The value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio combined with mean platelet volume-to-platelet count ratio in predicting the prognosis of patients with septic shock
-
摘要:目的
探讨早期外周血中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR)、平均血小板体积与血小板计数比值(MPV/PLT)对感染性休克患者预后的评估价值。
方法回顾性分析112例住院治疗的感染性休克患者的临床资料,根据28 d预后情况分为存活组69例和死亡组43例。比较2组患者年龄、性别、入院时休克指数、氧合指数、C反应蛋白(CRP)、降钙素原(PCT)、白细胞(WBC)、血乳酸(Lac)、急性生理学与慢性健康状况评分系统Ⅱ(APACHEⅡ)评分、序贯器官衰竭评估(SOFA)评分、D-二聚体等临床资料和入院24 h内NLR、MPV/PLT。绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,评估各项指标对感染性休克患者28 d死亡风险的预测价值;采用多因素Logistic回归分析法分析感染性休克患者预后的危险因素;采用Kaplan-Meier生存曲线分析不同NLR-MPV/PLT评分与总生存时间的相关性。
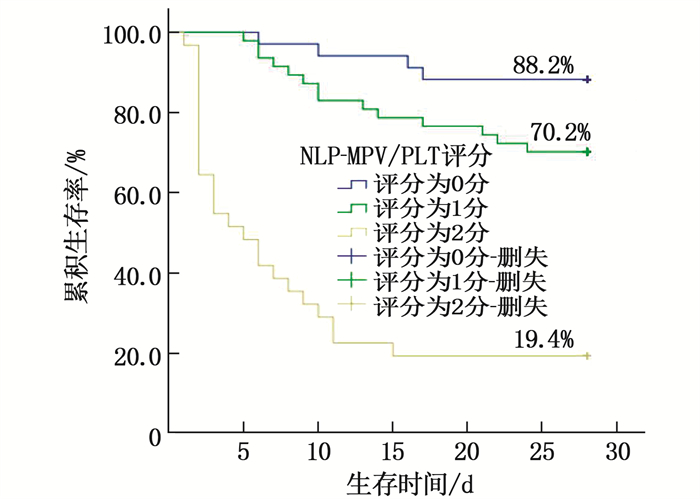
结果2组患者年龄、性别、休克指数、氧合指数、CRP比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);死亡组NLR、MPV/PLT、WBC、PCT、Lac、D-二聚体、APACHEⅡ评分、SOFA评分高于存活组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。NLR预测患者死亡风险的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.724,当最佳截断值为12.49时,敏感度为74.4%,特异度为68.1%;MPV/PLT预测患者死亡风险的AUC为0.731,当最佳截断值为0.10时,敏感度为74.4%,特异度为69.6%。NLR、MPV/PLT、WBC、PCT、Lac、D-二聚体是感染性休克患者28 d死亡的独立影响因素(P < 0.05)。根据NLR-MPV/PLT评分将感染性休克患者分为0分组、1分组、2分组,其28 d累积生存率分别为88.2%、70.2%、19.4%,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论早期NLR、MPV/PLT对感染性休克患者的预后具有较高的预测价值,可作为有效而简便的评估指标用于急诊患者的早期诊断和后续治疗的临床指导。
-
关键词:
- 感染性休克 /
- 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值 /
- 平均血小板体积与血小板计数比值 /
- 预后
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the value of early peripheral blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) combined with mean platelet volume-to-platelet count ratio (MPV/PLT) in evaluating the prognosis in patients with septic shock.
MethodsA total of 112 patients with infectious stroke who were hospitalized were retrospectively selected. According to the prognosis of the patients within 28 days, they were divided into survival group(n=69) and death group (n=43). Age, gender, shock index, oxygenation index, C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), white blood cell (WBC), lactic acid (Lac), acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ(APACHEⅡ) score, sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score, D-dimer, NLR and MPV/PLT within 24 hours after admission were recorded. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to evaluate the clinical predictive value of various indicators for the 28-day mortality risk of patients with septic shock. Multivariate Logistic regression was used to analyze the risk factors for the prognosis of patients with septic shock. Kaplan-Meier survival curve was used to analyze the correlations of different NLR-MPV/PLT scores with overall survival.
ResultsThere were no significant differences in age, gender, shock index, oxygenation index, and CRP between the two groups (P>0.05). Compared with the survival group, NLR, MPV/PLT, WBC, PCT, Lac, D-dimer, APACHEⅡ score and SOFA score in the death group were higher than those in the control group(P < 0.05). The area under the curve (AUC) of NLR in predicting death risk was 0.724, when the optimal cut-off value was 12.49, the sensitivity was 74.4% and the specificity was 68.1%. The AUC for MPV/PLT in predicting death risk was 0.731, with a sensitivity of 74.4% and specificity of 69.6% when the optimal cut-off value was 0.10. NLR, MPV/PLT, WBC, PCT, Lac and D-dimer were independent influencing factors of death in septic shock patients at 28 d (P < 0.05). Patients with septic shock were divided into 0 score group, one score group, two scores group according to NLR-MPV/PLT score, the 28-day cumulative survival rates were 88.2%, 70.2% and 19.4%, respectively(P < 0.05).
ConclusionEarly NLR and MPV/PLT have high predictive value for the prognosis of septic shock patients, which can be used as effective and simple evaluation index for early diagnosis of emergency patients and clinical guidance for follow-up treatment.
-
-
表 1 存活组与死亡组患者临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)][M(P25, P75)]
指标 存活组(n=69) 死亡组(n=43) χ2/t/z P 年龄/岁 69.13±13.83 71.56±13.76 -0.905 0.376 性别 男 36(52.17) 26(60.47) 0.737 0.391 女 33(47.83) 17(39.53) 既往病史 高血压病 48(69.57) 25(58.14) 1.524 0.217 糖尿病 21(30.43) 15(34.88) 0.240 0.624 冠心病 19(27.54) 10(23.26) 0.253 0.615 休克指数 1.34±0.18 1.38±0.21 -1.122 0.409 氧合指数 266.09±42.31 251.58±52.63 1.605 0.111 CRP/(mg/L) 95.43±17.19 100.50±16.63 -1.563 0.121 WBC/(×109/L) 12.09±5.97 15.29±7.03 -2.572 0.011 PCT/(ng/mL) 44.37±20.64 52.99±18.58 -2.233 0.028 Lac/(mmol/L) 5.24±2.55 6.81±2.77 -3.055 0.003 D-二聚体/(ng/mL) 1 460.00(777.00, 2 598.00) 3 491.00(1 646.00, 6 249.00) -3.309 0.001 NLR 10.95±6.06 15.04±4.53 -3.816 0.001 MPV/PLT 0.09±0.05 0.13±0.06 -3.578 0.001 APACHEⅡ评分/分 21.90±4.61 24.26±3.19 -2.942 0.004 SOFA评分/分 9.52±2.01 10.63±2.63 -2.512 0.013 CRP: C反应蛋白; WBC: 白细胞; PCT: 降钙素原; Lac: 乳酸; NLR: 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值;
MPV/PLT: 平均血小板体积与血小板计数比值; APACHEⅡ: 急性生理学与慢性健康状况评分系统Ⅱ;
SOFA: 序贯器官衰竭评估。表 2 各项指标对感染性休克患者28 d死亡风险的预测价值
指标 AUC 敏感度/% 特异度/% 截断值 P 95%CI 年龄/岁 0.552 79.1 33.3 65.50 0.360 0.442~0.661 休克指数 0.546 14.0 97.1 1.65 0.411 0.435~0.658 氧合指数 0.407 11.6 94.2 320.50 0.099 0.295~0.519 CRP/(mg/L) 0.570 72.1 43.5 92.23 0.214 0.462~0.678 WBC/(×109/L) 0.626 65.1 60.9 13.05 0.026 0.519~0.732 PCT/(ng/mL) 0.631 93.0 33.3 29.00 0.020 0.528~0.734 Lac/(mmol/L) 0.685 65.1 71.0 6.15 0.001 0.583~0.786 D-二聚体/(ng/mL) 0.706 58.1 81.2 3 108.50 0.001 0.601~0.811 NLR 0.724 74.4 68.1 12.49 0.001 0.631~0.817 MPV/PLT 0.731 74.4 69.6 0.10 0.001 0.638~0.823 APACHEⅡ评分/分 0.665 60.5 66.7 23.50 0.003 0.564~0.765 SOFA评分/分 0.616 67.4 56.5 9.50 0.040 0.507~0.725 表 3 感染性休克患者28 d死亡风险的多因素Logistic回归分析
因素 回归系数 标准误 Wald P OR 95%CI WBC 3.079 1.026 9.001 0.003 21.739 2.908~162.501 SOFA评分 0.686 0.640 1.150 0.284 1.986 0.567~6.957 APACHEⅡ评分 0.243 0.628 0.149 0.699 1.275 0.373~4.360 PCT 1.772 0.882 4.039 0.044 5.885 1.045~33.149 Lac 1.812 0.639 8.048 0.005 6.122 1.751~21.406 D-二聚体 1.366 0.654 4.360 0.037 3.921 1.087~14.137 NLR 1.781 0.627 8.083 0.004 5.938 1.739~20.274 MPV/PLT 1.989 0.644 9.531 0.002 7.308 2.067~25.833 -
[1] EVANS L, RHODES A, ALHAZZANI W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2021, 47(11): 1181-1247. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y
[2] CHIU C, LEGRAND M. Epidemiology of sepsis and septic shock[J]. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol, 2021, 34(2): 71-76. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000958
[3] HWANG S Y, SHIN T G, JO I J, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in critically-ill septic patients[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2017, 35(2): 234-239. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.10.055
[4] 赵雪, 周坤鹏, 李鹏飞, 等. 早期平均血小板体积变化对脓毒症休克患者预后的预测价值[J]. 中华老年多器官疾病杂志, 2021, 20(5): 326-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLQG202105002.htm [5] 程宁宁, 樊尚荣. "2016年脓毒症和感染性休克处理国际指南"解读[J]. 中华产科急救电子杂志, 2017, 6(3): 180-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHCJ201703012.htm [6] CECCONI M, EVANS L, LEVY M, et al. Sepsis and septic shock[J]. The Lancet, 2018, 392(10141): 75-87. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30696-2
[7] 商娜. 脓毒症流行病学研究[J]. 中国急救医学, 2013, 33(1): 8-12. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90031-1016277067.htm [8] SARl R, KARAKURT Z, AY M, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of treatment response and mortality in septic shock patients in the intensive care unit[J]. Turk J Med Sci, 2019, 49(5): 1336-1349. doi: 10.3906/sag-1901-105
[9] LIBERSKI P S, SZEWCZYK M, KRZYCH Ł J. Haemogram-derived indices for screening and prognostication in critically ill septic shock patients: a case-control study[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2020, 10(9): 638. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10090638
[10] LUBIS B, HASBY A Y, PUTRA A O, et al. Hubungan Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) terhadap mortalitas pasien sepsis di unit perawatan intensif RSUP Haji Adam Malik Pada Tahun 2018[J]. Maj Anest Cri Care, 2021, 39(1): 12-18.
[11] KIM C H, KIM S J, LEE M J, et al. An increase in mean platelet volume from baseline is associated with mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0119437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119437
[12] AL HARBI G, CHAARI A. Platelets parameters in septic shock: clinical usefulness and prognostic value[J]. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis, 2020, 31(7): 421-425. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000937
[13] 林怀德, 周稳兰, 朱蔚岗. 糖皮质激素治疗对感染性休克患者免疫炎症状态及预后的影响[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2021, 41(11): 2543-2549. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYSB202111008.htm [14] STIEL L, MEZIANI F, HELMS J. Neutrophil activation during septic shock[J]. Shock, 2018, 49(4): 371-384. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000980
[15] TANG D L, WANG H C, BILLIAR T R, et al. Emerging mechanisms of immunocoagulation in sepsis and septic shock[J]. Trends Immunol, 2021, 42(6): 508-522. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.04.001
[16] GORECKI G, COCHIOR D, MOLDOVAN C, et al. Molecular mechanisms in septic shock (Review)[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(4): 1161. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10595
[17] 庄雪明, 王诗波, 虞大为, 等. 脓毒性休克患者抗菌肽LL-37与降钙素原联合检测价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(5): 96-100. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20201396 [18] CARVELLI J, PIPEROGLOU C, BOURENNE J, et al. Imbalance of circulating innate lymphoid cell subpopulations in patients with septic shock[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2179. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02179
[19] 许晓兰, 王海霞, 吴晓燕, 等. 早期感染性休克相关性血小板减少症的危险因素及对预后的影响[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2021, 33(8): 938-943. [20] VARDON-BOUNES F, GARCIA C, PITON A, et al. Evolution of platelet activation parameters during septic shock in intensive care unit[J]. Platelets, 2022, 33(6): 918-925.





 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
