Research of resourcefulness of main caregivers of stroke patients based on structural equation model and its influencing factors
-
摘要:目的
分析脑卒中患者主要照护者的智谋现状,基于结构方程模型分析智谋及其影响因素间的作用路径与机制。
方法采用便利抽样法选取在银川市3所三级甲等医院神经内科住院的脑卒中患者的主要照护者作为研究对象,最终共纳入308例主要照护者。收集主要照护者的一般人口学资料和智谋量表、中文版知觉压力量表、疲劳量表评估结果,通过主成分分析法提取潜变量,采用AMOS 24.0软件构建脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋影响因素的结构方程模型。
结果脑卒中患者主要照护者的知觉压力得分为(24.98±6.36)分,疲劳得分为(5.31±2.86)分,智谋得分为(83.98±12.85)分; 相关性分析结果显示,知觉压力得分与智谋得分呈负相关(r=-0.313, P < 0.01), 疲劳得分与智谋得分呈负相关(r=-0.305, P < 0.01), 知觉压力得分与疲劳得分呈正相关(r=0.261, P < 0.01)。脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋影响因素的结构方程模型拟合较好,知觉压力对智谋具有最强的直接负向效应(β=-0.33, P < 0.05), 疲劳对智谋具有直接负向效应(β=-0.28, P < 0.05), 并通过知觉压力和社会文化因子中的文化程度和职业产生间接效应,社会文化因子对智谋有直接正向效应(β=0.27, P < 0.05)。
结论脑卒中患者主要照护者的智谋处于中等水平,且受知觉压力、疲劳、职业和文化程度的影响。医护人员应及时评估脑卒中患者主要照护者的知觉压力、疲劳、职业和文化程度,提供多元化的健康宣教途径和个性化的精神支持与物质支持,以减轻主要照护者压力,缓解其疲劳,提高其智谋水平,促进其身心健康。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the current situation of resourcefulness among the main caregivers of stroke patients, and to analyze its action pathway and influencing mechanism by using Structural Equation Model.
MethodsConvenience sampling method was adopted to select the main caregivers of stroke patients hospitalized in the department of neurology of three hospitals with grade Ⅲ level A in Yinchuan City as the research objects, and a total of 308 main caregivers were finally included. The general demographic information, results of Resourcefulness Scale, Chinese version of the Stress Perception Scale and Fatigue Scale were collected. The latent variables were extracted by the principal component analysis. AMOS 24.0 software was used to construct a structural equation model for influencing factors of the intelligence of main caregivers of stroke patients.
ResultsThe scores of perceived stress, fatigue and resourcefulness of the main caregivers of stroke patients were (24.98±6.36), (5.31±2.86) and (83.98±12.85), respectively. Correlation analysis showed that perceived stress score was negatively correlated with intelligence score (r=-0.313, P < 0.01), fatigue score was negatively correlated with intelligence score (r=-0.305, P < 0.01), perceived stress score was positively correlated with fatigue score (r=0.261, P < 0.01). The structural equation model of influencing factors on the wisdom of the main caregivers of stroke patients was well fitted. Perceived stress had the strongest direct negative effect on resourcefulness (β=-0.33, P < 0.05). Fatigue had a direct negative effect on resourcefulness (β=-0.28, P < 0.05), and had an indirect effect through perceived stress and education level and occupation in social and cultural factors. Social and cultural factors had direct positive effects on resourcefulness (β=0.27, P < 0.05).
ConclusionThe resourcefulness of the main caregivers of stroke patients is at a medium level, which is affected by perceived stress, fatigue, occupation and education level. Medical staff should assess primary caregivers of patients with cerebral apoplexy in perceived stress, fatigue, professional and cultural level, provide diversified health education ways and the individuation of spiritual and material support so as to relieve the caregiver stress and fatigue, improve the level of primary caregivers of patients with cerebral apoplexy obtain guidance, and promote their physical and mental health.
-
Keywords:
- stroke /
- primary caregiver /
- resourcefulness /
- influencing factors /
- Structural Equation Model
-
脑卒中是中国成人致死、致残的首位病因,临床发病率较高[1]。约80%的脑卒中患者接受居家照护,其主要照护者承担着照护全过程的责任与义务[2]。对主要照护者而言,长期照护脑卒中患者也是重大应激事件,可严重影响其身心健康[3-4]。主要照护者是指与患者有亲属关系的配偶、父母、子女、兄弟姐妹及家庭其他亲属,不收取劳动报酬且承担大部分照护任务的人[5]。研究[6]指出,主要照护者的身心健康影响着患者的康复效果及预后,故其需要在整个照护过程中具有自我调节能力和认知能力。智谋在应对心理-生理压力反应时具有自我调节能力,是一种有效的认知行为,对个体有正性认知及健康促进作用[7]。智谋是在压力与应对理论和自我控制理论的基础上发展而来,由个人智谋和社会智谋组成,其中个人智谋指个体独立完成事务的能力,社会智谋指个体无法独立完成事务时向外界获得帮助的能力[8]。因此,智谋体现了个体对内外环境的应激所具备的资源以及积极应对的能力。ZAUSZNIEWSKI J A等[9]指出,脑卒中患者主要照护者感知压力较大,对智谋训练的需求较高。本研究以压力与应对理论为指导,基于结构方程模型探讨脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋现状及其影响因素的作用机制,以期为制订脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋的干预策略提供参考依据。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
采用便利抽样法选取2020年12月—2021年8月在银川市3所三级甲等医院神经内科住院的脑卒中患者的主要照护者作为研究对象。纳入标准: ①所照护的患者符合第4届全国脑血管病会议制定的脑卒中诊断标准并经头颅影像学检查(CT或MRI检查)证实者; ②脑卒中患者亲属,年龄≥18岁者; ③在患者住院期间承担主要照护任务(病房疫情期间实施陪护管控,仅允许1位照护者陪护)者; ④意识清楚,沟通无障碍,能基本阅读并理解相关调查问卷内容者; ⑤签署知情同意书且自愿参与本研究者。排除标准: ①所照护的患者伴有严重心、脑、肺等并发症者; ②既往有精神疾病患病史者; ③照护患者期间发生重大疾病或应激事件等者; ④收取照护相关报酬者。根据估算总体均数的样本量计算公式,本研究得出样本量为298, 最终发放调查问卷311份,回收有效问卷308份,有效问卷回收率为99.04%。
1.2 研究工具
1.2.1 一般资料调查问卷
研究者自行设计一般资料调查问卷,内容包括脑卒中患者主要照护者的性别、年龄、与患者关系、职业、工作状态、婚姻状况、文化程度、每天睡眠时间、每天照护患者时间、是否照护其他人及家庭月收入等。
1.2.2 智谋量表
本研究采用由ZAUSZNIEWSKI J A等[8]编制,并由柯熹等[10]翻译的中文版智谋量表,包括2个维度,共28个条目,其中16个条目测量个人智谋, 12个条目测量社会智谋。总分0~140分,得分越高,表示智谋水平越高。该量表Cronbach′s α系数为0.86, 具有较高的信效度。
1.2.3 中文版知觉压力量表
本研究采用杨廷忠[11]汉化的中文版知觉压力量表,包括2个维度(分别为紧张感和失控感)共14个条目。各条目均采用5级计分法,得分越高,表示感知到的压力越大, 0~28分为正常范围, 29~42分为压力较大, 43~56分为压力过大。该量表Cronbach′s α系数为0.78, 信效度较好。
1.2.4 疲劳量表
该量表[12]包括2个维度共14个条目,维度分别为躯体疲劳(第1~8个条目)和脑力疲劳(第9~14个条目)。疲劳总分为躯体疲劳得分与脑力疲劳得分之和,得分越高,表示疲劳感越重。该量表Cronbach′s α系数为0.809, 具有较好的信效度。
1.3 资料收集方法
调查前,所有研究对象表示自愿参加并签署知情同意书; 调查时,研究者向研究对象说明调查目的、意义及问卷填写注意事项,并承诺调查的匿名性与保密性。采用一对一方式收集资料,若研究对象不能自行填写问卷,由研究者逐一询问后协助其填写; 调查后,现场核对信息并回收问卷。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 25.0统计学软件分析数据,采用AMOS 24.0软件构建结构方程模型并进行模型检验。计数资料以[n(%)]描述,比较采用χ2检验; 符合正态分布的计量资料以(x±s)描述,非正态分布的计量资料以[M(P25, P75)]描述; 相关性分析采用Pearson相关分析法或Spearman相关分析法; 脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋的影响因素分析采用独立样本t检验、ANOVA检验; 采用主成分分析法,依据条目因子载荷量和组合的特点划分和命名潜在影响因素。P <0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 不同特征的脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋得分比较
不同年龄、文化程度、职业、工作状态、每天睡眠时间、每天照护患者时间的照护者智谋得分比较,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05); 不同性别、与患者关系、婚姻状况、照护其他人情况、家庭月收入的照护者智谋得分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 不同特征的脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋量表得分比较(x±s)特征 分类 n 占比/% 智谋得分/分 t/F P 性别 男 139 45.13 83.47±13.72 -0.630 0.529 女 169 54.87 84.40±12.10 年龄 18~44岁 206 66.88 85.84±13.32 6.983 0.001 45~59岁 87 28.25 79.90±10.95 ≥60岁 15 4.87 82.13±12.22 与患者关系 配偶 43 13.96 80.98±10.68 0.793 0.530 父母 3 0.97 85.00±20.88 儿女 230 74.68 84.35±12.56 兄弟姐妹 10 3.25 87.10±14.41 其他亲属 22 7.14 84.45±11.89 文化程度 小学及以下 23 7.47 73.13±9.16 10.047 0.001 初中 88 28.57 83.53±12.55 高中或中专 88 28.57 82.47±12.73 大专及以上 109 35.39 87.86±12.34 职业 农民 48 15.58 78.42±11.02 4.553 0.001 工人 86 27.92 83.52±12.26 商贩或个体户 72 23.38 83.50±12.79 机关/事业单位职工 67 21.75 88.36±10.48 其他 35 11.36 83.98±12.85 工作状态 在职 225 73.05 85.11±12.70 4.249 0.015 退休 32 10.39 83.37±12.61 无业或失业 51 16.56 79.39±12.81 婚姻状况 未婚 49 15.91 86.86±14.61 1.802 0.167 已婚 250 81.17 83.56±12.52 离异或丧偶 9 2.92 80.00±10.03 每天睡眠时间 <6 h 59 19.16 81.47±12.45 4.703 0.010 6~8 h 233 75.65 84.04±12.28 >8 h 16 5.19 92.44±15.61 每天照护患者时间 <9 h 59 19.16 81.47±12.45 4.922 0.008 9~16 h 233 75.65 84.04±12.28 >16 h 16 5.19 92.44±15.61 照护其他人 否 282 91.56 83.79±12.97 -0.852 0.395 是 26 8.44 86.04±11.45 家庭月收入 ≤1 000元人民币 16 5.19 82.37±10.60 2.268 0.081 >1 000~ <3 000元人民币 74 24.03 83.01±13.92 3 000~ <5 000元人民币 132 42.86 82.74±12.01 ≥5 000元人民币 86 27.92 87.02±13.21 2.2 主要照护者知觉压力、疲劳与智谋得分
脑卒中患者主要照护者的知觉压力得分为(24.98±6.36)分,其中失控感维度得分(11.23±3.96)分、紧张感维度得分(13.74±3.55)分; 疲劳得分为(5.31±2.86)分,其中躯体疲劳维度得分(3.78±2.14)分、脑力疲劳维度得分(1.53±1.24)分; 智谋得分为(83.98±12.85)分,其中个人智谋维度得分(51.32±8.33)分、社会智谋维度得分(32.66±6.97)分。
2.3 主要照护者知觉压力、疲劳与智谋的相关性分析
相关性分析结果显示,知觉压力得分与智谋得分呈负相关(r=-0.313, P <0.01), 疲劳得分与智谋得分呈负相关(r=-0.305, P <0.01), 知觉压力得分与疲劳得分呈正相关(r=0.261, P <0.01)。
2.4 主要照护者智谋影响因素的结构方程模型构建
2.4.1 模型构建
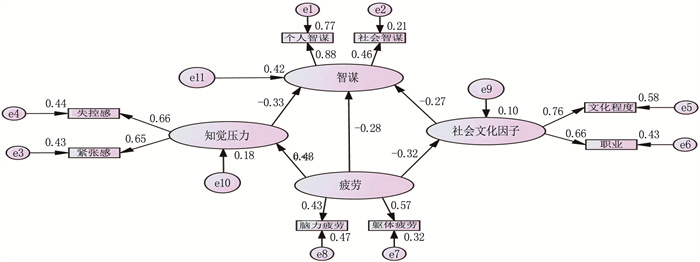
应用Harman单因素检验中的探索性因子分析进行共同方法偏差检验,结果显示,特征根>1的因子共有7个,最大因子解释的变异量为16.44%。经梳理文献,综合考虑研究目的及临床实际情况,本研究选取年龄、职业、工作状态、文化程度、每天睡眠时间、每天照护患者时间这6个单因素分析中差异有统计学意义的特征作为观测变量进行主成分分析,得出KMO检验值为0.588, Bartlett球性检验的χ2值为175.071, P <0.001, 提示数据适合进行主成分分析。利用正交旋转中的方差最大化旋转方法,取特征值>1.0的3个因子(特征值分别为1.181、1.145、1.085), 方差贡献率为68.22%。公因子1命名为社会文化因子,公因子2命名为照护因子,公因子3命名为个人因子,构建结构方程模型潜变量,见表 2。将构建的结构方程模型潜变量和相关性分析中差异有统计学意义的变量纳入结构方程模型,构建脑卒中患者主要照护者影响因素的理论模型。删除无意义的路径(照护因子和个人因子)后(修正指数P>0.05), 得到拟合较好的模型,见图 1。
表 2 脑卒中患者主要照护者变量与赋值潜变量 观察变量 赋值 社会文化因子 职业 农民=1, 工人=2, 商贩/个体户=3, 机关/事业单位职工=4, 其他=5 文化程度 小学及以下=1, 初中=2, 高中或中专=3, 大专及以上=4 照护因子 每天睡眠时间 <6 h=1, 6~8 h=2, >8 h=3 每天照护患者时间 <9 h=1, 9~16 h=2, >16 h=3 个人因子 工作状态 在职=1, 退休=2, 无业或失业=3 年龄 18~44岁=1, 45~59岁=2, ≥60岁=3 2.4.2 路径结果分析及评价
各因素对脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋的影响效应由强至弱依次为知觉压力、疲劳、社会文化因子,见表 3。知觉压力对智谋具有最强的直接负向效应(β=-0.33, P <0.05); 疲劳对智谋具有直接负向效应(β=-0.28, P <0.05), 并通过知觉压力和社会文化因子中的文化程度和职业产生间接效应; 社会文化因子对智谋有直接正向效应(β=0.27, P <0.05)。该模型中,脑卒中患者主要照护者的知觉压力、疲劳、文化程度和职业解释了智谋18.3%的变异量(调整后R2=0.183)。修正后的模型拟合优度结果显示, CMIN/DF=0.431, RMR=0.134, GFI=0.995, NFI=0.983, RFI=0.968, IFI=1.024, CFI=1.000, RMSEA <0.001, 表明模型拟合较好。
表 3 脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋影响因素的路径分析路径 直接效应 间接效应 总效应 β P β P β P 知觉压力→智谋 -0.33 <0.05 — — -0.33 <0.05 疲劳→智谋 -0.28 <0.05 -0.23 <0.05 -0.51 <0.05 社会文化因子→智谋 0.27 <0.05 — — 0.27 <0.05 3. 讨论
本研究结果显示,脑卒中患者主要照护者的智谋得分为(83.98±12.85)分,处于中等水平,与相关研究[13-14]结果相似。分析可能原因: ①本研究中,脑卒中患者主要照护者年龄多为18~44岁,学习新知识的能力较强,但高频率的照护工作占据了其日常活动与休息时间,且大部分照护者为患者子女,本身承担着较多的照护家庭的任务,引起照护者角色冲突。多重的照护压力会使主要照护者分身乏术,逐步破坏其心理平衡机制,影响智谋发挥。②脑卒中患者主要照护者个人智谋高于社会智谋得分。照护者受中国“百善孝为先”传统理念的影响,认为照护父母是自身分内之事,不便寻求外界的帮助和支持,故而自身照护技能、情感支持和经济支持等多方面需求得不到满足[15]。③本研究中,主要照护者职业占比最高的为工人,忙碌的工作可能使照护者不能保证专心学习患者疾病相关知识和照护技能。因此,临床医护人员不仅应关注患者的健康状况,还应及时关注脑卒中患者主要照护者的身心健康和需求,可通过微信、电话或家庭随访等途径提供必要支持,以提升主要照护者的智谋水平。
本研究结果显示,知觉压力与脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋呈负相关,即压力得分越高,智谋得分越低,与KOBISKE K R等[16]研究结果一致。根据压力与应对理论,个体应对压力性事件时,会调动自身的内外部资源[4]。智谋是心理健康最重要的预测因子[17], 相当于个体内外部资源。智谋与精神需求之间存在相互作用[18]。照护者受自我价值理念的影响,不愿主动向其他人寻求精神与物质方面的帮助和支持,长期照护可导致心理压力无法缓解,进而降低照护信心。医护人员应向患者及其家庭其他成员讲述主要照护者处境,并鼓励患者及其他家庭成员多关心和支持主要照护者,让照护者重拾信心,感受自我存在价值,体会付出的意义。医护人员可通过访谈或远程网络等交流方式了解主要照护者的需求,尽量满足其需求,还可开通情感热线,鼓励患者及照护者表达内心想法,抒发内心情感。此处,医护人员可建议脑卒中患者主要照护者独立进行祈祷或冥想,促进内心平和,减小心理压力,从而减轻负性情绪。
疲劳指个体自身感知的一种强烈而持久的倦怠感及无力感[19], 是脑卒中患者主要照护者认知行为反应不良的重要表现[20]。本研究结果显示,知觉压力在疲劳与智谋之间存在中介效应,即疲劳症状越重表现出沉重的压力以及较低的智谋水平。由此说明,智谋得分高的主要照护者可通过个人应对以及寻求帮助等方式缓解心理压力,从而改善身心疲劳状况[21-22]。另外,脑卒中患者主要照护者社会文化因子是疲劳与智谋的中介变量,文化程度较低和(或)无职业的主要照护者因内外部资源经常受限,在照护过程中易感到身心疲惫,导致认知行为退缩,影响心理健康。医护人员不仅应关注脑卒中患者主要照护者的身心健康状况,还应根据个体的社会文化因子(职业和文化程度)评估其认知需求,并根据不同职业和文化程度实施个性化的针对性护理干预措施,及时评估其疲劳水平,采取对应措施缓解其躯体疲劳和认知疲劳,以提高照护者的智谋水平,改善其生活质量。
本研究结果显示,脑卒中患者主要照护者的文化程度和职业是其智谋的主要影响因素。文化程度与智谋呈正相关,即文化程度越高,智谋得分越高,与AU T Y等[23]研究结果一致。分析可能原因,文化程度较高的主要照护者,阅读能力和理解能力较强,与医护人员的通交流顺畅,容易理解、掌握照护知识和技能,而文化程度较低的主要照护者,缺乏知识理解能力和获取知识的路径,容易产生挫败感和无助感。此外,主要照护者若为机关/事业单位职工,相较于农民可能拥有更多的人力资源和社会资源,在面对突发事件时,应对能力灵活,能够借助各种内外部资源应对和适应各种应激事件[24]。医护人员应根据脑卒中患者主要照护者的文化程度和职业选择针对性干预策略,对于文化程度较高或就职机关/事业单位的主要照护者,可采取指导-合作型方式,提供多元化教育方式(包括推送小程序或推荐书籍、网课等多种途径),提升其疾病认知水平; 对于文化程度较低或为农民的主要照护者,可通过线下面对面沟通交流或微信发送相关小视频等简单易懂的方式进行宣教,同时帮助其寻求社会援助,以提升其智谋水平。
结构方程模型最大的优点在于可同时处理许多因变量,尤其是变量之间存在多层关系时非常实用[25]。多元线性回归模型不能很好地拟合非线性数据,在建立回归模型前,需要先判断各自变量之间是否存在线性关系[26], 而且实际应用过程中往往存在误用现象,需要特别注意[27]。鉴于此,本研究基于文献分析结果和压力与应对理论构建脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋影响因素的结构方程模型,弥补了单因素与多因素线性回归统计方法的不足,分析了知觉压力、疲劳和文化程度与职业对智谋的影响,明确了脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋的预测因素以及各因素间的路径关系,或可为制订智谋干预策略及提升智谋水平提供理论依据。
-
表 1 不同特征的脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋量表得分比较(x±s)
特征 分类 n 占比/% 智谋得分/分 t/F P 性别 男 139 45.13 83.47±13.72 -0.630 0.529 女 169 54.87 84.40±12.10 年龄 18~44岁 206 66.88 85.84±13.32 6.983 0.001 45~59岁 87 28.25 79.90±10.95 ≥60岁 15 4.87 82.13±12.22 与患者关系 配偶 43 13.96 80.98±10.68 0.793 0.530 父母 3 0.97 85.00±20.88 儿女 230 74.68 84.35±12.56 兄弟姐妹 10 3.25 87.10±14.41 其他亲属 22 7.14 84.45±11.89 文化程度 小学及以下 23 7.47 73.13±9.16 10.047 0.001 初中 88 28.57 83.53±12.55 高中或中专 88 28.57 82.47±12.73 大专及以上 109 35.39 87.86±12.34 职业 农民 48 15.58 78.42±11.02 4.553 0.001 工人 86 27.92 83.52±12.26 商贩或个体户 72 23.38 83.50±12.79 机关/事业单位职工 67 21.75 88.36±10.48 其他 35 11.36 83.98±12.85 工作状态 在职 225 73.05 85.11±12.70 4.249 0.015 退休 32 10.39 83.37±12.61 无业或失业 51 16.56 79.39±12.81 婚姻状况 未婚 49 15.91 86.86±14.61 1.802 0.167 已婚 250 81.17 83.56±12.52 离异或丧偶 9 2.92 80.00±10.03 每天睡眠时间 <6 h 59 19.16 81.47±12.45 4.703 0.010 6~8 h 233 75.65 84.04±12.28 >8 h 16 5.19 92.44±15.61 每天照护患者时间 <9 h 59 19.16 81.47±12.45 4.922 0.008 9~16 h 233 75.65 84.04±12.28 >16 h 16 5.19 92.44±15.61 照护其他人 否 282 91.56 83.79±12.97 -0.852 0.395 是 26 8.44 86.04±11.45 家庭月收入 ≤1 000元人民币 16 5.19 82.37±10.60 2.268 0.081 >1 000~ <3 000元人民币 74 24.03 83.01±13.92 3 000~ <5 000元人民币 132 42.86 82.74±12.01 ≥5 000元人民币 86 27.92 87.02±13.21 表 2 脑卒中患者主要照护者变量与赋值
潜变量 观察变量 赋值 社会文化因子 职业 农民=1, 工人=2, 商贩/个体户=3, 机关/事业单位职工=4, 其他=5 文化程度 小学及以下=1, 初中=2, 高中或中专=3, 大专及以上=4 照护因子 每天睡眠时间 <6 h=1, 6~8 h=2, >8 h=3 每天照护患者时间 <9 h=1, 9~16 h=2, >16 h=3 个人因子 工作状态 在职=1, 退休=2, 无业或失业=3 年龄 18~44岁=1, 45~59岁=2, ≥60岁=3 表 3 脑卒中患者主要照护者智谋影响因素的路径分析
路径 直接效应 间接效应 总效应 β P β P β P 知觉压力→智谋 -0.33 <0.05 — — -0.33 <0.05 疲劳→智谋 -0.28 <0.05 -0.23 <0.05 -0.51 <0.05 社会文化因子→智谋 0.27 <0.05 — — 0.27 <0.05 -
[1] WANG Y J, LI Z X, GU H Q, et al. China Stroke Statistics: an update on the 2019 report from the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in Neurological Diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, the Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and Institute for Global Neuroscience and Stroke Collaborations[J]. Stroke Vasc Neurol, 2022, 7(5): 415-450. doi: 10.1136/svn-2021-001374
[2] OKOYE E C, OKORO S C, AKOSILE C O, et al. Informal caregivers' well-being and care recipients' quality of life and community reintegration-findings from a stroke survivor sample[J]. Scand J Caring Sci, 2019, 33(3): 641-650. doi: 10.1111/scs.12657
[3] LOBO E H, FRØLICH A, KENSING F, et al. mHealth applications to support caregiver needs and engagement during stroke recovery: a content review[J]. Res Nurs Health, 2021, 44(1): 213-225. doi: 10.1002/nur.22096
[4] 张旭, 任蔚虹, 泮燕红. 家庭赋权方案对首发脑卒中患者主要照顾者的影响研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(2): 133-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHHL201802001.htm [5] 田月. 脑卒中患者家庭主要照顾者焦虑现状及影响因素研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2021. [6] JOO H, LIANG D. Economic burden of informal care attributable to stroke among those aged 65 years or older in China[J]. Int J Stroke, 2017, 12(2): 205-207. doi: 10.1177/1747493016675501
[7] 盛丽敏. 住院结直肠癌患者智谋现状及影响因素的研究[D]. 湖州: 湖州师范学院, 2022. [8] ZAUSZNIEWSKI J A, LAI C Y, TITHIPHONTUMRONG S. Development and testing of the resourcefulness scale for older adults[J]. J Nurs Meas, 2006, 14(1): 57-68. doi: 10.1891/jnum.14.1.57
[9] ZAUSZNIEWSKI J A, SWEETKO J S, SHE H Y, et al. Documenting the need for teaching resourcefulness skills to family caregivers[J]. Appl Nurs Res, 2022, 67: 151627. doi: 10.1016/j.apnr.2022.151627
[10] 柯熹, 吴美华, 刘雅清, 等. 中文版智谋量表信效度分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2015, 21(15): 1737-1740. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2907.2015.15.001 [11] 杨廷忠. 社会转型中城市人群心理压力研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2002, 23(6): 473-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHLX200206023.htm [12] CHALDER T, BERELOWITZ G, PAWLIKOWSKA T, et al. Development of a fatigue scale[J]. J Psychosom Res, 1993, 37(2): 147-153. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(93)90081-P
[13] BEKHET A K. Effects of positive cognitions and resourcefulness on caregiver burden among caregivers of persons with dementia[J]. Int J Ment Health Nurs, 2013, 22(4): 340-346. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0349.2012.00877.x
[14] 王冬华, 马娜, 张赣, 等. 急诊科护士智谋对攻击及暴力管理态度的影响[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2020, 37(11): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFHL202011011.htm [15] UGUR H G, ERCI B. The effect of home care for stroke patients and education of caregivers on the caregiver burden and quality of life[J]. Acta Clin Croat, 2019, 58(2): 321-332.
[16] KOBISKE K R, BEKHET A K, GARNIER-VILLARREAL M, et al. Predeath grief, resourcefulness, and perceived stress among caregivers of partners with young-onset dementia[J]. West J Nurs Res, 2019, 41(7): 973-989. doi: 10.1177/0193945918806689
[17] GRAHAM K, BIRT L, MACGREGOR A, et al. "It's my own fault": accounts and consequences of falling when living with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Musculoskelet Care, 2019, 17(4): 346-353. doi: 10.1002/msc.1426
[18] ZAUSZNIEWSKI J A, HERBELL K, BURANT C. Is there more to resourcefulness than personal and social skills[J]. West J Nurs Res, 2019, 41(3): 372-387. doi: 10.1177/0193945918790930
[19] AARONSON L S, TEEL C S, CASSMEYER V, et al. Defining and measuring fatigue[J]. Image J Nurs Scholarsh, 1999, 31(1): 45-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.1999.tb00420.x
[20] PATTYN N, VAN CUTSEM J, DESSY E, et al. Bridging exercise science, cognitive psychology, and medical practice: is cognitive fatigue a remake of the emperor's new clothes[J]. Front Psychol, 2018, 9: 1246. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01246
[21] VAN DER VELDE M Y, AERDEN L A M, VAN OORT A, et al. Caregiver strain and fatigue are independent determinants of anxiety among patients early after stroke[J]. Neuropsychol Rehabil, 2022: 1-12.
[22] 周彩峰, 李雅楠, 王瑞霞, 等. 脑瘫患儿父母疲劳状况及影响因素研究[J]. 中国护理管理, 2017, 17(12): 1669-1673. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLHL201712027.htm [23] AU T Y, ZAUSZNIEWSKI J A, KING T M. Health-seeking behaviors and sexuality in rectal cancer survivors in Taiwan: associations with spirituality and resourcefulness[J]. Oncol Nurs Forum, 2012, 39(5): E390-E397.
[24] IŞSEVER O, BEKTAS M. Effects of learned resourcefulness, work-life quality, and burnout on pediatric nurses' intention to leave job[J]. Perspect Psychiatr Care, 2021, 57(1): 263-271.
[25] 王惠文, 张瑛. 结构方程模型的预测建模方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2007, 33(4): 477-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJHK200704022.htm [26] 钱莹, 方秀男. 多元线性回归模型及实例应用[J]. 中国科技信息, 2022, 11(4): 73-74. [27] 梁英, 张玉海. 多元线性回归方法的正确应用和表达[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2020, 28(2): 230-232. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 刘长秀,乔桂圆. 智谋水平在护士感知压力与快感缺失间的中介效应. 中国健康心理学杂志. 2025(02): 281-286 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄雪玉,刘素娟,吴柳清. 基于结构方程模型的VTE患者抗凝延续性药学服务应用研究. 生命科学仪器. 2024(04): 82-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李吉博,冯永文,吴文峰,范学政,李海霞. 白术内酯Ⅲ对自发性高血压大鼠脑卒中的影响及机制研究. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(22): 71-76 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号

