Influence of pulsatilla saponin on proliferation, migrationand invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells and its possible mechanism
-
摘要:目的
探讨白头翁皂苷对胃癌细胞HGC-27增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响及其可能机制。
方法采用不同浓度白头翁皂苷(12.5、25.0、50.0 μmol/L)处理人胃癌细胞HGC-27, 分别设为低白头翁皂苷组、中白头翁皂苷组、高白头翁皂苷组,另将正常培养的HGC-27细胞设为对照组。将si-NC、si-circNRIP1、pcDNA、pcDNA-circNRIP1转染至HGC-27细胞,分别设为si-NC组、si-circNRIP1组、pcDNA组、pcDNA-circNRIP1组。向HGC-27细胞中转染pcDNA、pcDNA-circNRIP1, 均加入50.0 μmol/L白头翁皂苷培养,分别记为白头翁皂苷+pcDNA组、白头翁皂苷+pcDNA-circNRIP1组。通过CCK-8法、平板克隆形成实验和Transwell实验分别检测细胞增殖、克隆形成和迁移、侵袭能力; 采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)法检测环状RNA核受体相互作用蛋白1 (circNRIP1)表达量; 采用蛋白质印迹法(Western blot)检测E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)、N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)的蛋白表达情况。
结果对照组、低白头翁皂苷组、中白头翁皂苷组、高白头翁皂苷组细胞增殖抑制率、E-cadherin蛋白水平依次升高,细胞克隆形成数量、迁移数量、侵袭数量依次减少, N-cadherin蛋白水平、circNRIP1表达量依次降低,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05); pcDNA-circNRIP1组circNRIP1表达量高于pcDNA组, si-circNRIP1组circNRIP1表达量低于si-NC组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); si-circNRIP1组细胞增殖抑制率和E-cadherin蛋白水平高于si-NC组, N-cadherin蛋白水平低于si-NC组,细胞克隆形成数量、迁移数量和侵袭数量少于si-NC组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 白头翁皂苷+pcDNA-circNRIP1组细胞增殖抑制率和E-cadherin蛋白水平低于白头翁皂苷+pcDNA组, N-cadherin蛋白水平高于白头翁皂苷+pcDNA组,细胞克隆形成数量、迁移数量和侵袭数量多于白头翁皂苷+pcDNA组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论白头翁皂苷可抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭活性且呈现浓度依赖性,其作用机制或与下调circNRIP1表达有关。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the influence of pulsatilla saponin on proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells and its possible mechanism.
MethodsHuman gastric cancer HGC-27 cells were treated with different doses of pulsatilla saponin (12.5, 25.0, 50.0 μmol/L) and named as low-dose pulsatilla saponin group, medium-dose pulsatilla saponin group and high-dose pulsatilla saponin group, and the normal cultured HGC-27 cells were named as control group. The si-NC, si-circNRIP1, pcDNA and pcDNA-circNRIP1 were transfected into HGC-27 cells, and were named as si-NC group, si-circNRIP1 group, pcDNA group and pcDNA-circNRIP1 group respectively. HGC-27 cells were transfected with pcDNA and pcDNA-circNRIP1 and cultured with 50.0 μmol/L pulsatilla saponin, and were named as pulsatilla saponin plus pcDNA group and pulsatilla saponin plus pcDNA-circNRIP1 group respectively. CCK-8 assay, colony formation assay and Transwell assay were used to detect the proliferation, clone formation and migration, and invasion respectively; quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the expression of circular RNA nuclear receptor interacting protein 1 (circNRIP1); Western blot was used to detect the expressions of E-cadherin and N-cadherin proteins.
ResultsIn the control group, low-dose pulsatilla saponin group, medium-dose pulsatilla saponin group and high-dose pulsatilla saponin group, the inhibition rates of cell proliferation and the levels of E-cadherin protein significantly increased gradually, the number of cell clone formation, migration and invasion significantly decreased gradually, and the expressions of N-cadherin protein and circNRIP1 significantly decreased gradually (P < 0.05); the expression level of circNRIP1 in the pcDNA-circNRIP1 group was significantly higher than that in the pcDNA group, while the expression level of circNRIP1 in the si-circNRIP1 group was significantly lower than thatin the si-NC group (P < 0.05); the inhibition rate of cell proliferation and level of E-cadherin protein in the si-circNRIP1 group were significantly higher than those in the si-NC group, while the level of N-cadherin protein and the number of cell clone formation, migration and invasion were significantly lower than those in the si-NC group (P < 0.05); the inhibition rate of cell proliferation and level of E-cadherin protein in the pulsatilla saponin plus pcDNA-circNRIP1 group were significantly lower than those in the pulsatilla saponin plus pcDNA group, while the level of N-cadherin protein and the number of cell clone formation, migration and invasion were significantly higher than those in the pulsatilla saponin plus pcDNA group (P < 0.05).
ConclusionPulsatilla saponin can inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner, and its mechanism may be associated with down-regulation of circNRIP1 expression.
-
-
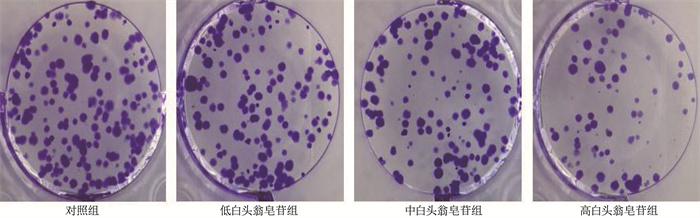
表 1 4组细胞增殖抑制率和细胞克隆形成数量比较(x±s)
组别 n 细胞增殖抑制率/% 细胞克隆形成数量/个 对照组 9 0±0 103.89±6.92 低白头翁皂苷组 9 10.50±1.06* 85.56±3.50* 中白头翁皂苷组 9 23.51±1.29*# 63.11±2.85*# 高白头翁皂苷组 9 44.71±2.37*#△ 42.44±2.31*#△ 与对照组比较, *P < 0.05; 与低白头翁皂苷组比较, #P < 0.05; 与中白头翁皂苷组比较, △P < 0.05。 表 2 4组细胞迁移、侵袭数量和E-cadherin、N-cadherin蛋白表达情况比较(x±s)
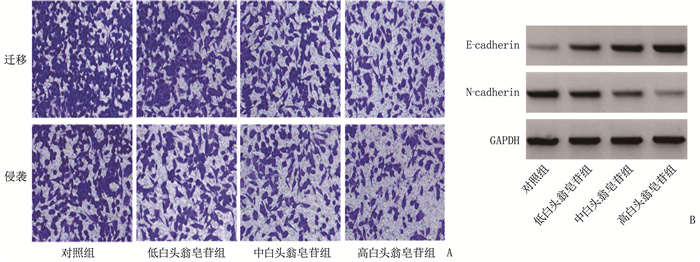
组别 n 迁移数量/个 侵袭数量/个 E-钙黏蛋白 N-钙黏蛋白 对照组 9 221.56±11.92 163.00±7.27 0.22±0.03 0.89±0.06 低白头翁皂苷组 9 182.00±7.42* 132.67±5.12* 0.38±0.04* 0.64±0.05* 中白头翁皂苷组 9 149.78±6.41*# 98.00±4.35*# 0.56±0.06*# 0.43±0.04*# 高白头翁皂苷组 9 105.11±5.13*#△ 70.33±3.53*#△ 0.77±0.06*#△ 0.21±0.02*#△ 与对照组比较, *P < 0.05; 与低白头翁皂苷组比较, #P < 0.05; 与中白头翁皂苷组比较, △P < 0.05。 表 3 4组细胞circNRIP1表达量比较(x±s)
组别 n circNRIP1 对照组 9 1.00±0 低白头翁皂苷组 9 0.71±0.05* 中白头翁皂苷组 9 0.48±0.05*# 高白头翁皂苷组 9 0.22±0.02*#△ circNRIP1: 环状RNA核受体相互作用蛋白1。与对照组比较, *P < 0.05; 与低白头翁皂苷组比较, #P < 0.05; 与中白头翁皂苷组比较, △P < 0.05。 表 4 各组circNRIP1转染效率检测结果比较(x±s)
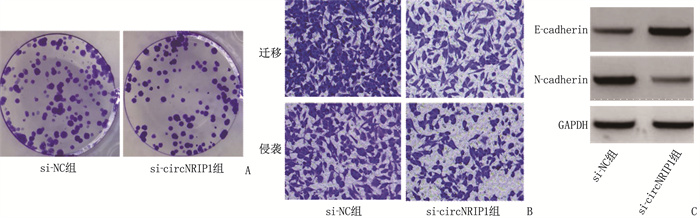
组别 n circNRIP1 pcDNA组 9 1.00±0 pcDNA-circNRIP1组 9 2.71±0.10* si-NC组 9 1.00±0 si-circNRIP1组 9 0.46±0.05# 与pcDNA组比较, *P < 0.05; 与si-NC组比较, #P < 0.05。 表 5 抑制circNRIP1对HGC-27细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭相关指标的影响(x±s)
组别 n 细胞增殖抑制率/% 细胞克隆形成数量/个 迁移数量/个 侵袭数量/个 E-cadherin蛋白水平 N-cadherin蛋白水平 si-NC组 9 0±0 102.56±9.27 218.00±10.31 165.00±11.22 0.21±0.03 0.85±0.07 si-circNRIP1组 9 36.38±2.15* 53.11±2.88* 125.00±8.03* 85.78±5.53* 0.64±0.06* 0.32±0.03* 与si-NC组比较, *P < 0.05。 表 6 过表达circNRIP1对白头翁皂苷处理的HGC-27细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭相关指标的影响(x±s)
组别 n 细胞增殖抑制率/% 细胞克隆形成数量/个 迁移数量/个 侵袭数量/个 E-cadherin蛋白水平 N-cadherin蛋白水平 白头翁皂苷+pcDNA组 9 44.36±1.94 41.89±3.14 106.44±7.24 72.00±4.97 0.76±0.07 0.19±0.03 白头翁皂苷+pcDNA-circNRIP1组 9 15.53±1.20* 79.44±2.71* 162.11±9.47* 114.56±6.24* 0.41±0.05* 0.53±0.05* 与白头翁皂苷+pcDNA组比较, *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 沈乃营, 鲁峰刚, 张毅, 等. 胃癌组织中Foxp3+Tregs和pDCs与胃微生物群失调的关系[J]. 解剖学研究, 2021, 43(5): 503-507, 513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDJP202105006.htm [2] 李沙沙, 李绪露. GAS5基因启动子甲基化在老年胃癌组织中的水平及其与临床病理特征的相关性[J]. 解剖学研究, 2019, 41(4): 278-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDJP201904009.htm [3] LIU Z M, YANG X L, JIANG F, et al. Matrine involves in the progression of gastric cancer through inhibiting miR-93-5p and upregulating the expression of target gene AHNAK[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2020, 121(3): 2467-2477. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29469
[4] ZHOU Y, XU Q H, SHANG J J, et al. Crocin inhibits the migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells via miR-320/KLF5/HIF-1α signaling[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(10): 17876-17885. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28418
[5] 官紫祎, 陈兰英, 罗颖颖, 等. 基于糖酵解机制的白头翁皂苷多成分协同抑制人肺癌NCI-H460细胞增殖作用研究[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(21): 5289-5297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO201921023.htm [6] DU Z. CircNRIP1: An emerging star in multiple cancers[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2023, 241: 154281. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154281
[7] LIANG L, LI L. Down-regulation of circNRIP1 promotes the apoptosis and inhibits the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by miR-182/ROCK1 axis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 6279-6288. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S221633
[8] ZHANG X, WANG S, WANG H X, et al. Circular RNA circNRIP1 acts as a microRNA-149-5p sponge to promote gastric cancer progression via the AKT1/mTOR pathway[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 20. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0935-5
[9] XU G S, LI M L, WU J, et al. Circular RNA circNRIP1 sponges microRNA-138-5p to maintain hypoxia-induced resistance to 5-fluorouracil through HIF-1α-dependent glucose metabolism in gastric carcinoma[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 2789-2802. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S246272
[10] 薛淑一. 白头翁皂苷B4通过Notch通路对肝癌的抑制作用及其机制研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2019. [11] YANG F, HU A P, LI D, et al. Circ-HuR suppresses HuR expression and gastric cancer progression by inhibiting CNBP transactivation[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 158. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1094-z
[12] XIE M Y, YU T, JING X M, et al. Exosomal circSHKBP1 promotes gastric cancer progression via regulating the miR-582-3p/HUR/VEGF axis and suppressing HSP90 degradation[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 112. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01208-3
[13] LI Y Y, XU Q F, YANG W, et al. Oleanolic acid reduces aerobic glycolysis-associated proliferation by inhibiting yes-associated protein in gastric cancer cells[J]. Gene, 2019, 712: 143956-143966. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.143956
[14] 官紫祎, 陈兰英, 罗颖颖, 等. 白头翁皂苷对NCI-H460细胞增殖、凋亡的影响及其差异表达蛋白筛选[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019, 25(18): 49-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX201918008.htm [15] 陈兰英, 周朦静, 崔亚茹, 等. 白头翁皂苷干预糖酵解途径抑制SW480人结直肠癌细胞增殖作用研究[J]. 中药材, 2019, 42(3): 652-656. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYCA201903038.htm [16] XU E, XIA X F, JIANG C Y, et al. GPER1 silencing suppresses the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT-mediated EMT[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 591239.
[17] JIANG Y, WANG W, WU X, et al. Pizotifen inhibits the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 19(2): 817-824.
[18] LI M, CAI J, HAN X, et al. Downregulation of circNRIP1 suppresses the paclitaxel resistance of ovarian cancer via regulating the miR-211-5p/HOXC8 axis[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 9159-9171.
[19] LI X H, MA N Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Circular RNA circNRIP1 promotes migration and invasion in cervical cancer by sponging miR-629-3p and regulating the PTP4A1/ERK1/2 pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(5): 399.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 王莉娜,闫婷. 孕晚期基于胎心监护的临床护理对胎儿窘迫及新生儿窒息发生情况的影响. 临床医学研究与实践. 2023(19): 168-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赖锡妹,邝彩红. 电子胎心监护联合超声脐动脉血流动力学指标对胎儿窘迫的预测效能分析. 影像研究与医学应用. 2022(10): 72-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 路会景,王阳,于艳艳,陈英红. 彩超检测胎儿大脑中动脉、肾动脉预测妊娠晚期胎儿宫内窘迫. 河南大学学报(医学版). 2021(04): 273-276+282 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张晓微. 彩超监测胎儿脐血流指标在预测胎儿宫内缺氧中的应用. 黑龙江医药. 2020(01): 188-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄鹂鹂,林淑娟,区凯敏. 脐动脉血不同pH值与胎儿宫内窘迫的相关性及预后分析. 中国医药科学. 2020(19): 128-131 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 袁景春,周镇光,李瑞华. 脐动脉血气分析与乳酸水平对新生儿窒息的诊断价值. 中国医药科学. 2019(23): 116-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号