Evaluation of serum amyloid A combined with polyligand proteosan-1 in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by sepsis and predictive value for prognosis
-
摘要:目的
分析血清淀粉样蛋白A(SAA)联合多配体蛋白聚糖-1(SDC-1)对脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征病情评估及预后预测价值。
方法选择158例脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者为研究对象,根据柏林定义将患者分为轻中度组[氧合指数(OI)>100 mmHg]和重度组(OI≤100 mmHg)。检测所有患者血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平,分析患者血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平与OI的关系。同时,根据患者肺水肿严重程度不同,将158例脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者分为轻度肺水肿组(血管外肺水指数≤10 mL/kg)和重度肺水肿组(血管外肺水指数>10 mL/kg), 比较不同肺水肿程度患者血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平。观察脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者28 d后预后情况,并根据预后结果分为病死组与存活组。使用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析血清SAA联合SDC-1预测脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者病死的效能。
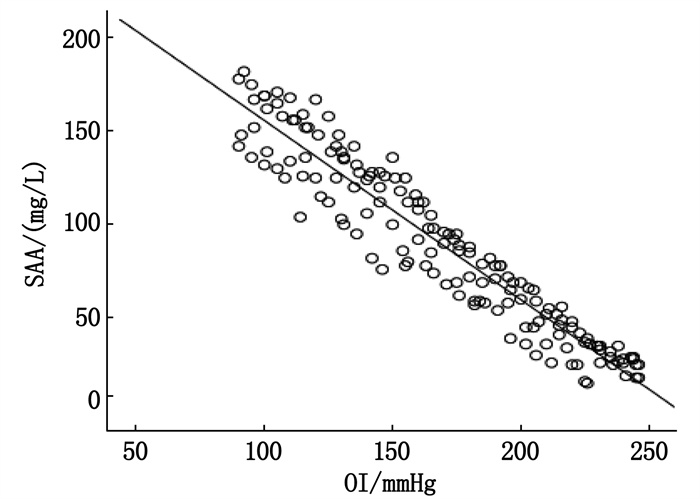
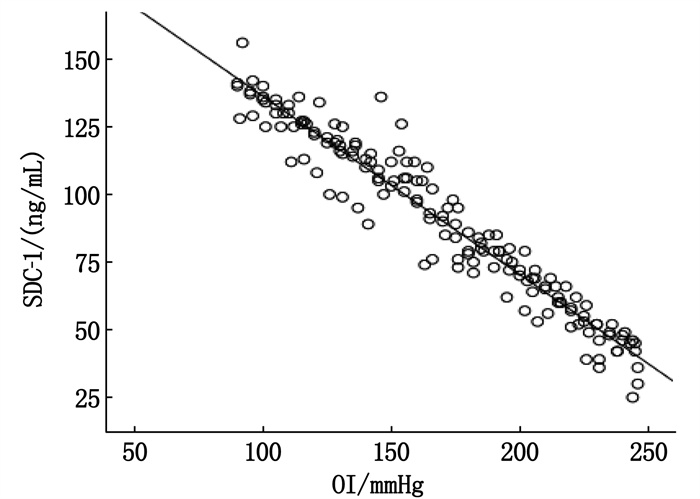
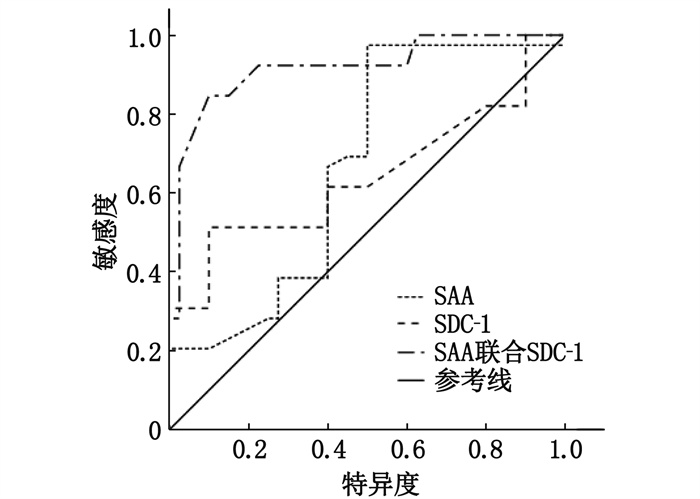
结果重度组血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平均高于轻中度组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 经Pearson相关性分析,脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平与OI呈负相关(r=-0.951、-0.967, P < 0.05); 重度肺水肿组血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平均高于轻度肺水肿组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 158例脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者中,治疗28 d后死亡36例,占22.78%; 病死组治疗前及治疗72 h血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平均高于存活组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 经ROC曲线分析,血清SAA联合SDC-1预测脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者病死的敏感度为92.48%、特异度为68.09%, ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.918。
结论血清SAA、SDC-1与脓毒症所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征病情严重程度有关,两者联合预测的预后不良效能较好,值得进一步研究应用。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the value of serum amyloid A(SAA) combined with polyligand proteosan-1(SDC-1) in the assessment of disease conditions and in predicting prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by sepsis.
MethodsA total of 158 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to sepsis were selected as study subjects. According to the Berlin definition, the patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome were divided into mild to moderate group[oxygenation index(OI)>100 mmHg] and severe group (OI≤100 mmHg). The expression levels of SAA and SDC-1 in serum of all patients were detected, and the relationships of the expression levels of SAA and SDC-1 with OI in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome were analyzed. According to the severity of pulmonary edema, 158 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by sepsis were divided into mild pulmonary edema group (extravascular pulmonary edema edema ≤10 mL/kg) and severe pulmonary edema group (extravascular pulmonary edema edema >10 mL/kg), and the expression levels of SAA and SDC-1 in serum of patients with different degrees of pulmonary edema were compared. The prognosis of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome after 28 days was observed and they were divided into death group and survival group according to prognosis results. The predictive efficacy of serum SAA combined with SDC-1 in predicting death of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome was analyzed by receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC).
ResultsThe serum levels of SAA and SDC-1 in the severe group were higher than those in mild and moderate group, and the difference was significant(P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that the expression levels of SAA and SDC-1 in the serum of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome were negatively correlated with OI(r=-0.951 and -0.967, P < 0.05). The levels of SAA and SDC-1 in severe pulmonary edema group were higher than those in mild pulmonary edema group (P < 0.05). Among 158 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, 36(22.78%) died after 28 days of treatment. The expression levels of SAA and SDC-1 in serum of the death group were higher than those of the survival group before treatment and 72 h after treatment (P < 0.05). According to ROC curve analysis, the sensitivity and specificity of serum SAA combined with SDC-1 to predict death in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome were 92.48% and 68.09%, and the area under ROC curve(AUC) was 0.918.
ConclusionSerum SAA and SDC-1 are related to the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by sepsis, the combined effect of SAA and SDC-1 is better in predicting poor prognosis, which is worthy of further study and application.
-
-
表 1 轻中度组与重度组血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平比较(x±s)
组别 n SAA/(mg/L) SDC-1/(ng/mL) 轻中度组 93 56.38±5.81 63.43±8.17 重度组 65 101.43±12.59* 99.72±11.05* SAA: 淀粉样蛋白A; SDC-1: 多配体蛋白聚糖-1。
与轻中度组比较, *P < 0.05。表 2 不同肺水肿程度患者血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平比较(x±s)
组别 n SAA/(mg/L) SDC-1/(ng/mL) 轻度肺水肿组 83 58.68±6.43 61.46±7.19 重度肺水肿组 75 98.72±11.04* 101.52±12.78* 与轻度肺水肿组比较, *P < 0.05。 表 3 病死组与存活组治疗前及治疗72 h血清SAA、SDC-1表达水平比较(x±s)
组别 n SAA/(mg/L) SDC-1/(ng/mL) 治疗前 治疗72 h 治疗前 治疗72 h 存活组 122 57.81±6.83 32.46±3.75 68.78±6.92 40.41±4.16 病死组 36 130.45±16.07* 134.82±18.96* 113.54±13.76* 116.25±15.72* 与存活组比较, *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 王玉, 黄栋, 梁宗安. 降钙素原与白蛋白比值对急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者预后的预测价值[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2020, 19(3): 240-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHW202003010.htm [2] VILLAR J, FERRANDO C, MARTÍNEZ D, et al. Dexamethasone treatment for the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2020, 8(3): 267-276. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30417-5
[3] 王丽姝, 莫玉珍, 王锋, 等. 微小RNA-215调控TLR4/NF-κB信号通路在急性呼吸窘迫综合征炎症反应中的作用[J]. 广西医学, 2021, 43(18): 2202-2208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYYX202118013.htm [4] 中国中西医结合学会检验医学专业委员会. 血清淀粉样蛋白A在感染性疾病中临床应用的专家共识[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2019, 42(3): 186-192. [5] 高嵩, 吴丁烨, 高飞, 等. 多配体聚糖-1检测联合肺部超声评估ARDS患者血管外肺水的程度[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2021, 33(8): 990-993. [6] FORCE ADT, RANIERI VM, RUBENFELD GD, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition[J]. JAMA, 2012, 307(23): 2526-2533.
[7] 中华医学会重症医学分会. 急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征诊断和治疗指南(2006)[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2007, 16(4): 343-349. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK200701000.htm [8] 叶红, 纪勤炯, 张凌, 等. 老年急性冠脉综合征患者血清淀粉样蛋白A和超敏C反应蛋白水平与冠状动脉病变程度的关系[J]. 中国临床保健杂志, 2021, 24(1): 70-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZBJ202101021.htm [9] 马建永, 于丽侠, 张海旺, 等. 感染性休克患者治疗前后血清血管附黏蛋白-1与血浆多配体蛋白聚糖-1变化及其临床意义[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2020, 21(9): 1018-1021. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYC202009017.htm [10] HODGIN K S, JONES C L, YOUNGER J W. Fatigue and Pain Severity in Gulf War Illness Is Associated With Changes in Inflammatory Cytokines and Positive Acute Phase Proteins[J]. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 2022, 64(11): 905-911.
[11] WEI Y, WANG S, WANG D, et al. Expression and clinical significance of serum amyloid A and interleukin?6 in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 2020, 19(3): 2089-2094.
[12] 张涛, 李娟. 血清suPAR及多配体蛋白聚糖4水平与社区获得性肺炎严重程度和预后的相关性研究[J]. 中国医刊, 2020, 55(2): 195-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYI202002024.htm [13] VIETRI L, BENNETT D, CAMELI P, et al. Serum amyloid A in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Respir Investig, 2019, 57(5): 430-434.
[14] FAN Y, ZHANG G, VONG C T, et al. Serum amyloid A3 confers protection against acute lung injury in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected mice[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2020, 318(2): L314-L322.
[15] 瞿转, 王惠明. 血清淀粉样蛋白A联合降钙素原在鉴别诊断ANCA相关性血管炎患者肺部细菌感染与肺损害中的价值探讨[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2021, 21(12): 969-974. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCSB202112001.htm [16] ZHAN Y, YANG C J, ZHANG Q H, et al. Silent information regulator type-1 mediates amelioration of inflammatory response and oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. J Biochem, 2021, 169(5): 613-620.
[17] 裴戌锋, 严友纪, 黄芳, 等. 血清ESM-1、VE-Cad、CC16水平与脓毒症并发急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者炎性因子及预后的关系研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2022, 22(13): 2570-2574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX202213033.htm [18] SUZUKI K, OKADA H, TAKEMURA G, et al. Recombinant thrombomodulin protects against LPS-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome via preservation of pulmonary endothelial glycocalyx[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2020, 177(17): 4021-4033.




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
