Effect of Shenmai Injection on survival of patients with gastric cancer in phase Ⅱ to Ⅲ based on propensity score matching
-
摘要:目的
探讨参麦注射液在真实世界环境下对Ⅱ~Ⅲ期胃癌患者生存期的影响。
方法收集2012年1月1日—2022年12月1日符合纳入标准的433例胃癌患者为研究对象, 将其分为参麦组(中西医联合治疗)和对照组(单纯西医治疗)。应用倾向性评分匹配(PSM)均衡组间混杂因子; 采用Cox回归模型评估胃癌预后风险因子; 采用Kaplan-Meier法和Log-rank检验比较2组患者的总生存期(OS)和无进展生存期(PFS)。
结果共纳入433例符合纳入标准的患者, PSM后2组各有65例患者。PSM后,参麦组中位OS、中位PFS分别为35.27、22.63个月,均长于对照组的17.83、14.97个月,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001、P=0.003)。PSM后,参麦组1、3、5年生存率分别为90.7%、49.3%、34.8%, 高于对照组的67.7%、19.8%、4.9%, 差异有统计学意义(χ2=21.983, P < 0.001)。生存预后的多因素分析显示,影响胃癌的独立危险因素为侵犯脉管(P=0.046), 腺癌含印戒细胞癌(P=0.001), TNM分期Ⅲa期(P=0.012)、Ⅲb期(P=0.035)、Ⅲc期(P=0.046)。参麦注射液联合艾迪注射液(P < 0.001)、鸦胆子注射液(P=0.001)、根治性手术(P=0.004)、化疗(P=0.005)可以使胃癌患者生存获益。
结论参麦注射液联合西医方法治疗Ⅱ、Ⅲ期胃癌较单纯西医治疗更具优势。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the effect of Shenmai Injection on survival of patients with gastric cancer in phase Ⅱ to Ⅲ in a real-world environment.
MethodsFrom January 1, 2012 to December 1, 2022, 433 patients with gastric cancer who met the inclusion criteria were collected as research objects and divided into the Shenmai group (treated with traditional Chinese and western medicine) and the control group (treated with western medicine). Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to balance the confounding factors between groups; the Cox regression model was used to evaluate the risk factors for prognosis of gastric cancer; the Kaplan-Meier method and Log-rank test were used to compare the overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) of patients in both groups.
ResultsA total of 433 patients met the inclusion criteria were enrolled in this study, and were assigned into two groups after PSM, with 65 cases in each group. After PSM, the median OS and PFS in the Shenmai group were 35.27 and 22.63 months respectively, which were significantly longer than 17.83 and 14.97 months in the control group (P < 0.001, P=0.003). After PSM, the 1-, 3- and 5-year survival rates in the Shenmai group were 90.7%, 49.3% and 34.8% respectively, which were significantly higher than 67.7%, 19.8% and 4.9% in the control group (χ2=21.983, P < 0.001). Multivariable analysis of survival prognosis showed that the independent risk factors influencing gastric cancer were vascular invasion (P=0.046), adenocarcinoma with signet-ring cell carcinoma (P=0.001), phase Ⅲa (P=0.012), phase Ⅲb (P=0.035) and phase Ⅲc (P=0.046) of TNM staging. Shenmai Injection combined with Aidi injection (P < 0.001), Yadanzi Injection (P=0.001), radical surgery (P=0.004) and chemotherapy (P=0.005) were able to benefit the survival of gastric cancer patients.
ConclusionThe combination of Shenmai Injection and western medicine has more advantages than simple western medicine treatment in treating patients with gastric cancer in phase Ⅱ to Ⅲ.
-
Keywords:
- real-world researches /
- propensity score matching /
- gastric cancer /
- Shenmai Injection /
- survival
-
胃癌是中国最常见的消化系统肿瘤,发病率和致死率排名第2位。按照全球卫生组织的预测, 2020年中国胃癌发病案例达47.9万例,死亡案例达37.4万例,分别占全世界胃癌发生和致死总量的44.0%和48.6%[1]。胃癌早期症状不明显,甚至无症状,并缺乏特异性的生物标志物和检测手段用于识别早期胃癌的发生,大多数胃癌患者确诊时已发展至进展期或失去手术机会[2]。
参麦注射液作为临床上常用的抗肿瘤药物之一,其主要成分为红参、麦冬。多项研究[3-5]表明参麦注射液具有提高肿瘤患者免疫力、辅助化疗增效减毒、改善患者生活质量等作用。既往研究对参麦注射液影响胃癌患者生存期仍缺乏高级别临床循证依据,且存在单中心、小样本的局限性。本研究收集5家大型医院10年内的相关胃癌病例,采用回顾性队列研究,运用倾向性评分匹配(PSM)来均衡组间混杂因子,以探讨参麦注射液对Ⅱ~Ⅲ期胃癌患者生存期的影响,现将结果报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
数据来源于扬州市中医院、扬州大学附属医院、苏北人民医院、仪征市中医院及江都中医院共5家医院的医院信息系统。收集2012年1月1日—2022年12月1日的胃癌患者病例数据。统计患者基本信息(性别、年龄、吸烟史、饮酒史等)、临床信息(组织分化、病理类型、TNM分期等)和医嘱信息等,并对数据进行标准化处理。
纳入标准: ①临床病理诊断为胃癌者; ② TNM分期为Ⅱ、Ⅲ期者; ③患者年龄≥18岁者; ④患者的临床信息和病历完整。剔除标准: ①患者关键数据不详; ②并发其他恶性肿瘤者; ③并发严重的肾脏、消化道、心脑血管疾病的患者; ④失访或拒绝随访的患者。
1.2 信息处理与PSM
共纳入433例患者,分为对照组(单纯西医治疗)302例和参麦组(参麦联合西医治疗)131例,西医治疗为手术治疗、化疗、放疗、抗血管治疗。采用Logistic回归模型对2组患者实施1∶1的PSM, 其中包含患者性别、年龄、胃癌家族史、根治性手术史、化疗史、放疗史、抗血管治疗史、原发肿瘤位置、TNM分期情况等多个因素。
1.3 观察指标
将患者的总生存期(OS)作为主要观察技术指标,即从确诊胃癌到病逝或随访到2022年12月1日。将患者的无进展生存期(PFS)作为次要观察技术指标,即从确诊胃癌到病情发展或随访到2022年12月1日。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 25.0进行数据分析,利用卡方检验和Fisher确切概率法比较组间计数资料差异,采用Kaplan-Meier法描绘生存曲线,采用Log-rank检验比较组间生存率的差异,建立Cox比例风险回归模型对胃癌预后进行多因素分析, P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 PSM前后组间基线临床特征比较
实施PSM后, 2组患者各65例,共130例。匹配前, 2组间存在大量混杂因子,在吸烟史(P=0.007)、原发肿瘤部位(P < 0.001)、切除边缘(P < 0.001)、脉管侵犯(P=0.008)、TNM分期(P=0.032)、化疗史(P < 0.001)、根治性手术史(P < 0.001)等方面的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。匹配后,2组上述临床混杂因子均衡,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2组患者匹配前后基本临床信息比较[n(%)]特征 分类 PSM匹配前 P PSM匹配后 P 参麦组(n=131) 对照组(n=302) 参麦组(n=65) 对照组(n=65) 年龄 18~39岁 1(0.8) 5(1.7) 0.763 1(1.5) 1(1.5) 1.000 40~59岁 41(31.3) 95(31.5) 19(29.2) 19(29.2) ≥60岁 89(67.9) 202(66.9) 45(69.2) 45(69.2) 性别 男 97(74.0) 238(78.8) 0.277 49(75.4) 46(70.8) 0.553 女 34(26.0) 64(21.2) 16(24.6) 19(29.2) 吸烟史 是 26(19.8) 31(10.3) 0.007 10(15.4) 10(15.4) 1.000 否 105(80.2) 271(89.7) 55(84.6) 55(84.6) 饮酒史 是 11(8.4) 22(7.3) 0.689 6(9.22) 6(9.22) 1.000 否 120(91.6) 280(92.7) 59(90.8) 59(90.8) 家族史 是 0 3(1.0) 0.557 0 0 1.000 否 131(100.0) 299(99.0) 65(100.0) 65(100.0) 组织分化 高分化 30(22.9) 76(25.2) 0.549 16(24.6) 12(18.5) 0.695 中分化 80(61.1) 189(62.6) 38(58.5) 41(63.1) 低分化 21(16.0) 37(12.3) 11(16.9) 12(18.5) 原发肿瘤部位 胃窦 8(6.1) 28(9.3) < 0.001 5(7.7) 5(7.7) 0.175 胃体 15(11.5) 46(15.2) 9(13.8) 11(16.9) 贲门 42(32.1) 98(32.5) 22(33.8) 19(29.2) 其他 11(8.4) 55(18.2) 7(10.8) 10(15.4) 多个部位 23(17.6) 60(19.9) 9(13.8) 16(24.6) 不详 32(24.4) 15(5.0) 13(20.0) 4(6.2) 病理类型 腺癌 102(77.9) 239(79.1) 0.120 48(73.8) 44(67.7) 0.706 印戒细胞癌 5(3.8) 7(2.3) 4(6.2) 4(6.2) 腺癌含印戒细胞癌 17(13.0) 24(7.9) 8(6.2) 7(10.8) 其他 5(3.8) 29(9.6) 4(6.2) 9(13.8) 不详 2(1.5) 3(1.0) 1(1.5) 1(1.5) 切除边缘 阳性 10(7.6) 6(2.0) < 0.001 5(7.7) 2(3.1) 0.212 阴性 91(69.5) 264(87.4) 47(72.3) 55(84.6) 不详 30(22.9) 32(10.6) 13(20.0) 8(12.3) 脉管侵犯 阳性 49(37.4) 76(25.2) 0.008 27(41.5) 17(26.2) 0.177 阴性 26(19.8) 49(16.2) 12(18.5) 16(24.6) 不详 56(42.7) 177(58.6) 26(40.0) 32(49.2) TNM分期 Ⅱa期 10(7.6) 48(15.9) 0.032 8(12.3) 6(9.2) 0.814 Ⅱb期 17(13.0) 56(18.5) 9(13.8) 12(18.5) Ⅲa期 43(32.8) 86(28.5) 17(26.2) 17(26.2) Ⅲb期 41(31.3) 85(28.1) 23(35.4) 19(29.2) Ⅲc期 20(15.3) 27(8.9) 8(12.3) 11(16.9) 化疗史 是 113(86.3) 292(96.7) < 0.001 62(95.4) 57(87.7) 0.115 否 18(13.7) 10(3.3) 3(4.6) 8(12.3) 放疗史 是 18(13.7) 45(15.2) 0.688 10(15.4) 10(15.4) 1.000 否 113(86.3) 256(84.8) 55(84.6) 55(84.6) 根治性手术史 是 112(85.5) 290(96.0) < 0.001 60(92.3) 63(96.9) 0.321 否 8(6.1) 6(2.0) 3(4.6) 2(3.1) 不详 11(8.4) 6(2.0) 2(3.1) 0 抗血管治疗史 是 12(9.2) 26(8.6) 0.852 8(12.3) 6(9.2) 0.571 否 119(90.8) 276(91.4) 57(87.7) 59(90.8) 2.2 PSM前后组间生存分析
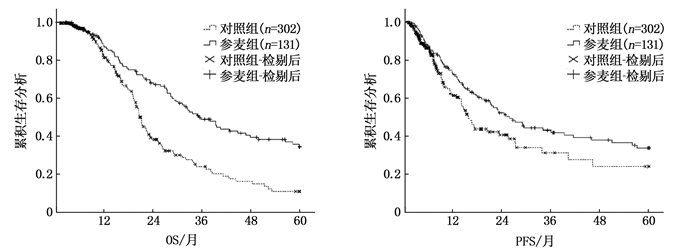
PSM前,参麦组中位OS为35.27个月,中位PFS为22.97个月,分别长于对照组的20.70个月和14.90个月,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.001、P=0.023), 见图 1; PSM后,参麦组中位OS、中位PFS分别为35.27、22.63个月,均长于对照组的17.83、14.97个月,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001、P=0.003), 见图 2。
PSM前,参麦组1、3、5年生存率分别为87.4%、49.1%、34.3%, 高于对照组的81.7%、23.9%、10.4%, 差异有统计学意义(χ2=22.676, P < 0.001); PSM后,参麦组1、3、5年生存率分别为90.7%、49.3%、34.8%, 高于对照组的67.7%、19.8%、4.9%, 差异亦有统计学意义(χ2=21.983, P < 0.001)。见图 3。
2.3 PSM后影响生存预后的多因素分析
运用Cox回归模型对PSM后的患者临床特征资料与基本信息进行胃癌预后的多因素分析,结果显示,最终影响患者生存预后的独立保护因素分别为参麦组(P=0.001)、化疗(P=0.019), 而影响其生存预后的独立危险因素分别为侵犯脉管(P=0.046)、腺癌含印戒细胞癌(P=0.001)、Ⅲa期(P=0.012)、Ⅲb期(P=0.035)、Ⅲc期(P=0.046)。见表 2。
表 2 影响胃癌患者生存期的多因素Cox回归分析变量 类别 n 多因素分析
HR(95%CI)P 组别 对照组 65 1(参照) 参麦组 65 0.219(0.086~0.558) 0.001 年龄 18~39岁 2 1(参照) 40~59岁 38 1.087(0.046~25.917) 0.959 ≥60岁 90 1.200(0.065~22.049) 0.902 性别 男 95 1(参照) 女 35 0.725(0.297~1.769) 0.480 吸烟史 否 110 1(参照) 是 20 2.702(0.716~10.197) 0.143 饮酒史 否 118 1(参照) 是 12 0.793(0.123~5.115) 0.807 原发肿瘤部位 胃窦 10 1(参照) 胃体 20 0.264(0.048~1.449) 0.125 贲门 41 0.412(0.097~1.749) 0.230 其他 17 1.209(0.220~6.660) 0.827 多个部位 25 0.834(0.162~4.297) 0.828 病理类型 腺癌 92 1(参照) 印戒细胞癌 8 0.578(0.127~2.621) 0.477 腺癌含印戒细胞癌 15 6.680(2.106~21.186) 0.001 其他 13 1.810(0.510~6.418) 0.358 肿瘤分化程度 高分化 28 1(参照) 中分化 79 1.546(0.499~4.797) 0.450 低分化 23 2.737(0.578~12.952) 0.204 肿瘤切缘 阴性 102 1(参照) 阳性 7 3.374(0.959~11.866) 0.058 侵犯脉管 阴性 28 1(参照) 阳性 44 4.660(1.025~21.177) 0.046 侵犯神经 阴性 23 1(参照) 阳性 42 0.514(0.100~2.651) 0.692 临近结构侵犯 否 54 1(参照) 是 67 0.545(0.202~1.472) 0.232 根治性手术史 否 5 1(参照) 是 123 3.997(0.231~69.270) 0.341 化疗史 否 11 1(参照) 是 119 0.113(0.018~0.701) 0.019 放疗史 否 110 1(参照) 是 20 1.495(0.549~4.069) 0.431 抗血管治疗史 否 116 1(参照) 是 14 1.085(0.357~3.296) 0.886 TNM分期 Ⅱa期 14 1(参照) Ⅱb期 21 1.124(0.150~8.423) 0.909 Ⅲa期 34 7.765(1.579~38.184) 0.012 Ⅲb期 42 6.575(1.146~37.706) 0.035 Ⅲc期 19 8.139(1.041~63.614) 0.046 2.4 参麦联合西医治疗情况分析
根据收集到的数据和临床经验,参麦注射液常与以下西医治疗方法联用,例如根治性手术、化疗、放疗和抗血管治疗。对其进行多因素分析,相较于单独使用参麦注射液,联合根治性手术(HR=0.238, P=0.004)或化疗(HR=0.235, P=0.005)可以显著提高胃癌患者的生存率,见表 3。
表 3 参麦注射液同不同西医治疗方法联合使用对胃癌生存期的影响不同西医治疗手段 组别 应用比率 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P 根治性手术 对照组(n=65) 63(96.9) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 60(92.3) 0.238(0.089~0.634) 0.004 化疗 对照组(n=65) 57(87.7) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 62(95.4) 0.235(0.085~0.650) 0.005 放疗 对照组(n=65) 10(15.4) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 10(15.4) 1.000(0.011~90.333) 1.000 抗血管治疗 对照组(n=65) 6(9.2) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 8(12.3) 0(0~55.373) 0.711 2.5 参麦联合中医治疗情况分析
联合中医治疗的方法包括中药煎剂、鸦胆子注射液、香菇多糖注射液、艾迪注射液等。将这些常用的药品引入多因素Cox回归模型,参照为对照组,结果表明,联合复方苦参注射液和参芪扶正注射液并未显著改善胃癌患者的生存状况(P>0.05), 而与中药煎剂、鸦胆子注射液等中药制剂的联用则可使患者生存显著获益(P < 0.05), 其中艾迪注射液和参麦注射液的联合应用使胃癌患者的生存获益最为显著(HR=0.002, P < 0.05)。见表 4。
表 4 参麦注射液联合其他中药制剂对胃癌生存预后的影响组别 联合用药 n 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P 对照组 65 1.000(参照) 参麦组 中药汤剂 61 0.180(0.068~0.480) 0.001 鸦胆子注射液 31 0.047(0.008~0.284) 0.001 香菇多糖注射液 29 0.065(0.008~0.511) 0.009 艾迪注射液 26 0.002(0~0.023) < 0.001 复方苦参注射液 25 0.222(0.036~1.362) 0.104 参芪扶正注射液 22 0.209(0.023~1.882) 0.163 参芪十一味颗粒 20 0.004(0~0.371) 0.017 3. 讨论
在全球范围内,胃癌严重危害着人类的健康,而胃癌患者被查出时,一般已是中晚期。对于常规的西医治疗方法如外科手术、化疗、放疗和免疫学疗法等,虽然能够有效延长患者的生存期,但也存在费用昂贵、毒副反应强、患者生存质量差等缺点。中医立足于“辨病”与“辨证”相结合的思维特点,有着增效、减毒、提高患者生活质量和减少并发症的优势。因此,中西医联合治疗不仅可以有效治疗中晚期胃癌,而且可以减轻患者术后正气亏虚和化疗引起癌毒内蕴的情况,同时提高患者生活质量,延长患者的生存期。
根据中医的辨证理论,胃癌属于“胃脘痛”“噎嗝”“反胃”“积聚”等范畴,发病病位在胃,又与脾、肝、肾密切相关。情志、饮食、正虚是其主要危险因素[6]。《金匮要略》曰: “跌阳脉浮而涩,浮则为虚,虚则伤脾,脾伤则不磨,朝食暮吐,暮食朝吐,宿食不化,名曰反胃。”《医宗必读·积聚》曰: “积之成也,正气不足,而后邪气聚。”由此可见,邪毒滋扰致脾胃运化失建,后天生化乏源,而脾胃升清降浊失衡,又导致患者痰、瘀、郁、毒相互交织搏结。因此,脾虚毒聚是其关键病机,总属本虚标实的范畴。参麦注射液源自《医学启源》中的生脉散,由红参、麦冬提取物混合组成,具有益气固脱、养阴生津的功效[7]。研究[8-9]表明,参麦注射液的主要成分含有人参皂苷、人参多糖、麦冬皂苷等,人参皂苷通过调节肿瘤抑制因子、自然杀伤(NK)细胞等来发挥抗肿瘤、调节免疫功能、减轻化疗毒副反应等作用。研究[10]表明麦冬皂苷可以通过抑制基质金属蛋白酶-2(MMP-2)、基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)的表达来抑制人胃癌MGC-803细胞的侵袭和迁移能力。
本研究通过在真实世界环境中收集多家医院胃癌患者的医院信息系统(HIS)数据,通过PSM的方法,使参麦组与对照组的混杂因素均衡可比,进而在真实世界中研究参麦注射液对Ⅱ、Ⅲ期胃癌患者生存期的影响。本研究发现,参麦组相较于对照组可使中位OS和中位PFS分别延长17.44个月和7.66个月; 与对照组相比,参麦组的1、3、5年生存率也显著提高; Cox比例风险回归模型分析发现,病理类型为腺癌含印戒细胞癌,侵犯脉管, TNM分期为Ⅲa期、Ⅲb期、Ⅲc期对胃癌患者的生存预后可产生负面影响,这也符合临床上胃癌Ⅲ~Ⅳ期的患者生存预后较差的情况; 参麦组、化疗这2个因素对其产生正面影响,进一步证明参麦注射液可以使胃癌患者的生存明显获益。
由于在真实世界环境下不同患者的治疗方案存在差异,本研究进一步探讨了参麦注射液联合不同中西医治疗手段的关联作用,发现参麦注射液联合根治性手术和化疗的胃癌患者生存获益显著,可以有效发挥增效减毒的作用。同时,中医治疗手段关联分析表明,胃癌患者生存获益明显主要与联合中药煎剂、鸦胆子注射液、艾迪注射液、香菇多糖注射液和参芪十一味颗粒相关,其中与艾迪注射液联用获益最为显著。因此,对于接受根治性手术和化疗的临床胃癌患者,可以联合应用参麦注射液、艾迪注射液、鸦胆子注射液,从而达到增效减毒、延长生存期、提高生活质量的功效,为临床用药决策提供一定的参考。
-
表 1 2组患者匹配前后基本临床信息比较[n(%)]
特征 分类 PSM匹配前 P PSM匹配后 P 参麦组(n=131) 对照组(n=302) 参麦组(n=65) 对照组(n=65) 年龄 18~39岁 1(0.8) 5(1.7) 0.763 1(1.5) 1(1.5) 1.000 40~59岁 41(31.3) 95(31.5) 19(29.2) 19(29.2) ≥60岁 89(67.9) 202(66.9) 45(69.2) 45(69.2) 性别 男 97(74.0) 238(78.8) 0.277 49(75.4) 46(70.8) 0.553 女 34(26.0) 64(21.2) 16(24.6) 19(29.2) 吸烟史 是 26(19.8) 31(10.3) 0.007 10(15.4) 10(15.4) 1.000 否 105(80.2) 271(89.7) 55(84.6) 55(84.6) 饮酒史 是 11(8.4) 22(7.3) 0.689 6(9.22) 6(9.22) 1.000 否 120(91.6) 280(92.7) 59(90.8) 59(90.8) 家族史 是 0 3(1.0) 0.557 0 0 1.000 否 131(100.0) 299(99.0) 65(100.0) 65(100.0) 组织分化 高分化 30(22.9) 76(25.2) 0.549 16(24.6) 12(18.5) 0.695 中分化 80(61.1) 189(62.6) 38(58.5) 41(63.1) 低分化 21(16.0) 37(12.3) 11(16.9) 12(18.5) 原发肿瘤部位 胃窦 8(6.1) 28(9.3) < 0.001 5(7.7) 5(7.7) 0.175 胃体 15(11.5) 46(15.2) 9(13.8) 11(16.9) 贲门 42(32.1) 98(32.5) 22(33.8) 19(29.2) 其他 11(8.4) 55(18.2) 7(10.8) 10(15.4) 多个部位 23(17.6) 60(19.9) 9(13.8) 16(24.6) 不详 32(24.4) 15(5.0) 13(20.0) 4(6.2) 病理类型 腺癌 102(77.9) 239(79.1) 0.120 48(73.8) 44(67.7) 0.706 印戒细胞癌 5(3.8) 7(2.3) 4(6.2) 4(6.2) 腺癌含印戒细胞癌 17(13.0) 24(7.9) 8(6.2) 7(10.8) 其他 5(3.8) 29(9.6) 4(6.2) 9(13.8) 不详 2(1.5) 3(1.0) 1(1.5) 1(1.5) 切除边缘 阳性 10(7.6) 6(2.0) < 0.001 5(7.7) 2(3.1) 0.212 阴性 91(69.5) 264(87.4) 47(72.3) 55(84.6) 不详 30(22.9) 32(10.6) 13(20.0) 8(12.3) 脉管侵犯 阳性 49(37.4) 76(25.2) 0.008 27(41.5) 17(26.2) 0.177 阴性 26(19.8) 49(16.2) 12(18.5) 16(24.6) 不详 56(42.7) 177(58.6) 26(40.0) 32(49.2) TNM分期 Ⅱa期 10(7.6) 48(15.9) 0.032 8(12.3) 6(9.2) 0.814 Ⅱb期 17(13.0) 56(18.5) 9(13.8) 12(18.5) Ⅲa期 43(32.8) 86(28.5) 17(26.2) 17(26.2) Ⅲb期 41(31.3) 85(28.1) 23(35.4) 19(29.2) Ⅲc期 20(15.3) 27(8.9) 8(12.3) 11(16.9) 化疗史 是 113(86.3) 292(96.7) < 0.001 62(95.4) 57(87.7) 0.115 否 18(13.7) 10(3.3) 3(4.6) 8(12.3) 放疗史 是 18(13.7) 45(15.2) 0.688 10(15.4) 10(15.4) 1.000 否 113(86.3) 256(84.8) 55(84.6) 55(84.6) 根治性手术史 是 112(85.5) 290(96.0) < 0.001 60(92.3) 63(96.9) 0.321 否 8(6.1) 6(2.0) 3(4.6) 2(3.1) 不详 11(8.4) 6(2.0) 2(3.1) 0 抗血管治疗史 是 12(9.2) 26(8.6) 0.852 8(12.3) 6(9.2) 0.571 否 119(90.8) 276(91.4) 57(87.7) 59(90.8) 表 2 影响胃癌患者生存期的多因素Cox回归分析
变量 类别 n 多因素分析
HR(95%CI)P 组别 对照组 65 1(参照) 参麦组 65 0.219(0.086~0.558) 0.001 年龄 18~39岁 2 1(参照) 40~59岁 38 1.087(0.046~25.917) 0.959 ≥60岁 90 1.200(0.065~22.049) 0.902 性别 男 95 1(参照) 女 35 0.725(0.297~1.769) 0.480 吸烟史 否 110 1(参照) 是 20 2.702(0.716~10.197) 0.143 饮酒史 否 118 1(参照) 是 12 0.793(0.123~5.115) 0.807 原发肿瘤部位 胃窦 10 1(参照) 胃体 20 0.264(0.048~1.449) 0.125 贲门 41 0.412(0.097~1.749) 0.230 其他 17 1.209(0.220~6.660) 0.827 多个部位 25 0.834(0.162~4.297) 0.828 病理类型 腺癌 92 1(参照) 印戒细胞癌 8 0.578(0.127~2.621) 0.477 腺癌含印戒细胞癌 15 6.680(2.106~21.186) 0.001 其他 13 1.810(0.510~6.418) 0.358 肿瘤分化程度 高分化 28 1(参照) 中分化 79 1.546(0.499~4.797) 0.450 低分化 23 2.737(0.578~12.952) 0.204 肿瘤切缘 阴性 102 1(参照) 阳性 7 3.374(0.959~11.866) 0.058 侵犯脉管 阴性 28 1(参照) 阳性 44 4.660(1.025~21.177) 0.046 侵犯神经 阴性 23 1(参照) 阳性 42 0.514(0.100~2.651) 0.692 临近结构侵犯 否 54 1(参照) 是 67 0.545(0.202~1.472) 0.232 根治性手术史 否 5 1(参照) 是 123 3.997(0.231~69.270) 0.341 化疗史 否 11 1(参照) 是 119 0.113(0.018~0.701) 0.019 放疗史 否 110 1(参照) 是 20 1.495(0.549~4.069) 0.431 抗血管治疗史 否 116 1(参照) 是 14 1.085(0.357~3.296) 0.886 TNM分期 Ⅱa期 14 1(参照) Ⅱb期 21 1.124(0.150~8.423) 0.909 Ⅲa期 34 7.765(1.579~38.184) 0.012 Ⅲb期 42 6.575(1.146~37.706) 0.035 Ⅲc期 19 8.139(1.041~63.614) 0.046 表 3 参麦注射液同不同西医治疗方法联合使用对胃癌生存期的影响
不同西医治疗手段 组别 应用比率 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P 根治性手术 对照组(n=65) 63(96.9) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 60(92.3) 0.238(0.089~0.634) 0.004 化疗 对照组(n=65) 57(87.7) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 62(95.4) 0.235(0.085~0.650) 0.005 放疗 对照组(n=65) 10(15.4) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 10(15.4) 1.000(0.011~90.333) 1.000 抗血管治疗 对照组(n=65) 6(9.2) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 8(12.3) 0(0~55.373) 0.711 表 4 参麦注射液联合其他中药制剂对胃癌生存预后的影响
组别 联合用药 n 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P 对照组 65 1.000(参照) 参麦组 中药汤剂 61 0.180(0.068~0.480) 0.001 鸦胆子注射液 31 0.047(0.008~0.284) 0.001 香菇多糖注射液 29 0.065(0.008~0.511) 0.009 艾迪注射液 26 0.002(0~0.023) < 0.001 复方苦参注射液 25 0.222(0.036~1.362) 0.104 参芪扶正注射液 22 0.209(0.023~1.882) 0.163 参芪十一味颗粒 20 0.004(0~0.371) 0.017 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] SMYTH E C, NILSSON M, GRABSCH H I, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-648. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
[3] 张国平, 李攀, 费浙钧, 等. 参麦注射液联合FOLFOX方案化疗治疗进展期胃癌近期疗效及对患者免疫功能和肿瘤标志物的影响[J]. 中国基层医药, 2021, 28(12): 1839-1843. [4] 孙慧. 参麦注射液治疗消化系统恶性肿瘤的临床疗效分析[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2012, 25(4): 595-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJYY201204047.htm [5] 刘包欣子, 邵杰, 舒鹏, 等. FOLFOX4方案联合参麦注射液对胃癌患者骨髓功能和免疫功能的影响[J]. 西部中医药, 2020, 33(9): 8-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSZY202009003.htm [6] 杨蝶, 张禹森, 张晓春. 复方苦参注射液对胃癌患者生存期的影响: 一项真实世界回顾性、多中心队列研究[J]. 中医杂志, 2022, 63(23): 2259-2265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ202223011.htm [7] 刘学梅, 段世玲, 刘勇峰. 参麦注射液联合化疗治疗进展期胃癌29例[J]. 河南中医, 2015, 35(9): 2285-2287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZY201509124.htm [8] 张艳, 周淑如, 韩仕阳, 等. 人参皂苷对免疫功能的调节作用及机制[J/OL]. 江苏大学学报(医学版): 1-9[2022-12-16]. [9] 王冬雪, 吴新民, 蔺冬梅, 等. 人参皂苷抗胃癌作用研究进展[J]. 特产研究, 2022, 44(3): 118-123, 128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TCYA202203019.htm [10] 杨婧, 孙超, 姜泽群, 等. 麦冬皂苷B对人胃癌MGC-803细胞侵袭和迁移能力的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(6): 2742-2745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201906110.htm -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王庆颖,张晓春,侯超. 基于真实世界证据的扶正清毒法治疗胃癌疗效评价及其用药规律分析. 中国中西医结合消化杂志. 2024(03): 226-232 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 步玉晴,张奇,张利飞,张芬,魏明秀,王晶晶,王霞,王慧纬,张洪珍. 参麦注射液联合化疗治疗老年晚期胃癌近期疗效及不良反应观察. 现代中西医结合杂志. 2024(18): 2563-2566 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
