Establishment of a Nomogram for prognosis of liver metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
-
摘要:目的
分析非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)肝转移患者的临床特征及预后因素,并构建生存率列线图。
方法收集监测、流行病学和最终结果(SEER)数据库具有完整临床信息的NSCLC患者79 977例,分为肝转移组和非肝转移组,并将肝转移组随机分为训练集与验证集。采用χ2检验比较肝转移组的临床特征; 采用Cox回归分析筛选独立预后因素,并用于构建预测1、3年总生存率(OS)和癌症特异性生存率(CSS)的列线图。
结果性别、年龄、原发部位、组织学分类、病理分级、肿瘤直径、T分期、N分期、远处转移、手术、化疗、放疗与肝转移相关(P < 0.001)。多因素分析发现,性别、年龄、肿瘤直径、组织学类型、病理分级、原发部位手术、化疗、骨转移、脑转移均是OS和CSS影响的独立危险因素(P < 0.05)。受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线和校准曲线显示列线图具有良好的预测性能。基于建立的列线图对患者进行风险分层,低风险组的预后优于高风险组。
结论本研究构建的列线图能较为准确地预测NSCLC肝转移患者的预后情况。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with liver metastasis, and to construct a prognostic nomogram.
MethodsA total of 79 977 NSCLC patients with complete clinical information were collected from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, and were divided into liver metastasis group and non-liver metastasis group. The liver metastasis group was randomly divided into training set and verification set. Chi square test was used to compare the clinical characteristics of liver metastasis group. The independent prognostic factors were screened by Cox regression analysis and used to construct nomograms for predicting 1- and 3-year overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS).
ResultsGender, age, primary site, histological classification, pathological grade, tumor size, T stage, N stage, distant metastasis, surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy were related to liver metastasis (P < 0.01). Multivariate analysis found that gender, age, tumor size, histological type, pathological grade, primary site surgery, chemotherapy, bone metastasis, and brain metastasis were independent risk factor associated with OS and CSS (P < 0.05). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and calibration curve showed that the nomogram had good predictive performance. Risk stratification among patients was carried out based on the established nomograms, and the low-risk group had a better prognosis than the high-risk group.
ConclusionThe nomograms constructed in this study can more accurately predict the prognosis of NSCLC patients with liver metastasis.
-
肺癌在全球恶性肿瘤中的发病率和致死率均居前列。约85%的肺癌患者为非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC), 超过50%的患者在确诊时已处于晚期阶段[1]。肝转移是NSCLC患者常见且预后最差的转移类型[2],晚期肝转移的发生率可达20%[3], 患者中位总生存时间(OS)约为7个月[4-5]。相较于脑转移与骨转移,目前有关NSCLC肝转移的临床特征、治疗方式、预后评估的研究仍比较欠缺。本研究基于监测、流行病学和最终结果(SEER)数据库探讨NSCLC肝转移患者的临床特征及预后相关因素,并构建OS和癌症特异性生存率(CSS)列线图,通过更准确地预测NSCLC肝转移患者的生存情况,及早识别出高风险患者并采取分层治疗,现将结果报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
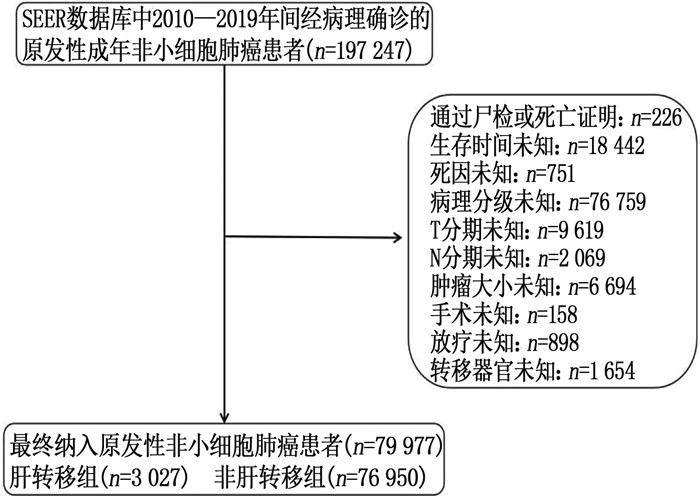
使用SEER*Stat软件(8.3.9版)下载2010—2019年诊断为原发性NSCLC患者的临床资料。纳入标准: ①年龄≥18岁的成年患者; ②患者只有1个原发性肿瘤; ③经阳性组织学确诊为NSCLC者; ④患者具有完整的临床病理及生存信息。排除标准: ①通过尸检或仅根据死亡证明获得诊断者; ②生存时间及死亡原因未知者; ③病理分级、TNM分期、肿瘤直径、转移器官、治疗记录缺失或不完整者。最终纳入79 977例原发性NSCLC患者,并分为肝转移组与非肝转移组。具体流程见图 1。
本研究以OS和CSS为结局指标, OS被定义为肺癌诊断至任何原因导致的死亡的随访时间, CSS被定义为肺癌诊断至因肺癌死亡的随访时间。本研究已签署《SEER数据使用协议》,鉴于数据库的公开数据均已消除识别信息,因此不需要知情同意和伦理审查。
1.2 统计学分析
将原发性NSCLC患者分为肝转移组与非肝转移组,并将肝转移组又分为训练集与验证集(比例为7∶3), 训练集用于构建列线图和风险分类系统,验证集用于验证模型。年龄和肿瘤直径的最佳截断值由X-tile软件确定。采用χ2检验比较分析肝转移组的临床特征。采用Cox比例风险回归分析筛选独立预后因素,将单因素分析中P < 0.05的因素纳入多因素分析。根据多因素分析的结果建立OS和CSS列线图,并使用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线和校准曲线验证模型的区分度和校准度。基于训练集患者的列线图总分建立风险分类系统,将患者分为高风险和低风险预后组,通过Kaplan-Meier方法和Log-rank检验比较组间的生存差异。采用SPSS 26.0和R 4.1.2软件进行数据处理。随机分组、χ2检验和Cox回归分析使用SPSS软件。列线图和校准曲线使用R软件的“survival”和“rms”包生成。ROC曲线使用“survival”和“timeROC”包绘制。Kaplan-Meier生存曲线使用“survival”“tibble”“survminer”和“ggplot2”包制作。检验水准(α)为0.05。
2. 结果
2.1 肝转移与非肝转移NSCLC患者的临床特征比较
纳入的NSCLC患者的临床特征见表 1。结果表明,性别、年龄、原发部位、组织学分类、病理分级、肿瘤直径、T分期、N分期、远处转移、手术、化疗、放疗与肝转移相关,组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001); NSCLC患者中,男性、年龄18~71岁、肺上叶部位、鳞癌、低分化程度、肿瘤直径>2.6 cm、T4期、N2期、有骨转移、无脑转移、无肺转移患者发生肝转移的比率相对较高。从治疗方面来看,肝转移患者更少接受原发部位和转移部位手术以及放疗,而更多接受化疗。此外,发生肝转移患者的中位生存时间短于未发生者。
表 1 肝转移与非肝转移NSCLC患者临床特征比较[n(%)]临床特征 分类 总例数(n=79 977) 肝转移(n=3 027) 无肝转移(n=76 950) P 生存状态 存活 31 681(39.6) 147(4.9) 31 534(41.0) < 0.001 死于原发肿瘤 40 202(50.3) 2 793(92.3) 37 409(48.6) 死于其他原因 8 094(10.1) 87(2.9) 8 007(10.4) 性别 女 39 115(48.9) 1 270(42.0) 37 845(49.2) < 0.001 男 40 862(51.1) 1 757(58.0) 39 105(50.8) 年龄 18~71岁 48 994(61.3) 2 014(66.5) 46 980(61.1) < 0.001 72~79岁 20 239(25.3) 653(21.6) 19 586(25.5) ≥80岁 10 744(13.4) 360(11.9) 10 384(13.5) 原发部位 肺上叶 47 260(59.1) 1 660(54.8) 45 600(59.3) < 0.001 肺中叶 3 547(4.4) 135(4.5) 3 412(4.4) 肺下叶 23 979(30.0) 882(29.1) 23 097(30.0) 气管及其他 5 191(6.5) 350(11.6) 4 841(6.3) 组织学分类 肺腺癌 7 080(8.9) 503(16.6) 6 577(8.5) < 0.001 鳞状细胞肺癌 25 969(32.5) 884(29.2) 25 085(32.6) 其他 46 928(58.7) 1 640(54.2) 45 288(58.9) 病理分级 高分化 8 762(11.0) 105(3.5) 8 657(11.3) < 0.001 中分化 32 216(40.3) 738(24.4) 31 478(40.9) 低分化 37 629(47.0) 2 102(69.4) 35 527(46.2) 未分化 1 370(1.7) 82(2.7) 1 288(1.7) 肿瘤直径 0.1~2.6 cm 28 456(35.6) 367(12.1) 28 089(36.5) < 0.001 >2.6~ < 5.6 cm 32 425(40.5) 1 388(45.9) 31 037(40.3) ≥5.6 cm 19 096(23.9) 1 272(42.0) 17 824(23.2) 偏侧性 右侧 46 621(58.3) 1 722(56.9) 44 899(58.3) 0.110 左侧 33 356(41.7) 1 305(43.1) 32 051(41.7) T分期 T1 24 798(31.0) 253(8.4) 24 545(31.9) < 0.001 T2 26 698(33.4) 798(26.4) 25 900(33.7) T3 15 063(18.8) 846(27.9) 14 217(18.5) T4 13 418(16.8) 1 130(37.3) 12 288(16.0) N分期 N0 44 166(55.2) 556(18.4) 43 610(56.7) < 0.001 N1 8 440(10.6) 278(9.2) 8 162(10.6) N2 21 033(26.3) 1 503(49.7) 19 530(25.4) N3 6 338(7.9) 690(22.8) 5 648(7.3) 骨转移 无 72 117(90.2) 1 399(46.2) 70 718(91.9) < 0.001 有 7 860(9.8) 1 628(53.8) 6 232(8.1) 脑转移 无 73 612(92.0) 218(72.2) 71 425(92.8) < 0.001 有 6 365(8.0) 840(27.8) 5 525(7.2) 肺转移 无 72 827(91.1) 1 975(65.2) 70 852(92.1) < 0.001 有 7 150(8.9) 1 052(34.8) 6 098(7.9) 原发部位手术 无 38 353(48.0) 2 938(97.1) 35 415(46.0) < 0.001 有 41 624(52.0) 89(2.9) 41 535(54.0) 转移部位手术 无 77 848(97.3) 2 908(96.1) 74 940(97.4) < 0.001 有 2 129(2.7) 119(3.9) 2 010(2.6) 化疗 无 46 379(58.0) 1 150(38.0) 45 229(58.8) < 0.001 有 33 598(42.0) 1 877(62.0) 31 721(41.2) 放疗 无 51 511(64.4) 1 637(54.1) 49 874(64.8) < 0.001 有 28 466(35.6) 1 390(45.9) 27 076(35.2) 中位生存时间/月 28.0(27.5~28.5) 5.0(4.7~5.3) 30.0(29.5~30.5) < 0.001 中位生存时间以中位数(95%置信区间)表示。 2.2 NSCLC肝转移患者OS和CSS的预后因素
单因素分析结果显示, N分期、偏侧性、转移部位手术、放疗、肺转移与OS无显著相关性(P>0.05), N分期、原发部位、偏侧性、转移部位手术、放疗与CSS无显著相关性(P>0.05)。多因素分析发现,年龄、性别、肿瘤直径、组织学类型、病理分级、原发部位手术、化疗、骨转移、脑转移均是OS和CSS的独立影响因素(P < 0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 OS和CSS的多因素Cox回归分析变量(参照) OS CSS HR(95%CI) P HR(95%CI) P 性别(女性) 男性 1.109(1.012~1.216) 0.027 1.106(1.007~1.214) 0.035 年龄(18~71岁) < 0.001 0.001 72~79岁 1.193(1.069~1.331) 0.002 1.171(1.047~1.309) 0.006 ≥80岁 1.260(1.098~1.447) 0.001 1.246(1.083~1.433) 0.002 肿瘤部位(肺上叶) 0.086 — — 肺中叶 0.926(0.745~1.152) 0.492 — — 肺下叶 0.934(0.844~1.034) 0.190 — — 气管及其他 1.134(0.984~1.308) 0.083 — — 组织学分类(肺腺癌) < 0.001 < 0.001 鳞状细胞肺癌 0.999(0.868~1.151) 0.994 1.000(0.866~1.155) 0.999 其他 0.821(0.719~0.937) 0.003 0.825(0.721~0.945) 0.005 病理分级(高分化) < 0.001 0.001 中分化 1.056(0.807~1.381) 0.692 1.057(0.807~1.385) 0.687 低分化 1.301(1.002~1.687) 0.048 1.290(0.993~1.677) 0.057 未分化 1.461(1.004~2.127) 0.048 1.472(1.008~2.150) 0.045 肿瘤直径(0.1~2.6 cm) 0.035 0.047 >2.6~ < 5.6 cm 0.864(0.735~1.016) 0.077 0.867(0.736~1.021) 0.087 ≥5.6 cm 0.971(0.820~1.148) 0.727 0.969(0.817~1.150) 0.721 T分期(T1) 0.055 0.056 T2 1.205(0.982~1.477) 0.074 1.217(0.990~1.497) 0.063 T3 1.219(0.996~1.491) 0.055 1.207(0.980~1.487) 0.076 T4 1.306(1.071~1.591) 0.008 1.313(1.070~1.612) 0.009 骨转移(无) 有 1.317(1.202~1.444) < 0.001 1.312(1.194~1.441) < 0.001 脑转移(无) 有 1.228(1.108~1.360) < 0.001 1.230(1.108~1.365) < 0.001 肺转移(无) — — 有 — — 1.061(0.959~1.174) 0.253 原发部位手术(无) 有 0.558(0.415~0.750) < 0.001 0.556(0.411~0.752) < 0.001 化疗(无) 有 0.436(0.397~0.480) < 0.001 0.436(0.396~0.481) < 0.001 2.3 预后列线图的构建
基于OS和CSS的独立危险因素分别构建列线图。根据列线图可得到每个因素对应的分值,通过分值相加得到的总分定位在总分轴上即可确定1、3年OS和CSS的估计概率。
在OS和CCS列线图中,化疗对预后的影响最为显著,其次是原发部位手术; 病理分级、有无骨转移、有无脑转移、年龄和组织学类型对预后的影响中等,而肿瘤直径及性别对预后的影响不大。见图 2。
2.4 列线图的评价和验证
ROC曲线显示, OS列线图训练集1、3年的曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.755、0.756, 在验证集中分别为0.736、0.755。CSS列线图训练集1、3年的AUC分别为0.751、0.750, 在验证集中分别为0.734、0.750, 表明模型具有良好的区分能力。1、3年OS和CSS的校准曲线接近45°对角线,提示列线图预测的存活率与实际观察值具有良好的一致性。见图 3。
2.5 风险分层系统
使用X-tile软件计算列线图总分与预后相关的最佳临界值,结果显示最佳OS阈值为204.22, 最佳CSS阈值为203.90。训练集和验证集的Kaplan-Meier曲线显示,低风险组的预后优于高风险组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001), 提示该风险分层能够较准确地识别出高危患者群体,并将患者分成预后有显著差异的2个风险亚组。见图 4。
3. 讨论
肝转移是影响NSCLC患者预后和引起死亡风险增高的关键因素[6], 即使是单一肝脏转移的患者,也需要给予足够的治疗强度。本研究主要分析了SEER数据库中NSCLC患者临床特征与肝转移发生率的关系,进一步建立了预测NSCLC肝转移患者生存率的列线图,其中包含了化疗、原发部位手术、病理分级、骨转移、脑转移、年龄、组织学类型、肿瘤直径和性别共9个变量, ROC曲线和校准曲线结果表明,列线图具有良好的预测效能,可以为更早发现高危患者及更有效地治疗肝转移患者提供临床指导。
本研究中,年轻患者发生肝转移的风险较高,其原因可能是年轻患者拥有较好的血管生成微环境,由此可促进肿瘤生长和转移,且其较长的生存期增加了发生转移的风险时间,同时肿瘤需要更具侵袭性才能逃脱年轻个体的免疫监测。此外,老年患者因细胞增殖变慢,激素浓度以及细胞对激素的反应性发生改变,肿瘤生长转移的血管化生受损,因而肿瘤的侵袭性降低[7]。因此,临床上对年龄较小的肺癌患者应加强监测,以了解是否发生肝转移,并制订完善的临床策略以改善预后。本研究证实, NSCLC肝转移患者的生存时间与性别、年龄、组织学类型、病理分级、肿瘤直径、骨转移、脑转移、原发部位手术、化疗等因素有关; 其中,肿瘤病理分级越高,组织侵袭性越强,相应的生存期也越短; 肿瘤越大,患者的预后越差,这可能是因为更大的肿瘤会产生更多的克隆形成细胞,且随着肿瘤增大,肿瘤细胞对治疗的敏感性也会降低[8]。合并远处转移的肺癌患者预后不良这一结论已达成普遍共识,有研究[9]进一步发现多器官多灶转移与更短的无进展生存期(PFS)(0~1个器官为5.7个月, 2~3个器官为3.5个月, ≥4个器官为2.7个月)和较低的疾病缓解率(36%、29.8%、18.2%)相关,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。
NSCLC肝转移患者的预后较差。目前单一的治疗方法都有一定的局限性,且长期疗效不佳,而综合治疗往往能够提高疗效,但仍需进一步研究来阐明最佳治疗方案。由于已出现肝转移灶,相当比率的患者不能接受根治性肺切除术。本研究发现原发部位手术可较为显著地改善患者的生存率,回顾性研究[10]也显示姑息性肺切除术的死亡率低于2%, 5年生存率为11%~30%。当肝转移灶为单个或局限于1个肝叶时,可选择手术切除。研究[11]提出,虽然肝转移瘤手术近期疗效佳,但长期预后不佳,中位PFS仅为6.3个月,最终均死于肿瘤进展。本研究同样发现肝转移灶手术治疗的效果并不理想。
对于不能手术的肺癌肝转移患者,应以全身化疗为主[12]。由于肝内药物浓度低,化疗有效缓解期较短。肝动脉化疗栓塞通过超选择栓塞肿瘤供应血管,可明显提高局部控制率,但栓塞后会使侧支循环及新生毛细血管形成,导致血液药物浓度减小,也会影响治疗效果。有研究[11]进一步表明全身化疗联合局部介入治疗的有效率为65%,中位PFS为7.9个月,疗效优于单独手术及化疗。还有研究[13]推断对于直径较大的肝转移病灶,可先用消融术减小肿瘤负荷,而后用动脉化疗栓塞术进一步提高疗效。在肝转移灶数目不超过5个且肿瘤直径小于6 cm的情况下,放疗可用于肺癌肝转移患者。本研究中,放疗并不能改善患者的OS和CCS, 这可能与放疗后肝脏常出现新的转移有关。指南[14]提示,放疗仍可作为转移性NSCLC患者缓解疼痛、减轻并发症、提高生活质量的姑息性治疗,并在寡灶性疾病、中枢神经系统转移和联合治疗中发挥积极的作用。
目前靶向和免疫治疗已成为肺癌转移治疗的重要方向,晚期NSCLC患者的5年生存率已提高至22%[15]。肺癌的分型也由病理组织学分类进一步细分为基于基因的分子亚型,约73.9%的NSCLC患者可检测出相关驱动基因突变[16],这部分患者可从特定的靶向药物中获益。研究[17]提出,对于野生型NSCLC伴肝转移者,化疗联合贝伐珠单抗仍能提供更好的整体生存效益。此外,对于驱动基因野生型的晚期NSCLC患者,免疫治疗是目前一线治疗的基石[18]。需要注意的是,免疫治疗对肝转移的疗效不佳[19], 这可能与肝脏中免疫细胞多处于免疫耐受状态,分化的细胞亚群多发挥促肿瘤生长作用,从而形成免疫抑制性的肿瘤微环境密切相关[20]。免疫染色结果[9]也显示,肝转移患者的PD-L1表达和CD8+肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞密度的比率均低于无肝转移的患者(0%与30.8%, P=0.088)。研究[20]发现,阿特珠单抗联合贝伐珠单抗治疗可显著提高NSCLC肝转移人群的生存获益,有望成为新的标准的一线治疗方案。Mata分析[21]提示,在晚期野生型NSCLC患者的一线治疗中,免疫联合化疗的长期生存率显著优于标准化疗。此外,免疫联合放疗可以更大程度地减少T细胞的凋亡,缓解免疫抑制,提高疗效[22]。
本研究存在的局限性: ① SEER数据库未收录靶向和免疫治疗的具体信息,因此无法纳入该预后分析。② SEER数据库缺乏详尽的治疗方案、部分肿瘤标志物等关键指标,可能会影响预测模型的准确性和全面性。③回顾性研究可能会导致固有偏倚,只纳入病例数据完整的患者可能会导致选择偏倚。④本研究中缺少独立的外部验证,可能会影响预测模型的实用普遍性。
综上所述,本研究基于化疗、原发部位手术、病理分级、骨转移、脑转移、年龄、组织学类型、肿瘤直径和性别共9个指标建立的NSCLC肝转移患者生存率列线图的区分能力良好,可准确评估患者的OS和CSS,并对优化个体化治疗提供参考。
-
表 1 肝转移与非肝转移NSCLC患者临床特征比较[n(%)]
临床特征 分类 总例数(n=79 977) 肝转移(n=3 027) 无肝转移(n=76 950) P 生存状态 存活 31 681(39.6) 147(4.9) 31 534(41.0) < 0.001 死于原发肿瘤 40 202(50.3) 2 793(92.3) 37 409(48.6) 死于其他原因 8 094(10.1) 87(2.9) 8 007(10.4) 性别 女 39 115(48.9) 1 270(42.0) 37 845(49.2) < 0.001 男 40 862(51.1) 1 757(58.0) 39 105(50.8) 年龄 18~71岁 48 994(61.3) 2 014(66.5) 46 980(61.1) < 0.001 72~79岁 20 239(25.3) 653(21.6) 19 586(25.5) ≥80岁 10 744(13.4) 360(11.9) 10 384(13.5) 原发部位 肺上叶 47 260(59.1) 1 660(54.8) 45 600(59.3) < 0.001 肺中叶 3 547(4.4) 135(4.5) 3 412(4.4) 肺下叶 23 979(30.0) 882(29.1) 23 097(30.0) 气管及其他 5 191(6.5) 350(11.6) 4 841(6.3) 组织学分类 肺腺癌 7 080(8.9) 503(16.6) 6 577(8.5) < 0.001 鳞状细胞肺癌 25 969(32.5) 884(29.2) 25 085(32.6) 其他 46 928(58.7) 1 640(54.2) 45 288(58.9) 病理分级 高分化 8 762(11.0) 105(3.5) 8 657(11.3) < 0.001 中分化 32 216(40.3) 738(24.4) 31 478(40.9) 低分化 37 629(47.0) 2 102(69.4) 35 527(46.2) 未分化 1 370(1.7) 82(2.7) 1 288(1.7) 肿瘤直径 0.1~2.6 cm 28 456(35.6) 367(12.1) 28 089(36.5) < 0.001 >2.6~ < 5.6 cm 32 425(40.5) 1 388(45.9) 31 037(40.3) ≥5.6 cm 19 096(23.9) 1 272(42.0) 17 824(23.2) 偏侧性 右侧 46 621(58.3) 1 722(56.9) 44 899(58.3) 0.110 左侧 33 356(41.7) 1 305(43.1) 32 051(41.7) T分期 T1 24 798(31.0) 253(8.4) 24 545(31.9) < 0.001 T2 26 698(33.4) 798(26.4) 25 900(33.7) T3 15 063(18.8) 846(27.9) 14 217(18.5) T4 13 418(16.8) 1 130(37.3) 12 288(16.0) N分期 N0 44 166(55.2) 556(18.4) 43 610(56.7) < 0.001 N1 8 440(10.6) 278(9.2) 8 162(10.6) N2 21 033(26.3) 1 503(49.7) 19 530(25.4) N3 6 338(7.9) 690(22.8) 5 648(7.3) 骨转移 无 72 117(90.2) 1 399(46.2) 70 718(91.9) < 0.001 有 7 860(9.8) 1 628(53.8) 6 232(8.1) 脑转移 无 73 612(92.0) 218(72.2) 71 425(92.8) < 0.001 有 6 365(8.0) 840(27.8) 5 525(7.2) 肺转移 无 72 827(91.1) 1 975(65.2) 70 852(92.1) < 0.001 有 7 150(8.9) 1 052(34.8) 6 098(7.9) 原发部位手术 无 38 353(48.0) 2 938(97.1) 35 415(46.0) < 0.001 有 41 624(52.0) 89(2.9) 41 535(54.0) 转移部位手术 无 77 848(97.3) 2 908(96.1) 74 940(97.4) < 0.001 有 2 129(2.7) 119(3.9) 2 010(2.6) 化疗 无 46 379(58.0) 1 150(38.0) 45 229(58.8) < 0.001 有 33 598(42.0) 1 877(62.0) 31 721(41.2) 放疗 无 51 511(64.4) 1 637(54.1) 49 874(64.8) < 0.001 有 28 466(35.6) 1 390(45.9) 27 076(35.2) 中位生存时间/月 28.0(27.5~28.5) 5.0(4.7~5.3) 30.0(29.5~30.5) < 0.001 中位生存时间以中位数(95%置信区间)表示。 表 2 OS和CSS的多因素Cox回归分析
变量(参照) OS CSS HR(95%CI) P HR(95%CI) P 性别(女性) 男性 1.109(1.012~1.216) 0.027 1.106(1.007~1.214) 0.035 年龄(18~71岁) < 0.001 0.001 72~79岁 1.193(1.069~1.331) 0.002 1.171(1.047~1.309) 0.006 ≥80岁 1.260(1.098~1.447) 0.001 1.246(1.083~1.433) 0.002 肿瘤部位(肺上叶) 0.086 — — 肺中叶 0.926(0.745~1.152) 0.492 — — 肺下叶 0.934(0.844~1.034) 0.190 — — 气管及其他 1.134(0.984~1.308) 0.083 — — 组织学分类(肺腺癌) < 0.001 < 0.001 鳞状细胞肺癌 0.999(0.868~1.151) 0.994 1.000(0.866~1.155) 0.999 其他 0.821(0.719~0.937) 0.003 0.825(0.721~0.945) 0.005 病理分级(高分化) < 0.001 0.001 中分化 1.056(0.807~1.381) 0.692 1.057(0.807~1.385) 0.687 低分化 1.301(1.002~1.687) 0.048 1.290(0.993~1.677) 0.057 未分化 1.461(1.004~2.127) 0.048 1.472(1.008~2.150) 0.045 肿瘤直径(0.1~2.6 cm) 0.035 0.047 >2.6~ < 5.6 cm 0.864(0.735~1.016) 0.077 0.867(0.736~1.021) 0.087 ≥5.6 cm 0.971(0.820~1.148) 0.727 0.969(0.817~1.150) 0.721 T分期(T1) 0.055 0.056 T2 1.205(0.982~1.477) 0.074 1.217(0.990~1.497) 0.063 T3 1.219(0.996~1.491) 0.055 1.207(0.980~1.487) 0.076 T4 1.306(1.071~1.591) 0.008 1.313(1.070~1.612) 0.009 骨转移(无) 有 1.317(1.202~1.444) < 0.001 1.312(1.194~1.441) < 0.001 脑转移(无) 有 1.228(1.108~1.360) < 0.001 1.230(1.108~1.365) < 0.001 肺转移(无) — — 有 — — 1.061(0.959~1.174) 0.253 原发部位手术(无) 有 0.558(0.415~0.750) < 0.001 0.556(0.411~0.752) < 0.001 化疗(无) 有 0.436(0.397~0.480) < 0.001 0.436(0.396~0.481) < 0.001 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] CAMPOS-BALEA B, DE CASTRO CARPEÍO J, MASSUTÑ B, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma: an analysis of the SEER database[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2020, 11(11): 3357-3364. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13681
[3] FANG Y J, SU C X. Research progress on the microenvironment and immunotherapy of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with liver metastases[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 893716. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.893716
[4] 孟春柳, 徐利明, 魏佳, 等. 晚期小细胞肺癌和非小细胞肺癌不同转移部位预后意义的比较[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2019, 46(21): 1101-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2019.21.916 [5] LI J, ZHU H G, SUN L, et al. Prognostic value of site-specific metastases in lung cancer: a population based study[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(14): 3079-3086. doi: 10.7150/jca.30463
[6] CHOI M G, CHOI C M, LEE D H, et al. Different prognostic implications of hepatic metastasis according to front-line treatment in non-small cell lung cancer: a real-world retrospective study[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2021, 10(6): 2551-2561. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-206
[7] RⅡHIMÄKI M, HEMMINKI A, FALLAH M, et al. Metastatic sites and survival in lung cancer[J]. Lung Cancer, 2014, 86(1): 78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.07.020
[8] SHAN Q G, FAN Y L, GUO J, et al. Relationship between tumor size and metastatic site in patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: a large SEER-based study[J]. PeerJ, 2019, 7: e7822. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7822
[9] QIAO M, ZHOU F, HOU L K, et al. Efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with different metastases[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(1): 34. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-1471
[10] NOVELLO S, BARLESI F, CALIFANO R, et al. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guide-lines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016(27 suppl 5): v1-v27.
[11] 王森, 魏元东, 赵智毅, 等. 非小细胞肺癌肝转移的危险因素分析及不同疗法的比较[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2016, 20(9): 936-939. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ201609019.htm [12] 孙基峰, 罗婧, 徐利明, 等. 广泛期小细胞肺癌肝转移治疗模式探讨[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2019, 25(6): 577-580. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYK201906008.htm [13] 许田慧, 刘宝刚. 晚期肺癌肝转移的综合治疗进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2019, 27(12): 2200-2203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2019.12.042 [14] ZHU Z F, NI J J, CAI X W, et al. International consensus on radiotherapy in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2022, 11(9): 1763-1795. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-644
[15] MILLER K D, NOGUEIRA L, DEVASIA T, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(5): 409-436. doi: 10.3322/caac.21731
[16] WEN S W, DAI L, WANG L, et al. Genomic signature of driver genes identified by target next-generation sequencing in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncologist, 2019, 24(11): e1070-e1081. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0572
[17] JIANG P P, GENG L Y, MAO Z Y, et al. First-line chemotherapy plus immune checkpoint inhibitors or bevacizumab in advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer without EGFR mutations or ALK fusions[J]. Immunotherapy, 2022: Online ahead of print.
[18] GRANT J M, HERBST S R, GOLDBERG B S, 等. 驱动基因阴性的转移性非小细胞肺癌最佳免疫治疗方案的选择[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2022, 25(7): 555-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ202207018.htm [19] 张国伟, 程瑞瑞, 张国俊, 等. 有或无肝转移的晚期非小细胞肺癌应用纳武利尤单抗的疗效差异: 一项回顾性队列研究[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2021, 29(15): 2615-2619. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXZL202115009.htm [20] 方瑜佳, 周娟, 苏春霞. 非小细胞肺癌肝转移免疫微环境及未来干预策略[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2020, 30(10): 750-758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGAZ202010005.htm [21] SHENG L, GAO J, XU Q, et al. Selection of optimal first-line immuno-related therapy based on specific pathological characteristics for patients with advanced driver-gene wild-type non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2021, 13: 17588359211018537.
[22] CORRAO G, MARVASO G, FERRARA R, et al. Stereotatic radiotherapy in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: combining immunotherapy and radiotherapy with a focus on liver metastases[J]. Lung Cancer, 2020, 142: 70-79.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王娟,倪云峰,刘勇世,滕鑫,菅利华,贠俊茹. 基于T淋巴细胞亚群、肿瘤标志物的非小细胞肺癌患者化疗预后预测模型的构建. 中国医刊. 2025(03): 312-316 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李宏,唐乐,李慧敏,罗琴. 中国人群肺腺癌生存概率列线图的建立与验证:一项基于SEER的大型回顾性队列研究. 新疆医科大学学报. 2024(01): 126-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘建,师金,田国. 基于SEER数据库的年轻肺腺癌晚期患者预后预测及风险分层的模型构建. 解放军医学杂志. 2024(08): 889-896 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李雨玲,张君智,陈璇. IgG和FIB在非小细胞肺癌患者预后预测中的价值. 中国基层医药. 2024(11): 1601-1606 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵璇,王岩,王秀丽,贾慧民. 2011-2021年新疆癌症中心非小细胞肺癌患者预后分析. 中华肿瘤防治杂志. 2023(21): 1293-1300 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
