Analysis of network pharmacological mechanism of Zhenlian Mingmu Capsule in treatment of diabetic retinopathy
-
摘要:目的
探讨贞莲明目胶囊治疗糖尿病视网膜病变的作用机制。
方法利用网络药理学筛选贞莲明目胶囊治疗糖尿病视网膜病变关键靶点, 并通过分子对接预测活性成分的结合部位。结合网络药理学结果,构建糖尿病视网膜病变大鼠模型。将60只大鼠随机分为正常组、模型组、羟苯磺酸钙片组和贞莲明目胶囊组,每组15只。正常组、模型组给予2 mL生理盐水,每日1次灌胃; 羟苯磺酸钙片组、贞莲明目胶囊组分别给予相应浓度的治疗药物(2 mL), 每日1次灌胃。给药4周后,取大鼠视网膜进行检测,比较视网膜厚度、白细胞介素(IL)-1β、IL-6、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)水平和血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)、核转录因子-κB(NF-κB)蛋白表达水平。
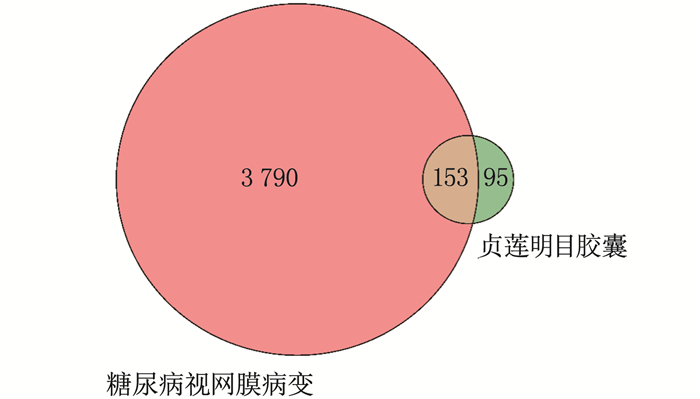
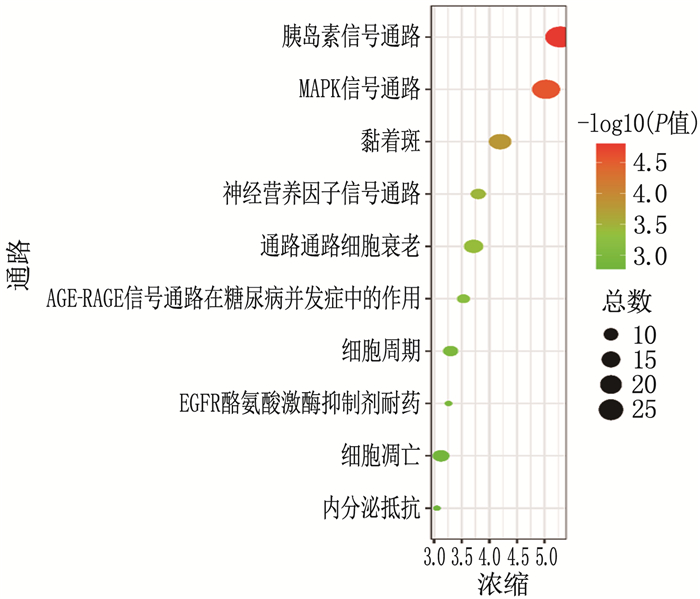
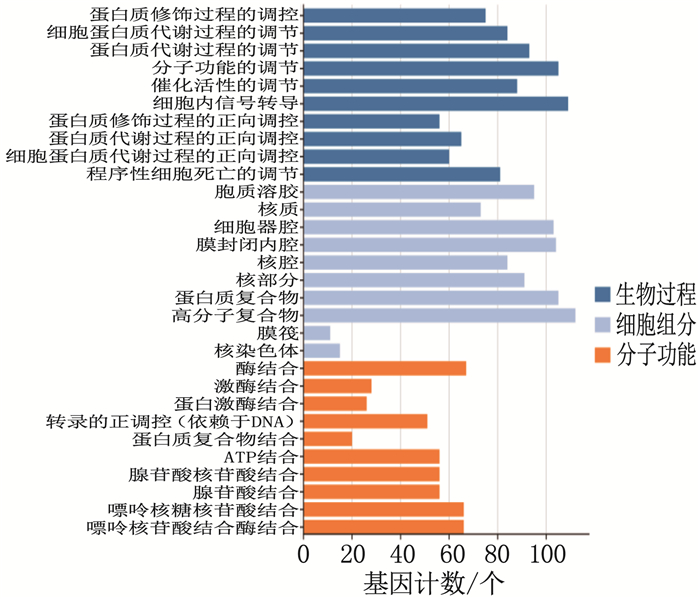
结果网络药理学共筛选出贞莲明目胶囊有效成分2 367种,作用靶点248个,糖尿病视网膜病变相关靶点3 943个,其交集靶点153个。基因本体(GO)和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)分析得出主要涉及信号转导、炎症反应、细胞凋亡等生物学反应过程,主要参与IL-1β、EGF/EGFR/P13K/AKT、IL-6/STAT3、肿瘤蛋白P53(TP53)和胱天蛋白酶3(CASP3)等信号通路的调控。分子对接结果表明,筛选得到的主要活性成分与靶点有较强的结合。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠视网膜厚度降低, IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、VEGF、NF-κB升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组比较,羟苯磺酸钙片组大鼠视网膜厚度升高, IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、VEGF、NF-κB降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与羟苯磺酸钙片组比较,贞莲明目胶囊组大鼠视网膜厚度升高, IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、VEGF、NF-κB降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论贞莲明目胶囊对糖尿病视网膜病变的治疗或许具有积极作用,其作用机制可能与调节IL-1β、EGF/EGFR/P13K/AKT、IL6/STAT3、TP53和CASP3信号通路有关。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the mechanism of Zhenlian Mingmu Capsule in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
MethodsThe key targets of Zhenlian Mingmu Capsule in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy were screened by network pharmacology, and the binding sites of active ingredients were predicted by molecular docking. Combined with the results of network pharmacology, a rat model of diabetic retinopathy was established. Sixty rats were randomly divided into normal group, model group, calcium hydroxybenzene sulfonate tablet group and Zhenlian Mingmu Capsule group, with 15 rats in each group. The normal group and the model group were given 2 mL normal saline and gavage once a day; the calcium hydroxybenzene sulfonate tablet group and Zhenlian Mingmu Capsule group were respectively given the corresponding concentration of therapeutic drugs (2 mL), once a day. After 4 weeks of administration, retinal thickness, interleukin (IL) -1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels, and protein expression levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB) were measured.
ResultsA total of 2 367 active ingredients of Zhenlian Mingmu Capsule were identified by network pharmacology, with 248 targets, 3 943 targets related to diabetic retinopathy, and 153 intersection targets. According to the analysis of Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), it was mainly involved in biological reaction processes such as signal transduction, inflammation and apoptosis, and mainly involved in the regulation of IL-1β, EGF/EGFR/P13K/AKT, IL-6/STAT3, TP53 and CASP3 signal pathways. The results of molecular docking showed that the main active ingredients obtained by screening had strong binding with the target. Compared with the normal group, retinal thickness in the model group was significantly decreased, and IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, VEGF, NF-κB were significantly increased (P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the retinal thickness of rats in the calcium hydroxybenzene sulfonate tablet group was significantly increased, and IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, VEGF, NF-κB were significantly decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the calcium hydroxybenzene sulfonate tablet group, retinal thickness in the Zhenlian Mingmu Capsule group was significantly increased, and IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, VEGF, NF-κB were significantly decreased (P < 0.05).
ConclusionZhenlian Mingmu Capsule may have a positive effect in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy, and its mechanism may be related to the regulation of IL-1β, EGF/EGFR/P13K/AKT, IL6/STAT3, TP53 and CASP3 signaling pathways.
-
支气管哮喘(BA)是以喘息、胸闷、呼吸困难等为主要临床症状的慢性气道炎症性呼吸系统疾病[1-2]。支气管收缩、气道神经控制、过敏、细胞因子及炎症反应、免疫及先天易感性是BA的主要发病机制[3]。家族遗传性BA患者支气管组织中发现自噬激活激酶1(ULK1)、自噬相关蛋白5(Atg5)、自噬相关蛋白(Beclin1)等表达异常改变[4], 预示BA的发生发展可能与自噬水平异常关系密切,这也可能为BA的治疗提供新思路。哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)是自噬的负性调控因子,可磷酸化调控ULK1的不同位点,影响自噬相关蛋白13(Atg13)与FIP200复合物的形成,调控自噬启动及发生[5]。但mTOR/ULK1/Atg13通路介导的自噬反应在BA发生发展中的调控机制的相关研究较少。罗氟司特为一种新型、高度选择性磷酸二酯酶4抑制剂,体内外研究[6]证实其具有抗炎、免疫调节及改善气道重塑作用,被批准应用于慢性阻塞性肺疾病的治疗,但其在BA中的应用还处于探索阶段。本研究建立BA小鼠模型,给予罗氟司特药物干预治疗,并从mTOR/ULK1/Atg13自噬调控方面,探究其对气道炎症的影响机制,以期为罗氟司特在BA领域的应用提供理论依据。
1. 资料和方法
1.1 实验材料
1.1.1 动物
SPF级健康雄性C57BL/6J小鼠,体质量20~22 g, 6~7周龄,购自于北京医科大学实验动物科学部[SCXK(京) 2018-0003], 所有小鼠于动物房中饲养(12 h光照及12 h黑暗交替照明,温度25 ℃, 湿度50%)。本试验经伦理委员会批准(ICAU-202004032651), 试验动物符合3R原则。
1.1.2 主要试剂及仪器
罗氟司特(货号YJ-23180R, 上海雅吉生物科技有限公司); 雷帕霉素(货号R8140-25, 北京索莱宝科技有限公司); 自噬抑制剂(3-甲基腺嘌呤, 3MA)(货号YT66820, 北京伊塔生物科技有限公司); γ-干扰素(INF-γ)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒(货号ZN2638-ADL、ZN2764-XRL,北京百奥莱博科技有限公司); 磷酸化mTOR(p-mTOR)、白细胞介素-33(IL-33)、Atg13、mTOR、ULK1特定位点Ser757蛋白(ULK1 Ser757)、自噬标记蛋白微管相关蛋白轻链3B(LC3B)、Beclin1、B细胞淋巴瘤-2(Bcl-2)、IL-33, 黏液高分泌性标志蛋白(黏蛋白MUC5AC)抗体(美国abcam公司); 磷酸化Atg13(p-Atg13)(货号13007, 美国Signalway Antibody公司)、磷酸化ULK1 Ser757蛋白(p-ULKl Ser757)[货号6888T, 赛信通(上海)生物试剂有限公司)];动物肺功能仪(型号FinePointeTMPFT, 美国Buxco公司)等。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 小鼠BA模型建立及分组给药
取小鼠,参照文献[7]用卵清蛋白(OVA)50 μg于1、5、8 d腹腔注射致敏,并于22~28 d用1% OVA生理盐水溶液雾化吸入建立小鼠BA模型,若小鼠出现呼吸喘促、哮鸣音、搔鼻、打喷嚏、口鼻处有白色黏性分泌物增多现象,表明造模成功。共造模成功50只小鼠,随机分为模型组、罗氟司特组、自噬激活剂-mTOR抑制剂(雷帕霉素)组,罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组,自噬抑制剂(3MA)组,每组10只。另取10只正常小鼠,于相同时间以相同方法给予等量生理盐水,作为正常对照组。各组小鼠均于造模成功后开始给药,罗氟司特参照文献[8]设置剂量1.0 mg/kg(生理盐水稀释至0.10 mg/mL, 按10 mL/kg体积灌胃给药, 1次/d); 雷帕霉素(1.0 mg/kg)及3MA (10 mg/kg)参照文献[9-10]设置剂量并经腹腔注射给药, 2次/周; 罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组灌胃给予罗氟司特(1.0 mg/kg)的同时,腹腔注射雷帕霉素溶液(1.0 mg/kg); 模型组及正常对照组灌胃给予10 mL/kg生理盐水,各组小鼠连续给药4周。
1.2.2 小鼠肺功能检测
给药期间,观察小鼠呼吸及皮毛状态、口鼻等部位分泌物形成情况,咳嗽(或气喘)等肺系疾病特异性症状变化。给药结束后,用4%戊巴比妥钠溶液1 mL/kg腹腔注射麻醉小鼠后,于颈部正中处剪开皮肤,剥离周围组织分离气管,行气管插管术,用动物肺功能测定仪测定小鼠吸气阻力、呼气阻力、肺通气顺应性等肺功能变化。
1.2.3 支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF)中嗜酸粒细胞及中性粒细胞计数及炎症因子检测
检测完小鼠肺功能后,麻醉、暴露气管,结扎主支气管,输液针气管插管并固定,经气管注入4 ℃含酚红缓冲液5 mL, 轻轻按摩胸部20~30 s后,回收BALF, 共3次(回收率>90%), 将回收后的BALF于4 ℃、1 500转/min(5 cm有效离心半径)离心10 min, 取上清液, 1 mL磷酸缓冲溶液重悬细胞后,取10 μL于光学显微镜下进行细胞总数计数[(4个大格细胞总数/4)×104/mL]。取100 μL细胞重悬液,快速迪夫染色后,封片置于20倍光学显微镜下观察并分类计数,计数公式=(χ/200)×细胞总数,χ=5个视野中细胞所占百分比相加再除以5。取上清液,按ELISA试剂盒说明书检测INF-γ、TNF-α水平。
1.2.4 透射电镜检测及标本采集
处死小鼠,沿支气管束走行方向,剪下约0.3 cm×0.3 cm组织块,浸入2.5%戊二醛后,送入电镜室检查自噬泡形成情况。取左肺组织,置于-80 ℃保存,取完整右肺组织迅速置于4%多聚甲醛中固定24 h,常规透明、浸蜡、包埋后,切成5 μm切片。
1.2.5 小鼠肺组织苏木精-伊红(HE)、过碘酸-雪夫(PAS)染色及TUNEL染色观察
取右肺相同部位切片,按HE及PAS染色试剂盒说明书方法进行染色、封片后,置于光学显微镜下观察组织病理变化及杯状细胞化生状况。取肺组织切片,按TUNEL染色试剂盒说明书方法染色、封片后,在光学显微镜下观察细胞凋亡情况,用Image-pro plus软件系统检测棕黄色凋亡细胞数目,细胞凋亡率=凋亡细胞数/细胞总数×100%。
1.2.6 蛋白质印迹法(Western blot)检测肺组织Atg13、p-Atg13、mTOR、p-mTOR、ULK1 Ser757、p-ULKl Ser757、LC3B、Beclin1、Bcl-2、IL-33、MUC5AC蛋白相对表达水平
取1.2.4中冰冻肺组织, 4 ℃解冻后,冰上均浆、离心提取蛋白,二喹啉甲酸(BCA)法测蛋白总浓度后,取100 μg蛋白上样,并进行电泳及转膜反应,加入一抗[Atg13、p-Atg13、mTOR、p-mTOR、ULK1 Ser757、p-ULKl Ser757、LC3B、Beclin1、Bcl-2、IL-33、MUC5AC, 1 ∶ 800; β-actin(内参), 1 ∶ 1 000]抗体, 4 ℃摇床孵育过夜,加入辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)羊抗兔二抗(1 ∶ 2 000), 37 ℃摇床孵育2 h, 增强化学发光法显色,以化学发光仪观察条带并拍照,以Image-J软件分析各组蛋白相对表达。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 22.0软件统计分析数据,数据以(x ±s)表示,多组间比较行单因素方差分析,进一步2组间比较行SNK-q检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 罗氟司特对小鼠一般行为的影响
正常对照组小鼠呼吸均匀正常,口唇鼻等部位无异常分泌物出现。模型组及罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组小鼠呼吸急促,搔鼻、打喷嚏,口鼻处白色黏性分泌物增多。雷帕霉素组小鼠呼吸减慢、俯伏不动、口鼻处白色黏性分泌物增多现象进一步加重。罗氟司特组及3MA组小鼠呼吸及节律渐复平稳、均匀,口鼻处白色黏性分泌物减少,搔鼻、打喷嚏现象减少或消失。
2.2 罗氟司特对小鼠肺功能的影响
与正常对照组相比,模型组小鼠吸气阻力、呼气阻力升高,肺通气顺应性降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 预示肺功能下降; 与模型组相比,罗氟司特组及3MA组小鼠吸气阻力、呼气阻力降低,肺通气顺应性升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 肺功能改善;与模型组相比,雷帕霉素组肺功能进一步降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与罗氟司特组比较,罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组小鼠吸气阻力、呼气阻力升高,肺通气顺应性降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 各组小鼠肺功能比较(x ±s)组别 n 吸气阻力/(cmH2O·s/mL) 呼气阻力/(cmH2O·s/mL) 肺通气顺应性/(mL/cm) 正常对照组 10 1.79±0.23 1.78±0.22 0.26±0.04 模型组 10 3.09±0.23* 3.08±0.23* 0.11±0.02* 罗氟司特组 10 2.52±0.21# 2.19±0.20# 0.17±0.03# 3MA组 10 2.53±0.20# 2.20±0.22# 0.18±0.04# 雷帕霉素组 10 3.96±0.23#△ 3.97±0.26#△ 0.04±0.02#△ 罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组 10 3.06±0.20△ 3.10±0.24△ 0.12±0.03△ 与正常对照组比较, *P < 0.05; 与模型组比较, #P < 0.05; 与罗氟司特组比较, △P < 0.05。 2.3 罗氟司特对小鼠BALF中性粒细胞及嗜酸粒细胞数目及炎性因子INF-γ、TNF-α水平的影响
与正常对照组相比,模型组小鼠BALF中性粒细胞、嗜酸粒细胞数目增多, INF-γ、TNF-α水平升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,罗氟司特组及3MA组小鼠中性粒细胞、嗜酸粒细胞数目减少, INF-γ、TNF-α水平降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 与模型组比较,雷帕霉素组中性粒细胞、嗜酸粒细胞数目增多,INF-γ、TNF-α水平升高(P < 0.05)。与罗氟司特组相比,罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组小鼠中性粒细胞、嗜酸粒细胞数目增多, INF-γ、TNF-α水平升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 2。
表 2 小鼠BALF中性粒细胞、嗜酸粒细胞数目及INF-γ、TNF-α水平比较(x ±s)组别 n 中性粒细胞/(×103/mL) 嗜酸粒细胞/(×103/mL) γ-干扰素/(ng/mL) 肿瘤坏死因子-α/(ng/mL) 正常对照组 10 0.61±0.19 0.61±0.19 69.93±3.89 16.99±0.88 模型组 10 7.56±0.36* 22.85±2.23* 192.06±8.26* 146.24±7.19* 罗氟司特组 10 2.58±0.24# 8.61±0.60# 89.58±4.04# 84.18±4.08# 3MA组 10 2.53±0.12# 8.69±0.63# 89.13±4.12# 85.33±4.24# 雷帕霉素组 10 9.28±0.33#△ 39.28±3.01#△ 225.58±9.24#△ 219.39±8.95#△ 罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组 10 7.62±0.33△ 22.93±2.01△ 199.02±8.19△ 144.63±7.30△ 与正常对照组比较, *P < 0.05; 与模型组比较, #P < 0.05; 与罗氟司特组比较, △P < 0.05。 2.4 罗氟司特对小鼠肺组织结构变化及杯状细胞化生的影响
正常对照组小鼠肺组织结构完整,染色均匀; HE染色显示模型组及罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组小鼠气道、血管周围、肺间质等部位炎症细胞浸润、支气管管壁增厚等病理损伤严重; PAS染色可见气道上皮有大量呈紫红色的杯状细胞增生,黏液分泌增多。罗氟司特组及3MA组小鼠肺组织炎症细胞浸润、支气管壁增厚、杯状细胞化生等病理损伤缓解; 雷帕霉素组显示肺组织炎症细胞浸润、支气管壁增厚、杯状细胞化生等病理损伤进一步加重。见图 1。
2.5 罗氟司特对小鼠肺组织气道上皮细胞自噬及凋亡的影响
正常对照组小鼠肺组织支气管上皮细胞结构正常,上皮细胞胞浆中几乎未见自噬泡形成及凋亡。电镜观察可见模型组小鼠支气管上皮细胞中,双层膜结构的细胞自噬泡聚集较多,部分自噬泡中可见吞噬物形成,TUNEL染色可见肺组织支气管上皮细胞棕黄色颗粒物质沉积增多,相较正常对照组凋亡率增高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,罗氟司特组及3MA组小鼠肺组织支气管上皮细胞自噬泡形成减少,上皮细胞凋亡率降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 与模型组相比,雷帕霉素组小鼠肺组织支气管上皮细胞自噬泡形成进一步增加,细胞凋亡率进一步升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与罗氟司特组相比,罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组小鼠肺组织支气管上皮细胞自噬泡形成增多,上皮细胞凋亡率增高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 3、图 2。
表 3 各组细胞凋亡率比较(x ±s)组别 n 细胞凋亡率/% 正常对照组 10 8.21±0.20 模型组 10 32.09±1.65* 罗氟司特组 10 16.39±0.83# 3MA组 10 16.25±0.84# 雷帕霉素组 10 50.03±1.86#△ 罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组 10 31.68±1.49△ 与正常对照组比较, *P < 0.05; 与模型组比较, #P < 0.05; 与罗氟司特组比较, △P < 0.05。 2.6 罗氟司特对小鼠mTOR、p-mTOR、Atg13、p-Atg13、ULK1 Ser757、p-ULKl Ser757、LC3B蛋白表达的影响
与正常对照组相比,模型组小鼠肺组织p-mTOR/mTOR、p-Atg13/Atg13、p-ULKl Ser757/ULK1 Ser757表达降低, LC3B表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,罗氟司特组及3MA组小鼠肺组织p-mTOR/mTOR、p-Atg13/Atg13、p-ULKl Ser757/ULK1 Ser757表达升高,LC3B表达降低,雷帕霉素组小鼠p-mTOR/mTOR、p-Atg13/Atg13、p-ULKl Ser757/ULK1 Ser757表达进一步降低, LC3B表达进一步升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与罗氟司特组相比,罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组小鼠p-mTOR/mTOR、p-Atg13/Atg13、p-ULKl Ser757/ULK1 Ser757表达降低, LC3B表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图 3、表 4。
表 4 各组小鼠肺组织mTOR、p-mTOR、Atg13、p-Atg13、ULK1 Ser757、p-ULKl Ser757、LC3B蛋白表达(x ±s)组别 n p-mTOR/mTOR p-Atg13/Atg13 p-ULKl Ser757/ULK1 Ser757 LC3B/β-Actin 正常对照组 10 1.12±0.10 1.16±0.08 1.19±0.10 1.11±0.08 模型组 10 0.46±0.04* 0.48±0.05* 0.50±0.09* 2.39±0.29* 罗氟司特组 10 0.79±0.07# 0.72±0.06# 0.82±0.08# 1.77±0.19# 3MA组 10 0.85±0.08# 0.79±0.08# 0.81±0.09# 1.81±0.18# 雷帕霉素组 10 0.12±0.01#△ 0.14±0.02#△ 0.19±0.01#△ 2.96±0.22#△ 罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组 10 0.45±0.04△ 0.49±0.05△ 0.51±0.06△ 2.41±0.28△ mTOR: 哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白; p-mTOR: 磷酸化哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白; Atg13: 自噬相关蛋白13; p-Atg13: 磷酸化Atg13; ULK1 Ser757: ULK1特定位点Ser757蛋白; p-ULKl Ser757: 磷酸化ULK1特定位点Ser757蛋白; LC3B: 微管相关蛋白轻链3B。
与正常对照组比较, *P < 0.05; 与模型组比较, #P < 0.05; 与罗氟司特组比较, △P < 0.05。2.7 罗氟司特对小鼠Bcl-2、Beclin1、IL-33、MUC5AC蛋白表达的影响
与正常对照组相比,模型组小鼠肺组织Bcl-2蛋白表达降低, Beclin1、IL-33、MUC5AC蛋白表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,罗氟司特组及3MA组小鼠肺组织Bcl-2蛋白表达升高, Beclin1、IL-33、MUC5AC表达降低,雷帕霉素组小鼠Bcl-2蛋白表达进一步降低, Beclin1、IL-33、MUC5AC蛋白表达进一步升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 与罗氟司特组相比,罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组小鼠织Bcl-2蛋白表达降低, Beclin1、IL-33、MUC5AC表达升高(P < 0.05)。见表 5、图 4。
表 5 各组小鼠肺组织Bcl-2、Beclin1、IL-33、MUC5AC蛋白表达比较(x ±s)组别 n Bcl-2/β-Actin Beclin1/β-Actin IL-33/β-Actin MUC5AC/β-Actin 正常对照组 10 1.12±0.10 1.16±0.08 1.19±0.10 1.11±0.08 模型组 10 0.36±0.03* 2.56±0.05* 2.35±0.05* 2.24±0.29* 罗氟司特组 10 0.64±0.06# 1.82±0.16# 1.67±0.16# 1.79±0.19# 3MA组 10 0.70±0.07# 1.89±0.18# 1.61±0.17# 1.72±0.18# 雷帕霉素组 10 0.10±0.01#△ 2.99±0.22#△ 2.88±0.21#△ 2.86±0.26#△ 罗氟司特+雷帕霉素组 10 0.35±0.04△ 2.59±0.25△ 2.13±0.20△ 2.21±0.22△ Bcl-2: B细胞淋巴瘤-2; Beclin1: 自噬相关蛋白; IL-33: 白细胞介素-33。
与正常对照组比较, *P < 0.05; 与模型组比较, #P < 0.05; 与罗氟司特组比较, △P < 0.05。3. 讨论
气道慢性炎症、气道高黏液分泌可阻塞气流,导致BA患者呼吸困难[11]。MUC5AC是气道黏液高分泌标志蛋白,其表达升高,可反映BA气道黏液高反应状态[12]。本研究建立小鼠BA模型后,发现小鼠气道中嗜酸性粒细胞、中性粒细胞等炎症细胞聚集增多,支气管肺组织炎症浸润及杯状细胞化生增多, MUC5AC表达升高,肺功能下降严重,提示小鼠BA造模成功。吸入性糖皮质激素对大部分急性加重期BA患者治疗效果不甚显著,寻找特异性有效的治疗药物,一直是临床研究的热点之一[13]。临床报道[14]发现,罗氟司特对急性加重期BA患者气道重塑及肺功能损伤的改善效果优于糖皮质激素药物布地奈德,预示其在BA领域的应用具有广阔前景。本研究结果显示,罗氟司特干预组可显著缓解BA小鼠肺通气下降,抑制MUC5AC表达,并对支气管肺组织炎症浸润及杯状细胞化生有明显缓解作用,证实了罗氟司特在BA方面的应用价值,但其具体分子生物学机制还需进一步探究。
细胞自噬与BA的发生发展关系密切,并逐渐成为BA机制研究的热点之一[15]。研究[16-17]发现,哮喘患者及模型大鼠支气管组织中存在自噬激活现象,并认为LC3B表达与BA气道上皮细胞自噬有关[18]。本研究结果显示,模型组大鼠气道上皮细胞自噬泡数量及气道组织中自噬标记蛋白LC3B、Beclin1表达均升高的同时,气道上皮细胞凋亡率也显著增加,用自噬抑制剂3MA抑制自噬后,气道上皮细胞凋亡率显著降低,小鼠BA症状也显著缓解。罗氟司特干预组出现与3MA组相同的自噬及气道上皮细胞凋亡率降低现象,提示罗氟司特治疗BA的作用可能是通过抑制自噬、缓解BA气道上皮细胞凋亡而实现的。
mTOR/ULK1/Atg13通路是参与自噬、炎症、凋亡调节的关键通路。研究[19]发现, mTOR磷酸化活化水平增加,可促进Atg13-FIP200及ULK1 Ser757位点磷酸化,来阻断自噬复合物的形成,从而抑制自噬小体形成,阻断自噬启动; 另外mTOR也可直接调控抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达,使Bcl-2能通过竞争性调节BH3受体域作用,抑制Beclin1依赖的自噬形成[20]。研究[21]发现,炎症信号因子IL-33是刺激气道炎症应激反应、促进气道上皮细胞凋亡及自噬标记蛋白LC3B异常表达升高的主要原因。本研究结果显示,模型组小鼠肺组织中mTOR/ULKl Ser757/Atg13通路磷酸化水平、Bcl-2抗凋亡蛋白异常降低,而Beclin1、LC3B自噬蛋白及炎症因子IL-33蛋白异常升高,提示mTOR/ULK1/Atg13通路磷酸化活化水平降低,可能参与BA小鼠肺组织炎症、自噬、凋亡过程。雷帕霉素可抑制p-mTOR水平, ULK1/Atg13通路磷酸化活化水平降低的同时,小鼠气道上皮细胞炎症、自噬、凋亡反应进一步加重, BA小鼠病理症状也进一步加重,但这与金华良等[22]报道的雷帕霉素促进自噬,缓解BA病理症状的机制相反,推测可能是雷帕霉素用量不一致及疾病程度不一致有关。罗氟司特与3MA干预组显示,mTOR/ULK1/Atg13通路磷酸化活化水平增高,肺组织炎症、自噬、凋亡反应降低。但雷帕霉素在促进自噬,加重BA症状的同时,还可减弱罗氟司特发挥的促进mTOR/ULK1/Atg13通路磷酸化活化、阻断自噬、抑制肺组织炎症及气道上皮细胞凋亡等作用。
综上所述,罗氟司特可通过促进mTOR/ULK1/Atg13通路磷酸化活化,阻断自噬,抑制肺组织炎症及气道上皮细胞凋亡,缓解BA病理症状。这为罗氟司特在BA领域的开发应用提供了一定参考。但BA自噬调控机制复杂,涉及多条途径、调控网络,罗氟司特调控自噬、缓解BA病理症状的其他调控机制还有待进一步研究。
-
表 1 贞莲明目胶囊重要性前10位有效成分
序号 代号 分子标识 英文名 口服利用率/% 类药性 涉及药物 1 CQGQMHNZSQ MOL000098 quercetin 46.43 0.28 车前子、枸杞子、墨旱莲、女贞子、三七 2 DSSQGQNZ MOL000675 oleic acid 33.13 0.14 丹参、三七、枸杞子、女贞子 3 DSMHNZ MOL000006 luteolin 36.16 0.25 丹参、墨旱莲、女贞子 4 NZ4 MOL000422 kaempferol 41.88 0.24 女贞子 5 DS62 MOL007154 tanshinone iia 49.89 0.40 丹参 6 BMGQHJNZSQ MOL000358 beta-sitosterol 36.91 0.75 白茅根、枸杞子、黄精、女贞子、三七 7 BMDHGQJMSQ MOL000449 Stigmasterol 43.83 0.76 白茅根、地黄、枸杞子、决明子、三七 8 GQ33 MOL009637 4-methoxyphenyl 43.47 0.15 枸杞子 9 HJ7 MOL002714 baicalein 33.52 0.21 黄精 10 DS57 MOL007145 salviolone 31.72 0.24 丹参 表 2 核心靶点与贞莲明目胶囊主要成分模拟对接参数
靶蛋白 主要成分 对接总分 碰撞参数 IL-1β 槲皮素 6.022 -3.466 油酸 7.081 -1.898 木犀草素 5.826 -2.603 山奈酚 5.752 -2.575 丹参酮ⅡA 8.011 -1.994 AKT1 槲皮素 5.263 -3.359 油酸 7.375 -3.230 木犀草素 7.318 -1.511 山奈酚 6.216 -2.049 丹参酮ⅡA 5.143 -2.691 TP53 槲皮素 6.645 -3.105 油酸 6.731 -2.979 木犀草素 7.780 -2.761 山奈酚 6.326 -3.469 丹参酮ⅡA 6.810 -1.648 CASP3 槲皮素 8.090 -2.511 油酸 5.190 -1.968 木犀草素 5.443 -3.400 山奈酚 5.768 -1.595 丹参酮ⅡA 6.859 -1.558 EGF 槲皮素 7.622 -3.209 油酸 6.875 -2.330 木犀草素 7.779 -1.879 山奈酚 6.417 -1.720 丹参酮ⅡA 5.020 -2.558 IL-1β: 白细胞介素-1β; AKT1: RACα丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶;
TP53: 肿瘤蛋白P53; CASP3: 胱天蛋白酶3;
EGF: 表皮生长因子。表 3 各组大鼠视网膜厚度、视网膜炎症指标情况(x±s)
组别 视网膜厚度/μm IL-1β/(ng/L) IL-6/(ng/L) TNF-α/(ng/L) 正常组(n=15) 184.72±16.57 26.24±3.15 37.09±3.07 273.18±35.57 模型组(n=15) 115.07±10.48* 58.09±7.48* 78.14±9.32* 806.36±106.25* 羟苯磺酸钙片组(n=15) 136.50±11.27# 42.73±6.95# 56.18±7.29# 503.49±62.63# 贞莲明目胶囊组(n=15) 161.97±15.43△ 31.02±5.65△ 44.68±6.71△ 361.49±44.06△ IL-1β: 白细胞介素-1β; IL-6: 白细胞介素-6; TNF-α: 肿瘤坏死因子-α。与正常组比较, * P < 0.05;
与模型组比较, # P < 0.05; 与羟苯磺酸钙片组比较, △ P < 0.05。表 4 各组大鼠视网膜中VEGF、NF-κB蛋白表达(x±s)
组别 VEGF NF-κB 正常组(n=15) 1.02±0.17 1.11±0.28 模型组(n=15) 4.39±0.38* 6.52±1.26* 羟苯磺酸钙片组(n=15) 3.06±0.41# 4.13±0.95# 贞莲明目胶囊组(n=15) 1.71±0.32△ 1.53±0.34△ VEGF: 血管内皮生长因子; NF-κB: 核转录因子-κB。
与正常组比较, * P < 0.05; 与模型组比较, # P < 0.05;
与羟苯磺酸钙片组比较, △ P < 0.05。 -
[1] RODRÍGUEZ M L, PÉREZ S, MENA-MOLLÁ S, et al. Oxidative stress and microvascular alterations in diabetic retinopathy: future therapies[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 4940825.
[2] GROENEVELD Y, TAVENIER D, BLOM J W, et al. Incidence of sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy in people with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and numbers needed to screen: a systematic review[J]. Diabet Med, 2019, 36(10): 1199-1208. doi: 10.1111/dme.13908
[3] ZHANG Y H, AN X D, DUAN L Y, et al. Effect of Chinese patent medicines on ocular fundus signs and vision in calcium dobesilate-treated persons with non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 799337. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.799337
[4] 赵旭芳. 贞莲明目胶囊治疗肝肾阴虚、痰湿瘀阻型NPDR临床疗效观察[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2021. [5] 李国建, 尹瑞生, 任崇禧, 等. 贞莲明目胶囊治疗糖尿病视网膜黄斑水肿55例临床观察[J]. 光明中医, 2007, 22(7): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2007.07.029 [6] 孙鹏, 孟岩, 张剑, 等. NGF联合抗VEGF对糖尿病模型大鼠视网膜组织中氧化应激和VEGF表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2022, 42(11): 2773-2776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2022.11.050 [7] 戴淑香, 王广梅, 黄德莲, 等. 中药联合全视网膜光凝治疗糖尿病视网膜病变的观察及护理[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2017, 21(6): 49-51. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201706015 [8] 程梅, 方朝晖, 盛凤霞, 等. 盐酸川芎嗪眼部雾化联合耳尖放血对气阴两虚型糖尿病视网膜病变的疗效观察[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(10): 71-75. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20211277 [9] OSHITARI T. Neurovascular impairment and therapeutic strategies in diabetic retinopathy[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 19(1): 439. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010439
[10] BHATWADEKAR A D, SHUGHOURY A, BELAMKAR A, et al. Genetics of diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of irreversible blindness in the industrialized world[J]. Genes, 2021, 12(8): 1200. doi: 10.3390/genes12081200
[11] AN X D, JIN D, DUAN L Y, et al. Direct and indirect therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine as an add-on for non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Chin Med, 2020, 15: 99. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00380-4
[12] QIAN S H, QIAN Y J, HUO D X, et al. Tanshinone Ⅱa protects retinal endothelial cells against mitochondrial fission induced by methylglyoxal through glyoxalase 1[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 857: 172419. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172419
[13] CHAI G R, LIU S, YANG H W, et al. Quercetin protects against diabetic retinopathy in rats by inducing heme oxygenase-1 expression[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2021, 16(7): 1344-1350. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.301027
[14] SAFARPOUR S, PIRZADEH M, EBRAHIMPOUR A, et al. Protective effect of kaempferol and its nanoparticles on 5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity in rats[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 2022: 2273000.
[15] AFIFI S M, AMMAR N M, KAMEL R, et al. β-sitosterol glucoside-loaded nanosystem ameliorates insulin resistance and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(5): 1023. doi: 10.3390/antiox11051023
[16] HE J B, WANG H, LIU Y, et al. Blockade of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 prevents inflammation and vascular leakage in diabetic retinopathy[J]. J Ophthalmol, 2015, 2015: 605946.
[17] ELEKOFEHINTI O O, OYEDOKUN V O, IWALOYE O, et al. Momordica charantia silver nanoparticles modulate SOCS/JAK/STAT and P13K/Akt/PTEN signalling pathways in the kidney of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. J Diabetes Metab Disord, 2021, 20(1): 245-260. doi: 10.1007/s40200-021-00739-w
[18] 张金锋, 徐志龙, 吴梦, 等. 丹参酮ⅡA通过抑制信号通路延缓膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨退变及抑制局部炎症的研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2021, 56(23): 1918-1926. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYX202123008.htm [19] HAN X J, XU T S, FANG Q J, et al. Quercetin hinders microglial activation to alleviate neurotoxicity via the interplay between NLRP3 inflammasome and mitophagy[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 44: 102010. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102010
[20] LIU C, LIU H, LU C, et al. Kaempferol attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriatic skin inflammation in a mouse model[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2019, 198(3): 403-415. doi: 10.1111/cei.13363
[21] JAYARAMAN S, DEVARAJAN N, RAJAGOPAL P, et al. β-sitosterol circumvents obesity induced inflammation and insulin resistance by down-regulating IKKβ/NF-κB and JNK signaling pathway in adipocytes of type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(7): 2101. doi: 10.3390/molecules26072101
[22] CHOI S H, KOH D I, CHO S Y, et al. Temporal and differential regulation of KAISO-controlled transcription by phosphorylated and acetylated p53 highlights a crucial regulatory role of apoptosis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2019, 294(35): 12957-12974. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008100
[23] GONZALEZ-RELLAN M J, FONDEVILA M F, FERNANDEZ U, et al. O-GlcNAcylated p53 in the liver modulates hepatic glucose production[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 5068. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25390-0
[24] KANAMORI Y, FINOTTI A, MAGNO L D, et al. Enzymatic spermine metabolites induce apoptosis associated with increase of p53, caspase-3 and miR-34a in both neuroblastoma cells, SJNKP and the N-myc-amplified form IMR5[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(8): 1950. doi: 10.3390/cells10081950
[25] 米倚林, 易南星, 许晓彤, 等. 山奈酚抑制软骨凋亡延缓小鼠膝骨关节炎的实验研究[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2022, 28(17): 1299-1306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYY202217004.htm [26] LIU R, HAO D L, XU W Y, et al. β-Sitosterol modulates macrophage polarization and attenuates rheumatoid inflammation in mice[J]. Pharm Biol, 2019, 57(1): 161-168. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1577461
[27] GREGORIO K C R, LAURINDO C P, MACHADO U F. Estrogen and glycemic homeostasis: the fundamental role of nuclear estrogen receptors ESR1/ESR2 in glucose transporter GLUT4 regulation[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(1): 99. doi: 10.3390/cells10010099
[28] CHEN Q, HE Y, WANG X F, et al. LncRNA PTGS2 regulates islet β-cell function through the miR-146a-5p/RBP4 axis and its diagnostic value in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(10): 11316-11328.
[29] 张辛宁, 王乐琪, 李莎莎, 等. 丹参从瘀论治抑郁症的潜在靶点及作用机制研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2021, 32(9): 1300-1308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXY202109012.htm [30] YI H, PENG H Y, WU X Y, et al. The therapeutic effects and mechanisms of quercetin on metabolic diseases: pharmacological data and clinical evidence[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 6678662.
[31] XIA H T, LIU J Y, YANG W L, et al. Integrated strategy of network pharmacological prediction and experimental validation elucidate possible mechanism of bu-Yang herbs in treating postmenopausal osteoporosis via ESR1[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 654714.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 吴杨. 罗氟司特联合布地奈德对支气管哮喘患者肺功能小气道参数的影响. 中国药物与临床. 2025(03): 192-196 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
