Effect of Shenmai Injection on survival of patients with gastric cancer in phase Ⅱ to Ⅲ based on propensity score matching
-
摘要:目的
探讨参麦注射液在真实世界环境下对Ⅱ~Ⅲ期胃癌患者生存期的影响。
方法收集2012年1月1日—2022年12月1日符合纳入标准的433例胃癌患者为研究对象, 将其分为参麦组(中西医联合治疗)和对照组(单纯西医治疗)。应用倾向性评分匹配(PSM)均衡组间混杂因子; 采用Cox回归模型评估胃癌预后风险因子; 采用Kaplan-Meier法和Log-rank检验比较2组患者的总生存期(OS)和无进展生存期(PFS)。
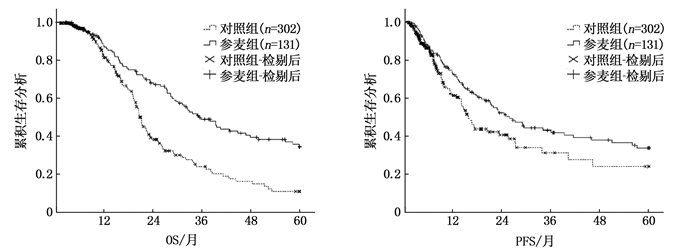
结果共纳入433例符合纳入标准的患者, PSM后2组各有65例患者。PSM后,参麦组中位OS、中位PFS分别为35.27、22.63个月,均长于对照组的17.83、14.97个月,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001、P=0.003)。PSM后,参麦组1、3、5年生存率分别为90.7%、49.3%、34.8%, 高于对照组的67.7%、19.8%、4.9%, 差异有统计学意义(χ2=21.983, P < 0.001)。生存预后的多因素分析显示,影响胃癌的独立危险因素为侵犯脉管(P=0.046), 腺癌含印戒细胞癌(P=0.001), TNM分期Ⅲa期(P=0.012)、Ⅲb期(P=0.035)、Ⅲc期(P=0.046)。参麦注射液联合艾迪注射液(P < 0.001)、鸦胆子注射液(P=0.001)、根治性手术(P=0.004)、化疗(P=0.005)可以使胃癌患者生存获益。
结论参麦注射液联合西医方法治疗Ⅱ、Ⅲ期胃癌较单纯西医治疗更具优势。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the effect of Shenmai Injection on survival of patients with gastric cancer in phase Ⅱ to Ⅲ in a real-world environment.
MethodsFrom January 1, 2012 to December 1, 2022, 433 patients with gastric cancer who met the inclusion criteria were collected as research objects and divided into the Shenmai group (treated with traditional Chinese and western medicine) and the control group (treated with western medicine). Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to balance the confounding factors between groups; the Cox regression model was used to evaluate the risk factors for prognosis of gastric cancer; the Kaplan-Meier method and Log-rank test were used to compare the overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) of patients in both groups.
ResultsA total of 433 patients met the inclusion criteria were enrolled in this study, and were assigned into two groups after PSM, with 65 cases in each group. After PSM, the median OS and PFS in the Shenmai group were 35.27 and 22.63 months respectively, which were significantly longer than 17.83 and 14.97 months in the control group (P < 0.001, P=0.003). After PSM, the 1-, 3- and 5-year survival rates in the Shenmai group were 90.7%, 49.3% and 34.8% respectively, which were significantly higher than 67.7%, 19.8% and 4.9% in the control group (χ2=21.983, P < 0.001). Multivariable analysis of survival prognosis showed that the independent risk factors influencing gastric cancer were vascular invasion (P=0.046), adenocarcinoma with signet-ring cell carcinoma (P=0.001), phase Ⅲa (P=0.012), phase Ⅲb (P=0.035) and phase Ⅲc (P=0.046) of TNM staging. Shenmai Injection combined with Aidi injection (P < 0.001), Yadanzi Injection (P=0.001), radical surgery (P=0.004) and chemotherapy (P=0.005) were able to benefit the survival of gastric cancer patients.
ConclusionThe combination of Shenmai Injection and western medicine has more advantages than simple western medicine treatment in treating patients with gastric cancer in phase Ⅱ to Ⅲ.
-
Keywords:
- real-world researches /
- propensity score matching /
- gastric cancer /
- Shenmai Injection /
- survival
-
-
表 1 2组患者匹配前后基本临床信息比较[n(%)]
特征 分类 PSM匹配前 P PSM匹配后 P 参麦组(n=131) 对照组(n=302) 参麦组(n=65) 对照组(n=65) 年龄 18~39岁 1(0.8) 5(1.7) 0.763 1(1.5) 1(1.5) 1.000 40~59岁 41(31.3) 95(31.5) 19(29.2) 19(29.2) ≥60岁 89(67.9) 202(66.9) 45(69.2) 45(69.2) 性别 男 97(74.0) 238(78.8) 0.277 49(75.4) 46(70.8) 0.553 女 34(26.0) 64(21.2) 16(24.6) 19(29.2) 吸烟史 是 26(19.8) 31(10.3) 0.007 10(15.4) 10(15.4) 1.000 否 105(80.2) 271(89.7) 55(84.6) 55(84.6) 饮酒史 是 11(8.4) 22(7.3) 0.689 6(9.22) 6(9.22) 1.000 否 120(91.6) 280(92.7) 59(90.8) 59(90.8) 家族史 是 0 3(1.0) 0.557 0 0 1.000 否 131(100.0) 299(99.0) 65(100.0) 65(100.0) 组织分化 高分化 30(22.9) 76(25.2) 0.549 16(24.6) 12(18.5) 0.695 中分化 80(61.1) 189(62.6) 38(58.5) 41(63.1) 低分化 21(16.0) 37(12.3) 11(16.9) 12(18.5) 原发肿瘤部位 胃窦 8(6.1) 28(9.3) < 0.001 5(7.7) 5(7.7) 0.175 胃体 15(11.5) 46(15.2) 9(13.8) 11(16.9) 贲门 42(32.1) 98(32.5) 22(33.8) 19(29.2) 其他 11(8.4) 55(18.2) 7(10.8) 10(15.4) 多个部位 23(17.6) 60(19.9) 9(13.8) 16(24.6) 不详 32(24.4) 15(5.0) 13(20.0) 4(6.2) 病理类型 腺癌 102(77.9) 239(79.1) 0.120 48(73.8) 44(67.7) 0.706 印戒细胞癌 5(3.8) 7(2.3) 4(6.2) 4(6.2) 腺癌含印戒细胞癌 17(13.0) 24(7.9) 8(6.2) 7(10.8) 其他 5(3.8) 29(9.6) 4(6.2) 9(13.8) 不详 2(1.5) 3(1.0) 1(1.5) 1(1.5) 切除边缘 阳性 10(7.6) 6(2.0) < 0.001 5(7.7) 2(3.1) 0.212 阴性 91(69.5) 264(87.4) 47(72.3) 55(84.6) 不详 30(22.9) 32(10.6) 13(20.0) 8(12.3) 脉管侵犯 阳性 49(37.4) 76(25.2) 0.008 27(41.5) 17(26.2) 0.177 阴性 26(19.8) 49(16.2) 12(18.5) 16(24.6) 不详 56(42.7) 177(58.6) 26(40.0) 32(49.2) TNM分期 Ⅱa期 10(7.6) 48(15.9) 0.032 8(12.3) 6(9.2) 0.814 Ⅱb期 17(13.0) 56(18.5) 9(13.8) 12(18.5) Ⅲa期 43(32.8) 86(28.5) 17(26.2) 17(26.2) Ⅲb期 41(31.3) 85(28.1) 23(35.4) 19(29.2) Ⅲc期 20(15.3) 27(8.9) 8(12.3) 11(16.9) 化疗史 是 113(86.3) 292(96.7) < 0.001 62(95.4) 57(87.7) 0.115 否 18(13.7) 10(3.3) 3(4.6) 8(12.3) 放疗史 是 18(13.7) 45(15.2) 0.688 10(15.4) 10(15.4) 1.000 否 113(86.3) 256(84.8) 55(84.6) 55(84.6) 根治性手术史 是 112(85.5) 290(96.0) < 0.001 60(92.3) 63(96.9) 0.321 否 8(6.1) 6(2.0) 3(4.6) 2(3.1) 不详 11(8.4) 6(2.0) 2(3.1) 0 抗血管治疗史 是 12(9.2) 26(8.6) 0.852 8(12.3) 6(9.2) 0.571 否 119(90.8) 276(91.4) 57(87.7) 59(90.8) 表 2 影响胃癌患者生存期的多因素Cox回归分析
变量 类别 n 多因素分析
HR(95%CI)P 组别 对照组 65 1(参照) 参麦组 65 0.219(0.086~0.558) 0.001 年龄 18~39岁 2 1(参照) 40~59岁 38 1.087(0.046~25.917) 0.959 ≥60岁 90 1.200(0.065~22.049) 0.902 性别 男 95 1(参照) 女 35 0.725(0.297~1.769) 0.480 吸烟史 否 110 1(参照) 是 20 2.702(0.716~10.197) 0.143 饮酒史 否 118 1(参照) 是 12 0.793(0.123~5.115) 0.807 原发肿瘤部位 胃窦 10 1(参照) 胃体 20 0.264(0.048~1.449) 0.125 贲门 41 0.412(0.097~1.749) 0.230 其他 17 1.209(0.220~6.660) 0.827 多个部位 25 0.834(0.162~4.297) 0.828 病理类型 腺癌 92 1(参照) 印戒细胞癌 8 0.578(0.127~2.621) 0.477 腺癌含印戒细胞癌 15 6.680(2.106~21.186) 0.001 其他 13 1.810(0.510~6.418) 0.358 肿瘤分化程度 高分化 28 1(参照) 中分化 79 1.546(0.499~4.797) 0.450 低分化 23 2.737(0.578~12.952) 0.204 肿瘤切缘 阴性 102 1(参照) 阳性 7 3.374(0.959~11.866) 0.058 侵犯脉管 阴性 28 1(参照) 阳性 44 4.660(1.025~21.177) 0.046 侵犯神经 阴性 23 1(参照) 阳性 42 0.514(0.100~2.651) 0.692 临近结构侵犯 否 54 1(参照) 是 67 0.545(0.202~1.472) 0.232 根治性手术史 否 5 1(参照) 是 123 3.997(0.231~69.270) 0.341 化疗史 否 11 1(参照) 是 119 0.113(0.018~0.701) 0.019 放疗史 否 110 1(参照) 是 20 1.495(0.549~4.069) 0.431 抗血管治疗史 否 116 1(参照) 是 14 1.085(0.357~3.296) 0.886 TNM分期 Ⅱa期 14 1(参照) Ⅱb期 21 1.124(0.150~8.423) 0.909 Ⅲa期 34 7.765(1.579~38.184) 0.012 Ⅲb期 42 6.575(1.146~37.706) 0.035 Ⅲc期 19 8.139(1.041~63.614) 0.046 表 3 参麦注射液同不同西医治疗方法联合使用对胃癌生存期的影响
不同西医治疗手段 组别 应用比率 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P 根治性手术 对照组(n=65) 63(96.9) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 60(92.3) 0.238(0.089~0.634) 0.004 化疗 对照组(n=65) 57(87.7) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 62(95.4) 0.235(0.085~0.650) 0.005 放疗 对照组(n=65) 10(15.4) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 10(15.4) 1.000(0.011~90.333) 1.000 抗血管治疗 对照组(n=65) 6(9.2) 1.000(参照) 参麦组(n=65) 8(12.3) 0(0~55.373) 0.711 表 4 参麦注射液联合其他中药制剂对胃癌生存预后的影响
组别 联合用药 n 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P 对照组 65 1.000(参照) 参麦组 中药汤剂 61 0.180(0.068~0.480) 0.001 鸦胆子注射液 31 0.047(0.008~0.284) 0.001 香菇多糖注射液 29 0.065(0.008~0.511) 0.009 艾迪注射液 26 0.002(0~0.023) < 0.001 复方苦参注射液 25 0.222(0.036~1.362) 0.104 参芪扶正注射液 22 0.209(0.023~1.882) 0.163 参芪十一味颗粒 20 0.004(0~0.371) 0.017 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] SMYTH E C, NILSSON M, GRABSCH H I, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-648. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
[3] 张国平, 李攀, 费浙钧, 等. 参麦注射液联合FOLFOX方案化疗治疗进展期胃癌近期疗效及对患者免疫功能和肿瘤标志物的影响[J]. 中国基层医药, 2021, 28(12): 1839-1843. [4] 孙慧. 参麦注射液治疗消化系统恶性肿瘤的临床疗效分析[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2012, 25(4): 595-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJYY201204047.htm [5] 刘包欣子, 邵杰, 舒鹏, 等. FOLFOX4方案联合参麦注射液对胃癌患者骨髓功能和免疫功能的影响[J]. 西部中医药, 2020, 33(9): 8-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSZY202009003.htm [6] 杨蝶, 张禹森, 张晓春. 复方苦参注射液对胃癌患者生存期的影响: 一项真实世界回顾性、多中心队列研究[J]. 中医杂志, 2022, 63(23): 2259-2265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ202223011.htm [7] 刘学梅, 段世玲, 刘勇峰. 参麦注射液联合化疗治疗进展期胃癌29例[J]. 河南中医, 2015, 35(9): 2285-2287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZY201509124.htm [8] 张艳, 周淑如, 韩仕阳, 等. 人参皂苷对免疫功能的调节作用及机制[J/OL]. 江苏大学学报(医学版): 1-9[2022-12-16]. [9] 王冬雪, 吴新民, 蔺冬梅, 等. 人参皂苷抗胃癌作用研究进展[J]. 特产研究, 2022, 44(3): 118-123, 128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TCYA202203019.htm [10] 杨婧, 孙超, 姜泽群, 等. 麦冬皂苷B对人胃癌MGC-803细胞侵袭和迁移能力的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(6): 2742-2745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201906110.htm -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 欧冬冬. 乙酰半胱氨酸雾化联合罗红霉素分散片对重症支原体肺炎患儿的影响. 中外医学研究. 2025(05): 123-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 姜秀明,李建卫. 乙酰半胱氨酸雾化吸入联合盐酸莫西沙星氯化钠注射治疗老年重症肺炎的效果观察. 中国药物滥用防治杂志. 2024(12): 2284-2285+2288 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号