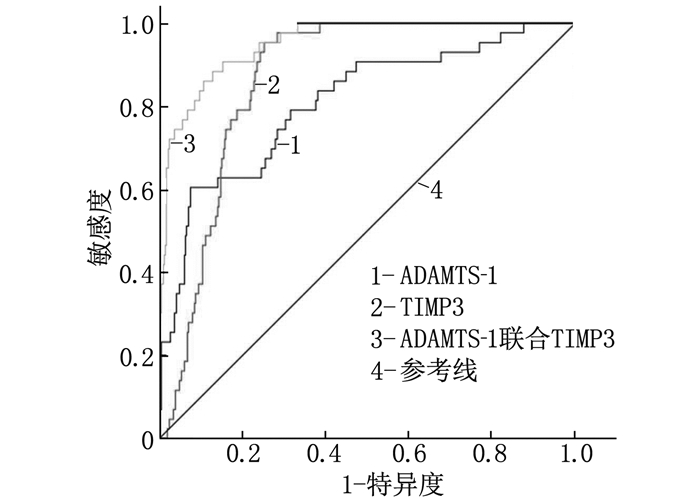
结果与非ISR组相比,ISR组患者总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、ADAMTS-1水平升高,TIMP3水平降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);ISR组血清ADAMTS-1水平与Gensini积分呈正相关(P < 0.05),TIMP3水平与Gensini积分呈负相关(P < 0.05);ISR组ADAMTS-1水平与TIMP3水平呈负相关(r=-0.616,P < 0.001);多因素Logistic回归分析发现,ADAMTS-1高水平、TIMP3低水平均为ISR发生的独立危险因素(P < 0.05);ROC曲线显示,ADAMTS-1与TIMP3联合预测ISR发生的曲线下面积显著大于两者单独预测(P < 0.05)。
结论ADAMTS-1和TIMP3水平与冠心病患者PCI后ISR的发生密切相关,两者是ISR发生的独立危险因素,对预测ISR发生具有重要价值。
-
关键词:
- 冠心病 /
- 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗 /
- 支架内再狭窄 /
- 组织金属蛋白酶抑制因子3 /
- 含凝血酶敏感素1型基序的解聚素样金属蛋白酶
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate relationships of the levels of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 1 (ADAMTS-1) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (TIMP3) in the serum with intrastent restenosis (ISR) in patients with coronary heart disease after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
MethodsA total of 455 patients with coronary heart disease who underwent PCI were selected as study objects, and were divided into ISR group (43 cases) and non-ISR group (412 cases) according to the imaging observation results of coronary angiography after one year of follow-up; Gensini score and the number of stenotic branches were used to evaluate the degree of stenosis; Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) method was used to detect the levels of ADAMTS-1 and TIMP3; Spearman's method was used to analyze the correlations of ADAMTS-1 and TIMP3 levels with Gensini score after angiography; Pearson correlation coefficient method was used to analyze the correlation between ADAMTS-1 and TIMP3; Logistic regression was used to analyze the influencing factors of the occurrence of ISR; receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the predictive value of ADAMTS-1 and TIMP3 for occurrence of ISR.
ResultsCompared with the non-ISR group, the levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and ADAMTS-1 levels in the ISR group were significantly increased, while the level of TIMP3 was significantly decreased (P < 0.05); in the ISR group, the level of serum ADAMTS-1 was significantly positively correlated with Gensini score (P < 0.05); the level of TIMP3 was significantly negatively correlated with Gensini score (P < 0.05); the level of ADAMTS-1 was significantly negatively correlated with the level of TIMP3 in the ISR group(r=-0.616, P < 0.001); multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that high level of ADAMTS-1 and low level of TIMP3 were independent risk factors for ISR (P < 0.05); compared with the single prediction of ADAMTS-1 or TIMP3, the area under the ROC curve of the combined prediction of ADAMTS-1 and TIMP3 for ISR was significantly increased (P < 0.05).
ConclusionThe levels of ADAMTS-1 and TIMP3 are closely related to the occurrence of ISR in patients with coronary heart disease after PCI. They are independent risk factors for the occurrence of ISR and have important value for predicting the occurrence of ISR.
-
-
表 1 2组患者临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
临床资料 分类 非ISR组(n=412) ISR组(n=43) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 57.34±7.68 56.92±8.36 0.338 0.735 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 22.90±2.40 23.28±2.71 0.976 0.330 性别 男 201(48.79) 20(46.51) 0.015 0.902 女 211(51.21) 23(53.49) TC/(mmol/L) 3.69±0.76 4.97±0.88 10.347 < 0.001 TG/(mmol/L) 1.57±0.49 2.13±0.74 6.742 < 0.001 HDL-C/(mmol/L) 1.04±0.45 0.94±0.29 1.426 0.155 LDL-C/(mmol/L) 2.01±0.49 2.84±0.31 10.876 < 0.001 狭窄数目 单支 116(28.16) 12(27.91) 0.050 0.975 双支 185(44.90) 20(46.51) 3支及以上 111(26.94) 11(25.58) 狭窄部位 左前降支 60(14.56) 5(11.63) 0.619 0.892 左回旋支 105(25.49) 13(30.23) 右冠状动脉 162(39.32) 16(37.21) 右主干 85(20.63) 9(20.93) 吸烟 有 230(55.83) 21(48.84) 0.769 0.381 无 182(44.17) 22(51.16) 糖尿病 有 45(10.92) 5(11.63) 0.013 0.908 无 367(89.08) 38(88.37) 高血压病 有 150(36.41) 14(32.56) 0.250 0.617 无 262(63.59) 29(67.44) TC: 总胆固醇; TG: 甘油三酯; HDL-C: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇。 表 2 2组患者PCI后血清ADAMTS-1、TIMP3水平比较(x±s)
组别 n ADAMTS-1/(μg/L) TIMP3/(ng/mL) 非ISR组 412 9.01±2.68 1.51±0.68 ISR组 43 12.84±3.90 0.75±0.30 t — 8.488 7.250 P — < 0.001 < 0.001 ADAMTS-1: 含凝血酶敏感素1型基序的解聚素样
金属蛋白酶; TIMP3: 组织金属蛋白酶抑制因子3。表 3 PCI后发生ISR影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析
因素 wald χ2 β SE OR 95%CI P ADAMTS-1 6.774 0.351 0.135 1.421 1.091~1.851 0.009 TIMP3 7.960 0.403 0.143 1.497 1.131~1.981 0.004 -
[1] 刘韦华, 马敏涛. 超声斑点追踪技术评价冠心病患者经皮冠状动脉介入术后左室的收缩功能[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(5): 87-90, 95. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20200907 [2] 梁婧, 何学玲, 唐倩, 等. 红细胞分布宽度与经皮冠状动脉介入术后支架内再狭窄及预后的关系[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(21): 63-66, 73. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20213620 [3] SANTAMARIA S, DE GROOT R. ADAMTS proteases in cardiovascular physiology and disease[J]. Open Biol, 2020, 10(12): 200333. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200333
[4] 郭晓亮, 袁宇, 段长恩. ADAMTs-1、CF6、CARP在冠心病合并慢性心力衰竭中的意义[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2021, 27(4): 329-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYK202104003.htm [5] FAN D, KASSIRI Z. Biology of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3(TIMP3), and its therapeutic implications in cardiovascular pathology[J]. Front Physiol, 2020, 11: 661. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00661
[6] 陈旭杰, 罗明. 慢性心力衰竭患者血清miR-21、TIMP3表达及其与心肌重构和心功能的相关性[J]. 交通医学, 2020, 34(3): 230-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTYX202003004.htm [7] SAGGESE T, THAMBYAH A, WADE K, et al. Differential response of bovine mature nucleus pulposus and notochordal cells to hydrostatic pressure and glucose restriction[J]. Cartilage, 2020, 11(2): 221-233. doi: 10.1177/1947603518775795
[8] 刘镇, 雷荣. PCI治疗后β2微球蛋白变化与冠心病患者支架内再狭窄的关系[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2019, 27(11): 985-989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3949.2019.11.012 [9] 葛均波, 徐永健. 内科学[M]. 8版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013: 103-110. [10] CHENG G, CHANG F J, WANG Y, et al. Factors influencing stent restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with coronary heart disease: a clinical trial based on 1-year follow-up[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 240-247. doi: 10.12659/MSM.908692
[11] 杜丹, 董利平. 急性冠状动脉综合征患者经皮冠状动脉介入术后血清microRNA-224水平变化及与支架内再狭窄的关系[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2021, 29(4): 317-321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KDYZ202104009.htm [12] 杨悦, 宋昱, 贾克刚. 心脏瓣膜疾病手术前后血流动力学异常与vWF和ADAMTS13的关系[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2021, 27(6): 569-573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYK202106005.htm [13] 田晋帆, 宋现涛, 贺毅, 等. 血清补体C1q与经皮冠状动脉药物洗脱支架植入后支架内再狭窄相关性分析[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2021, 13(2): 162-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZXX202102009.htm [14] HE M W, PANG J L, SUN H Y, et al. Overexpression of TIMP3 inhibits discogenic pain by suppressing angiogenesis and the expression of substance P in nucleus pulposus[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 21(3): 1163-1171.
[15] ZENG W, LIU Y, LI W T, et al. CircFNDC3B sequestrates miR-937-5p to derepress TIMP3 and inhibit colorectal cancer progression[J]. Mol Oncol, 2020, 14(11): 2960-2984.
[16] 甄宇治, 宋适恒, 邢军. 芪苈强心胶囊联合托伐普坦片对冠心病慢性心力衰竭MMPs/TIMPs调节作用的研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2021, 39(9): 165-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS202109041.htm [17] KREBBER M M, VAN DIJK C G M, VERNOOIJ R W M, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in extracellular matrix remodeling during left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(18): 6742.
[18] 刘永辉, 孟嘉天, 孟自力, 等. 心室减负荷对缺血性心力衰竭MMPs/TIMPs的影响[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2021, 50(12): 131-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYZ202112029.htm [19] VOJTUSEK I K, LAGANOVIC M, BUREK KAMENARIC M, et al. First characterization of ADAMTS-4 in kidney tissue and plasma of patients with chronic kidney disease-A potential novel diagnostic indicator[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2022, 12(3): 648.
-
期刊类型引用(21)
1. 田丰,安丽,谷芬,刘丽文,陈曦. 超声新参数预测骨科住院患者下肢深静脉血栓. 中国医学影像学杂志. 2025(01): 85-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴路凤,张文静,王艳英. 彩色多普勒超声对下肢深静脉瓣膜功能不全与深静脉血栓形成的诊断价值. 影像研究与医学应用. 2024(04): 151-153 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郑兆霞,田丰,宋爱华. 围手术期应用彩色多普勒超声血流动力学监测对髋关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓的预防效果研究. 中国医师进修杂志. 2024(04): 342-346 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 江瑞平,王霞. 彩色多普勒超声诊断下肢深静脉血栓形成的临床价值分析. 影像研究与医学应用. 2024(07): 98-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王蕾,路鑫铭. 超声血流参数、D-二聚体手术前后变化及复合模型在创伤骨折患者下肢DVT预警中的应用价值. 临床误诊误治. 2024(05): 55-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 郭荣,余墨声,赵月强,朱占永,罗莎,谭植襄,陶瑞,王芳. 齐踝及齐膝弹力裤对大腿吸脂病人深静脉血栓预防效果的对比研究. 临床外科杂志. 2024(05): 541-544 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 雷秀平. 血小板参数、凝血指标预测下肢创伤性骨折术后深静脉血栓形成的临床价值. 河南外科学杂志. 2024(04): 142-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王祝青,马娟娟,郑斌. 下肢骨折术后D-D及凝血四项指标预测并发深静脉血栓风险的价值. 贵州医药. 2024(08): 1296-1297 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 江萍,连育才. 彩色多普勒超声联合D-二聚体水平检测在骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓中的诊断价值分析. 现代诊断与治疗. 2024(08): 1204-1206 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 高文汇,张玮玮,王妮荣,张佳齐,戴靖华,李欣微,卫建峰,余淑珍. 术前血管超声参数预测妇科恶性肿瘤患者术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的价值. 中华麻醉学杂志. 2024(08): 937-940 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 齐明基. 超声弹性成像评分联合杨氏模量平均值对下肢深静脉血栓形成分期的评估价值研究. 现代诊断与治疗. 2024(09): 1361-1363 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 李姗姗. 彩色多普勒超声联合血浆D-二聚体对下肢静脉血栓的诊断价值. 实用医学影像杂志. 2024(04): 265-268 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 梁艳兰,庄淑婉,覃素英. 下肢静脉彩色多普勒超声联合D–二聚体对妇科术后下肢DVT的诊断价值. 深圳中西医结合杂志. 2024(15): 70-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 钱奎,马红英,郑志友. 超声弹性成像联合二维超声诊断下肢深静脉血栓的价值分析. 中国现代医学杂志. 2024(23): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 江文杰,段俊林,卢景宜,万志东. 骨折患者凝血功能的变化分析. 智慧健康. 2024(30): 41-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 刘伟. 系统溶栓与综合介入治疗中老年急性混合型下肢深静脉血栓的效果观察. 中国现代药物应用. 2023(10): 24-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 吕长伟,刘萍. 彩色多普勒超声用于下肢深静脉血栓形成诊断中的价值. 中国社区医师. 2023(19): 87-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 张源,吴丹,王丹. 下肢深静脉血栓应用彩色多普勒超声的诊断效能分析. 世界复合医学. 2023(06): 127-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 刘敏. 彩色多普勒超声在骨折术后患者下肢深静脉血栓形成中的诊断价值及相关参数分析. 影像研究与医学应用. 2023(14): 24-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 胡志江,孙琦,仲慧丹. 彩色多普勒超声诊断下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓的价值. 中国实用医刊. 2023(17): 83-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 李悦. 彩色多普勒超声诊断下肢静脉血栓的价值分析. 影像研究与医学应用. 2023(22): 173-175 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
