Evaluation method for anemia and nutritional status in hemodialysis patients based on bioelectrical impedance vector analysis
-
摘要:目的
探讨基于生物电阻抗矢量分析(BIVA)和机器学习算法建立的预测模型对维持性血液透析(MHD)患者贫血和营养状况的预测价值。
方法收集人体成分分析仪(BCM)测得的MHD患者生物电信号数据和白蛋白(Alb)、血红蛋白(Hb)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、总胆固醇(TC)等血生化指标数据,基于BIVA和3种机器学习算法(随机森林、支持向量机和Adaboost算法)分别建立3个预测模型,比较3个模型对Alb、LDL-C、Hb、TC指标的预测效能。
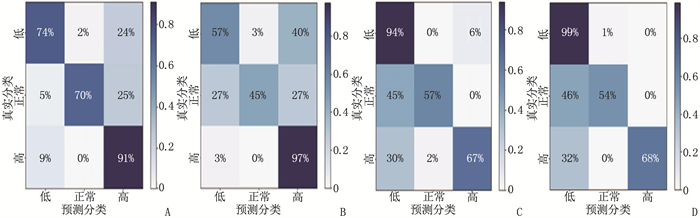
结果个体相关性分析结果显示,生物电学指标与营养指标(Alb、LDL-C、Hb、TC)显著相关(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);3个模型中,基于随机森林算法的模型性能最佳,预测Alb、LDL-C、Hb、TC的准确率分别为0.880、0.879、0.904、0.937。
结论基于BIVA和机器学习算法(随机森林算法)建立的预测模型在MHD患者贫血和营养状况评估中具有较高价值,可辅助临床决策。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the predictive value of a predictive model based on bioelectrical impedance vector analysis (BIVA) and machine learning algorithm for anemia and nutritional status in maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients.
MethodsThe bioelectrical signial data of MHD patients measured by body composition monitor (BCM) and albumin (Alb), hemoglobin (Hb), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC) and other blood biochemical indexes data were collected. Three prediction models were established based on BIVA and three machine learning algorithms (random forest, support vector machine and Adaboost algorithm) respectively, and the prediction efficiency of the three models on Alb, LDL-C, Hb and TC indexes was compared.
ResultsThe results of individual correlation analysis showed that the bioelectrical indexes were significantly correlated with the nutritional indexes (Alb, LDL-C, Hb, TC) (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Among the three models, the model based on random forest algorithm had the best performance, and the accuracies of predicting Alb, LDL-C, Hb and TC were 0.880, 0.879, 0.904 and 0.937, respectively.
ConclusionPredictive models based on BIVA and machine learning algorithms (random forest algorithms) have high value in the assessment of anemia and nutritional status in MHD patients and can assist clinical decision making.
-
长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)指长度超过200个核苷酸的RNA分子,通常不含开放阅读框,因此较少编码或不编码蛋白质[1]。lncRNA通过其复杂的三维结构与蛋白质等生物大分子相互作用,参与细胞分化和生长的调控[2]。lncRNA在细胞中的分布位置不同,其生物学功能和作用机制亦不同,细胞核内的lncRNA主要调控基因的表观遗传修饰和转录水平,而细胞质中的lncRNA则主要调控翻译水平和转录后基因表达[3]。此外, lncRNA能作为竞争性内源RNA(ceRNA), 通过与多种miRNA结合,调控相关基因的表达及其信号通路[4]。目前, lncRNA已被证实参与多种恶性肿瘤相关的生物学进程。例如,在结直肠癌中, lncRNA TUG1/miR-197/TYMS轴不仅促进肿瘤生长和复发,还增强了肿瘤细胞对5-氟尿嘧啶的耐药性[5]。2011年,研究人员在前列腺癌细胞系及组织中首次鉴定出一种长度约为1 900个核苷酸的lncRNA, 并将其命名为前列腺癌相关转录物1(PCAT1)。后续研究显示, PCAT1的过表达能够促进前列腺癌的进展,提示其可能是一个潜在的致癌因子。本文综述了lncRNA PCAT1在不同类型肿瘤中的促癌作用,旨在为后续研究提供参考。
长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)指长度超过200个核苷酸的RNA分子,通常不含开放阅读框,因此较少编码或不编码蛋白质[1]。lncRNA通过其复杂的三维结构与蛋白质等生物大分子相互作用,参与细胞分化和生长的调控[2]。lncRNA在细胞中的分布位置不同,其生物学功能和作用机制亦不同,细胞核内的lncRNA主要调控基因的表观遗传修饰和转录水平,而细胞质中的lncRNA则主要调控翻译水平和转录后基因表达[3]。此外, lncRNA能作为竞争性内源RNA(ceRNA), 通过与多种miRNA结合,调控相关基因的表达及其信号通路[4]。目前, lncRNA已被证实参与多种恶性肿瘤相关的生物学进程。例如,在结直肠癌中, lncRNA TUG1/miR-197/TYMS轴不仅促进肿瘤生长和复发,还增强了肿瘤细胞对5-氟尿嘧啶的耐药性[5]。2011年,研究人员在前列腺癌细胞系及组织中首次鉴定出一种长度约为1 900个核苷酸的lncRNA, 并将其命名为前列腺癌相关转录物1(PCAT1)。后续研究显示, PCAT1的过表达能够促进前列腺癌的进展,提示其可能是一个潜在的致癌因子。本文综述了lncRNA PCAT1在不同类型肿瘤中的促癌作用,旨在为后续研究提供参考。
长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)指长度超过200个核苷酸的RNA分子,通常不含开放阅读框,因此较少编码或不编码蛋白质[1]。lncRNA通过其复杂的三维结构与蛋白质等生物大分子相互作用,参与细胞分化和生长的调控[2]。lncRNA在细胞中的分布位置不同,其生物学功能和作用机制亦不同,细胞核内的lncRNA主要调控基因的表观遗传修饰和转录水平,而细胞质中的lncRNA则主要调控翻译水平和转录后基因表达[3]。此外, lncRNA能作为竞争性内源RNA(ceRNA), 通过与多种miRNA结合,调控相关基因的表达及其信号通路[4]。目前, lncRNA已被证实参与多种恶性肿瘤相关的生物学进程。例如,在结直肠癌中, lncRNA TUG1/miR-197/TYMS轴不仅促进肿瘤生长和复发,还增强了肿瘤细胞对5-氟尿嘧啶的耐药性[5]。2011年,研究人员在前列腺癌细胞系及组织中首次鉴定出一种长度约为1 900个核苷酸的lncRNA, 并将其命名为前列腺癌相关转录物1(PCAT1)。后续研究显示, PCAT1的过表达能够促进前列腺癌的进展,提示其可能是一个潜在的致癌因子。本文综述了lncRNA PCAT1在不同类型肿瘤中的促癌作用,旨在为后续研究提供参考。
1. PCAT1概述
人类PCAT1基因位于8号染色体的126 552 462至127 419 050区域,总长度为866 589 bp, 邻近c-Myc癌基因上游约725 kb处的染色体8q24.21区域(图 1A)。通过RNAfold WebServer在线软件(http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAWebSuite/RNAfold.cgi)预测二级结构发现, PCAT1含有多个茎环结构(图 1B), 提示其可能参与基因的转录或转录后调控[6]。利用GeneCards数据库(https://www.genecards.org/)分析显示, PCAT1在多种正常组织中均有表达(图 2)。由于染色体8q24区域频繁发生基因扩增,并且含有与前列腺癌易感性相关的单核苷酸多态性(SNP)位点,该区域受到广泛关注。YANG M L等[7]发现PCAT1 rs2632159位点的SNP可增加结直肠癌的易感性,而ZHANG Y等[8]发现PCAT1 rs1026411位点的SNP是胃癌患者不良预后的独立预测因子。
目前, PCAT1已被发现在多种恶性肿瘤中高表达,并且其表达水平与肿瘤大小和预后等临床病理特征密切相关。机制研究[9]发现,转录因子GATA6可靶向结合PCAT1启动子并诱导其表达,从而调控下游Fyn相关激酶(FRK), 促进非小细胞肺癌的发生和转移。PCAT1可通过与特定蛋白质相互作用,调节许多关键的生物过程。例如, PCAT1可以与急性髓系白血病细胞中的卷曲蛋白6(FZD6)直接结合,提高其稳定性,激活Wnt信号通路,从而促进癌细胞增殖、细胞周期进展并抑制细胞凋亡[10]。DING C等[11]研究发现,干扰PCAT1表达可显著降低卵巢癌细胞中细胞周期蛋白D1(Cyclin D1)和细胞周期依赖性激酶4(CDK4)的表达,抑制细胞周期进程,为提高癌细胞对紫杉醇化疗的敏感性提供了新的思路。PCAT1还可与组蛋白甲基转移酶增强子Zeste同源物2(EZH2)相互作用,调控胃癌细胞中磷酸酶与张力蛋白同源物(PTEN)的表达,诱导胃癌细胞对顺铂的耐药性[12]。此外, PCAT1通过充当某些微小RNA(miRNA)的“海绵分子”调节基因表达。例如, ZANG B等[13]发现, PCAT1通过充当miR-508-3p的“海绵”,抑制其表达,从而上调其靶基因膜联蛋白A10(ANXA10)的表达,促进食管鳞状细胞癌细胞的增殖。在非小细胞肺癌细胞中, PCAT1通过竞争性吸附miR-149-5p上调富含亮氨酸重复序列免疫球蛋白样结构域2(LRIG2)的表达,推动非小细胞肺癌的恶性进展[4]。这些研究表明,PCAT1可通过不同作用方式或机制调控相关基因的表达,从而促进癌细胞的恶性表型。
1. PCAT1概述
人类PCAT1基因位于8号染色体的126 552 462至127 419 050区域,总长度为866 589 bp, 邻近c-Myc癌基因上游约725 kb处的染色体8q24.21区域(图 1A)。通过RNAfold WebServer在线软件(http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAWebSuite/RNAfold.cgi)预测二级结构发现, PCAT1含有多个茎环结构(图 1B), 提示其可能参与基因的转录或转录后调控[6]。利用GeneCards数据库(https://www.genecards.org/)分析显示, PCAT1在多种正常组织中均有表达(图 2)。由于染色体8q24区域频繁发生基因扩增,并且含有与前列腺癌易感性相关的单核苷酸多态性(SNP)位点,该区域受到广泛关注。YANG M L等[7]发现PCAT1 rs2632159位点的SNP可增加结直肠癌的易感性,而ZHANG Y等[8]发现PCAT1 rs1026411位点的SNP是胃癌患者不良预后的独立预测因子。
目前, PCAT1已被发现在多种恶性肿瘤中高表达,并且其表达水平与肿瘤大小和预后等临床病理特征密切相关。机制研究[9]发现,转录因子GATA6可靶向结合PCAT1启动子并诱导其表达,从而调控下游Fyn相关激酶(FRK), 促进非小细胞肺癌的发生和转移。PCAT1可通过与特定蛋白质相互作用,调节许多关键的生物过程。例如, PCAT1可以与急性髓系白血病细胞中的卷曲蛋白6(FZD6)直接结合,提高其稳定性,激活Wnt信号通路,从而促进癌细胞增殖、细胞周期进展并抑制细胞凋亡[10]。DING C等[11]研究发现,干扰PCAT1表达可显著降低卵巢癌细胞中细胞周期蛋白D1(Cyclin D1)和细胞周期依赖性激酶4(CDK4)的表达,抑制细胞周期进程,为提高癌细胞对紫杉醇化疗的敏感性提供了新的思路。PCAT1还可与组蛋白甲基转移酶增强子Zeste同源物2(EZH2)相互作用,调控胃癌细胞中磷酸酶与张力蛋白同源物(PTEN)的表达,诱导胃癌细胞对顺铂的耐药性[12]。此外, PCAT1通过充当某些微小RNA(miRNA)的“海绵分子”调节基因表达。例如, ZANG B等[13]发现, PCAT1通过充当miR-508-3p的“海绵”,抑制其表达,从而上调其靶基因膜联蛋白A10(ANXA10)的表达,促进食管鳞状细胞癌细胞的增殖。在非小细胞肺癌细胞中, PCAT1通过竞争性吸附miR-149-5p上调富含亮氨酸重复序列免疫球蛋白样结构域2(LRIG2)的表达,推动非小细胞肺癌的恶性进展[4]。这些研究表明,PCAT1可通过不同作用方式或机制调控相关基因的表达,从而促进癌细胞的恶性表型。
1. PCAT1概述
人类PCAT1基因位于8号染色体的126 552 462至127 419 050区域,总长度为866 589 bp, 邻近c-Myc癌基因上游约725 kb处的染色体8q24.21区域(图 1A)。通过RNAfold WebServer在线软件(http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAWebSuite/RNAfold.cgi)预测二级结构发现, PCAT1含有多个茎环结构(图 1B), 提示其可能参与基因的转录或转录后调控[6]。利用GeneCards数据库(https://www.genecards.org/)分析显示, PCAT1在多种正常组织中均有表达(图 2)。由于染色体8q24区域频繁发生基因扩增,并且含有与前列腺癌易感性相关的单核苷酸多态性(SNP)位点,该区域受到广泛关注。YANG M L等[7]发现PCAT1 rs2632159位点的SNP可增加结直肠癌的易感性,而ZHANG Y等[8]发现PCAT1 rs1026411位点的SNP是胃癌患者不良预后的独立预测因子。
目前, PCAT1已被发现在多种恶性肿瘤中高表达,并且其表达水平与肿瘤大小和预后等临床病理特征密切相关。机制研究[9]发现,转录因子GATA6可靶向结合PCAT1启动子并诱导其表达,从而调控下游Fyn相关激酶(FRK), 促进非小细胞肺癌的发生和转移。PCAT1可通过与特定蛋白质相互作用,调节许多关键的生物过程。例如, PCAT1可以与急性髓系白血病细胞中的卷曲蛋白6(FZD6)直接结合,提高其稳定性,激活Wnt信号通路,从而促进癌细胞增殖、细胞周期进展并抑制细胞凋亡[10]。DING C等[11]研究发现,干扰PCAT1表达可显著降低卵巢癌细胞中细胞周期蛋白D1(Cyclin D1)和细胞周期依赖性激酶4(CDK4)的表达,抑制细胞周期进程,为提高癌细胞对紫杉醇化疗的敏感性提供了新的思路。PCAT1还可与组蛋白甲基转移酶增强子Zeste同源物2(EZH2)相互作用,调控胃癌细胞中磷酸酶与张力蛋白同源物(PTEN)的表达,诱导胃癌细胞对顺铂的耐药性[12]。此外, PCAT1通过充当某些微小RNA(miRNA)的“海绵分子”调节基因表达。例如, ZANG B等[13]发现, PCAT1通过充当miR-508-3p的“海绵”,抑制其表达,从而上调其靶基因膜联蛋白A10(ANXA10)的表达,促进食管鳞状细胞癌细胞的增殖。在非小细胞肺癌细胞中, PCAT1通过竞争性吸附miR-149-5p上调富含亮氨酸重复序列免疫球蛋白样结构域2(LRIG2)的表达,推动非小细胞肺癌的恶性进展[4]。这些研究表明,PCAT1可通过不同作用方式或机制调控相关基因的表达,从而促进癌细胞的恶性表型。
2. PCAT1在消化系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
本课题组前期研究发现,PCAT1在胰腺癌组织中的高表达与患者预后不良紧密相关。PCAT1通过诱导E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)mRNA的m6A修饰并促进其降解,从而下调E-cadherin的表达,推动胰腺癌细胞上皮-间质转化(EMT)进程、迁移和侵袭[2]。SADI KHOSROSHAHI N等[14]评估100份伊朗患者的结直肠肿瘤组织后发现, PCAT1高表达与结直肠肿瘤的发生显著相关,因此, PCAT1可作为结直肠癌的预后生物学标志物。PCAT1可靶向锌指蛋白217(ZNF217), 调节与EMT相关的转移相关蛋白2(MTA2)/转移相关蛋白3(MTA3)/Snail家族锌指蛋白1(Snai1)/E-cadherin信号传导通路,加速结直肠癌的发生和发展[15]。PCAT1还可通过调节Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)与B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)的比例,增加结肠癌细胞的活力,诱导细胞增殖,并抑制其对化疗药的敏感性[16]。FANG X等[17]发现,结直肠癌细胞系外泌体中的PCAT1可通过miR-329-3p/神经导向因子1(Netrin-1)轴,推动T84细胞的迁移、EMT及增殖。此外, PCAT1可以通过靶向miR-149-5p调节结直肠癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和凋亡[18]。相关研究[13]表明, PCAT1能促进食管鳞状细胞癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,从而加快癌症的发生和进展。HUANG L J等[19]通过在实验中敲除PCAT1, 降低了癌细胞中细胞周期蛋白B1(cyclin B1)和细胞分裂周期蛋白2(CDC2)的表达,导致细胞周期停滞在G2/M期,并增强了食管鳞状细胞癌细胞对紫杉醇的敏感性。机制研究[13]显示, miR-326是PCAT1的直接靶标; PCAT1可以降低miR-326表达,从而对丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(AKT)信号通路起到抑制作用,通过miR-508-3p靶向调节ANXA10, 在食管鳞状细胞癌恶性进展中扮演重要角色。PCAT1在胃癌组织中的表达显著上调[20], 并与患者的不良预后紧密相关[12, 21]。在胃癌细胞中, PCAT1可以作为miR-128的“分子海绵”,通过上调锌指E盒结合同源异型盒1(ZEB1), 或者通过与EZH2蛋白结合,以表观遗传调控方式下调PTEN的表达,从而增强胃癌细胞对顺铂的耐药性[12, 20]。SUN D等[22]研究证实,转录因子YY1可以与PCAT1启动子结合,上调PCAT1的表达。PCAT1进一步通过与miR-216a-3p竞争结合,上调B细胞淋巴瘤因子3(BCL3)的表达,在胆管癌中发挥促癌作用。
2. PCAT1在消化系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
本课题组前期研究发现,PCAT1在胰腺癌组织中的高表达与患者预后不良紧密相关。PCAT1通过诱导E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)mRNA的m6A修饰并促进其降解,从而下调E-cadherin的表达,推动胰腺癌细胞上皮-间质转化(EMT)进程、迁移和侵袭[2]。SADI KHOSROSHAHI N等[14]评估100份伊朗患者的结直肠肿瘤组织后发现, PCAT1高表达与结直肠肿瘤的发生显著相关,因此, PCAT1可作为结直肠癌的预后生物学标志物。PCAT1可靶向锌指蛋白217(ZNF217), 调节与EMT相关的转移相关蛋白2(MTA2)/转移相关蛋白3(MTA3)/Snail家族锌指蛋白1(Snai1)/E-cadherin信号传导通路,加速结直肠癌的发生和发展[15]。PCAT1还可通过调节Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)与B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)的比例,增加结肠癌细胞的活力,诱导细胞增殖,并抑制其对化疗药的敏感性[16]。FANG X等[17]发现,结直肠癌细胞系外泌体中的PCAT1可通过miR-329-3p/神经导向因子1(Netrin-1)轴,推动T84细胞的迁移、EMT及增殖。此外, PCAT1可以通过靶向miR-149-5p调节结直肠癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和凋亡[18]。相关研究[13]表明, PCAT1能促进食管鳞状细胞癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,从而加快癌症的发生和进展。HUANG L J等[19]通过在实验中敲除PCAT1, 降低了癌细胞中细胞周期蛋白B1(cyclin B1)和细胞分裂周期蛋白2(CDC2)的表达,导致细胞周期停滞在G2/M期,并增强了食管鳞状细胞癌细胞对紫杉醇的敏感性。机制研究[13]显示, miR-326是PCAT1的直接靶标; PCAT1可以降低miR-326表达,从而对丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(AKT)信号通路起到抑制作用,通过miR-508-3p靶向调节ANXA10, 在食管鳞状细胞癌恶性进展中扮演重要角色。PCAT1在胃癌组织中的表达显著上调[20], 并与患者的不良预后紧密相关[12, 21]。在胃癌细胞中, PCAT1可以作为miR-128的“分子海绵”,通过上调锌指E盒结合同源异型盒1(ZEB1), 或者通过与EZH2蛋白结合,以表观遗传调控方式下调PTEN的表达,从而增强胃癌细胞对顺铂的耐药性[12, 20]。SUN D等[22]研究证实,转录因子YY1可以与PCAT1启动子结合,上调PCAT1的表达。PCAT1进一步通过与miR-216a-3p竞争结合,上调B细胞淋巴瘤因子3(BCL3)的表达,在胆管癌中发挥促癌作用。
2. PCAT1在消化系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
本课题组前期研究发现,PCAT1在胰腺癌组织中的高表达与患者预后不良紧密相关。PCAT1通过诱导E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)mRNA的m6A修饰并促进其降解,从而下调E-cadherin的表达,推动胰腺癌细胞上皮-间质转化(EMT)进程、迁移和侵袭[2]。SADI KHOSROSHAHI N等[14]评估100份伊朗患者的结直肠肿瘤组织后发现, PCAT1高表达与结直肠肿瘤的发生显著相关,因此, PCAT1可作为结直肠癌的预后生物学标志物。PCAT1可靶向锌指蛋白217(ZNF217), 调节与EMT相关的转移相关蛋白2(MTA2)/转移相关蛋白3(MTA3)/Snail家族锌指蛋白1(Snai1)/E-cadherin信号传导通路,加速结直肠癌的发生和发展[15]。PCAT1还可通过调节Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)与B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)的比例,增加结肠癌细胞的活力,诱导细胞增殖,并抑制其对化疗药的敏感性[16]。FANG X等[17]发现,结直肠癌细胞系外泌体中的PCAT1可通过miR-329-3p/神经导向因子1(Netrin-1)轴,推动T84细胞的迁移、EMT及增殖。此外, PCAT1可以通过靶向miR-149-5p调节结直肠癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和凋亡[18]。相关研究[13]表明, PCAT1能促进食管鳞状细胞癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,从而加快癌症的发生和进展。HUANG L J等[19]通过在实验中敲除PCAT1, 降低了癌细胞中细胞周期蛋白B1(cyclin B1)和细胞分裂周期蛋白2(CDC2)的表达,导致细胞周期停滞在G2/M期,并增强了食管鳞状细胞癌细胞对紫杉醇的敏感性。机制研究[13]显示, miR-326是PCAT1的直接靶标; PCAT1可以降低miR-326表达,从而对丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(AKT)信号通路起到抑制作用,通过miR-508-3p靶向调节ANXA10, 在食管鳞状细胞癌恶性进展中扮演重要角色。PCAT1在胃癌组织中的表达显著上调[20], 并与患者的不良预后紧密相关[12, 21]。在胃癌细胞中, PCAT1可以作为miR-128的“分子海绵”,通过上调锌指E盒结合同源异型盒1(ZEB1), 或者通过与EZH2蛋白结合,以表观遗传调控方式下调PTEN的表达,从而增强胃癌细胞对顺铂的耐药性[12, 20]。SUN D等[22]研究证实,转录因子YY1可以与PCAT1启动子结合,上调PCAT1的表达。PCAT1进一步通过与miR-216a-3p竞争结合,上调B细胞淋巴瘤因子3(BCL3)的表达,在胆管癌中发挥促癌作用。
3. PCAT1在泌尿/生殖系统癌症中的促癌作用
PCAT1的促癌作用最初在前列腺癌中被发现和证实。后续研究[23]显示, PCAT1与FK506结合蛋白51(FKBP51)结合,取代了PH结构域亮氨酸富集重复蛋白(PHLPP)/FKBP51/核因子κB激酶α(IKKα)复合物中的PHLPP, 从而激活去势抵抗性前列腺癌细胞中的AKT和核因子κB (NF-κB)信号通路,诱导前列腺癌的发展。JIANG X等[24]研究发现,转录因子AP-2γ(TFAP2C)可以促进PCAT1的转录。PCAT1通过与c-Myc结合并增强其稳定性,提高了铁死亡抑制因子胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆向转运蛋白溶质载体家族7成员11(SLC7A11)的转录水平。同时, PCAT1作为miR-25-3p的“分子海绵”上调SLC7A11的表达,增强了癌细胞对多西他赛的耐药性。这揭示了TFAP2C/PCAT1/c-Myc/miR-25-3p/SLC7A11轴在前列腺癌化疗抵抗中的分子机制。
PCAT1在卵巢癌细胞系及癌组织中高表达,通过上调Wnt和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶2(NEK2)通路相关基因,调控细胞迁移、增殖和凋亡[25]。此外, PCAT1通过靶向抑制miR-129-5p(一种抑制细胞增殖和诱导凋亡的分子),从而促进卵巢癌的发展[26]。GE X等[27]发现,宫颈癌细胞系中PCAT1表达水平较高。PCAT1通过调控PCAT1/miR-128/高尔基体膜蛋白1(GOLM1)轴,促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和增殖,并提升其对放疗的抵抗力。在子宫内膜癌组织中, PCAT1高表达与肿瘤恶性程度高及患者总体生存期较短显著相关。下调PCAT1可显著降低子宫内膜癌细胞中Bcl-2、波形蛋白(Vimentin)和N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)等促癌蛋白的表达,同时增加E-cadherin和Bad等抑癌蛋白的表达[28]。在乳腺癌组织中, PCAT1表达水平与患者不良临床结果和乳腺癌病理等级呈显著正相关[29]。PCAT1通过靶向性别决定区Y框蛋白4(SOX4)、缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)/受体识别相关蛋白1(RACK1)通路和配对样同源框转录因子2(PITX2)/miR-134-3p轴,有效调控乳腺癌细胞的代谢、凋亡和增殖,促进乳腺癌的迁移和入侵[29-31]。
3. PCAT1在泌尿/生殖系统癌症中的促癌作用
PCAT1的促癌作用最初在前列腺癌中被发现和证实。后续研究[23]显示, PCAT1与FK506结合蛋白51(FKBP51)结合,取代了PH结构域亮氨酸富集重复蛋白(PHLPP)/FKBP51/核因子κB激酶α(IKKα)复合物中的PHLPP, 从而激活去势抵抗性前列腺癌细胞中的AKT和核因子κB (NF-κB)信号通路,诱导前列腺癌的发展。JIANG X等[24]研究发现,转录因子AP-2γ(TFAP2C)可以促进PCAT1的转录。PCAT1通过与c-Myc结合并增强其稳定性,提高了铁死亡抑制因子胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆向转运蛋白溶质载体家族7成员11(SLC7A11)的转录水平。同时, PCAT1作为miR-25-3p的“分子海绵”上调SLC7A11的表达,增强了癌细胞对多西他赛的耐药性。这揭示了TFAP2C/PCAT1/c-Myc/miR-25-3p/SLC7A11轴在前列腺癌化疗抵抗中的分子机制。
PCAT1在卵巢癌细胞系及癌组织中高表达,通过上调Wnt和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶2(NEK2)通路相关基因,调控细胞迁移、增殖和凋亡[25]。此外, PCAT1通过靶向抑制miR-129-5p(一种抑制细胞增殖和诱导凋亡的分子),从而促进卵巢癌的发展[26]。GE X等[27]发现,宫颈癌细胞系中PCAT1表达水平较高。PCAT1通过调控PCAT1/miR-128/高尔基体膜蛋白1(GOLM1)轴,促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和增殖,并提升其对放疗的抵抗力。在子宫内膜癌组织中, PCAT1高表达与肿瘤恶性程度高及患者总体生存期较短显著相关。下调PCAT1可显著降低子宫内膜癌细胞中Bcl-2、波形蛋白(Vimentin)和N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)等促癌蛋白的表达,同时增加E-cadherin和Bad等抑癌蛋白的表达[28]。在乳腺癌组织中, PCAT1表达水平与患者不良临床结果和乳腺癌病理等级呈显著正相关[29]。PCAT1通过靶向性别决定区Y框蛋白4(SOX4)、缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)/受体识别相关蛋白1(RACK1)通路和配对样同源框转录因子2(PITX2)/miR-134-3p轴,有效调控乳腺癌细胞的代谢、凋亡和增殖,促进乳腺癌的迁移和入侵[29-31]。
3. PCAT1在泌尿/生殖系统癌症中的促癌作用
PCAT1的促癌作用最初在前列腺癌中被发现和证实。后续研究[23]显示, PCAT1与FK506结合蛋白51(FKBP51)结合,取代了PH结构域亮氨酸富集重复蛋白(PHLPP)/FKBP51/核因子κB激酶α(IKKα)复合物中的PHLPP, 从而激活去势抵抗性前列腺癌细胞中的AKT和核因子κB (NF-κB)信号通路,诱导前列腺癌的发展。JIANG X等[24]研究发现,转录因子AP-2γ(TFAP2C)可以促进PCAT1的转录。PCAT1通过与c-Myc结合并增强其稳定性,提高了铁死亡抑制因子胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆向转运蛋白溶质载体家族7成员11(SLC7A11)的转录水平。同时, PCAT1作为miR-25-3p的“分子海绵”上调SLC7A11的表达,增强了癌细胞对多西他赛的耐药性。这揭示了TFAP2C/PCAT1/c-Myc/miR-25-3p/SLC7A11轴在前列腺癌化疗抵抗中的分子机制。
PCAT1在卵巢癌细胞系及癌组织中高表达,通过上调Wnt和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶2(NEK2)通路相关基因,调控细胞迁移、增殖和凋亡[25]。此外, PCAT1通过靶向抑制miR-129-5p(一种抑制细胞增殖和诱导凋亡的分子),从而促进卵巢癌的发展[26]。GE X等[27]发现,宫颈癌细胞系中PCAT1表达水平较高。PCAT1通过调控PCAT1/miR-128/高尔基体膜蛋白1(GOLM1)轴,促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和增殖,并提升其对放疗的抵抗力。在子宫内膜癌组织中, PCAT1高表达与肿瘤恶性程度高及患者总体生存期较短显著相关。下调PCAT1可显著降低子宫内膜癌细胞中Bcl-2、波形蛋白(Vimentin)和N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)等促癌蛋白的表达,同时增加E-cadherin和Bad等抑癌蛋白的表达[28]。在乳腺癌组织中, PCAT1表达水平与患者不良临床结果和乳腺癌病理等级呈显著正相关[29]。PCAT1通过靶向性别决定区Y框蛋白4(SOX4)、缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)/受体识别相关蛋白1(RACK1)通路和配对样同源框转录因子2(PITX2)/miR-134-3p轴,有效调控乳腺癌细胞的代谢、凋亡和增殖,促进乳腺癌的迁移和入侵[29-31]。
4. PCAT1在头颈部癌中的促癌作用
SUR S等[32]研究发现,干扰PCAT1的表达可以激活头颈部鳞状细胞癌中的凋亡信号调节激酶1(ASK1)和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 MAPK), 并下调c-Myc和AKT1的表达,从而显著抑制癌细胞的增殖并诱导其凋亡。HU W等[33]检测50例喉癌患者的癌组织样本后发现, PCAT1的表达水平显著升高,且干扰PCAT1的表达可以抑制喉癌细胞的迁移、侵袭及移植瘤的生长,提示PCAT1可作为miR-210-3p的“分子海绵”在喉癌细胞中发挥促癌作用。
4. PCAT1在头颈部癌中的促癌作用
SUR S等[32]研究发现,干扰PCAT1的表达可以激活头颈部鳞状细胞癌中的凋亡信号调节激酶1(ASK1)和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 MAPK), 并下调c-Myc和AKT1的表达,从而显著抑制癌细胞的增殖并诱导其凋亡。HU W等[33]检测50例喉癌患者的癌组织样本后发现, PCAT1的表达水平显著升高,且干扰PCAT1的表达可以抑制喉癌细胞的迁移、侵袭及移植瘤的生长,提示PCAT1可作为miR-210-3p的“分子海绵”在喉癌细胞中发挥促癌作用。
4. PCAT1在头颈部癌中的促癌作用
SUR S等[32]研究发现,干扰PCAT1的表达可以激活头颈部鳞状细胞癌中的凋亡信号调节激酶1(ASK1)和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 MAPK), 并下调c-Myc和AKT1的表达,从而显著抑制癌细胞的增殖并诱导其凋亡。HU W等[33]检测50例喉癌患者的癌组织样本后发现, PCAT1的表达水平显著升高,且干扰PCAT1的表达可以抑制喉癌细胞的迁移、侵袭及移植瘤的生长,提示PCAT1可作为miR-210-3p的“分子海绵”在喉癌细胞中发挥促癌作用。
5. PCAT1血液系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
临床常见的血液系统肿瘤包括各种类型的白血病、多发性骨髓瘤和淋巴瘤等。SHEN X等[34]研究显示,PCAT1在多发性骨髓瘤的肿瘤组织和细胞系中高表达。PCAT1通过调控p38和c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)信号通路,促进多发性骨髓瘤的进展和化疗耐药。此外, PCAT1还可以作为miR-129的“分子海绵”,通过调控丝裂原活化蛋白3激酶7(MAP3K7)/NF-κB通路推动多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖和细胞周期进程[35]。YUAN Y等[10]发现,在急性髓系白血病细胞中, PCAT1可以与FZD6蛋白结合并提高其稳定性,激活β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)/Wnt信号通路,从而诱导癌细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡。
5. PCAT1血液系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
临床常见的血液系统肿瘤包括各种类型的白血病、多发性骨髓瘤和淋巴瘤等。SHEN X等[34]研究显示,PCAT1在多发性骨髓瘤的肿瘤组织和细胞系中高表达。PCAT1通过调控p38和c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)信号通路,促进多发性骨髓瘤的进展和化疗耐药。此外, PCAT1还可以作为miR-129的“分子海绵”,通过调控丝裂原活化蛋白3激酶7(MAP3K7)/NF-κB通路推动多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖和细胞周期进程[35]。YUAN Y等[10]发现,在急性髓系白血病细胞中, PCAT1可以与FZD6蛋白结合并提高其稳定性,激活β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)/Wnt信号通路,从而诱导癌细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡。
5. PCAT1血液系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
临床常见的血液系统肿瘤包括各种类型的白血病、多发性骨髓瘤和淋巴瘤等。SHEN X等[34]研究显示,PCAT1在多发性骨髓瘤的肿瘤组织和细胞系中高表达。PCAT1通过调控p38和c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)信号通路,促进多发性骨髓瘤的进展和化疗耐药。此外, PCAT1还可以作为miR-129的“分子海绵”,通过调控丝裂原活化蛋白3激酶7(MAP3K7)/NF-κB通路推动多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖和细胞周期进程[35]。YUAN Y等[10]发现,在急性髓系白血病细胞中, PCAT1可以与FZD6蛋白结合并提高其稳定性,激活β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)/Wnt信号通路,从而诱导癌细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡。
6. PCAT1在其他系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
PCAT1在非小细胞肺癌组织中高表达,并与肿瘤大小、远处转移和肿瘤分期密切相关。PCAT1高表达的患者生存时间显著缩短[4]。PCAT1通过上调SRY相关HMG盒基因2(SOX2), 直接抑制环磷酸鸟苷-腺苷酸合成酶(cGAS)/干扰素基因刺激因子(STING)通路,进而抑制抗肿瘤免疫反应并促进肿瘤发生[36]。体外实验[9]发现, PCAT1能够诱导非小细胞肺癌细胞增殖,并维持其干细胞特性。PCAT1通过与角蛋白假尿苷合酶1(DKC1)蛋白结合,进一步通过血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)/AKT/Bcl-2/胱天蛋白酶9(caspase 9)通路调控非小细胞肺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭、凋亡及EMT进程[37]。此外, PCAT1通过结合miR-129促进ATP结合盒亚家族B成员1(ABCB1)的表达,或通过调节AKT/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)信号通路,使癌细胞对顺铂或吉非替尼产生耐药性[38-39]。在骨肉瘤组织中, PCAT1的表达显著升高,且高水平的PCAT1与患者较差的预后相关。PCAT1可通过靶向miR-508-3p调节ZEB1的表达,促进骨肉瘤细胞的侵袭和增殖[40]。ZHANG P H等[41]研究发现, PCAT1可通过靶向胶质瘤干细胞中的miR-129-5p, 上调高迁移率族蛋白B1(HMGB1)的表达,从而降低肿瘤细胞的放射敏感性,并维持神经胶质瘤干细胞的干性。此外,已有研究[42]指出, PCAT1在多形胶质母细胞瘤中参与DNA损伤反应,但其具体机制尚未明确。
6. PCAT1在其他系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
PCAT1在非小细胞肺癌组织中高表达,并与肿瘤大小、远处转移和肿瘤分期密切相关。PCAT1高表达的患者生存时间显著缩短[4]。PCAT1通过上调SRY相关HMG盒基因2(SOX2), 直接抑制环磷酸鸟苷-腺苷酸合成酶(cGAS)/干扰素基因刺激因子(STING)通路,进而抑制抗肿瘤免疫反应并促进肿瘤发生[36]。体外实验[9]发现, PCAT1能够诱导非小细胞肺癌细胞增殖,并维持其干细胞特性。PCAT1通过与角蛋白假尿苷合酶1(DKC1)蛋白结合,进一步通过血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)/AKT/Bcl-2/胱天蛋白酶9(caspase 9)通路调控非小细胞肺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭、凋亡及EMT进程[37]。此外, PCAT1通过结合miR-129促进ATP结合盒亚家族B成员1(ABCB1)的表达,或通过调节AKT/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)信号通路,使癌细胞对顺铂或吉非替尼产生耐药性[38-39]。在骨肉瘤组织中, PCAT1的表达显著升高,且高水平的PCAT1与患者较差的预后相关。PCAT1可通过靶向miR-508-3p调节ZEB1的表达,促进骨肉瘤细胞的侵袭和增殖[40]。ZHANG P H等[41]研究发现, PCAT1可通过靶向胶质瘤干细胞中的miR-129-5p, 上调高迁移率族蛋白B1(HMGB1)的表达,从而降低肿瘤细胞的放射敏感性,并维持神经胶质瘤干细胞的干性。此外,已有研究[42]指出, PCAT1在多形胶质母细胞瘤中参与DNA损伤反应,但其具体机制尚未明确。
6. PCAT1在其他系统肿瘤中的促癌作用
PCAT1在非小细胞肺癌组织中高表达,并与肿瘤大小、远处转移和肿瘤分期密切相关。PCAT1高表达的患者生存时间显著缩短[4]。PCAT1通过上调SRY相关HMG盒基因2(SOX2), 直接抑制环磷酸鸟苷-腺苷酸合成酶(cGAS)/干扰素基因刺激因子(STING)通路,进而抑制抗肿瘤免疫反应并促进肿瘤发生[36]。体外实验[9]发现, PCAT1能够诱导非小细胞肺癌细胞增殖,并维持其干细胞特性。PCAT1通过与角蛋白假尿苷合酶1(DKC1)蛋白结合,进一步通过血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)/AKT/Bcl-2/胱天蛋白酶9(caspase 9)通路调控非小细胞肺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭、凋亡及EMT进程[37]。此外, PCAT1通过结合miR-129促进ATP结合盒亚家族B成员1(ABCB1)的表达,或通过调节AKT/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)信号通路,使癌细胞对顺铂或吉非替尼产生耐药性[38-39]。在骨肉瘤组织中, PCAT1的表达显著升高,且高水平的PCAT1与患者较差的预后相关。PCAT1可通过靶向miR-508-3p调节ZEB1的表达,促进骨肉瘤细胞的侵袭和增殖[40]。ZHANG P H等[41]研究发现, PCAT1可通过靶向胶质瘤干细胞中的miR-129-5p, 上调高迁移率族蛋白B1(HMGB1)的表达,从而降低肿瘤细胞的放射敏感性,并维持神经胶质瘤干细胞的干性。此外,已有研究[42]指出, PCAT1在多形胶质母细胞瘤中参与DNA损伤反应,但其具体机制尚未明确。
7. 总结与展望
现有研究已初步证实, lncRNA PCAT1在大多数癌症中发挥促进癌症发生和发展的作用。然而,关于PCAT1在神经系统、内分泌系统、皮肤及肌肉骨骼系统肿瘤中的作用及其机制的研究仍较为缺乏。目前, PCAT1在各类癌症中的信号通路研究尚处于初始阶段,其具体机制及与其他信号通路的相互作用仍需深入探讨。值得注意的是,已有研究[43]表明PCAT1在重塑肿瘤微环境中发挥关键作用,这为PCAT1作为促癌因子提供了新的依据。在临床研究方面,现有数据支持PCAT1可辅助临床检测,并作为预后标志物,但将PCAT1作为癌症治疗靶点的研究仍不充分。总之, PCAT1在多种癌症中高表达,其作用机制复杂且促癌方式多样,深入研究PCAT1有望为癌症治疗提供新的靶点和生物标志物。
7. 总结与展望
现有研究已初步证实, lncRNA PCAT1在大多数癌症中发挥促进癌症发生和发展的作用。然而,关于PCAT1在神经系统、内分泌系统、皮肤及肌肉骨骼系统肿瘤中的作用及其机制的研究仍较为缺乏。目前, PCAT1在各类癌症中的信号通路研究尚处于初始阶段,其具体机制及与其他信号通路的相互作用仍需深入探讨。值得注意的是,已有研究[43]表明PCAT1在重塑肿瘤微环境中发挥关键作用,这为PCAT1作为促癌因子提供了新的依据。在临床研究方面,现有数据支持PCAT1可辅助临床检测,并作为预后标志物,但将PCAT1作为癌症治疗靶点的研究仍不充分。总之, PCAT1在多种癌症中高表达,其作用机制复杂且促癌方式多样,深入研究PCAT1有望为癌症治疗提供新的靶点和生物标志物。
7. 总结与展望
现有研究已初步证实, lncRNA PCAT1在大多数癌症中发挥促进癌症发生和发展的作用。然而,关于PCAT1在神经系统、内分泌系统、皮肤及肌肉骨骼系统肿瘤中的作用及其机制的研究仍较为缺乏。目前, PCAT1在各类癌症中的信号通路研究尚处于初始阶段,其具体机制及与其他信号通路的相互作用仍需深入探讨。值得注意的是,已有研究[43]表明PCAT1在重塑肿瘤微环境中发挥关键作用,这为PCAT1作为促癌因子提供了新的依据。在临床研究方面,现有数据支持PCAT1可辅助临床检测,并作为预后标志物,但将PCAT1作为癌症治疗靶点的研究仍不充分。总之, PCAT1在多种癌症中高表达,其作用机制复杂且促癌方式多样,深入研究PCAT1有望为癌症治疗提供新的靶点和生物标志物。
-
表 1 男性患者主要生物电学指标与主要营养指标的个体相关性分析结果
指标 Ri Re Cm ρi ρe ε Alb 7.82×10-5 7.44×10-3** 3.24×10-3** 3.87×10-7 4.16×10-4** 0.23** TC -9.76×10-5 4.36×10-4 4.71×10-4** -6.20×10-6 1.99×10-5 0.03 ** LDL-C -1.38×10-4* 3.08×10-4 2.54×10-4* -8.85×10-6** 8.68×10-6 0.02** Hb 1.63×10-3* 0.03** 6.86×10-3** -4.47×10-5 1.26×10-3** 0.66** Ri: 细胞内电阻; Re: 细胞外电阻; Cm: 细胞膜电容; ρi: 细胞内电阻率; ρe: 细胞外电阻率; ε: 细胞膜介电常数; Alb: 白蛋白; TC: 总胆固醇; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; Hb: 血红蛋白。表中所列数据均为重复测量相关系数, * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01。 表 2 女性患者主要生物电学指标与主要营养指标的个体相关性分析结果
指标 Ri Re Cm ρi ρe ε Alb 9.91×10-5 6.99×10-3** 1.04×10-4 5.51×10-6 3.52×10-4** 6.88×10-3 TC -2.07×10-4 -6.91×10-4 3.57×10-5* -2.89×10-6 -4.77×10-6 2.27×10-3* LDL-C -1.92×10-4* -3.41×10-5 1.80×10-5 -6.33×10-6* 8.47×10-6 1.14×10-3 Hb 6.70×10-4 0.03** 2.20×10-4 -4.69×10-5 1.16×10-3** 0.02 Ri: 细胞内电阻; Re: 细胞外电阻; Cm: 细胞膜电容; ρi: 细胞内电阻率; ρe: 细胞外电阻率; ε: 细胞膜介电常数; Alb: 白蛋白; TC: 总胆固醇; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; Hb: 血红蛋白。表中所列数据均为重复测量相关系数, * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01。 表 3 基于支持向量机、Adaboost和随机森林算法的各模型参数
支持向量机 Adaboost 随机森林 核函数 gamma 决策树数量 决策树数量 决策树最大深度 最大特征数 sigmoid auto 70 130 8 auto 表 4 基于不同算法的3种模型对血红蛋白的分类结果
模型 类别 F1值 召回率 准确率 随机森林 男 0.818 0.778 0.908 女 0.785 0.760 0.897 总 0.808 0.773 0.904 支持向量机 男 0.353 0.346 0.645 女 0.321 0.318 0.707 总 0.345 0.342 0.666 AdaBoost 男 0.424 0.420 0.752 女 0.362 0.367 0.819 总 0.419 0.409 0.775 表 5 基于不同算法的3种模型对白蛋白的分类结果
模型 类别 F1值 召回率 准确率 随机森林 男 0.875 0.862 0.902 女 0.782 0.782 0.835 总 0.844 0.827 0.880 支持向量机 男 0.409 0.407 0.538 女 0.563 0.564 0.659 总 0.465 0.464 0.582 AdaBoost 男 0.664 0.648 0.773 女 0.595 0.588 0.735 总 0.640 0.627 0.760 表 6 基于不同算法的3种模型对低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的分类结果
模型 类别 F1值 召回率 准确率 随机森林 男 0.709 0.646 0.888 女 0.766 0.700 0.868 总 0.775 0.710 0.879 支持向量机 男 0.275 0.230 0.678 女 0.415 0.409 0.647 总 0.340 0.348 0.667 AdaBoost 男 0.327 0.345 0.771 女 0.547 0.538 0.759 总 0.502 0.487 0.766 表 7 基于不同算法的3种模型对总胆固醇的分类结果
模型 类别 F1值 召回率 准确率 随机森林 男 0.650 0.573 0.911 女 0.956 0.928 0.981 总 0.742 0.664 0.937 支持向量机 男 0.346 0.345 0.828 女 0.421 0.444 0.750 总 0.416 0.418 0.797 AdaBoost 男 0.418 0.408 0.849 女 0.288 0.317 0.760 总 0.395 0.388 0.818 -
[1] GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10225): 709-733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3
[2] COCKWELL P, FISHER L A. The global burden of chronic kidney disease[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10225): 662-664. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32977-0
[3] RAJA S M, SEYOUM Y. Intradialytic complications among patients on twice-weekly maintenance hemodialysis: an experience from a hemodialysis center in Eritrea[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2020, 21: 1-6. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1645-y
[4] HIYAMUTA H, YAMADA S, TANIGUCHI M, et al. Association of hyperphosphatemia with an increased risk of sudden death in patients on hemodialysis: ten-year outcomes of the Q-Cohort Study[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2021, 316: 25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.11.020
[5] KOZLOWSKA L, GROMADZINSKA J, ZWIECH R, et al. Effects of the malnutrition-eat additional meal (MEAM) diet on the serum levels of albumin and C-reactive protein in hemodialysis patients[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(24): 5352. doi: 10.3390/nu14245352
[6] 毛雅, 姚颖. 生物电阻抗分析的临床应用[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 医学版, 2022, 51(5): 706-711. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYX202205020.htm [7] 舒亮辉, 郑梦蕾. 生物电阻抗分析在维持性透析患者中的应用进展[J]. 中华肾病研究电子杂志, 2021, 10(2): 100-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHSB202102008.htm [8] BAKDASH J Z, MARUSICH L R. Repeated measures correlation[J]. Front Psychol, 2017, 8: 456. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00456
[9] WANG Y H, GAO L. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease associated with hemodialysis for end-stage renal disease[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 800950. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.800950
[10] GAFTER-GVILI A, SCHECHTER A, ROZEN-ZVI B. Iron deficiency Anemia in chronic kidney disease[J]. Acta Haematol, 2019, 142(1): 44-50. doi: 10.1159/000496492
[11] 林晶晶, 陈少华, 姚曦, 等. 维持性血液透析患者早期死亡率及相关危险因素分析[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2020, 36(8): 595-600. [12] 王明莉, 陈德政. 维持性血液透析患者血清铁蛋白水平与预后的关系[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2019, 19(4): 256-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCSB201904006.htm [13] SCHOTMAN J, ROLLEMAN N, VAN BORREN M, et al. Accuracy of bioimpedance spectroscopy in the detection of hydration changes in patients on hemodialysis[J]. J Ren Nutr, 2023, 33(1): 193-200. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2021.11.004
[14] PINEDA-JUÅREZ J A, LOZADA-MELLADO M, OGATA-MEDEL M, et al. Body composition evaluated by body mass index and bioelectrical impedance vector analysis in women with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nutrition, 2018, 53: 49-53. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.01.004
[15] MARINI E, SERGI G, SUCCA V, et al. Efficacy of specific bioelectrical impedance vector analysis (BIVA) for assessing body composition in the elderly[J]. J Nutr Health Aging, 2013, 17(6): 515-521. doi: 10.1007/s12603-012-0411-7
[16] MULASI U, KUCHNIA A J, COLE A J, et al. Bioimpedance at the bedside: current applications, limitations, and opportunities[J]. Nutr Clin Pract, 2015, 30(2): 180-193. doi: 10.1177/0884533614568155
[17] ZHANG Z J, YIN D H, CHEN H Z, et al. Evaluation of anemia, malnutrition, mineral, and bone disorder for maintenance hemodialysis patients based on bioelectrical impedance vector analysis (BIVA)[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2020, 24(12): 1162-1176. doi: 10.1007/s10157-020-01945-1
[18] ONOFRIESCU M, HOGAS S, VORONEANU L, et al. Bioimpedance-guided fluid management in maintenance hemodialysis: a pilot randomized controlled trial[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2014, 64(1): 111-118. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.01.420
[19] 赵新菊, 蔡砺, 宋韩明, 等. 生物电阻抗矢量分析法评价维持性血液透析患者干体重初探[J]. 中国血液净化, 2009, 8(4): 185-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJH200904006.htm





 下载:
下载:



 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
