Correlation between lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 level and cardiovascular disease in patients with obstructivesleep apnea syndrome
-
摘要:目的
观察阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征(OSAS)患者外周血中脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2(Lp-PLA2)水平, 探讨Lp-PLA2可否作为患者并发心血管疾病(CVD)的有效预测指标。
方法选取238例疑似OSAS的患者为研究对象,根据呼吸暂停低通气指数(AHI)分为非OSAS组53例和OSAS组185例(轻度42例,中度68例,重度75例),其中OSAS患者并发CVD 74例。采用酶联免疫吸附实验(ELISA)测定外周血Lp-PLA2水平,并分析其与OSAS患者并发CVD的关系。
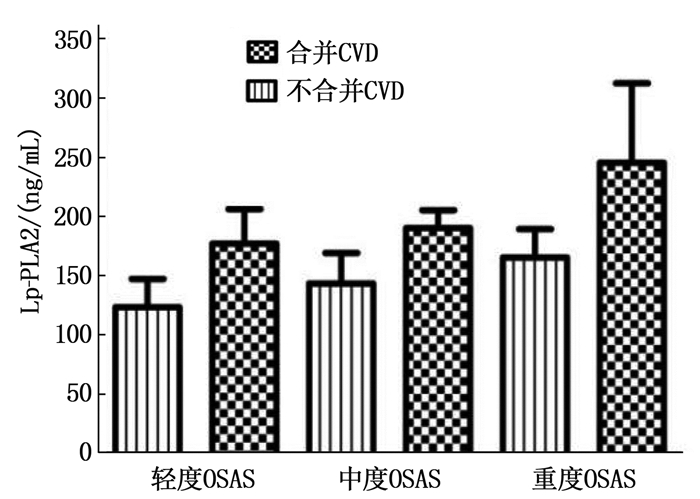
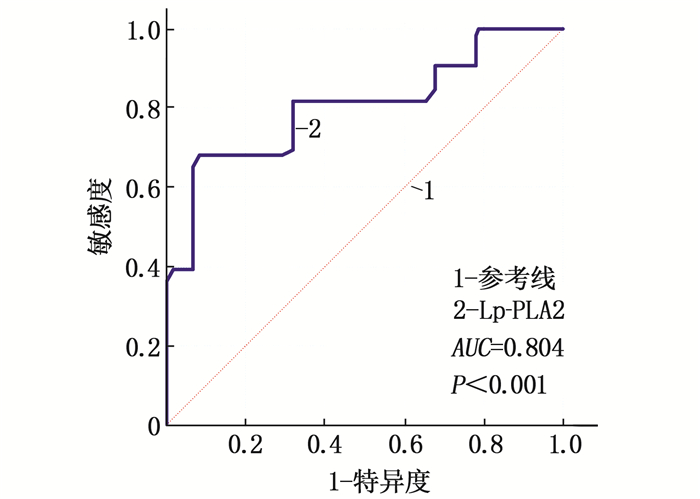
结果合并CVD的OSAS患者年龄、AHI、氧减饱和度指数(ODI)、Lp-PLA2均高于不合并CVD的OSAS患者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。在轻度、中度、重度OSAS患者中,合并CVD患者的Lp-PLA2水平高于不合并CVD患者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Lp-PLA2预测OSAS患者并发CVD的受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线的曲线下面积为0.804(0.740~0.859, P < 0.001), 截断值为235.1 ng/mL。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示, AHI(OR=1.044, 95%CI: 1.025~1.063, P < 0.001)、ODI(OR=1.035, 95%CI: 1.020~1.050, P < 0.001)、Lp-PLA2(OR=2.700, 95%CI: 1.412~5.164, P=0.003)及高血压(OR=2.648, 95%CI: 1.384~5.067, P=0.003)是OSAS患者并发CVD的独立影响因素。
结论Lp-PLA2可作为OSAS患者并发CVD的有效预测指标, Lp-PLA2>235.1 ng/mL提示患者并发CVD的风险较高。
-
关键词:
- 脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2 /
- 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征 /
- 心血管疾病 /
- 危险因素
Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the level of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) in peripheral blood of patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), and to explore whether Lp-PLA2 can be an effective predictor for patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD).
MethodsA total of 238 patients with suspected OSAS were selected as the research objects. According to the apnea hypopnea index (AHI), they were divided into non-OSAS group (n=53) and OSAS group (n=185) 42 mild cases, 68 moderate cases, and 75 severe cases). Among them, 74 patients with OSAS were complicated with CVD. The level of Lp-PLA2 in peripheral blood was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and its relationship with CVD in patients with OSAS was analyzed.
ResultsThe age, AHI, oxygen desaturation index (ODI), Lp-PLA2 of OSAS patients with CVD were significantly higher than those of OSAS patients without CVD(P < 0.05). Among patients with mild, moderate and severe OSAS, the Lp-PLA2 level in patients with CVD was significantly higher than that in in patients without CVD (P < 0.05). The area under receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of Lp-PLA2 for predicting CVD in OSAS patients was 0.804 (0.740 to 0.859, P < 0.001), and the cut-off value was 235.1 ng/mL. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that AHI (OR=1.044, 95%CI, 1.025 to 1.063, P < 0.001), ODI (OR=1.035, 95%CI, 1.020 to 1.050, P < 0.001), Lp-PLA2 (OR=2.700, 95%CI, 1.412 to 5.164, P=0.003) and hypertension (OR=2.648, 95%CI, 1.384 to 5.067, P=0.003) were independent influencing factors for CVD in OSAS patients.
ConclusionLp-PLA2 can be used as an effective predictor of OSAS patients complicated with CVD. Lp-PLA2>235.1 ng/mL indicates that patients have a higher risk of complicating CVD.
-
-
表 1 各组基线资料比较(x±s)[n(%)][M(P25, P75)]
基线资料 非OSAS组(n=53) 轻度OSAS组(n=42) 中度OSAS组(n=68) 重度OSAS组(n=75) F/H/χ2 P 人口特征 年龄/岁 51.1±7.2 50.6±6.6 52.5±5.6 53.4±6.7 2.149 0.095 男 37(69.8) 30(71.4) 50(73.5) 60(80.0) 2.041 0.564 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 27.1±2.0 27.1±2.2 27.6±2.4 28.0±2.1 2.266 0.082 既往史 吸烟史 11(20.8) 11(26.2) 14(20.6) 29(38.7) 7.594 0.055 高血压 17(32.1) 14(33.3) 30(44.1) 51(68.0) 21.390 < 0.001 糖尿病 11(20.8) 7(16.7) 16(23.5) 23(30.7) 3.385 0.336 高脂血症 10(18.9) 10(23.8) 16(23.5) 23(30.7) 2.466 0.482 CVD 10(18.9) 12(28.6) 26(38.2) 36(48.0) 12.652 0.005 PSG参数 AHI/(次/h) 2.3±1.4 9.2±3.2 22.1±4.1 49.6±12.1 521.800 < 0.001 ODI/(次/h) 2.6±1.7 8.0±3.3 20.2±10.6 50.3±20.3 176.951 < 0.001 最低SaO2/% 91.8±3.5 84.2±5.2 78.9±8.1 71.9±9.3 80.443 < 0.001 平均SaO2/% 96.2±1.5 94.8±2.8 93.3±3.3 91.9±4.1 20.297 < 0.001 TS90/% 0(0, 1.5) 3.1(0, 8.2) 16.4(1.5, 41.8) 21.2(3.9, 59.8) 109.707 < 0.001 实验室指标 Lp-PLA2/(ng/mL) 175.2±37.1 179.4±44.1 206.1±51.1 227.7±47.9 17.329 < 0.001 甘油三酯/(mmol/L) 1.7±0.6 1.7±0.6 1.8±0.6 2.2±1.2 6.120 0.001 总胆固醇/(mmol/L) 3.8±1.0 4.2±1.5 4.3±1.2 4.5±1.1 4.082 0.008 HDL-C/(mmol/L) 1.1±0.1 1.1±0.1 1.1±0.2 1.0±0.2 6.203 < 0.001 LDL-C/(mmol/L) 2.1±0.8 2.3±1.0 2.4±0.6 2.6±0.7 4.456 0.005 CVD: 心血管疾病; PSG: 多导睡眠监测; AHI: 呼吸暂停低通气指数; ODI: 氧减饱和度指数; SaO2: 动脉血氧饱和度; TS90%: 血氧饱和度 < 90% 的时间占监测总时间的百分比; Lp-PLA2: 脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; HDL-C: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇。 表 2 合并CVD与不合并CVD的OSAS患者人口特征、PSG及实验室指标比较(x±s)[n(%)][M(P25, P75)]
指标 OSAS合并CVD(n=74) OSAS不合并CVD(n=111) t/Z/χ2 P 人口特征 年龄/岁 54.4±6.6 51.2±5.9 3.346 0.001 男 58(78.4) 82(73.9) 0.513 0.474 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 27.9±2.2 27.4±2.3 1.481 0.140 PSG参数 AHI/(次/h) 34.4±19.2 27.9±17.9 2.338 0.020 ODI/(次/h) 34.8±26.3 26.5±19.9 2.288 0.024 最低SaO2/% 76.2±10.2 77.9±8.9 -1.154 0.251 平均SaO2/% 92.6±4.4 93.4±3.2 -1.378 0.171 TS90/% 14.9(2.3, 50.5) 9.6(1.6, 37.8) -0.033 0.974 实验室指标 Lp-PLA2/(ng/mL) 224.7±51.4 199.1±49.3 3.374 0.001 甘油三酯/(mmol/L) 2.0±1.0 1.9±0.9 0.730 0.467 总胆固醇/(mmol/L) 4.4±1.1 4.3±1.3 0.726 0.469 HDL-C/(mmol/L) 1.1±0.2 1.0±0.2 1.372 0.172 LDL-C/(mmol/L) 2.4±0.8 2.6±0.7 -1.606 0.110 PSG: 多导睡眠监测; AHI: 呼吸暂停低通气指数; ODI: 氧减饱和度指数; SaO2: 动脉血氧饱和度; TS90%: 血氧饱和度 < 90% 的时间占监测总时间的百分比; Lp-PLA2: 脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; HDL-C: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇。 表 3 变量赋值方法
变量 赋值 年龄/岁 直接纳入 AHI/(次/h) 直接纳入 ODI/(次/h) 直接纳入 Lp-PLA2/(ng/mL) ≤235.1=0,>235.1 =1 吸烟史 否=0, 是=1 高血压 否=0, 是=1 糖尿病 否=0, 是=1 高脂血症 否=0, 是=1 AHI: 呼吸暂停低通气指数; ODI: 氧减饱和度指数;
Lp-PLA2: 脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2。表 4 OSAS患者并发CVD的多因素Logistic回归分析
变量 β Wald χ2 OR 95%CI P 年龄 0.036 2.215 1.037 0.989~1.087 0.137 AHI 0.043 22.214 1.044 1.025~1.063 < 0.001 ODI 0.035 22.246 1.035 1.020~1.050 < 0.001 Lp-PLA2 0.993 9.014 2.700 1.412~5.164 0.003 吸烟史 0.340 1.166 1.405 0.758~2.607 0.280 高血压 0.974 8.651 2.648 1.384~5.067 0.003 糖尿病 0.365 1.265 1.441 0.762~2.724 0.261 高脂血症 0.591 3.373 1.806 0.961~3.396 0.066 -
[1] 杜江新, 达晶, 何尧利, 等. 单核细胞计数与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值对老年阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征患者心血管疾病的预测意义[J]. 中国医药, 2020, 15(5): 673-677. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYG202005010.htm [2] 尹恺, 刘达瑾. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征与高血压关系的研究进展[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 20(4): 662-666. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202204015.htm [3] HERNANDEZ A V, JEON A, DENEGRI-GALVAN J, et al. Use of adaptive servo ventilation therapy as treatment of sleep-disORdered breathing and heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Schlaf Atmung, 2020, 24(1): 49-63.
[4] HARADA G, TAKEUCHI D, INAI K, et al. Prevalence and risk factORs of sleep apnoea in adult patients with CHD[J]. Cardiol Young, 2019, 29(1): 71-77. doi: 10.1017/S1047951118001853
[5] VASHEGHANI-FARAHANI A, KAZEMNEJAD F, SADEGHNⅡAT-HAGHIGHI K, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and severity of cORonary artery disease[J]. Caspian J Intern Med, 2018, 9(3): 276-282.
[6] NAGAYOSHI M, LUTSEY P L, BENKESER D, et al. Association of sleep apnea and sleep duration with peripheral artery disease: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2016, 251: 467-475. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.06.040
[7] VOULGARIS A, ARCHONTOGEORGIS K, PAPANAS N, et al. Increased risk fOR cardiovascular disease in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (overlap syndrome)[J]. Clin Respir J, 2019, 13(11): 708-715. doi: 10.1111/crj.13078
[8] MAIOLINO G, BISOGNI V, ROSSITTO G, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 prognostic role in atherosclerotic complications[J]. WORld J Cardiol, 2015, 7(10): 609-620. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i10.609
[9] 刘莉, 叶鹏, Kheirandish-Gozal L, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停儿童内皮功能障碍与血浆脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2活性升高相关[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2017, 25(2): 175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201702012.htm [10] 常保强, 马令秋, 黄志勇, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征患者血浆脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2含量的变化[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2017, 24(5): 324-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2963.2017.05.003 [11] 何权瀛, 陈宝元. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征诊治指南(2011年修订版)解读[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2012, 35(1): 9-12. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2012.01.007 [12] 董文红, 吴晶, 余灿清, 等. 中国10个地区成年人自评健康状况与全因死亡、心血管疾病死亡风险的关联研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(5): 763-770. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200622-00872 [13] STONE N J, ROBINSON J G, LICHTENSTEIN A H, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a repORt of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task FORce on Practice Guidelines[J]. Circulation, 2014, 129(25 Suppl 2): S1-S45.
[14] 金萍萍, 杨琼, 李小刚. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征与缺血性脑卒中相关性研究现状与展望[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 24(8): 894-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNXG202208029.htm [15] 文芳, 王宏宇. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停与心血管相关疾病的关系研究进展[J]. 心血管病学进展, 2021, 42(4): 302-305. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXGB202104004.htm [16] YILDIRIM T, ALP R. The role of oxidative stress in the relation between fibromyalgia and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 21(1): 20-29.
[17] LAVIE L. Oxidative stress in obstructive sleep apnea and intermittent hypoxia: revisited: the bad ugly and good: implications to the heart and brain[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2015, 20: 27-45.
[18] CHARNIOT J C, KHANI-BITTAR R, ALBERTINI J P, et al. Interpretation of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 levels is influenced by cardiac disease, comORbidities, extension of atherosclerosis and treatments[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2013, 168(1): 132-138.
[19] 徐晓萍, 王梅蕾. 老年缺血性脑梗死患者LP-PLA2、神经功能与颈动脉粥样硬化斑块性质的关系研究[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2022, 17(6): 739-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTFS202206010.htm [20] HE S, CHOUSTERMAN B G, FENN A, et al. Lp-PLA2 antagonizes left ventricular healing after myocardial infarction by impairing the appearance of reparative macrophages[J]. Circ Heart Fail, 2015, 8(5): 980-987.
[21] 杨玉梅, 金晓烨, 贺丽. 脑梗死病人颈动脉粥样硬化斑块性质及神经功能损伤程度与血浆Lp-PLA2水平的关系[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 19(17): 2994-2998. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202117026.htm [22] Lp-PLA(2) STUDIES COLLABORATION, THOMPSON A, GAO P, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase a(2) and risk of coronary disease, stroke, and mortality: collaborative analysis of 32 prospective studies[J]. Lancet, 2010, 375(9725): 1536-1544.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王静,唐泊文,宋囡,李政. 健脾益气法治疗结直肠癌研究进展. 陕西中医. 2025(03): 420-423 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
