Values of contrast-enhanced ultrasound characteristics and quantitative parameters in diagnosing ambiguous thyroid nodules confirmed to category 4 of C-TIRADS by fine needle aspiration biopsy
-
摘要:目的
探讨超声造影(CEUS)特征及定量参数诊断中国甲状腺影像报告和数据系统(C-TIRADS)4类细针穿刺细胞学检查(FNAB)不明确甲状腺结节的价值。
方法回顾性分析C-TIRADS 4类并接受FNAB结果为不明确甲状腺结节72例患者的CEUS特征及参数比值。采用定量分析软件获取甲状腺结节CEUS时间-强度曲线(TIC); 比较2组结节造影剂达峰时间(TTP)、造影上升斜率(AS)、达峰强度(PI)、平均通过时间(MTT)及曲线下面积(AUC); 比较2组结节与周围正常甲状腺组织各造影参数比值, 包括结节与周围正常甲状腺组织造影剂达峰时间比值(R-TTP)、结节与周围正常甲状腺组织造影剂达峰强度比值(R-PI)、结节与周围正常甲状腺组织造影上升斜率比值(R-AS)、结节与周围正常甲状腺组织超声造影TIC曲线下面积比值(R-AUC); 分析CEUS鉴别诊断C-TIRADS 4类FNAB结果不明确甲状腺结节的价值。
结果甲状腺恶性结节(TMN)组患者年龄小于甲状腺良性结节(TBN)组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。2组结节造影剂灌注方式、灌注程度、是否均匀灌注、与周围正常甲状腺组织相比灌注速度及灌注后结节边界是否清晰等比较,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。TMN组TTP高于TBN组, PI、AS、AUC低于TBN组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。TMN组R-TTP高于TBN组, R-PI、R-AS及R-AUC低于TBN组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。CEUS灌注特征诊断甲状腺结节良恶性的灵敏度、特异度、漏诊率、误诊率、比数积、约登指数、阳性预测值、阴性预测值、阳性似然比、阴性似然比及总符合率分别为83.02%、73.68%、16.98%、26.32%、13.69、0.567、89.79%、60.87%、3.15、0.23、80.56%。
结论CEUS特征及定量参数可提高C-TIRADS 4类FNAB不明确甲状腺结节的诊断准确性,为临床决策提供较为可靠的依据。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the values of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) characteristics and quantitative parameters in diagnosing ambiguous thyroid nodules confirmed to category 4 of China Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (C-TIRADS) by fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB).
MethodsThe CEUS characteristics and parameter ratios of 72 patients with ambiguous thyroid nodules confirmed to category 4 of C-TIRADS by FNAB were retrospectively analyzed. Quantitative analysis software was used to obtain CEUS time-intensity curve (TIC) of thyroid nodules; the time to peak (TTP) of contrast agents, ascent slope (AS) of radiography, peak intensity (PI), mean transit time (MTT) and area under the curve (AUC) in nodules were compared between two groups; the ratios of nodules to various imaging parameters of surrounding normal thyroid tissues were compared between two groups, including the ratio of time to peak of contrast agents of nodules to surrounding normal thyroid tissues (R-TTP), the ratio of peak intensity of contrast agents of nodules to surrounding normal thyroid tissues (R-PI), the ratio of ascent slope of nodules to surrounding normal thyroid tissues (R-AS), and the ratio of the area under the TIC curve of nodules to surrounding normal thyroid tissues by CEUS imaging (R-AUC); the value of CEUS in differential diagnosis of ambiguous thyroid nodules confirmed to category 4 of C-TIRADS by FNAB was analyzed.
ResultsThe age of patients in thyroid malignant nodule (TMN) group was significantly smaller than that in thyroid benign nodule (TBN) group (P < 0.05). There were significant differences in the way of contrast agents perfusion, the degree of contrast agents perfusion, whether the nodular perfusion was even, the speed of contrast agents perfusion compared with the surrounding normal thyroid tissues, and whether the nodular boundary was clear after perfusion between the two groups (P < 0.05). In the TMN group, the TTP was significantly higher than that in the TBN group, while the PI, AS and AUC were significantly lower than those in the TBN group (P < 0.05). In the TMN group, the R-TTP was significantly higher than that in the TBN group, while the R-PI, R-AS and R-AUC were significantly lower than those in the TBN group (P < 0.05). For the diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules by CEUS perfusion characteristics, the sensitivity, specificity, missed diagnosis rate, misdiagnosis rate, ratio product, Yuden index, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio and total coincidence rate were 83.02%, 73.68%, 16.98%, 26.32%, 13.69, 0.567, 89.79%, 60.87%, 3.15, 0.23 and 80.56% respectively.
ConclusionCEUS characteristics and quantitative parameters can improve the diagnostic accuracy of ambiguous thyroid nodules confirmed to category 4 of C-TIRADS by FNAB, which can provide a reliable basis for clinical decision-making.
-
近年来,甲状腺癌的发病率呈上升且年轻化趋势,作为甲状腺检查的首选方法,可检出大量结节[1]。甲状腺结节分为甲状腺良性结节(TBN)和甲状腺恶性结节(TMN), 目前多采用最新的中国甲状腺影像报告和数据系统(C-TIRADS)[2]进行分类并联合细针穿刺细胞学检查(FNAB)诊断甲状腺结节性质,部分良性结节和恶性结节超声表现类似, C-TIRADS 4类又分为4a、4b、4c, 且分层跨度较大。FNAB是甲状腺结节病理诊断的有效方法,但穿刺结果与结节位置、大小、结节内部组织构成及医师经验等多种因素密切相关[3-4]。临床上C-TIRADS 4类FNAC穿刺结果不明确结节多见,超声造影(CEUS)可以显示结节内部细微血管供血情况,有利于结节性质判断[5]。本研究通过分析结节造影剂灌注特征及造影时间-强度曲线(TIC)各参数测值,探讨CEUS对72例经手术病理确诊的C-TIRADS 4类FNAB结果不明确甲状腺结节良恶性的鉴别诊断价值,现将结果报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
回顾性分析2020年12月—2022年12月在门诊或住院时超声诊断风险分层为C-TIRADS 4类结节并接受FNAB结果为不明确甲状腺结节患者72例,均为单发结节,其中男29例,女43例,年龄21~72岁,平均(41.35±5.19)岁; 结节径线0.5~2.8 cm, 平均(0.82±0.44) cm; 最大径线≤1.0 cm的结节共66例(91.67%), 径线>1.0 cm结节6例(8.33%)。纳入标准: ① C-TIRADS 4类结节者; ②接受FNAB、CEUS和结节切除手术者; ③ FNAB结果不明确者; ④术前及术后资料完整者,无严重基础疾病。排除标准: ①有造影剂使用禁忌证者; ②不接受进一步检查者。所有患者签署知情同意书并通过医院医学伦理委员会批准。
1.2 仪器与方法
1.2.1 仪器
采用Mindray Resona7CV仪器, L14-5WU探头,频率14 MHz, MI 0.77, 配备超声造影功能和时间-强度曲线(TIC)分析计算软件。造影剂为意大利Bracco公司生产的声诺维(SonoVue)(化学名: 六氟化硫微泡冻干粉),造影前采用5 mL生理盐水注入造影剂中稀释、震荡均匀配制成微泡混悬液备用。
1.2.2 CEUS检查
常规超声检查再次确定结节大小、分布部位及C-TIRADS分类情况,选择造影条件,调节图像增益及造影显示背景达到最佳,完整显示结节最大切面及周围正常甲状腺,经肘静脉留置针快速团注配制造影剂混悬液2 mL后,采用5 mL生理盐水冲管,同时点击计时器记录造影剂灌注全过程180 s并动态存图。选取结节感兴趣区(ROI1)及周围正常甲状腺组织区(ROI2), 应用定量分析软件系统获取TIC曲线进行各参数对比分析。
1.2.3 结节性质判断
判断恶性结节时,造影剂灌注以向心性延迟低灌注、灌注不均匀、灌注后边界模糊,造影剂消退后边界变化为主要特征; 判断良性结节时,造影剂灌注以弥散性均匀等灌注或高灌注、灌注后边缘清晰,造影剂消退后边界无变化、较正常甲状腺组织灌注时间早或同步灌注为主要特征[6]。
1.2.4 FNAB不明确定义
本研究中所有C-TIRADS 4类甲状腺结节经FNAB取材不理想、细胞数目少、细胞病理形态不典型(包括甲状腺细胞病理学Bethesda系统[7]中Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ类结节)等。
1.2.5 观察指标:
① 2组患者一般资料比较; ②良恶性结节CEUS灌注特征比较; ③比较结节CEUS各参数及与其周围正常甲状腺组织各参数比值,包括结节与周围正常甲状腺组织造影剂达峰时间比值(R-TTP)、结节与周围正常甲状腺组织造影剂达峰强度比值(R-PI)、结节与周围正常甲状腺组织造影上升斜率比值(R-AS)、结节与周围正常甲状腺组织超声造影TIC曲线下面积比值(R-AUC); ④分析CEUS灌注特征对C-TIRADS 4类FNAB不明确结节的诊断效能,包括灵敏度(Se)、特异度(Sp)、漏诊率、误诊率、比数积、约登指数、阳性预测值(PPV)、阴性预测值(NPV)、阳性似然比(LR+)、阴性似然比(LR-)、总符合率等。1.2.6质量控制: 检查及图像分析由2位具有10年以上丰富经验的甲状腺相关超声诊断及造影医师共同完成。
1.3 统计学分析
统计软件为MedCalc19.0, 以[n(%)]表示计数资料,组间计数资料比较采用卡方检验,计量数据以均数±标准差表示,比较采用独立样本t检验,分析CEUS灌注特征对C-TIRADS 4类FNAB结果不明确甲状腺结节的诊断效能, P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组患者一般资料比较
TMN组患者年龄小于TBN组,差异有统计学意义(t=2.346, P=0.022), 见表 1。
表 1 2组患者一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]一般资料 分类 TMN组(n=53) TBN组(n=19) χ2/t P 性别 男 21(39.62) 8(42.11) 0.035 0.851 女 32(60.38) 11(57.89) 年龄/岁 39.53±4.68 42.65±5.74 2.346 0.022 结节大小/cm 0.81±0.43 0.85±0.45 0.344 0.732 结节径线分布 ≤1.0 cm 49(92.45) 17(89.47) 0.160 0.689 >1.0 cm 4(7.55) 2(10.53) 结节部位分布 左侧叶 21(39.62) 7(36.84) 1.763 0.414 右侧叶 27(50.94) 8(42.11) 峡部 5(9.43) 4(21.05) 甲状腺功能异常 合并 5(9.43) 3(15.79) 0.564 0.453 不合并 48(90.57) 16(84.21) C-TIRADS分类 C-TR4a 14(26.42) 10(52.63) 5.844 0.054 C-TR4b 16(30.19) 6(31.58) C-TR4c 23(43.39) 3(15.79) 2.2 病理结果
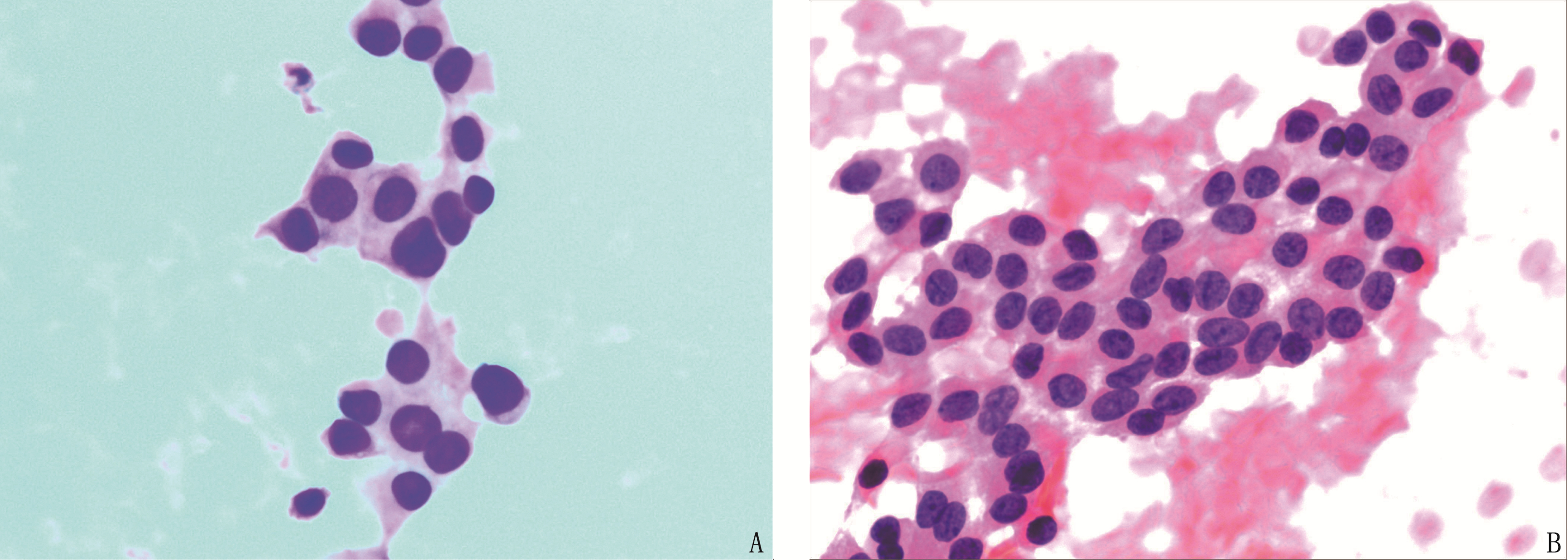
72例FNAB病理不明确结节中,取材不理想、细胞数目少共9例(12.50%), 甲状腺细胞病理学Bethesda系统诊断Ⅲ类结节30例(41.67%), Ⅳ类21例(29.17%), Ⅴ类12例(16.67%)。术后病理诊断良性19例,恶性53例。其中,良性结节中结节性甲状腺肿(NG)8例(42.11%), 甲状腺滤泡腺瘤(FA)6例(31.58%), 桥本氏甲状腺炎(HT)1例(5.26%), 亚急性甲状腺炎(ST)4例(21.05%); 53例恶性结节均为甲状腺乳头状癌(TPC)。见图 1。
2.3 CEUS灌注特征分析
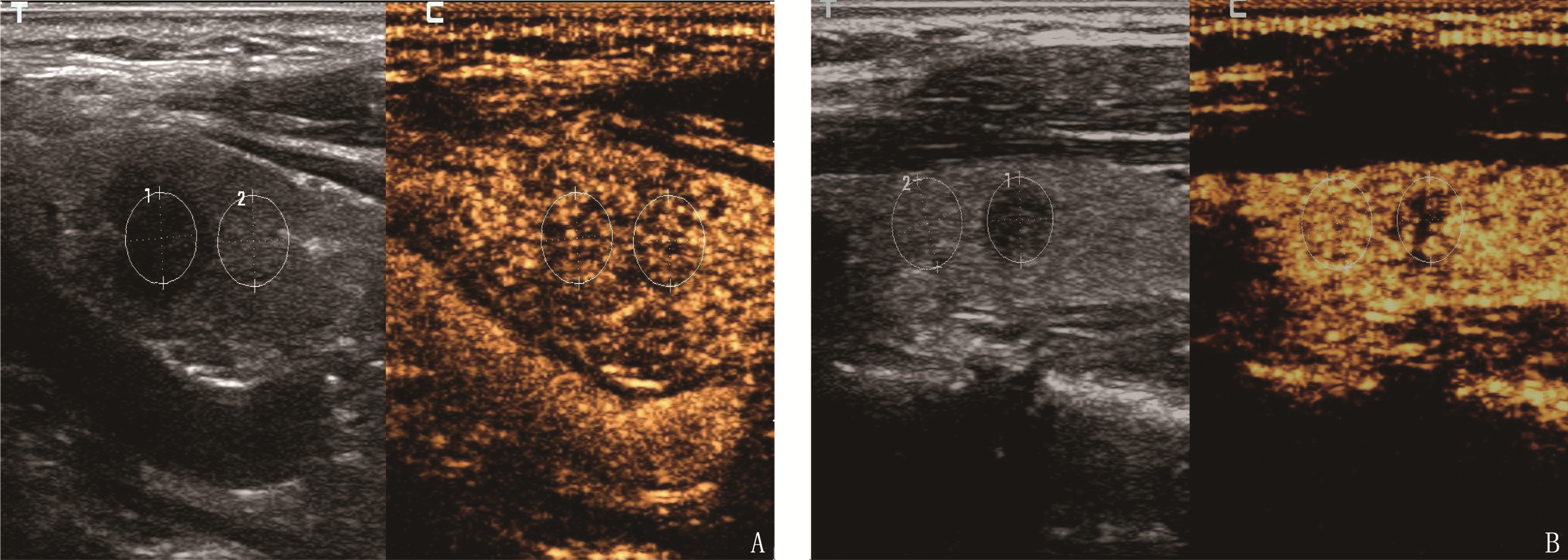
2组结节造影剂灌注方式、灌注程度、是否均匀灌注、与周围正常甲状腺组织相比灌注速度及灌注后结节边界是否清晰的差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 2、图 2。
表 2 2组结节CEUS灌注特征比较[n(%)]特征 分类 TBN(n=19) TMN(n=53) χ2 P 造影剂灌注方式 向心性 7(36.84) 39(73.58) 8.244 0.016 弥散性 9(47.37) 11(20.75) 离心性 3(15.79) 3(5.66) 造影剂灌注程度 无灌注 0 0 24.124 < 0.001 低灌注 3(15.79) 42(79.25) 等灌注 11(57.89) 7(13.21) 高灌注 5(26.32) 4(7.55) 均匀灌注 均匀 13(68.42) 7(13.21) 20.958 < 0.010 不均匀 6(31.58) 46(86.79) 与周围正常甲状腺组织相比灌注速度 快进 4(21.05) 4(7.55) 17.845 < 0.001 同步 12(63.16) 11(20.75) 延迟 3(15.79) 38(71.69) 与周围正常甲状腺组织相比退出速度 快退 2(10.53) 21(39.62) 3.575 0.167 同步 12(63.16) 26(49.06) 延迟 5(26.32) 6(11.32) 灌注后边缘 清晰 16(84.21) 4(7.55) 40.405 < 0.001 模糊 3(15.79) 49(92.45) 2.4 2组结节CEUS各参数及结节与周围正常甲状腺组织各参数比值比较
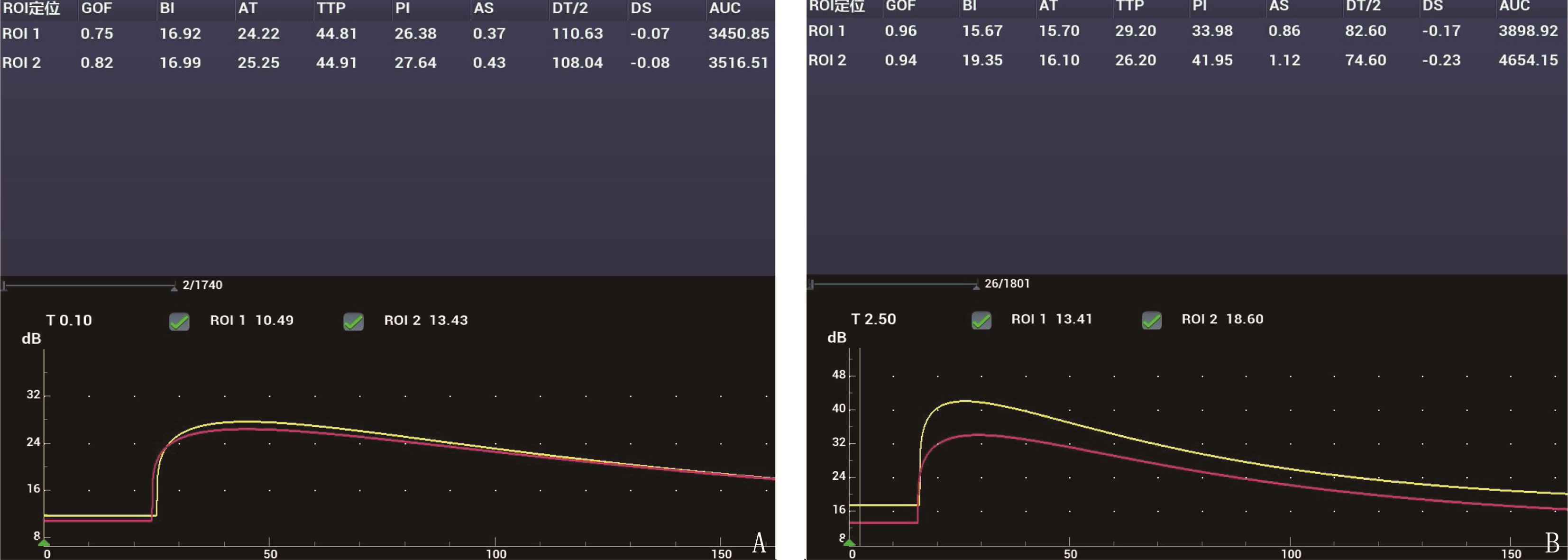
TMN组TTP高于TBN组,PI、AS及AUC低于TBN组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。TMN组R-TTP高于TBN组, R-PI、R-AS及R-AUC低于TBN组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 3、图 3。
表 3 2组CEUS参数及参数比的比较(x±s)组别 参数 参数比 TTP/S PI/dB AS MTT/S AUC/(dB·s) R-TTP R-PI R-AS R-AUC TMN组(n=53) 25.06±3.94 35.33±3.74 0.68±0.29 30.19±4.07 4 682.07±416.50 1.268±0.428 0.827±0.041 0.867±0.081 0.835±0.076 TBN组(n=19) 22.47±1.99 44.96±4.05 0.86±0.31 28.66±3.32 5 174.01±521.88 0.941±0.074 0.987±0.026 0.924±0.073 1.028±0.051 t -2.734 9.423 2.280 -1.471 4.125 -3.298 15.865 2.698 10.249 P 0.008 < 0.001 0.026 0.146 < 0.001 0.002 < 0.001 0.009 < 0.001 2.5 CEUS特征诊断甲状腺良恶性结节的效能分析
以病理诊断为金标准, CEUS灌注特征诊断TMN、TBN的例数及其诊断效能见表 4。
表 4 CEUS灌注特征诊断甲状腺良恶性结节情况及效能分析指标 分类 TMN TBN 病理结果 恶性 44 9 良性 5 14 诊断效能 Se/% - 83.02 Sp/% - 73.68 漏诊率/% - 16.98 误诊率/% - 26.32 比数积 - 13.69 约登指数 - 0.567 PPV/% - 89.79 NPV/% - 60.87 LR+ - 3.15 LR- - 0.23 总符合率/% - 80.56 Se: 灵敏度; Sp: 特异度; PPV: 阳性预测值;
NPV: 阴性预测值; LR+: 阳性似然比; LR-: 阴性似然比。
Se=a/a+c; Sp=d/d+b; 漏诊率=c/a+c; 误诊率=b/b+d;
约登指数=Se+Sp-1; 比数积=ad/bc; PPV=a/(a+b);
NPV=d/c+d; LR+=Se/(1-Sp); LR-=(1-Se)/Sp;
总符合率=(a+d)/(a+b+c+d)。a代表真阳性,
b代表假阳性,c代表假阴性, d代表真阴性。3. 讨论
超声造影剂微泡作为纯血池显影剂不进入组织间隙,通过肺脏呼吸代谢排出体外,造影剂微泡在组织微血管内移动过程中产生反射及散射效应而强化微血管内血流信号,可观察结节内微血管血供情况,有助于提高甲状腺结节性质鉴别[8-10]。早期亚急性甲状腺炎或桥本氏甲状腺炎等甲状腺内局限性低回声区因其常规超声图像特征与甲状腺恶性结节图像特征近似而被误诊为C-TIRADS 4类结节, C-TIRADS 4类甲状腺结节病理诊断以FNAB为主要手段,而FNAB结果与结节位置、大小及超声和病理医师经验等因素密切相关,且甲状腺恶性结节中微小乳头状癌多见。本研究72例结节中径线≤1.0 cm微小结节达90%以上,这可能是引起FNAB结果不明确的主要原因。
2020年中国C-TIRADS对4类甲状腺结节分为C-TR4a、C-TR4b及C-TR4c, 其恶性率分别为2%~10%、10%~50%、50%~90%[2]。本研究中, C-TR4a、4b、4c类结节恶性率分别为58.33%、72.73%、88.46%, 这可能是因为本研究纳入的研究对象均为C-TIRADS 4类FNAB结果不明确甲状腺结节,故C-TR4a和4b类结节的恶性率明显增高。本研究TMN主要CEUS表现为向心性灌注39例,低灌注42例,灌注不均匀46例,与周围正常甲状腺组织相比延迟灌注38例,灌注后边缘模糊49例,与TBN灌注特征相比均有显著差异(P < 0.05), 这可能与本研究中恶性结节均为甲状腺微小乳头状癌有关。恶性结节主要表现为滤泡上皮癌变出现浸润性生长,背景以广泛间质纤维化为主及砂砾体形成致结节内部微血管相对较稀疏且血供减少,致使恶性结节内部造影剂灌注方式、灌注程度、灌注速度及灌注均匀度较良性结节低,这与李亮等[11]和ZHAN J等[12]研究结论一致。本研究通过分析CEUS特征、造影参数及参数比值,结果显示TMN组TTP较TBN组高, PI、AS及AUC较TBN组低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 2组结节MTT无显著差异(P>0.05)。2组结节与周围正常甲状腺组织造影参数比值比较, TMN组R-TTP高于TBN组, R-PI、R-AS及R-AUC低于TBN组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 这与王丹等[13]研究结论一致。本研究通过CEUS灌注特征对72例C-TIRADS 4类FNAB不明确甲状腺结节进行鉴别诊断的灵敏度和特异度分别为83.02%、73.68%,这与张卫兵等[14]研究结果相近。由此可见,超声造影对C-TIRADS 4类FNAB结果不明确甲状腺结节性质的判断是一种理想的辅助诊断方法。
本研究的不足: ①本研究纳入样本量共72例,范围较局限,不具总体代表性; ②因超声医师在回顾分析过程中对结节常规超声图像和超声造影图像可能存在主观因素的影响,使结果具有局限性,需要进一步完善。
综上所述, CEUS通过造影剂在结节内微血管的灌注显影使甲状腺良恶性结节血供特点更加明显,在一定程度上提高了C-TIRADS 4类FNAB结果不明确甲状腺结节的诊断效能,有望辅助医师完善对甲状腺结节患者的临床决策。
-
表 1 2组患者一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
一般资料 分类 TMN组(n=53) TBN组(n=19) χ2/t P 性别 男 21(39.62) 8(42.11) 0.035 0.851 女 32(60.38) 11(57.89) 年龄/岁 39.53±4.68 42.65±5.74 2.346 0.022 结节大小/cm 0.81±0.43 0.85±0.45 0.344 0.732 结节径线分布 ≤1.0 cm 49(92.45) 17(89.47) 0.160 0.689 >1.0 cm 4(7.55) 2(10.53) 结节部位分布 左侧叶 21(39.62) 7(36.84) 1.763 0.414 右侧叶 27(50.94) 8(42.11) 峡部 5(9.43) 4(21.05) 甲状腺功能异常 合并 5(9.43) 3(15.79) 0.564 0.453 不合并 48(90.57) 16(84.21) C-TIRADS分类 C-TR4a 14(26.42) 10(52.63) 5.844 0.054 C-TR4b 16(30.19) 6(31.58) C-TR4c 23(43.39) 3(15.79) 表 2 2组结节CEUS灌注特征比较[n(%)]
特征 分类 TBN(n=19) TMN(n=53) χ2 P 造影剂灌注方式 向心性 7(36.84) 39(73.58) 8.244 0.016 弥散性 9(47.37) 11(20.75) 离心性 3(15.79) 3(5.66) 造影剂灌注程度 无灌注 0 0 24.124 < 0.001 低灌注 3(15.79) 42(79.25) 等灌注 11(57.89) 7(13.21) 高灌注 5(26.32) 4(7.55) 均匀灌注 均匀 13(68.42) 7(13.21) 20.958 < 0.010 不均匀 6(31.58) 46(86.79) 与周围正常甲状腺组织相比灌注速度 快进 4(21.05) 4(7.55) 17.845 < 0.001 同步 12(63.16) 11(20.75) 延迟 3(15.79) 38(71.69) 与周围正常甲状腺组织相比退出速度 快退 2(10.53) 21(39.62) 3.575 0.167 同步 12(63.16) 26(49.06) 延迟 5(26.32) 6(11.32) 灌注后边缘 清晰 16(84.21) 4(7.55) 40.405 < 0.001 模糊 3(15.79) 49(92.45) 表 3 2组CEUS参数及参数比的比较(x±s)
组别 参数 参数比 TTP/S PI/dB AS MTT/S AUC/(dB·s) R-TTP R-PI R-AS R-AUC TMN组(n=53) 25.06±3.94 35.33±3.74 0.68±0.29 30.19±4.07 4 682.07±416.50 1.268±0.428 0.827±0.041 0.867±0.081 0.835±0.076 TBN组(n=19) 22.47±1.99 44.96±4.05 0.86±0.31 28.66±3.32 5 174.01±521.88 0.941±0.074 0.987±0.026 0.924±0.073 1.028±0.051 t -2.734 9.423 2.280 -1.471 4.125 -3.298 15.865 2.698 10.249 P 0.008 < 0.001 0.026 0.146 < 0.001 0.002 < 0.001 0.009 < 0.001 表 4 CEUS灌注特征诊断甲状腺良恶性结节情况及效能分析
指标 分类 TMN TBN 病理结果 恶性 44 9 良性 5 14 诊断效能 Se/% - 83.02 Sp/% - 73.68 漏诊率/% - 16.98 误诊率/% - 26.32 比数积 - 13.69 约登指数 - 0.567 PPV/% - 89.79 NPV/% - 60.87 LR+ - 3.15 LR- - 0.23 总符合率/% - 80.56 Se: 灵敏度; Sp: 特异度; PPV: 阳性预测值;
NPV: 阴性预测值; LR+: 阳性似然比; LR-: 阴性似然比。
Se=a/a+c; Sp=d/d+b; 漏诊率=c/a+c; 误诊率=b/b+d;
约登指数=Se+Sp-1; 比数积=ad/bc; PPV=a/(a+b);
NPV=d/c+d; LR+=Se/(1-Sp); LR-=(1-Se)/Sp;
总符合率=(a+d)/(a+b+c+d)。a代表真阳性,
b代表假阳性,c代表假阴性, d代表真阴性。 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] ZHOU J Q, YIN L X, WEI X, et al. 2020 Chinese guidelines for ultrasound malignancy risk stratification of thyroid nodules: the C-TIRADS[J]. Endocrine, 2020, 70(2): 256-279. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02441-y
[3] DE KOSTER E J, KIST J W, VRIENS M R, et al. Thyroid ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: the positive influence of on-site adequacy assessment and number of needle passes on diagnostic cytology rate[J]. Acta Cytol, 2016, 60(1): 39-45. doi: 10.1159/000444917
[4] 薛海英, 董建党, 黄小艳. 超声引导下细针抽吸细胞学与粗针穿刺组织学在甲状腺微小结节诊断中的应用效果比较[J]. 中国实用医刊, 2020, 47(24): 80-83. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10760-1020025789.htm [5] 张坤, 姜珏, 王娟, 等. 人工智能联合超声造影对甲状腺TI-RADS 4类结节诊断价值的评估[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2021, 37(6): 610-613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2021.06.004 [6] 马淑梅, 闫瑞斌, 冯桃桃. 超声造影成像及参数特征对甲状腺TI-RADS4类结节良恶性的诊断价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2019, 35(10): 868-872. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2019.10.002 [7] CIBAS E S, ALI S Z. The 2017 Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology[J]. Thyroid, 2017, 27(11): 1341-1346. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0500
[8] 孟盈, 姚晓华, 王静, 等. ACR TI-RADS联合超声造影诊断甲状腺结节良恶性的价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2020, 36(11): 980-983. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2020.11.005 [9] 姜永玲, 胡彧. 中国超声甲状腺影像报告和数据系统与美国甲状腺协会超声模型对甲状腺结节诊断效能的比较研究[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26(5): 6-9. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20214598 [10] 宋玉林. 超声造影联合ARFI技术对甲状腺结节良恶性评估的临床应用价值[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2022, 20(2): 41-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202202011.htm [11] 李亮, 荣新, 张文, 等. 超声造影定量分析在甲状腺结节鉴别诊断中的应用价值[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2022, 24(11): 822-826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6978.2022.11.007 [12] ZHAN J, DING H. Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for evaluation of thyroid nodules[J]. Ultrasonography, 2018, 37(4): 288-297. doi: 10.14366/usg.18019
[13] 王丹, 姜珏, 王娟, 等. 超声造影对TI-RADS 4~5类甲状腺恶性结节的诊断价值[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2022, 36(11): 1166-1170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZD202211020.htm [14] 张卫兵, 秦爱平, 陈天奕, 等. 超声造影联合C-TIRADS分类诊断FNA细胞学不明确甲状腺结节[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2022, 38(9): 979-983. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCY202209006.htm -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 冯华梅,王春鹏,白立洁. 超声弹性成像联合超声造影对甲状腺结节微波消融治疗效果的预测分析. 医学影像学杂志. 2025(01): 32-35+52 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邵春晖,李培英,赵君智,罗永科,吕品,张毅. 多模态超声诊断C-TIRADS4类细针穿刺细胞学检查 TBSRTC Ⅲ类甲状腺结节的价值. 中华全科医学. 2025(03): 464-467+484 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郑斌,高峰,李静艳,魏玮,刘何利,黄梅,张震. 超声引导微波消融术与开放式手术治疗甲状腺良性大结节的临床疗效比较. 成都医学院学报. 2024(02): 294-297 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 饶红梅,史俊,陈桂月,戴海鹏. C-TI-RADS分类联合超声造影在甲状腺良恶性病灶中的鉴别诊断价值. 中国医学创新. 2024(35): 137-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号