Effect of hyperdynamic left ventricular ejection fraction on prognosis of early septic shock patients
-
摘要:目的
探讨高动力左室射血分数(HDLVEF)对早期感染性休克患者预后的影响。
方法选取苏北人民医院收治的96例感染性休克患者为研究对象。根据28 d内是否发生死亡将患者分为死亡组(n=40)和生存组(n=56)。采用独立样本t检验或卡方检验分析2组各项临床资料是否存在差异。采用二元Logistic回归模型评估感染性休克患者发生死亡的影响因素。采用Pearson和Spearman相关性分析探讨HDLVEF与急性生理学和慢性健康状况评价Ⅱ(APACHE Ⅱ)评分、序贯器官衰竭估计(SOFA)评分的相关性。釆用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价各指标对感染性休克患者发生死亡的预测价值。采用Kaplan-Meier曲线对感染性休克患者进行预后生存分析。
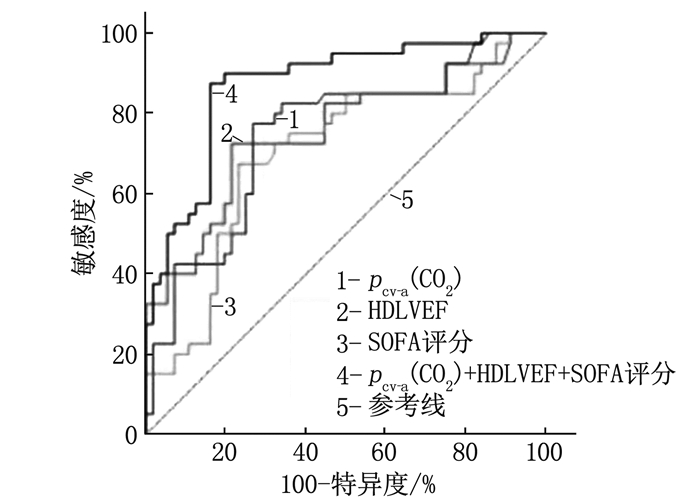
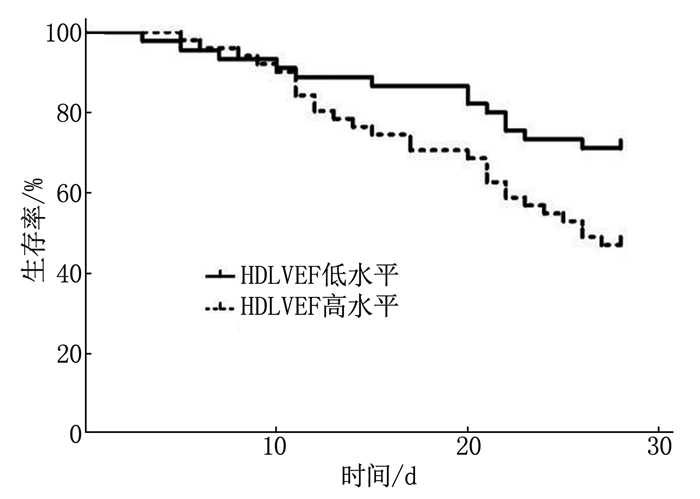
结果死亡组患者中心静脉动脉二氧化碳分压差[pcv-a(CO2)]、APACHE Ⅱ评分、SOFA评分及HDLVEF高于存活组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。二元Logistic回归分析显示,HDLVEF、pcv-a(CO2)和SOFA评分是感染性休克患者发生死亡的影响因素(P < 0.05)。Pearson及Spearman相关性分析显示,HDLVEF与SOFA评分、APACHE Ⅱ评分均呈正相关(P < 0.01)。ROC曲线显示,HDLVEF预测的曲线下面积(AUC)高于pcv-a(CO2)、SOFA评分。HDLVEF、SOFA评分联合pcv-a(CO2)诊断的AUC高于单一指标[HDLVEF、SOFA评分或pcv-a(CO2)],且敏感度和特异度分别为87.50%和83.93%。Kaplan-Meier曲线显示,HDLVEF高水平感染性休克患者的28 d生存率低于HDLVEF低水平患者(P < 0.05)。
结论HDLVEF水平是影响感染性休克患者发生死亡的重要因素,且其水平能够侧面反映患者病情,预测患者死亡情况,有望成为有效的临床指标。
-
关键词:
- 感染性休克 /
- 高动力左室射血分数 /
- 动脉血二氧化碳分压差 /
- 序贯器官衰竭估计评分 /
- 相关性 /
- 预后
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of hyperdynamic left ventricular ejection fraction (HDLVEF) on prognosis of patients with early septic shock.
MethodsA total of 96 patients with septic shock admitted to Northern Jiangsu People's Hospital were selected as study objects. Patients were divided into death group (n=40) and survival group (n=56) according to whether patients died within 28 days or not. Independent sample t test or Chi-square test were used to analyze whether there were significant differences in clinical data between the two groups. Influencing factors for occurrence of death in patients with septic shock were assessed by binary Logistic regression model. The correlations of HDLVEF with acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ (APACHE Ⅱ) and sequential organ failure estimation (SOFA) score were evaluated by Pearson and Spearman correlation analysis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the predictive value of indicators for death in patients with septic shock. Kaplan-Meier curve was used to analyze the prognostic survival of patients with septic shock.
ResultsThe differential pressure of central venous arterial carbon dioxide[pcv-a(CO2)], APACHE Ⅱ score, SOFA score and HDLVEF in the death group were higher than those in the survival group (P < 0.05). Binary Logistic regression analysis showed that HDLVEF, pcv-a(CO2) and SOFA score were infuencing factors for death in septic shock patients (P < 0.05). Pearson and Spearman correlation analysis showed that HDLVEF was positively correlated with SOFA score and APACHE Ⅱ score (P < 0.05). ROC curve showed that the area under the curve (AUC) of HDLVEF was higher than that of pcv-a(CO2) or SOFA. AUC of HDLVEF combined with SOFA score and pcv-a(CO2) was significantly higher than those of single index[HDLVEF, SOFA score or pcv-a(CO2)], and the sensitivity and specificity were 87.50% and 83.93%, respectively. Kaplan-Meier curve showed that the 28-day survival rate in patients with septic shock was lower in high HDLVEF level patients than those with low HDLVEF level(P < 0.05).
ConclusionThe level of HDLVEF is an important factor affecting the death of patients with septic shock, and it can reflect the patient's condition and predict the death of patients, which is expected to become an effective clinical indicator.
-
老年人群吞咽障碍由机体老化或疾病引发, 是一种以吞咽结构和功能改变为特征的疾病。研究[1]显示约2/3的住院老年患者合并吞咽障碍,严重影响生活质量。衰弱是指机体功能减退,在受到外界一系列刺激后发生的综合征,可出现并发症或不良事件等。老年患者生理储备能力下降,加之抗应激能力减弱[2], 一旦吞咽功能受损,其衰弱的发生率也会随之增高[3-4]。衰弱受多种因素影响,需同时采取多项措施以达到较好的干预效果[5]。集束化护理是将循证护理与临床实践相结合,针对某种护理问题提出联合干预方案[6-7]。本研究探讨接受集束化护理的老年吞咽障碍患者衰弱状态的改善情况,现报告如下。
老年人群吞咽障碍由机体老化或疾病引发, 是一种以吞咽结构和功能改变为特征的疾病。研究[1]显示约2/3的住院老年患者合并吞咽障碍,严重影响生活质量。衰弱是指机体功能减退,在受到外界一系列刺激后发生的综合征,可出现并发症或不良事件等。老年患者生理储备能力下降,加之抗应激能力减弱[2], 一旦吞咽功能受损,其衰弱的发生率也会随之增高[3-4]。衰弱受多种因素影响,需同时采取多项措施以达到较好的干预效果[5]。集束化护理是将循证护理与临床实践相结合,针对某种护理问题提出联合干预方案[6-7]。本研究探讨接受集束化护理的老年吞咽障碍患者衰弱状态的改善情况,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2022年8月—2023年12月本院老年医学科收治的105例洼田饮水试验(WST)≥3级、Fried衰弱表型量表(FP)评分≥33分的老年患者为研究对象,将其随机分为研究组55例和对照组50例。研究组接受集束化护理,对照组接受常规护理干预。纳入标准: ①年龄≥60岁者; ②需留置管路者[6]。排除标准: ①预期生存期 < 3个月者; ②合并严重器质性疾病者; ③严重精神疾病者。脱落标准: ①病情发生严重变化者; ②自行退出者。本研究经医院伦理委员会审查通过(审批号2019-P2-221-01)。本研究根据计算公式确定样本量,根据文献[8]得出每组样本量为45例,考虑失访率,最终纳入的样本量为105例。根据随机数字表法将患者分为研究组(55例)和对照组(50例)。患者均自愿参与本研究,且签署知情同意书。
1.1 一般资料
选取2022年8月—2023年12月本院老年医学科收治的105例洼田饮水试验(WST)≥3级、Fried衰弱表型量表(FP)评分≥33分的老年患者为研究对象,将其随机分为研究组55例和对照组50例。研究组接受集束化护理,对照组接受常规护理干预。纳入标准: ①年龄≥60岁者; ②需留置管路者[6]。排除标准: ①预期生存期 < 3个月者; ②合并严重器质性疾病者; ③严重精神疾病者。脱落标准: ①病情发生严重变化者; ②自行退出者。本研究经医院伦理委员会审查通过(审批号2019-P2-221-01)。本研究根据计算公式确定样本量,根据文献[8]得出每组样本量为45例,考虑失访率,最终纳入的样本量为105例。根据随机数字表法将患者分为研究组(55例)和对照组(50例)。患者均自愿参与本研究,且签署知情同意书。
1.2 方法
对照组接受常规护理,除药物治疗外,提供营养支持,尤其注意口腔以及心理护理,并给予患者管饲相关护理以及健康宣教。研究组在常规护理基础上接受集束化护理。①成立多学科小组,并统一对研究小组成员进行评估、干预及资料收集方面的培训; ②入院24 h内由多学科团队为老年患者完成综合评估,包括吞咽功能和衰弱评估[9]。根据《中国吞咽障碍康复管理指南(2023版)》对吞咽障碍进行评估,根据自身情况制订治疗方案,并选择相应的管饲方式[10]。③根据《中国成人患者肠外肠内营养临床应用指南(2023版)》推荐的方案,为患者选择营养制剂种类、肠内营养介入时机及肠内营养护理措施等早期肠内营养方案[11]。④根据《老年人吞咽障碍5Ws和1H管理的最佳实践建议》(2022年)相关内容[12],针对合并衰弱的吞咽障碍患者,制订一线、二线、三线康复模式及医疗机构至居家的连续治疗方案。住院期间,患者在治疗师指导下进行吞咽功能锻炼,康复护士协助进行呼吸功能训练和肢体康复训练[10]。患者出院时,康复护士为其制订居家康复计划,并提供出院服务,定期进行随访。⑤通过健康宣教提升患者对疾病的认识及治疗依从性,并根据患者情况,通过阅读、玩游戏、做手工等方式提高自我效能和改善认知功能。⑥本研究采用叙事护理作为心理护理框架,将家属纳入团队,参与决策的制订与实施,以增强社会支持度[13]。
1.2 方法
对照组接受常规护理,除药物治疗外,提供营养支持,尤其注意口腔以及心理护理,并给予患者管饲相关护理以及健康宣教。研究组在常规护理基础上接受集束化护理。①成立多学科小组,并统一对研究小组成员进行评估、干预及资料收集方面的培训; ②入院24 h内由多学科团队为老年患者完成综合评估,包括吞咽功能和衰弱评估[9]。根据《中国吞咽障碍康复管理指南(2023版)》对吞咽障碍进行评估,根据自身情况制订治疗方案,并选择相应的管饲方式[10]。③根据《中国成人患者肠外肠内营养临床应用指南(2023版)》推荐的方案,为患者选择营养制剂种类、肠内营养介入时机及肠内营养护理措施等早期肠内营养方案[11]。④根据《老年人吞咽障碍5Ws和1H管理的最佳实践建议》(2022年)相关内容[12],针对合并衰弱的吞咽障碍患者,制订一线、二线、三线康复模式及医疗机构至居家的连续治疗方案。住院期间,患者在治疗师指导下进行吞咽功能锻炼,康复护士协助进行呼吸功能训练和肢体康复训练[10]。患者出院时,康复护士为其制订居家康复计划,并提供出院服务,定期进行随访。⑤通过健康宣教提升患者对疾病的认识及治疗依从性,并根据患者情况,通过阅读、玩游戏、做手工等方式提高自我效能和改善认知功能。⑥本研究采用叙事护理作为心理护理框架,将家属纳入团队,参与决策的制订与实施,以增强社会支持度[13]。
1.3 观察指标
1.3 观察指标
1.3.1 衰弱状况评价
FP是由美国学者Fried等[12]提出,主要从生理层面评估衰弱状态,对老年患者结局有一定预测作用。量表包含5项: ①不明原因的体质量下降; ②步速减慢; ③握力下降; ④活动量下降; ⑤自诉疲乏。评价方法: 量表项目中选择“是”计1分,“否”计0分[13]。0分为无衰弱, 1~2分为衰弱前期, 3~5分即可诊断为衰弱[14]。
1.3.1 衰弱状况评价
FP是由美国学者Fried等[12]提出,主要从生理层面评估衰弱状态,对老年患者结局有一定预测作用。量表包含5项: ①不明原因的体质量下降; ②步速减慢; ③握力下降; ④活动量下降; ⑤自诉疲乏。评价方法: 量表项目中选择“是”计1分,“否”计0分[13]。0分为无衰弱, 1~2分为衰弱前期, 3~5分即可诊断为衰弱[14]。
1.3.2 吞咽功能情况
采用WST对吞咽功能进行评价。该试验是由日本康复医生洼田俊夫提出的一种评定吞咽障碍的经典方法,在临床上应用广泛。具体方法: 患者保持端坐位,饮用30 mL温水,观察患者吞咽所需时间及是否出现呛咳情况。评价方法: 5 s内一次性完成吞咽,无呛咳、无停顿为1级; 一次性完成吞咽,但超过5 s, 或分2次吞咽,但无呛咳、无停顿为2级; 能1次吞咽,但有呛咳为3级; 分2次及以上完成吞咽,且有呛咳为4级; 不能全部吞咽,有呛咳为5级[15]。
1.3.2 吞咽功能情况
采用WST对吞咽功能进行评价。该试验是由日本康复医生洼田俊夫提出的一种评定吞咽障碍的经典方法,在临床上应用广泛。具体方法: 患者保持端坐位,饮用30 mL温水,观察患者吞咽所需时间及是否出现呛咳情况。评价方法: 5 s内一次性完成吞咽,无呛咳、无停顿为1级; 一次性完成吞咽,但超过5 s, 或分2次吞咽,但无呛咳、无停顿为2级; 能1次吞咽,但有呛咳为3级; 分2次及以上完成吞咽,且有呛咳为4级; 不能全部吞咽,有呛咳为5级[15]。
1.3.3 生活质量
采用吞咽障碍特异性生活质量量表(SWAL-QOL)评估患者生活质量。该量表是评估吞咽障碍患者生活质量的工具[16], 具有良好的信效度。该量表共44个条目, 1分代表“非常符合”或“总是”, 5分代表“非常不符合”或“从不”,评分越高表明生活质量越高[17]。比较干预1个月后2组衰弱状况、吞咽障碍和生活质量状况。
1.3.3 生活质量
采用吞咽障碍特异性生活质量量表(SWAL-QOL)评估患者生活质量。该量表是评估吞咽障碍患者生活质量的工具[16], 具有良好的信效度。该量表共44个条目, 1分代表“非常符合”或“总是”, 5分代表“非常不符合”或“从不”,评分越高表明生活质量越高[17]。比较干预1个月后2组衰弱状况、吞咽障碍和生活质量状况。
1.4 统计学分析
采用Excel表格与SPSS 24.0软件对数据进行录入与分析。计量资料采用(x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验; 计数资料采用[n(%)]表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,组内比较采用秩检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
1.4 统计学分析
采用Excel表格与SPSS 24.0软件对数据进行录入与分析。计量资料采用(x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验; 计数资料采用[n(%)]表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,组内比较采用秩检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
105例患者中,因病情变化,对照组脱落2例,研究组脱落3例,最终研究组52例,对照组48例。2组一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2组一般临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]一般资料 分类 对照组(n=48) 研究组(n=52) 年龄/岁 68.38±6.29 66.71±6.01 性别 男 26(54.17) 29(55.77) 女 22(45.83) 23(44.23) 文化程度 小学及以下 14(29.17) 18(34.62) 中学及专科 24(50.00) 27(51.92) 本科及以上 10(20.83) 7(13.46) 婚姻状况 未婚 1(2.08) 2(3.85) 已婚 44(91.67) 45(86.54) 丧偶 3(6.25) 5(9.61) WST分级 3级 20(41.67) 24(46.15) 4级 18(37.50) 16(30.77) 5级 10(20.83) 12(23.08) WST: 洼田饮水试验。 2.1 一般资料
105例患者中,因病情变化,对照组脱落2例,研究组脱落3例,最终研究组52例,对照组48例。2组一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2组一般临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]一般资料 分类 对照组(n=48) 研究组(n=52) 年龄/岁 68.38±6.29 66.71±6.01 性别 男 26(54.17) 29(55.77) 女 22(45.83) 23(44.23) 文化程度 小学及以下 14(29.17) 18(34.62) 中学及专科 24(50.00) 27(51.92) 本科及以上 10(20.83) 7(13.46) 婚姻状况 未婚 1(2.08) 2(3.85) 已婚 44(91.67) 45(86.54) 丧偶 3(6.25) 5(9.61) WST分级 3级 20(41.67) 24(46.15) 4级 18(37.50) 16(30.77) 5级 10(20.83) 12(23.08) WST: 洼田饮水试验。 2.2 2组吞咽功能比较
干预前, 2组WST不同分级患者占比比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 干预1个月后, 2组WST分级为3、4、5级的患者占比与干预前比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.5)。干预1个月后,2组WST不同分级患者占比比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.5), 见表 2。
表 2 2组患者干预前后吞咽功能WST分级比较[n(%)]时点 组别 n 1级 2级 3级 4级 5级 干预前 研究组 52 — — 24(46.15) 16(30.77) 12(23.07) 对照组 48 — — 20(41.67) 18(37.50) 10(20.83) 干预1个月后 研究组 52 8(15.39)# 12(23.08)# 20(38.46)*# 11(21.15)*# 1(1.92)*# 对照组 48 4(8.33) 6(12.50) 27(56.25)* 9(18.75)* 2(4.17)* WST: 洼田饮水试验。与干预前比较, * P < 0.5; 与对照组比较, #P < 0.5。 2.2 2组吞咽功能比较
干预前, 2组WST不同分级患者占比比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 干预1个月后, 2组WST分级为3、4、5级的患者占比与干预前比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.5)。干预1个月后,2组WST不同分级患者占比比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.5), 见表 2。
表 2 2组患者干预前后吞咽功能WST分级比较[n(%)]时点 组别 n 1级 2级 3级 4级 5级 干预前 研究组 52 — — 24(46.15) 16(30.77) 12(23.07) 对照组 48 — — 20(41.67) 18(37.50) 10(20.83) 干预1个月后 研究组 52 8(15.39)# 12(23.08)# 20(38.46)*# 11(21.15)*# 1(1.92)*# 对照组 48 4(8.33) 6(12.50) 27(56.25)* 9(18.75)* 2(4.17)* WST: 洼田饮水试验。与干预前比较, * P < 0.5; 与对照组比较, #P < 0.5。 2.3 2组生活质量比较
干预前,研究组SWAL-QOL评分为(108.47±19.99)分,对照组为(109.17±20.34)分。2组干预前SWAL-QOL评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。干预1个月后,研究组SWAL-QOL评分为(143.07±16.55)分,对照组为(133.52±21.06)分; 2组SWAL-QOL评分均较干预前提高,且研究组高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.5)。
2.3 2组生活质量比较
干预前,研究组SWAL-QOL评分为(108.47±19.99)分,对照组为(109.17±20.34)分。2组干预前SWAL-QOL评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。干预1个月后,研究组SWAL-QOL评分为(143.07±16.55)分,对照组为(133.52±21.06)分; 2组SWAL-QOL评分均较干预前提高,且研究组高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.5)。
3. 讨论
当前关于吞咽障碍与衰弱的相关性研究[18]较少,但已有明确证据显示吞咽障碍与衰弱相关[19], 且两者相互影响。衰弱患者会出现肌肉功能衰退,极易引发吞咽障碍。同时,吞咽障碍的发生也会导致患者营养摄入不足、机体肌肉量或肌力流失或减退,进而引发衰弱[20]。研究[21]显示老年人群衰弱发生率为7.0%。此外,衰弱不仅在预测老年患者结局与不良事件中起重要作用,也是预测死亡的一个关键风险因素。随着衰弱状态的持续,衰弱改善程度会逐渐降低[18]。
研究[22]提出,管理衰弱相关吞咽障碍的干预措施,除纠正原发疾病及减少多重用药外,还需对老年人群的认知、心理及社会因素进行相应管理。集束化护理确保临床实施的每条护理措施均基于循证证据,能够改善衰弱及吞咽功能,并取得了良好临床效果[23]。在改善吞咽障碍方面,集束化护理在脑卒中患者中的应用最为广泛。准确有效的集束化护理策略在预防ICU获得性衰弱方面也表现出良好效果,能够降低ICU患者获得性衰弱的发生率,缩短机械通气时间,并提高自理能力。集束化护理作为一系列有循证依据的护理措施集合,在本研究中主要包括老年综合评估、营养干预、吞咽功能训练、认知功能锻炼及心理护理。其中,全面准确的综合评估为存在衰弱的老年吞咽障碍患者后续治疗计划的制订提供了参考。研究[23]显示,集束化护理干预可确保患者获得有效营养支持,改善吞咽功能,减少肠道不耐受情况,及时预防或延缓患者认知衰退[12],不断提高患者对疾病的认知,帮助患者重拾治疗信心。
衰弱与吞咽障碍均是老年评估的重点内容。尽早发现高危人群,并及时给予相应处理,能够延缓衰弱进展,改善吞咽功能及预后结局。本研究采用简易WST作为吞咽障碍的筛查工具。至今尚无公认的衰弱风险评估“金标准”,因此本研究选取国内常用的FP进行老年衰弱状态的评估。本研究选用信效度良好的SWAL-QOL评估老年人群的生活质量,该量表可广泛应用于各种原因导致的吞咽障碍,从生理、心理、社会等多维度全面评估老年患者的生活质量,且评估时不易受其他因素干扰。本研究有助于医务人员快速准确了解老年吞咽障碍患者的衰弱状态及生活质量,为进一步干预措施的实施提供理论依据。但本研究纳入的研究对象数量偏少,观察时间偏短,未来应加大样本量,延长跟踪时间,以期获得更精确的研究结果。
3. 讨论
当前关于吞咽障碍与衰弱的相关性研究[18]较少,但已有明确证据显示吞咽障碍与衰弱相关[19], 且两者相互影响。衰弱患者会出现肌肉功能衰退,极易引发吞咽障碍。同时,吞咽障碍的发生也会导致患者营养摄入不足、机体肌肉量或肌力流失或减退,进而引发衰弱[20]。研究[21]显示老年人群衰弱发生率为7.0%。此外,衰弱不仅在预测老年患者结局与不良事件中起重要作用,也是预测死亡的一个关键风险因素。随着衰弱状态的持续,衰弱改善程度会逐渐降低[18]。
研究[22]提出,管理衰弱相关吞咽障碍的干预措施,除纠正原发疾病及减少多重用药外,还需对老年人群的认知、心理及社会因素进行相应管理。集束化护理确保临床实施的每条护理措施均基于循证证据,能够改善衰弱及吞咽功能,并取得了良好临床效果[23]。在改善吞咽障碍方面,集束化护理在脑卒中患者中的应用最为广泛。准确有效的集束化护理策略在预防ICU获得性衰弱方面也表现出良好效果,能够降低ICU患者获得性衰弱的发生率,缩短机械通气时间,并提高自理能力。集束化护理作为一系列有循证依据的护理措施集合,在本研究中主要包括老年综合评估、营养干预、吞咽功能训练、认知功能锻炼及心理护理。其中,全面准确的综合评估为存在衰弱的老年吞咽障碍患者后续治疗计划的制订提供了参考。研究[23]显示,集束化护理干预可确保患者获得有效营养支持,改善吞咽功能,减少肠道不耐受情况,及时预防或延缓患者认知衰退[12],不断提高患者对疾病的认知,帮助患者重拾治疗信心。
衰弱与吞咽障碍均是老年评估的重点内容。尽早发现高危人群,并及时给予相应处理,能够延缓衰弱进展,改善吞咽功能及预后结局。本研究采用简易WST作为吞咽障碍的筛查工具。至今尚无公认的衰弱风险评估“金标准”,因此本研究选取国内常用的FP进行老年衰弱状态的评估。本研究选用信效度良好的SWAL-QOL评估老年人群的生活质量,该量表可广泛应用于各种原因导致的吞咽障碍,从生理、心理、社会等多维度全面评估老年患者的生活质量,且评估时不易受其他因素干扰。本研究有助于医务人员快速准确了解老年吞咽障碍患者的衰弱状态及生活质量,为进一步干预措施的实施提供理论依据。但本研究纳入的研究对象数量偏少,观察时间偏短,未来应加大样本量,延长跟踪时间,以期获得更精确的研究结果。
-
表 1 2组临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
指标 死亡组(n=40) 生存组(n=56) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 61.50±19.20 57.80±17.50 0.99 0.32 男 27(67.50) 30(53.57) 1.88 0.17 APACHE Ⅱ评分/分 32.87±9.29 25.15±6.88 4.45 < 0.01 SOFA评分/分 10.28±2.64 7.04±1.59 6.92 < 0.01 LVEDV/mL 94.61±9.02 97.61±9.89 1.52 0.13 体温/℃ 38.02±2.36 37.96±2.83 0.11 0.91 ScvO2/% 62.07±17.63 67.16±14.04 1.57 0.12 MAP/mmHg 57.05±16.64 62.80±11.54 1.88 0.06 CVP/mmHg 6.55±1.06 6.73±1.37 0.69 0.49 HDLVEF/% 79.95±4.27 73.30±3.09 8.40 < 0.01 pcv-a(CO2)/mmHg 8.77±1.32 7.03±1.28 6.48 < 0.01 心率/(次/min) 121.27±12.99 119.18±12.43 0.80 0.43 Lac/(mmol/L) 11.02±2.36 10.94±2.77 0.15 0.88 APACHE Ⅱ: 急性生理学和慢性健康状况评价Ⅱ; SOFA: 序贯器官衰竭估计; LVEDV: 左室舒张末期容积;
ScvO2: 中心静脉的血氧饱和度; MAP: 平均动脉压; CVP: 中心静脉压; HDLVEF: 高动力左室射血分数;
pcv-a(CO2): 中心静脉动脉二氧化碳分压差; Lac: 乳酸。表 2 二元Logistic回归模型分析感染性休克患者死亡的影响因素
因素 B SE Wald χ2 P OR(95%CI) pcv-a(CO2) 0.67 0.27 6.05 0.01 1.95(1.15~3.33) SOFA评分 0.62 0.22 8.22 < 0.01 1.87(1.22~2.86) HDLVEF 0.72 0.31 5.59 0.02 2.06(1.13~3.74) APACHE Ⅱ评分 0.62 0.41 2.31 0.13 1.85(0.84~4.12) 表 3 不同指标对感染性休克患者28 d死亡的预测价值
指标 AUC(95%CI) 最佳截断值 约登指数 灵敏度/% 特异度/% HDLVEF 0.754(0.651~0.858) 76.87 0.51 72.50 78.57 pcv-a(CO2) 0.750(0.648~0.851) 7.98 0.51 77.50 73.21 SOFA评分 0.706(0.597~0.815) 9.29 0.44 67.50 76.79 HDLVEF、pcv-a(CO2)联合SOFA评分 0.874(0.801~0.946) — 0.71 87.50 83.93 -
[1] VINDHYAL M R, LU L K, RANKA S, et al. Impact of underlying congestive heart failure on in-hospital outcomes in patients with septic shock[J]. J Intensive Care Med, 2022, 37(7): 965-969. doi: 10.1177/08850666211061472
[2] SIVAPALAN P, MEYHOFF T S, HJORTRUP P B, et al. Conservative vs. liberal fluid therapy in septic shock-Protocol for secondary Bayesian analyses of the CLASSIC trial[J]. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand, 2022, 66(6): 767-771. doi: 10.1111/aas.14058
[3] GROUP S C C T. Incidence of severe Sepsis and septic shock in German intensive care units: the prospective, multicentre INSEP study[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2016, 42(12): 1980-1989. doi: 10.1007/s00134-016-4504-3
[4] DUBRAWKA C A, BETTHAUSER K D, POPE H E, et al. Effect of vasopressin dose on hemodynamic response in obese patients with septic shock: a retrospective observational study[J]. Ann Pharmacother, 2021, 55(12): 1447-1454. doi: 10.1177/10600280211007213
[5] SAKAMOTO Y, MASHIKO K, MATSUMOTO H, et al. Selection of acute blood purification therapy according to severity score and blood lactic acid value in patients with septic shock[J]. Indian J Crit Care Med, 2010, 14(4): 175-179. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.76080
[6] DE LA TORRE-PRADOS M V, GARCIA-DE LA TORRE A, ENGUIX A, et al. Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin as prognostic biomarker in septic shock[J]. Minerva Anestesiol, 2016, 82(7): 760-766.
[7] RHODES A, EVANS L E, ALHAZZANI W, et al. Surviving Sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of Sepsis and septic shock: 2016[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2017, 43(3): 304-377. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6
[8] SCHNITTKE N, SCHMIDT J, BARVALIA U, et al. Assessment of dynamic changes in cardiac function during resuscitation of patients with suspected septic shock: a prospective, observational, cohort study[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2020, 38(12): 2653-2657. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.08.058
[9] MICEK S T, MCEVOY C, MCKENZIE M, et al. Fluid balance and cardiac function in septic shock as predictors of hospital mortality[J]. Crit Care, 2013, 17(5): R246. doi: 10.1186/cc13072
[10] 中华医学会重症医学分会. 成人严重感染与感染性休克血流动力学监测与支持指南[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2007, 46(4): 344-349. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK200701001.htm [11] 中国医师协会急诊医师分会. 中国急诊感染性休克临床实践指南[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2016, 25(3): 274-287. [12] OH TE, HUTCHINSONR, SHORT S, et al. Verification of the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation scoring system in a Hong Kong intensive care unit[J]. Crit Care Med, 1993, 21(5): 698-705. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199305000-00013
[13] YAGHOUBIAN A, BATTER, MOZAFARPOUR S, et al. Use of the Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score for Prediction of Intensive Care Unit Admission Due to Septic Shock after Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A Multicenter Study[J]. J Urol, 2019, 202(2): 314-318. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000195
[14] CHOTALIA M, ALI M, HEBBALLI R, et al. Hyperdynamic left ventricular ejection fraction in ICU patients with Sepsis[J]. Crit Care Med, 2022, 50(5): 770-779. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005315
[15] MALLAT J, PEPY F, LEMYZE M, et al. Central venous-to-arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure difference in early resuscitation from septic shock: a prospective observational study[J]. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2014, 31(7): 371-380. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000064
[16] VINCENT J L, LATERRE P F, COHEN J, et al. A pilot-controlled study of a polymyxin B-immobilized hemoperfusion cartridge in patients with severe Sepsis secondary to intra-abdominal infection[J]. Shock, 2005, 23(5): 400-405. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000159930.87737.8a
[17] PAONESSA J R, BRENNAN T, PIMENTEL M, et al. Hyperdynamic left ventricular ejection fraction in the intensive care unit[J]. Crit Care, 2015, 19(1): 288. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1012-8
[18] 王雪婷, 高雪花, 曹雯, 等. 血乳酸联合中心静脉-动脉血二氧化碳分压差与动脉-中心静脉血氧含量差比值预测脓毒性休克患者预后的应用价值[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2020, 32(1): 39-43. [19] 刘冬辉, 刘超, 文海燕, 等. 中心静脉压联合下腔静脉呼吸变异度在脓毒性休克患者液体复苏中的预测价值[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2021, 36(11): 1441-1444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NOTH202111009.htm [20] 王喆, 李华, 张劲松. 红细胞分布宽度对肺炎并感染性休克病人预后的预测价值[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2018, 43(11): 1437-1439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BANG201811045.htm [21] 张娟. 脉搏指示连续心排血量监测下液体复苏治疗感染性休克效果观察[J]. 交通医学, 2021, 35(6): 574-576. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTYX202106008.htm




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
