Correlation of prognostic nutritional index and related indicators with prognosis of postoperative patients with glioma
-
摘要:目的
探讨预后营养指数(PNI)及其他临床指标与脑胶质瘤术后患者预后的相关性。
方法回顾性选取行手术治疗的151例脑胶质瘤患者作为研究对象, 收集患者临床资料并进行随访。绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析不同指标对患者预后的预测效能,采用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,通过Log-rank检验和Cox回归分析探讨患者预后的影响因素。
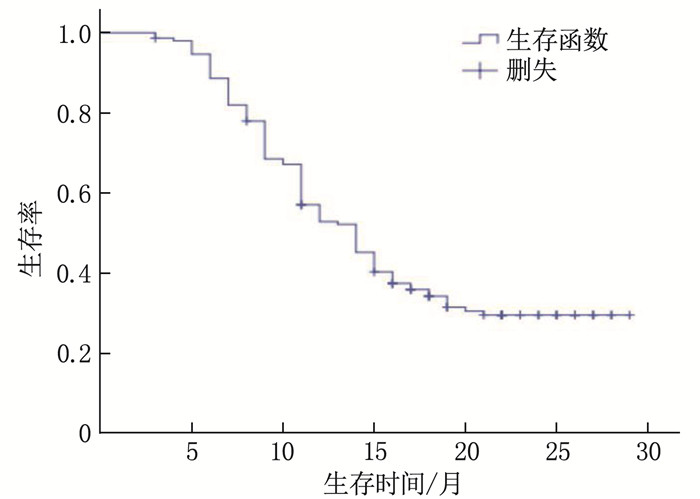
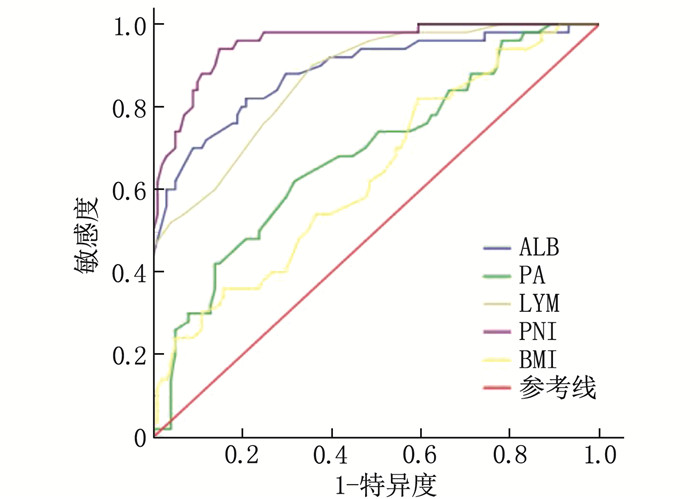
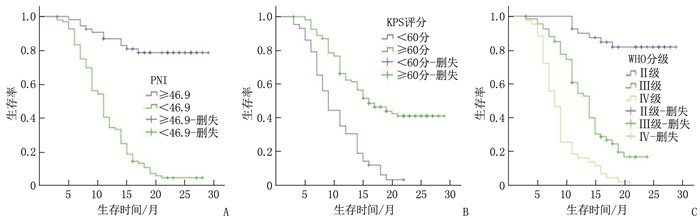
结果151例患者中位随访时间为13个月,平均生存周期21.89个月,随访期内死亡101例(占66.89%)。白蛋白(ALB)、前白蛋白(PA)、淋巴细胞计数(LYM)、PNI、体质量指数(BMI)和C反应蛋白(CRP)预测患者预后的最佳截断值分别为36.45 g/L、206.0 mg/L、1.85×109/L、46.9、21.45 kg/m2和8.55 mg/L, 曲线下面积分别为0.885、0.683、0.867、0.955、0.635和0.646。单因素分析显示, 世界卫生组织(WHO)中枢神经系统肿瘤分级(简称WHO分级)、术式、术前卡氏功能状态(KPS)评分、ALB、PA、LYM、BMI、CRP和PNI均为脑胶质瘤患者预后的影响因素(P < 0.05)。多因素Cox回归分析显示, PNI≥46.9、术前KPS评分≥60分和WHO分级Ⅱ级、Ⅲ级(相对于Ⅳ级)均为脑胶质瘤患者预后的保护因素(HR=0.925、0.964、0.122、0.577, P < 0.05)。WHO分级Ⅱ级、Ⅲ级、Ⅳ级患者的1年生存率分别为85.37%、50.75%、16.28%, PNI < 46.9和PNI≥46.9患者的1年生存率分别为34.38%和87.27%, 术前KPS评分 < 60分和KPS评分≥60分患者的1年生存率分别为30.23%和62.96%。
结论脑胶质瘤患者的临床预后较差, PNI、术前KPS评分和WHO分级均与患者预后相关。
-
关键词:
- 脑胶质瘤 /
- 营养指数 /
- 预后 /
- 中枢神经系统肿瘤分级 /
- 卡氏功能状态评分
Abstract:ObjectiveTo discuss the correlation of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) and related indicators with prognosis of postoperative patients with glioma.
MethodsA total of 151 patients with glioma were retrospectively selected as study objects, and relevant clinical data were collected and the follow-up was conducted. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was drawn to analyze the efficacy of different indicators in predicting prognosis. Kaplan-Meier method was used to draw the survival curve, and Log-rank test and Cox regression were used to analyze the influencing factors of prognosis.
ResultsOf the 151 patients, the median follow-up duration was 13 months, and the average survival period was 21.9 months. The death rate during the follow-up period was 66.89%(101 cases). The best cutoff values of albumin (ALB), prealbumin (PA), lymphocyte (LYM), PNI, body mass index (BMI) and C-reactive protein (CRP) in predicting the prognosis of patients were 36.45 g/L, 206.0 mg/L and 1.85× 109/L, 46.9, 21.45 kg/m2 and 8.55 mg/L, respectively, with areas under the curve of 0.885, 0.683, 0.867, 0.955, 0.635 and 0.646, respectively. Univariate analysis showed that World Health Organization (WHO) tumor grading for central nervous system (short for WHO grading), operation mode, preoperative Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) score, ALB, PA, LYM, BMI, CRP and PNI were the influencing factors of prognosis in glioma patients (P < 0.05). COX multivariate analysis showed that PNI ≥ 46.9, preoperative KPS score ≥60 and WHO grade Ⅱ and Ⅲ (compared with grade Ⅳ) are the protective factors for the prognosis of patients with glioma(HR=0.925, 0.964, 0.122 and 0.577 respectively, P < 0.05). The one-year survival rates of patients with grade Ⅱ, Ⅲ and Ⅳ of WHO were 85.37%, 50.75 and 16.28% respectively, and the one-year survival rates of patients with PNI < 46.9 and ≥46.9 were 34.38% and 87.27% respectively. The one-year survival rates of patients with preoperative KPS score < 60 and ≥60 were 30.23% and 62.96%, respectively.
ConclusionThe clinical prognosis of glioma is poor. PNI, preoperative KPS score and WHO grade are related to the clinical outcome of patients with glioma.
-
黄蜀葵花为锦葵科植物黄蜀葵的干燥花冠,其性甘、寒,归肾、膀胱经,始载于《嘉佑本草》[1], 具有清利湿热、消肿解毒之功效,是肾脏病常用的清利药之一,被广泛应用于慢性肾脏病蛋白尿的治疗[2]。近年来,大量临床试验及基础研究证实黄蜀葵花及其制剂还能够防治炎症性肠病、造影剂肾病、口腔溃疡、外伤创面等,疾病适用范围不断扩大,引起研究人员的广泛关注,但尚缺乏对黄蜀葵花研究的梳理与总结。CiteSpace是近年来广泛应用于各学科文献计量分析的可视化软件,有助于文献的脉络梳理和研究热点趋势分析[3-4]。本研究应用CiteSpace软件对CNKI数据库中有关黄蜀葵花的中文文献进行可视化分析,将相关数据转化分析并绘制成可视化图谱,以剖析黄蜀葵花的研究现状、研究热点以及研究趋势。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 数据来源与检索策略
采用计算机检索中国知网(CNKI)数据库,以“黄蜀葵花”为检索词,论文发表时间设定为建库至2023年3月31日,语言选择中文,纳入文献类型为期刊论文,注意排除科普论文、会议论文、学位论文以及重复发表的论文。将最终的检索结果以“refworks”格式导出,以“download”格式命名并保存。
1.2 文献分析方法
运用CiteSpace 5.7. R5软件对检索得到的结果进行分析,将最终检索的文献导入该软件,设定时间为建库至2023年3月,时间切片设定为1“自然年”,在Node Types区域选定“Author” “Institution” “Keyword”进行文献计量分析,并根据导出数据绘制可视化知识图谱。
2. 结果
2.1 发文量分布
自建库至2023年3月31日, CNKI数据库中搜索得到的黄蜀葵花相关文献共计319篇,排除科普论文、学位论文、会议论文以及重复发表论文后,共获得284篇相关文献。最终纳入分析的文献中,最早发表时间为1979年,其中1979—2002年发文量较少,共发表35篇,年平均发表论文约为1.46篇,增长趋势缓慢; 自2003年起,发文量呈现波动增长特点,特别是2009年后,每年发文量基本维持在10篇以上,且在2022年达到最高峰值23篇。发文量年度分布趋势见图 1。
2.2 研究作者分布
对最终纳入的284篇文献进行分析,结果显示节点数为559(代表559名作者),连线数为910,密度为0.005 8(见图 2)。图谱中,每个节点代表 1名作者,节点大小代表发文量多少; 节点之间的连线代表合作紧密程度,连线粗细代表作者之间合作等密切程度。发文量前10位的作者为刘志辉、谈献和、朱华云等(见表 1),作者研究范围涵盖药学、临床医学等方面。发文量前10位的专家中,6位来自于南京中医药大学及其附属医院,可见该院校对黄蜀葵花相关研究方面贡献较大,但院校内部缺乏紧密合作。
表 1 发文量5篇以上作者情况表作者 单位 发文量/篇 最早发表年份 刘志辉 南京中医药大学附属医院(江苏省中医院) 9 1999年 谈献和 南京中医药大学 8 2010年 朱华云 南京中医药大学 7 2009年 徐柏颐 江苏苏中药业集团股份有限公司 7 1996年 段金廒 南京中医药大学 6 2011年 张清华 山东省药学科学院 6 2018年 陈志武 安徽医科大学 6 2006年 余江毅 南京中医药大学附属医院(江苏省中医院) 6 1992年 潘武 南京中医药大学,沭阳县人民医院 6 2010年 2.3 研究机构共现分析
以研究机构为节点绘制机构共现图谱,图谱共有202个节点和142条连线,密度为0.007(见图 3)。研究机构发文量位于前10的研究机构见表 2, 其中发文量最多的研究机构是南京中医药大学,共发文69篇; 南京中医药大学附属医院及江苏省中医院分别发文42篇、7篇; 安徽医科大学发文量为第3位(19篇); 江苏苏中药业集团作为制药企业发文量位居第4名,发文17篇。从研究机构可视化图谱中可知,黄蜀葵花的研究多集中于中医药高等院校,说明这些机构是黄蜀葵花研究领域的主力军,其中部分院校与企业之间有较为紧密的合作,但是不同研究机构之间合作较少。
表 2 发文量位于前10位的机构情况表序号 机构名称 发文量/篇 1 南京中医药大学 69 2 南京中医药大学附属医院 42 3 安徽医科大学 19 4 江苏苏中药业集团 17 5 江苏省中医院 7 6 山东省药学科学院 6 7 安徽省医学科学研究所 5 8 辽宁中医药大学 4 9 沭阳县人民医院 3 10 天津中医药大学 3 2.4 研究热点分析
2.4.1 关键词共现分析
对纳入文献的关键词进行共现分析,以关键词作为节点绘制图谱,得到758个节点、763条连线,密度为0.021 8(见图 4)。图谱分析发现,与黄蜀葵花相关的高频研究主题包括黄蜀葵花、总黄酮、金丝桃苷、槲皮素、杨梅素和异槲皮苷等; 黄蜀葵花制剂中成药包括黄葵胶囊、芪葵颗粒等; 黄蜀葵花常与黄芪、大黄等药物共同研究; 黄蜀葵花治疗的疾病涉及慢性肾炎、蛋白尿、糖尿病、克罗恩病、口腔溃疡等; 研究方式有化学成分分析、结构鉴定、制备工艺、药理学研究、作用机制研究、临床疗效观察以及不良反应及安全性评价; 对不良反应的具体研究内容主要涉及肝损伤。
2.4.2 关键词聚类分析
对纳入文献的关键词采用谱聚类的方法进行聚类分析,图谱显示,聚类模块性指数Q值为0.663, 聚类轮廓性指数S值为0.916 6(见图 5)。该图谱共8个聚类标签,可归纳概括为3大研究方向: ①药物(黄蜀葵花、黄蜀葵、金丝桃苷、芪葵颗粒,涵盖单味药、有效成分以及院内制剂); ②疾病(克罗恩病等); ③机制研究(氧化应激、肠道菌群、钙超载等)。
2.4.3 关键词时区分析
对自建库至2023年3月相关文献进行分析,设定5年为1个时区,绘制关键词时区分析知识图谱,以反映黄蜀葵花研究热点的演化趋势,见图 6。节点间连线粗细与强度相关,图中X轴为文献发表时间, Y轴为聚类编号。由图 6可知,自1990年起,研究集中于对黄蜀葵花治疗乳糜尿、肾病的临床疗效观察, 2005年后研究者逐步开始研究黄蜀葵花药物成分及药理机制; 黄蜀葵及金丝桃苷的研究始终聚焦于成分鉴定、栽培及制备工艺; 另一个聚类关键词氧化应激常与细胞凋亡、炎症反应被共同研究,并且研究者将这些现代机制用于解释中医病机; 2005年前后,肠道菌群作为研究热点被越来越多的研究人员重视; 芪葵颗粒作为院内制剂研究逾20年,研究方向包括疗效观察、成分鉴定、药理机制、制备工艺等,是较为完备的药物研究方法; 对聚类关键词克罗恩病的研究主要集中在动物实验、机制探讨方面; 此外,钙超载与抑郁病的研究在2015—2020年成为新热点。
2.4.4 关键词突现分析
本研究对纳入分析的文献进行关键词突现可视化图谱绘制,红色条带表示持续突现时间段,以直观展示该领域研究热点演变(见图 7), 其中突现强度最高的3个关键词分别是槲皮素(强度3.13)、金丝桃苷(强度2.92)、黄蜀葵(强度2.33)。25个突现词可分为药物成分、制备工艺、疾病及机制4大类。关键词突现分析图谱可见,自1990年起对黄蜀葵花的临床应用,特别是对慢性肾炎、外治疗法、经验报道的探索,已成为研究热点,并持续至2000年。2005年以后,对黄蜀葵花化学成分的研究增多,表明学者已经开始重视寻找黄蜀葵花有效成分,并重视提取工艺的改良,该方面的研究持续至今。2015年以后出现了黄蜀葵花对克罗恩病的研究,表明黄蜀葵花已用于多种疾病的治疗。
3. 讨论
黄蜀葵花为锦葵科秋葵属草本植物黄蜀葵的干燥花冠[5], 具有利尿通淋、活血止血、消肿解毒的功效,主治淋证、吐血、衄血、崩漏、胎衣不下、痈肿疮毒、水火烫伤等[6]。黄蜀葵花化学成分复杂,现代药理学研究发现,其主要成分包含黄酮醇类化合物、有机酸、鞣酸类、甾类和长链烃类等化合物[1], 代表性成分有杨梅素、槲皮素、金丝桃苷、槲皮素-3-O-βD-葡萄糖苷、槲皮素-3′-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷等[7-8]。
本研究发现, 2002年后,黄蜀葵花相关研究发文量呈波动上升趋势, 2015和2022年达到高峰,可能与研究者应用新技术新方法开展对黄蜀葵花有效成分分析、新作用机制的研究有关。但期间发文量波动较大,能否说明该研究主题趋势尚无法定论。此外, 2023年数据不全,暂不列入分析。作者及机构合作分析方面,南京中医药大学及其附属医院是研究黄蜀葵花的主要机构,可能是源于南京中医药大学附属医院(江苏省中医院)肾内科团队首先从民间发现该药用于治疗肾脏病,较早地开展了相关研究。高校院校、制药企业各团队内部作者之间合作较密切,但团队之间合作较少,各机构间合作局限于本地内部,缺乏跨省市、跨机构的合作,因此无法进行优势整合,导致研究深度及广度有限,也对今后黄蜀葵花的深入研究提出了新要求。关键词分析发现,黄蜀葵花的研究集中于药物疗效观察、机制研究、成分提取、制备工艺等。
黄蜀葵花早在上世纪90年代由江苏省中医院肾内科根据民间用药经验而首先应用于肾病蛋白尿的治疗, 1995年首先报道运用黄蜀葵花醇提物治疗糖尿病肾病,可显著减少蛋白尿,且总有效率优于西药组[9]。随后,江苏省中医院与江苏苏中药业集团开展合作,成功研制单味成药黄葵胶囊,于1999年获得黄葵胶囊的新药证书,是院企联合成果转化成功的代表。此后,不断有临床研究[10-12]报道,单用黄蜀葵花制剂或联合ACEI/ARB类等药物能够改善慢性肾脏病、糖尿病肾病、慢性肾炎等肾脏病的蛋白定量及中医症状积分。近年来,分别由中国工程院院士陈香美教授和江苏省中医院孙伟教授牵头的黄蜀葵花制剂治疗原发性肾小球疾病和糖尿病肾病的2项临床研究[13-14]均证实,其能有效减轻蛋白尿,稳定肾功能,为治疗肾脏病获得高质量临床证据。黄蜀葵花治疗肾脏病的药理学研究[10, 15-16]多集中于单体,涉及免疫炎症、氧化应激、胰岛素抵抗、糖脂代谢、细胞焦亡和自噬及纤维化等多个途径。
《肘后方》曾记载“黄蜀葵花烧末敷”用以治疗小儿口疮,因此黄蜀葵花常用于外伤治疗。江苏省中医院研制了疮灵液、新生肌玉红膏,前者由黄蜀葵花、大黄、红花、诃子等组成,具有消炎解毒、活血生肌、收敛止渗的功效,临床用于各种感染性溃疡伴炎症者[17]; 新生肌玉红膏则是在《外科正宗》生肌玉红膏基础上,以黄蜀葵花、当归、甘草、白芷、紫草、血竭以及诃子为主要成分,用于治疗体表难愈性溃疡、糖尿病性溃疡等溃疡的愈合以及填充体内组织缺损[18]。安徽医科大学第一附属医院研制的黄蜀葵花糊化剂[19]用于口腔溃疡治疗,能够促进溃疡面愈合、镇痛,且组织刺激性小,无毒副作用。此外,尚有个人或生物医药公司研制含有黄蜀葵花的外用药物、漱口水及防晒液,已申报专利[20-21], 作用机制涉及抗炎、抗感染及组织修复等[22-23]。此外,近年来临床及基础实验研究[24-29]报道,黄蜀葵花制剂还可应用于炎症性肠病、冠状动脉性心脏病、造影剂肾病、抑郁症、神经元损伤等疾病的治疗。由此可见,利用黄蜀葵花功效开发内服及外用药物、扩大现有黄蜀葵花制剂的适应证是黄蜀葵花研究的热点,也是院所及企业合作研发的方向。
中国黄蜀葵花分布广泛、资源丰富,民间用药历史悠久,因此,加强和加深对黄蜀葵花的开发与应用值得引起科学家的注意。黄蜀葵花制剂已有一定转化研究基础,如何深化基础与临床研究,不仅有利于扩大黄蜀葵花制剂的临床适应证,对于已上市药物黄葵胶囊的深入研究也将具有深远的意义。本研究提示,江苏及安徽两省院校企业是黄蜀葵花研究集中的区域,研究热点涉及黄蜀葵花的有效成分、经验方、氧化应激、肠道菌群、克罗恩病、钙超载、成分鉴定、制备工艺等方面。本研究尚存在一定局限性: ①纳入文献的药物名称不规范,作者、机构等可能存在同名不同人、机构署名多样的情况,造成结果偏倚; ②未就黄蜀葵花主要药用成分研究作进一步分析; ③缺乏联合外文文献的融合分析。后续研究可着重聚焦以上方向,规范药物名称,扩大纳入文献范围,对黄蜀葵花的药用成分、作用机制进行深入分析,为黄蜀葵花的研究提供思路。
-
表 1 不同指标对患者预后的预测效能
指标 AUC 95%CI 最佳截断值 约登指数 P ALB/(g/L) 0.885 0.824~0.946 36.45 0.612 <0.001 PA/(mg/L) 0.683 0.592~0.774 206.00 0.303 <0.001 LYM/(×109/L) 0.867 0.809~0.926 1.85 0.544 <0.001 PNI 0.955 0.923~0.987 46.90 0.771 <0.001 BMI/(kg/m2) 0.635 0.542~0.729 21.45 0.226 0.007 CRP/(mg/L) 0.646 0.554~0.738 8.55 0.246 0.004 ALB: 白蛋白; PA: 前白蛋白; LYM: 淋巴细胞计数; PNI: 预后营养指数; BMI: 体质量指数; CRP: C反应蛋白。 表 2 患者临床预后影响因素的单因素分析
指标 分类 n 死亡/例 生存时间(95%CI)/月 Log-rank χ2 P 性别 男 81 49 17.35(15.27~19.44) 2.282 0.131 女 70 52 14.21(12.56~15.86) WHO分级 Ⅱ级 41 7 26.16(24.24~28.09) 91.277 <0.001 Ⅲ级 67 51 14.16(12.74~15.58) Ⅳ级 43 43 9.05(7.83~10.26) 术式 全切除术 58 19 21.89(19.61~24.17) 38.730 <0.001 部分切除术 93 82 12.69(11.32~14.07) 术前KPS评分 <60分 43 41 10.29(8.88~11.69) 32.926 <0.001 ≥60分 108 60 18.71(16.95~20.48) ALB <36.45 g/L 89 80 12.28(10.94~13.62) 43.469 <0.001 ≥36.45 g/L 62 21 22.53(20.25~24.80) PA <206.0 mg/L 88 69 13.83(12.16~15.50) 12.808 <0.001 ≥206.0 mg/L 63 32 19.60(17.30~21.91) LYM <1.85×109/L 70 65 12.08(10.80~13.36) 30.812 <0.001 ≥1.85×109/L 81 36 20.20(18.03~22.38) BMI <21.45 kg/m2 50 41 13.47(11.93~15.00) 4.554 0.033 ≥21.45 kg/m2 101 60 17.39(15.47~19.32) CRP <8.55 mg/L 99 58 17.85(15.94~19.76) 8.956 0.003 ≥8.55 mg/L 52 43 13.11(11.27~14.95) PNI <46.9 96 90 11.64(10.53~12.76) 71.030 <0.001 ≥46.9 55 11 25.14(23.08~27.21) WHO: 世界卫生组织; KPS: 卡氏功能状态; ALB: 白蛋白; PA: 前白蛋白; LYM: 淋巴细胞计数; PNI: 预后营养指数; BMI: 体质量指数; CRP: C反应蛋白。 表 3 患者预后影响因素的多因素Cox回归分析
因素 β S. E. HR(95%CI) Wald χ2 P PNI -0.078 0.024 0.925(0.882~0.970) 10.464 0.001 术前KPS评分 -0.037 0.010 0.964(0.945~0.983) 13.323 <0.001 WHO分级 Ⅱ级 -2.104 0.455 0.122(0.050~0.297) 21.402 <0.001 Ⅲ级 -0.550 0.228 0.577(0.369~0.901) 5.840 0.016 -
[1] FANGUSARO J, ONAR-THOMAS A, YOUNG POUSSAINT T, et al. Selumetinib in paediatric patients with BRAF-aberrant or neurofibromatosis type 1-associated recurrent, refractory, or progressive low-grade glioma: a multicentre, phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(7): 1011-1022. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30277-3
[2] WANG Z H, GAO L, GUO X P, et al. Development and validation of a nomogram with an autophagy-related gene signature for predicting survival in patients with glioblastoma[J]. Aging, 2019, 11(24): 12246-12269. doi: 10.18632/aging.102566
[3] HU C, CHEN K N, TANG X P. Prognostic value of preoperative controlling nutritional status in patients with glioblastoma[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2020, 198: 106129. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106129
[4] XIAO Y P, WEI G, MA M, et al. Association among prognostic nutritional index, post-operative infection and prognosis of stage Ⅱ/Ⅲ gastric cancer patients following radical gastrectomy[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2022, 76(10): 1449-1456. doi: 10.1038/s41430-022-01120-7
[5] 《中国中枢神经系统胶质瘤诊断和治疗指南》编写组. 中国中枢神经系统胶质瘤诊断和治疗指南(2015)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2016, 96(7): 485-509. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.07.003 [6] XU S C, TANG L, LI X Z, et al. Immunotherapy for glioma: current management and future application[J]. Cancer Lett, 2020, 476: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.02.002
[7] MLADENOVSK M, VALKOV I, OVCHAROV M, et al. High grade glioma surgery-clinical aspects and prognosis[J]. Folia Med (Plovdiv), 2021, 63(1): 35-41. doi: 10.3897/folmed.63.e55255
[8] ALAN O, TELLI T A, BASOGLU T, et al. Impact of prognostic nutritional index on survival in recurrent glioblastoma[J]. Neurocirugia, 2022, 33(1): 15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neucir.2020.11.005
[9] 李涛, 翟景光, 刘晓. 脑胶质瘤患者手术治疗预后不良的相关因素分析[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2022, 43(11): 1047-1051. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1256.2022.11.011 [10] RATHORE S, AKBARI H, DOSHI J, et al. Radiomic signature of infiltration in peritumoral edema predicts subsequent recurrence in glioblastoma: implications for personalized radiotherapy planning[J]. J Med Imaging, 2018, 5(2): 021219.
[11] LIANG R, ZHI Y, ZHENG G, et al. Analysis of long non-coding RNAs in glioblastoma for prognosis prediction using weighted gene co-expression network analysis, Cox regression, and L1-LASSO penalization[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 157-168.
[12] DEMIRELLI B, BABACAN N A, ERCELEP Ö, et al. Modified Glasgow prognostic score, prognostic nutritional index and ECOG performance score predicts survival better than sarcopenia, Cachexia and some inflammatory indices in metastatic gastric cancer[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2021, 73(2): 230-238. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2020.1749290
[13] WANG D, HU X, XIAO L, et al. Prognostic nutritional index and systemic immune-inflammation index predict the prognosis of patients with HCC[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2021, 25(2): 421-427. doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04492-7
[14] 徐日. 预后营养指数对胶质瘤患者预后的影响[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2020, 12(2): 203-206. [15] 晁储瑞, 赵伟峰, 刘慧敏, 等. 脑胶质瘤患者术前血液学指标与预后的关系[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2019, 33(11): 1105-1109. [16] SENGER A S, DINCER M, UZUN O, et al. Impact of preoperative prognostic nutritional index levels on morbidity in colorectal cancer surgery[J]. Ann Ital Chir, 2022, 92: 422-426.
[17] DING P A, GUO H H, SUN C Y, et al. Combined systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts chemotherapy response and prognosis in locally advanced gastric cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy with PD-1 antibody sintilimab and XELOX: a prospective study[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2022, 22(1): 121. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02199-9
[18] HE J, YIN H, XIA Y, et al. Prognostic nutritional index, a novel biomarker which predicts worse prognosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma[J]. Leuk Res, 2021, 110: 106664. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2021.106664
[19] DEME D, TELEKES A. Prognostic importance of albumin in oncology[J]. Orv Hetil, 2018, 159(3): 96-106. doi: 10.1556/650.2018.30885
[20] KIM Y J, OH H, LEE S J, et al. Prognostic significance of the postoperative prognostic nutritional index in patients with glioblastoma: a retrospective study[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 942. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08686-8
[21] 刘竞辉, 娄淼, 冀培刚, 等. 老年胶质瘤预后相关因素分析[J]. 中南大学学报: 医学版, 2018, 43(4): 403-409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYD201804013.htm [22] BARBAGALLO G M V, CERTO F, DI GREGORIO S, et al. Recurrent high-grade glioma surgery: a multimodal intraoperative protocol to safely increase extent of tumor resection and analysis of its impact on patient outcome[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2021, 50(1): E20. doi: 10.3171/2020.10.FOCUS20744
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 唐茁栋,王明友,王洪平,李亭燕,王川,刘绍江. 胫骨平台骨折术前下肢深静脉血栓形成列线图预测模型构建与验证. 创伤外科杂志. 2025(01): 43-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郭荣,余墨声,赵月强,朱占永,罗莎,谭植襄,陶瑞,王芳. 齐踝及齐膝弹力裤对大腿吸脂病人深静脉血栓预防效果的对比研究. 临床外科杂志. 2024(05): 541-544 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋峰,方灿军,胡靖,陈义. 中青年髋部骨折患者术前深静脉血栓形成的危险因素及列线图预测模型的构建. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(12): 32-37 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 李慧婷,汤益,刘燕. 彩色多普勒超声在下肢深静脉血栓诊断及溶栓效果评估中应用价值分析. 临床医学工程. 2023(07): 889-890 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杜茜,蔡晨盛. 彩色多普勒超声结合D-二聚体在偏瘫患者孤立性小腿肌间静脉血栓诊断中的价值. 现代医用影像学. 2023(11): 2113-2116 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 戴清月,高燕玲,卢金华,孙情,苏清岩,程熙. 老年脊髓损伤患者临床特征的回顾性分析. 中国医药科学. 2022(23): 183-187+196 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王杨,王晓春,李俊杰,高翔. 高频超声联合D-二聚体、纤维蛋白原对小腿肌间静脉丛血栓形成的诊断价值. 血管与腔内血管外科杂志. 2022(12): 1494-1498 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
